10、数据类型
变量的类型有等号(:=)的右边决定,不用显式声明
- 图形类型
- 图像Image
read_image(Image, 'fabrik')
- 区域(region):
gen_rectangle1(Rectangle, 30, 20, 100, 200)
- Xld轮廓
*把region转换为轮廓类型(xld)
gen_contour_region_xld(Rectangle, Contours, 'border')
注:当鼠标靠近变量窗口时可以查看该变量的类型。
![]()
- 控制类型
- 字符串:
*字符串用
str:='huanghai'
注:字符串用单引号,赋值用 :=
- 实型(浮点型)
*实型(浮点型)
f:=10.5
- 数组的相关操作
*定义一个空数组
tuple1:=[]
*定义一个空数组,并进行初始化
tuple2:=[1,2,3,4]
*创建一个数组,大小为100个元素,全部元素初始化值为44
tuple3:= gen_tuple_const(100,44)
**************************************************************
*数组存取
tuple1[0]:=1
i:=tuple1[0]
*也可以用算子来实现,选取tuple2数组的索引为2的元素(下标从0开始)
tuple_select (tuple2, 2, Selected)
*或
Selected:=subset(tupl2,2)
***************************************************************
*数组的合并
tuple4:=[5,6]
tuple5:=[tuple2,tuple4]
*也可以用算子来实现
tuple_concat(tuple4,tuple2,tuple42)
************************************************
*数组的长度(元素的个数)
tuple7:=[1,2,3,4,5]
i:=|tuple7|
*也可以用算子来实现
tuple_length (tuple7, Length)
************************************************
*截取数组中的某一段
*截取tuple3数组中索引从i1到i2之间的元素到tuple33数组中
tuple3:= gen_tuple_const(100,44)
i1:=2
i2:=3
tuple33:=tuple3[i1:i2]
*也可以用算子来实现
tuple_select_range (tuple3, i1, i2, tuple33)
************************************************
*去除数据
temp:=[1,2,3,4]
i:=2
temp1:=remove(temp,i)//删除索引为2的元素
*也可以用算子来实现
tuple_remove (temp, i, temp1)
************************************************
*查找元素
temp:=[1,2,3,4]
t1:=[3,4]
t2:=find(temp,t1)//结果t2==2,假若找不到则返回-1
*也可以用算子来实现
tuple_find (temp,t1,t2)
注:由上述例子中可以看出,对于数组的操作都可以用tuple_****算子来实现,上面的操作只是数组操作中常用的部分,详细看帮助文档。
- 句柄
*把Rectangle区域从大图片中剪裁出来,存放到ImageReduced中
reduce_domain (Image, Rectangle, ImageReduced)
*创建剪裁下来图像的句柄
create_shape_model (ImageReduced, 'auto', -0.39, 0.79, 'auto', 'auto', 'use_polarity', 'auto', 'auto', ModelID)
*清除句柄
clear_shape_model(ModelID)
- 比较运算符
1、
a:=10
b:=20
if(a>b)
a:=100
elseif(a=b)//这里应该用=,而不是用==
b:=100
a:=100
else
b:=100
endif
2、
if(a#b)//不等时用#
a:=b
endif
3、
if(a>10 and b<200)//与
a:=a+b
endif
4、
if(a>10 or b<200)//或
a:=a+b
endif
5、
if(not (b<200))//非
a:=a+b
endif
- 控制流
1、
for i := 1 to 5 by 1
if(i=2)
*continue
break
a:=a+1
endif
endfor
i:=2
2、
while (i)
i:=i-1
endwhile
注意:循环中的
3、switch语句只有在Halcon11以及往上的版本才支持。
switch(i)
case 1:
i:=2
case 2:
case 3:
i:=2
default:
i:=2
endswitch
- 全局变量与局部变量
- 变量的作用域(局部或全局):
(1)、声明:
HDelelop所有的变量都是默认为全局变量,也就是它们值存在于它们所在的函数中,因此不同函数的局部变量可以以相同的名字存在,它们相互没有干扰。与此相反,全部变量是整个程序中可以访问,使用全局变量必须使用算子global进行显式声明。
如:
声明一个全局的控制变量(变量名为File,可以随意修改)
global tuple File
声明一个全局的图像变量(变量名为Image,可随意修改)
global object Image
注:
关键字def允许在变量定义的地方标记一个显式声明,如,global def object Image,字只有把HDevelop程序到处为一种编程语言是才有意义,更多信息,参见global算子。
(2)、使用:
如果想在另外一个函数中访问全局变量,必须也要在该函数中再一次声明(如果不声明则会认为这个同名的
变量为局部变量)。
例:
global tuple File
global object Image
File:='Clip'
read_image (Image, File)
prcoess_image()//调用prcoess_image函数
*******************************************************************************
*********************prcoess_image()函数体************************************
global object Image//再次声明Image是全局变量
bin_threshold(Image, Region)//读取去全局变量,这时全区变量的值为'Clip'图片
File:='fuse'//修改File变量
read_image(Image,File)//修改Image变量
分析:由于全局变量Image在函数prcoess_image()中再次声明,所以它一直被认为是全局的变量使用 而File变量没有在函数prcoess_image()中再次声明,所以它被认为是一个prcoess_image()局部变量
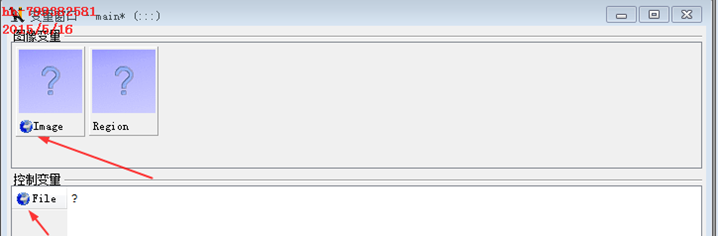
全局变量在变量窗口中有一个"地球"的标识



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号