Redisson分布式锁之非公平锁原理
1、基本配置
pom.xml依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.16.2</version>
</dependency>
Redisson配置
@Configuration
public class RedissonConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient(){
Config config = new Config();
// 单机
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379");
// 主从
// config.useMasterSlaveServers().setMasterAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379").addSlaveAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6389");
// 哨兵
// config.useSentinelServers().addSentinelAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379","redis://127.0.0.1:6389");
// 集群
// config.useClusterServers().addNodeAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379","redis://127.0.0.1:6389");
// 设置看门狗过期时间(锁默认释放时间)
// config.setLockWatchdogTimeout(10 * 1000);
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}
2、使用
// 1、获取key为"unFairLock"的锁对象
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("unFairLock");
// 2、加锁
lock.lock();
try {
// 进行具体的业务操作
...
} finally {
// 3、释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
3、加锁
3.1 获取锁
首先看下 RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("unFairLock") 初始化并返回对象 RedissonLock
public RLock getLock(String name) {
// 初始一个RedissonLock对象,构造方法中初始一些参数信息
return new RedissonLock(commandExecutor, name);
}
public RedissonLock(CommandAsyncExecutor commandExecutor, String name) {
super(commandExecutor, name);
this.commandExecutor = commandExecutor;
// 锁释放时间,也就是'看门狗'过期时间,默认 30*1000 ms,可在配置中进行更改
this.internalLockLeaseTime = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout();
// LockPubSub 后续会在获取锁失败以及释放锁的时候使用到
this.pubSub = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getSubscribeService().getLockPubSub();
}
进行加锁操作 lock.lock() ——> RedissonLock#lock 具体操作如下
public void lock() { try { lock(-1, null, false); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new IllegalStateException(); } }
private void lock(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, boolean interruptibly) throws InterruptedException { // 当前加锁的线程Id long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId(); // 尝试获取锁,并返回已经存在锁的过期时间,如果为null,则说明自己加锁成功 Long ttl = tryAcquire(-1, leaseTime, unit, threadId); // lock acquired // 说明加锁成功 if (ttl == null) { return; } // 未抢到锁,Redis订阅事件,,在释放锁的时候,lua脚本中会进行发布事件 RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = subscribe(threadId); if (interruptibly) { commandExecutor.syncSubscriptionInterrupted(future); } else { commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future); } // 如果没获取到锁,则进入循环获取 try { while (true) { // 再获取一次 ttl = tryAcquire(-1, leaseTime, unit, threadId); // lock acquired if (ttl == null) { break; } // waiting for message if (ttl >= 0) { try { // Semaphore.tryAcquire---指定时间内获取一个许可 // this.latch = new Semaphore(0); 所以,会阻塞 future.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } catch (InterruptedException e) { if (interruptibly) { throw e; } future.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } } else { if (interruptibly) { future.getNow().getLatch().acquire(); } else { future.getNow().getLatch().acquireUninterruptibly(); } } } } finally { unsubscribe(future, threadId); } }
获取锁,执行的方法 tryAcquire(-1,null,null,threadId) ——> RedissonLock#tryAcquireAsync(-1,-1,null,threadId)
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture;
if (leaseTime != -1) {
// 说明手动设置了锁释放时间,不会进行续期
ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
} else {
// 因为没有设置leaseTime,所以默认为-1,执行此段逻辑
ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, internalLockLeaseTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
return;
}
// lock acquired
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
if (leaseTime != -1) {
// 说明设置了锁释放时间,不会进行续期
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
} else {
// 进行锁的续命
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}
最终获取锁的逻辑 RedissonLock#tryLockInnerAsync 方法中执行lua脚本
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
// 选择redis节点(如果是集群),并执行lua脚本
return evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
// 判断当前key是否存在,第一次当然不存在,进入此分支
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
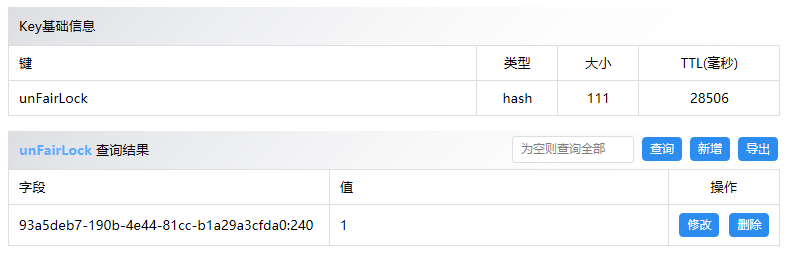
// 为哈希表中的字段值加上指定增量值 hincrby anyLock UUID:Thread 1
" redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
// 给当前key设置过期时间
" redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
" return nil; " +
"end; " +
// 如果key存在且当前线程已经持有锁, 重入
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
// 将加锁次数 +1
" redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
// 重置锁超时时间
" redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
" return nil; " +
"end; " +
// 如果加锁失败,则直接返回key的过期时间
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.singletonList(getRawName()), unit.toMillis(leaseTime), getLockName(threadId));
}
参数说明:
KEYS = Collections.singletonList(getRawName())
- KEYS[1]:getRawName(),就是key的名称,也就是获取锁对象时设置的"unFairLock"
ARGV = unit.toMillis(leaseTime), getLockName(threadId)
- ARGV[1]:unit.toMillis(leaseTime),锁过期的时间,默认30s
- ARGV[2]:getLockName(threadId),UUID:ThreadId,UUID来唯一标识一个客户端
从上述lua脚本可看出,这个锁是hash结构,最终存在Redis中的数据为:
3.2 获取锁成功
如默认锁的释放时间为30s,但是任务实际执行时间为35s,那么任务在执行到一半的时候锁就被其他线程给抢占了,这明显不符合需求。因此就出现了看门狗,专门进行续命操作,看门狗的存在是为了解决任务没执行完,锁就自动释放了场景。
在获取锁成功后(也就是lua脚本执行结束),如果返回null,代表着获取到锁,则会进行锁的续期,具体操作 scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId)
RedissonBaseLock#scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId) 开启续期任务
protected void scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId) {
ExpirationEntry entry = new ExpirationEntry();
// 如果传入key对应的value已经存在,就返回存在的value,不进行替换。如果不存在,就添加key和value,返回null
ExpirationEntry oldEntry = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(getEntryName(), entry);
if (oldEntry != null) {
// 如果不为null,说明是锁重入,当前线程对应的counter++,在释放锁的时候进行counter--操作
oldEntry.addThreadId(threadId);
} else {
// 一开始就是null,当前线程counter赋值1,并将threadId和counter对应的关系,存入一个Map中
entry.addThreadId(threadId);
// 调用定时任务
renewExpiration();
}
}
调用 renewExpiration() 开启定时任务
private void renewExpiration() {
// 上面已经传入,不为空
ExpirationEntry ee = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());
if (ee == null) {
return;
}
// 开启定时任务,时间是 internalLockLeaseTime/3 毫秒后执行
Timeout task = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
ExpirationEntry ent = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());
if (ent == null) {
return;
}
Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId();
if (threadId == null) {
return;
}
// 进行锁的续期
RFuture<Boolean> future = renewExpirationAsync(threadId);
future.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
log.error("Can't update lock " + getRawName() + " expiration", e);
EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.remove(getEntryName());
return;
}
if (res) {
// reschedule itself
// 循环调用,进行下一次的续期操作
renewExpiration();
} else {
cancelExpirationRenewal(null);
}
});
}
}, internalLockLeaseTime / 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
ee.setTimeout(task);
}
调用 renewExpirationAsync(threadId) 进行锁的续期,执行成功后,则会再次调用renewExpiration()下一次的续期操作,直到调用释放锁的时候,会删除定时任务
protected RFuture<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {
return evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
// 判断当前key中,是否还被线程UUID:ThreadId持有锁
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
// 如果持有,则对这个key进行续期
" redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
" return 1; " +
"end; " +
"return 0;",
Collections.singletonList(getRawName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
参数说明:
KEYS = Collections.singletonList(getRawName())
- KEYS[1]:getRawName(),就是key的名称,也就是获取锁对象时设置的"unFairLock"
ARGV = unit.toMillis(leaseTime), getLockName(threadId)
- ARGV[1]:unit.toMillis(leaseTime),锁过期的时间,默认30s
- ARGV[2]:getLockName(threadId),UUID:ThreadId,UUID来唯一标识一个客户端
3.3 获取锁失败
如果没有获取到锁的线程,先在redis中发布订阅消息,等待释放锁的线程发布通知
在上述获取锁的方法 Long ttl = tryAcquire(-1,null,null,threadId) 返回锁的过期时间,如果返回不是null,则说明获取锁失败,进行事件的订阅
// 未抢到锁,Redis订阅事件,,在释放锁的时候,lua脚本中会进行发布事件
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = subscribe(threadId);
RedissonClient#subscribe(threadId) 进行订阅
protected RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribe(long threadId) {
// getChannelName() - redisson_lock__channel:{unFairLock} 订阅事件通道,其中unFairLock就是设置的锁名称
return pubSub.subscribe(getEntryName(), getChannelName());
}
PublishSubscribe.subscribe(String entryName, String channelName) 订阅操作
public RFuture<E> subscribe(String entryName, String channelName) {
AsyncSemaphore semaphore = service.getSemaphore(new ChannelName(channelName));
RPromise<E> newPromise = new RedissonPromise<>();
semaphore.acquire(() -> {
if (!newPromise.setUncancellable()) {
semaphore.release();
return;
}
// 1、判断RedisLockEntry 是否存在
E entry = entries.get(entryName);
if (entry != null) {
entry.acquire();
semaphore.release();
entry.getPromise().onComplete(new TransferListener<E>(newPromise));
return;
}
// 2、创建RedisLockEntry
E value = createEntry(newPromise);
value.acquire();
E oldValue = entries.putIfAbsent(entryName, value);
if (oldValue != null) {
oldValue.acquire();
semaphore.release();
oldValue.getPromise().onComplete(new TransferListener<E>(newPromise));
return;
}
// 3、创建一个监听器,别的线程进行redis-pub命令之后进行调用
RedisPubSubListener<Object> listener = createListener(channelName, value);
// 4、底层交给netty调用redis-sub命令
service.subscribe(LongCodec.INSTANCE, channelName, semaphore, listener);
});
return newPromise;
}
PubSubLock.createEntry() 定义对象RedissonLockEntry,并初始semaphore信号量(jdk中的定义),用于获取锁失败后阻塞获取操作
protected RedissonLockEntry createEntry(RPromise<RedissonLockEntry> newPromise) {
return new RedissonLockEntry(newPromise);
}
public RedissonLockEntry(RPromise<RedissonLockEntry> promise) {
super();
// 定义Semaphore信号量,初始许可为0
this.latch = new Semaphore(0);
this.promise = promise;
}
事件订阅完成后,会进入while (true)死循环中,首先会再获取一次,因为可能之前获取锁的客户端刚好释放锁了,如果还没获取成功,那么就进入等待状态,等待时间是返回的锁key的ttl。
// Semaphore.tryAcquire---指定时间内获取一个许可
// this.latch = new Semaphore(0); 许可为0,所以,会阻塞
future.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
循环中每次都先试着获取锁,并得到已存在的锁的剩余时间。如果在重试中拿到了锁,则直接返回。如果锁当前还是被占用的,那么等待释放锁的消息
4、释放锁
释放锁 lock.unlock() ——> RedissonBaseLock#unlockAsync(long threadId) 中进行锁的释放和取消"看门狗"的操作
public RFuture<Void> unlockAsync(long threadId) {
RPromise<Void> result = new RedissonPromise<>();
// 释放锁
RFuture<Boolean> future = unlockInnerAsync(threadId);
future.onComplete((opStatus, e) -> {
// 取消"看门狗"续期线程
cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId);
if (e != null) {
result.tryFailure(e);
return;
}
// 如果返回null,则说明锁不是当前线程加的
if (opStatus == null) {
IllegalMonitorStateException cause = new IllegalMonitorStateException(
"attempt to unlock lock, not locked by current thread by node id: " + id + " thread-id: " + threadId);
result.tryFailure(cause);
return;
}
result.trySuccess(null);
});
return result;
}
解锁的具体操作 RedissonLock#unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) 也就是执行lua脚本
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
// 判断锁是否是当前线程加的(当前线程是否持有锁)如果不存在,返回nil 如果返回null,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
" return nil;" +
"end; " +
// 将线程对key加锁的重入次数减1
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
// 当前线程对这个key的重入锁次数counter还大于0,就表示当前线程对这个key不止加过一次锁,此时当然就不能删掉key
"if (counter > 0) then " +
// 重置下key的存活时间
" redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
" return 0; " +
"else " +
// counter不大于0,表示当前线程只对这个key加过一次锁,删除掉
" redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
// 发布Redis publish 指令,被其他获取不到锁的线程给监听到,进入下一轮的占锁操作
" redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
" return 1; " +
"end; " +
"return nil;",
Arrays.asList(getRawName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
参数说明:
KEYS = Arrays.asList(getRawName(), getChannelName())
- KEYS[1]:getRawName(),就是key的名称,也就是获取锁对象时设置的"unFairLock"
- KEYS[2]:getChannelName(),redis订阅通道的名称,redisson_lock__channel:{unFairLock}
ARGV = LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId)
- ARGV[1]:LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE,Redis发布事件时的message,为0
- ARGV[2]:internalLockLeaseTime,锁过期的时间,默认30s
- ARGV[3]:getLockName(threadId),UUID:ThreadId,UUID来唯一标识一个客户端
如果释放锁成功,也就是lua脚本执行结果不为null,则会取消“看门狗”线程 cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId)
protected void cancelExpirationRenewal(Long threadId) { ExpirationEntry task = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName()); if (task == null) { return; } if (threadId != null) { // 将Map中当前线程进行counter-- task.removeThreadId(threadId); } // task.hasNoThreads()判断存放线程Map.isEmpty();如果成立,则停止定时任务 if (threadId == null || task.hasNoThreads()) { Timeout timeout = task.getTimeout(); if (timeout != null) { // 停止定时任务 timeout.cancel(); } EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.remove(getEntryName()); } }
就这样,RedissonLock释放锁操作完成,并往未获取到锁订阅的通道redisson_lock__channel:{unFairLock}中,发布了一条message=0的事件,那么事件的接收又在哪操作,回到事件订阅的部分,其中有一行定义事件监听的代码
// 3、创建一个监听器,别的线程进行redis-pub命令之后进行调用
RedisPubSubListener<Object> listener = createListener(channelName, value);
private RedisPubSubListener<Object> createListener(String channelName, E value) {
// 定义监听redis发布的事件
RedisPubSubListener<Object> listener = new BaseRedisPubSubListener() {
@Override
public void onMessage(CharSequence channel, Object message) {
if (!channelName.equals(channel.toString())) {
return;
}
// 进行事件的处理
PublishSubscribe.this.onMessage(value, (Long) message);
}
@Override
public boolean onStatus(PubSubType type, CharSequence channel) {
if (!channelName.equals(channel.toString())) {
return false;
}
if (type == PubSubType.SUBSCRIBE) {
value.getPromise().trySuccess(value);
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
return listener;
}
事件处理最终会执 LockPubSub#onMessage(RedissonLockEntry value, Long message) 方法,因为在lua脚本中发布了一条message=0的事件,所以执行第一个if逻辑
protected void onMessage(RedissonLockEntry value, Long message) {
if (message.equals(UNLOCK_MESSAGE)) {
Runnable runnableToExecute = value.getListeners().poll();
if (runnableToExecute != null) {
runnableToExecute.run();
}
// semaphore.release() 进行信号量的释放
value.getLatch().release();
} else if (message.equals(READ_UNLOCK_MESSAGE)) {
while (true) {
Runnable runnableToExecute = value.getListeners().poll();
if (runnableToExecute == null) {
break;
}
runnableToExecute.run();
}
value.getLatch().release(value.getLatch().getQueueLength());
}
}
当执行 value.getLatch().release() 则会唤醒之前所有阻塞等待的线程,进行新一轮的抢锁操作(这也就是非公平锁体现的地方)
至此,释放锁-获取锁 就形成了遥相呼应。
5、其他的加锁方式
如果我们需要指定获取锁成功后持有锁的时长,可以执行下面方法,指定 leaseTime
lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
如果指定了 leaseTime,watchdog就不会再启用了。
如果不但需要指定持有锁的时长,还想避免锁获取失败时的死循环,可以同时指定 leaseTime 和 waitTime
boolean res = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
如果指定了 waitTime,只会在 waitTime 时间内循环尝试获取锁,超过 waitTime 如果还是获取失败,直接返回false。
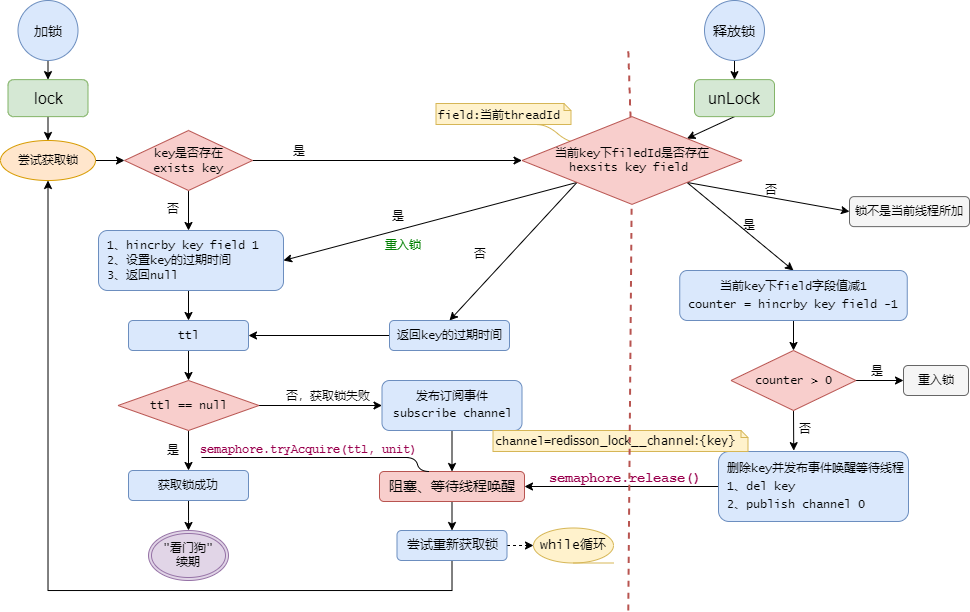
6、流程图
大体流程如下图: