Toast: http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/Toast.html
在部分手机中如果当把编辑完的消息发送完成之后,通常在手机下方会出现:”消息发送成功“的提示消息或相类似的提示消息,并且通常会短暂的停留之后会自动消失;那么这个就是一个典型的Toast应用;
消息提示框的种类有多种比如说:Dialog(在以后章节中会介绍)。而Toast与Dialog不同:Dialog是以独占的方式显示的,换句话说就是:如果不关闭它Dialog会一直显示于当前界面,而Toast则会短暂的停留之后自动关闭;
实现Toast其实很简单,在这里介绍三种方式:
- 直接使用静态方法:makeText(Context, int/CharSequence,int);
-
Toast toast = Toast.makeText(UsingIntent.this, "Some thing you want to show", Toast.LENGTH_LONG);
toast.show();
-
调用makeText方法,会以文本的方式来进行显示,因为它默认载入一个TextView,而第三参数可以通过:Toast的二个静态域LENGTH_LONG/LENGTH_SHORT来进行设置; 之所以返回一个Toast是为了方便扩展,比如调用setDuration方法;
2. 添加一些自己想要的效果,个人觉得有点像重写makeText方法的味道
// LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater) YouAcvity.this.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE); A View view = getLayoutInflater().inflate(your_layout_file,null); //B :A,B二者中选其一即可,在这里只是提供二种途径 Toast toast = new Toast(YouActivity.this); toast.setDuration(Toast.LENGTH_LONG); toast.setView(view); toast.show(); //别忘记invoke show方法
3. Toast消息提示框会在一定时间后自动消失,如果想永远停留该怎么办呢?能不能做得到呢?
首先告诉你永远停留是可以做得到的,可怎么去实现呢?
查看源码后获知,Toast.show方法是采用队列来进行显示,系统会依次取出一个Toast并显示,等到一定的时间后它会自动消失,系统再会取出下一Toast,直接在整个队列中没有Toast为止;在Toast类有个私有的静态内部类叫作:TN;因为TN是私有,那么该如何访问呢? 答案是反射。
1 try { 2 Field field =toast.getClass().getDeclaredField("mTN");
field.setAccessible(true); Object object = field.get(toast); 3 Method method=object.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("show",null);
5 //object 最后定义在类里面,这样方面多次使用,比如关闭Toast 4 method.invoke(object,new Object[0]); 6 //new Object[0]可以用null代替,但是因为是可变参数,所以最好使用new Object[0]
7 } catch (Exception e) 8 { 9 e.printStackTrace(); 10 }
如果有关闭Toast,可以使用(//method =object.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("hide",null););同时Toast提供一个其它的方法比如:setGravity方法;
Notification: http://developer.android.com/reference/android/app/Notification.html
- 理论基础:
- 状态条与状态栏:用图说明可能会更清楚,请见下图!
- 状态条:

- 状态栏:
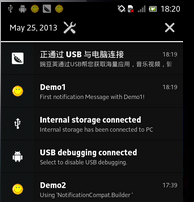 ,需要执行下拉动作,才可以查看整个状态栏具体信息。
,需要执行下拉动作,才可以查看整个状态栏具体信息。 - 关系:状态栏包含状态条!
- 状态条:
- Notification 有这些组件:
-
- 内容标题
- 大图标 : 通常显示在左侧
- 内容文本
- Content info: 译为备注信息应该会好点,Anyway ,you can believe your choice.
- 小图标
- 时间戳
- 状态条与状态栏:用图说明可能会更清楚,请见下图!
- 如何运用Notification
- 获取NotificationManager对象
- 获得Notification对象
- 设置Notification属性
- 设置PendingIntent
- Invoke notify方法
总体分这五步!!!
Notification设计哲学是:管理通知对象,通知实体对象,Build对象(内部类),以及PendingIntent!
管理通知对象:NotificationManager: 拥有发布,更新,取消等通知功能。
通知实体对象:拥有多个实体属性
Build对象:用于创建通知实体对象以及设置相关属性
PendingIntent: 如果要启动新的Activity通常是调用startActivity,startActivityForResult;而PendingIntent是对Intent的进一步封装,以便当我们查看Notification执行相应动作时转入对应的Activity.
在Andorid 3.0以下创建通知对象通常是直接利用:Notification的构建函数进行,而伴随的Android os的更新升级,更多时候是使用另外二个支持类(内部类):NotificationCompat.Builder,Notification.Builder 这二者功能类似,主要区别在于:NotificationCompat.Builder可以兼容API level 4,并且它是由:SupportLibrary提供。
实码演练:这时提供一个小Demo。
Layout file:

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" 4 android:layout_height="fill_parent"> 5 6 <Button 7 android:id="@+id/notification_demo1" 8 android:layout_width="match_parent" 9 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 10 android:text="@string/notification_btn_string1" 11 /> 12 <Button 13 android:id="@+id/notification_demo2" 14 android:layout_width="match_parent" 15 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 16 android:text="@string/notification_btn_string2" 17 /> 18 <Button 19 android:id="@+id/notification_demo2_1" 20 android:layout_width="match_parent" 21 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 22 android:text="@string/notification_btn_string2_1" 23 /> 24 <Button 25 android:id="@+id/notification_demo3" 26 android:layout_width="match_parent" 27 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 28 android:text="@string/notification_btn_string3" 29 /> 30 <Button 31 android:id="@+id/notification_demo4" 32 android:layout_width="match_parent" 33 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 34 android:text="@string/notification_btn_string4" 35 /> 36 <Button 37 android:id="@+id/notification_demo5" 38 android:layout_width="match_parent" 39 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 40 android:text="@string/notification_btn_string5" 41 /> 42 </LinearLayout>
Code

1 package com.ringcentral.wolf.ch04; 2 3 4 import com.ringcentral.wolf.R; 5 import com.ringcentral.wolf.ch03.UsingIntent; 6 7 import android.app.Activity; 8 import android.app.Notification; 9 import android.app.NotificationManager; 10 import android.app.PendingIntent; 11 import android.content.Intent; 12 import android.os.Bundle; 13 import android.support.v4.app.NotificationCompat; 14 import android.support.v4.app.TaskStackBuilder; 15 import android.view.View; 16 import android.view.View.OnClickListener; 17 import android.widget.Button; 18 19 public class NotificationTest extends Activity implements OnClickListener { 20 private NotificationManager nManager; 21 private Button demo1; 22 private Button demo2; 23 private Button demo2_1; 24 private Button demo3; 25 private Button demo4; 26 private Button demo5; 27 28 NotificationCompat.Builder builder; 29 @Override 30 public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState ){ 31 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 32 setContentView(com.ringcentral.wolf.R.layout.notification); 33 nManager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE); 34 demo1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.notification_demo1); 35 demo2 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.notification_demo2); 36 demo2_1= (Button) findViewById(R.id.notification_demo2_1); 37 demo3 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.notification_demo3); 38 demo4 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.notification_demo4); 39 demo5 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.notification_demo5); 40 builder = new NotificationCompat.Builder(this); 41 42 43 demo1.setOnClickListener(this); 44 demo2.setOnClickListener(this); 45 demo3.setOnClickListener(this); 46 demo4.setOnClickListener(this); 47 demo5.setOnClickListener(this); 48 demo2_1.setOnClickListener(this); 49 } 50 51 @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") 52 private void demo1(int id){ 53 /** 54 * 也可以调用构造方法,设置属性 55 */ 56 Notification notification = new Notification(); 57 notification.icon = R.drawable.smile; 58 notification.number = 2<<2; 59 notification.when = System.currentTimeMillis(); 60 notification.tickerText="You have a new message!! Come from Demo1"; 61 notification.defaults=Notification.DEFAULT_SOUND; 62 //notification.flags =Notification.FLAG_NO_CLEAR; 63 notification.flags=Notification.FLAG_ONGOING_EVENT; 64 65 PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, getIntent(), 0); 66 notification.setLatestEventInfo(this, "Demo1", "First notification Message with Demo1!", pendingIntent); 67 68 nManager.notify(id,notification); 69 70 } 71 72 private void demo2(int id){ 73 builder.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.smile) 74 .setContentTitle("Demo2") 75 .setContentText("Using 'NotificationCompat.Builder '"); 76 builder.setDefaults(Notification.DEFAULT_VIBRATE).setTicker("You have a new message!! Come from Demo2"); 77 78 Intent intent = new Intent(this,UsingIntent.class); 79 80 TaskStackBuilder stackBuilder = TaskStackBuilder.create(this); 81 stackBuilder.addParentStack(UsingIntent.class); 82 stackBuilder.addNextIntent(intent); 83 84 PendingIntent pendingIntent = stackBuilder.getPendingIntent(0,PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT); 85 86 builder.setContentIntent(pendingIntent); 87 nManager.notify(id, builder.build()); 88 } 89 private void demo2_1(int id){ 90 builder.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.smile) 91 .setContentTitle("Demo2_1") 92 .setContentText("Using 'getActivity '"); 93 builder.setDefaults(Notification.DEFAULT_VIBRATE).setTicker("You have a new message!! Come from Demo2_1"); 94 95 Intent intent = new Intent(this,UsingIntent.class); 96 intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK|Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK ); 97 98 PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT); 99 builder.setContentIntent(pendingIntent); 100 nManager.notify(id, builder.build()); 101 } 102 private void clear1(int id){ 103 nManager.cancel(id); 104 } 105 private void clearAll(){ 106 nManager.cancelAll(); 107 } 108 /** 109 * 如果要更新通知,简单:保持 id 不变,进行重新绘制;新产生的通知会自动覆盖旧通知!!! 110 */ 111 private void update(int id){ 112 builder.setContentTitle("Update Demo2"); 113 builder.setContentText("Update Demo"); 114 builder.setDefaults(Notification.DEFAULT_VIBRATE).setTicker("Updte a new message!! Come from Demo2"); 115 Intent intent = new Intent(this,UsingIntent.class); 116 117 TaskStackBuilder stackBuilder = TaskStackBuilder.create(this); 118 stackBuilder.addParentStack(UsingIntent.class); 119 stackBuilder.addNextIntent(intent); 120 121 PendingIntent pendingIntent = stackBuilder.getPendingIntent(0,PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT); 122 builder.setContentIntent(pendingIntent); 123 nManager.notify(id, builder.build()); 124 125 } 126 @Override 127 public void onClick(View v) { 128 switch (v.getId()) { 129 case R.id.notification_demo1: 130 demo1(R.id.notification_demo1); 131 break; 132 case R.id.notification_demo2: 133 demo2(R.id.notification_demo2); 134 break; 135 case R.id.notification_demo2_1: 136 demo2_1(R.id.notification_demo2); 137 break; 138 case R.id.notification_demo3: 139 clear1(R.id.notification_demo1); 140 break; 141 case R.id.notification_demo4: 142 clearAll(); 143 break; 144 case R.id.notification_demo5: 145 update(R.id.notification_demo2); 146 break; 147 default: 148 break; 149 } 150 151 } 152 153 }
如果要有震动效果,请在manifest file中设置:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.VIBRATE"/>
备注:这只是提供Demo代码,并不能直接复制,如果要练习,要本地化;另外UsingIntent类很简单就是一Activity,因为在这里就没有提供。
如果是android 4.1及以后本版,还可以使用BigView,考虑到普及率不高,这里不于解释,感兴趣的同学可以直接上官网。
利用PendingIntent设置Activity比较重要,它有二种方式:
- 创建后台推栈基于Intent启动的Activity
- 先创建Intent对象
- TaskStackBuilder.create()来创建一个任务栈
- 调用addParentStack()把后台推栈添加到栈中,调用addNextIntent()来添加Intent对象
- 用TastStackBuilder对象调用getPendingIntent()获得一个PendingIntent。
- 最后调用:setContentIntent把PendingIntent对象作为参数。
- 不创建后台推栈,可以设置一个专用的Activity
- 第一步也是先创建Intent对象
- 设置Flags:
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK|Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK );
- PendingIntent.getActivity(.....)
- 最后调用:setContentIntent把PendingIntent对象作为参数。
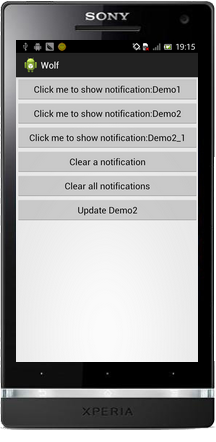
Demo程序主界面:
【Dylan童鞋】
关注Dylan童鞋,请搜索微信号:DylanTongXue 。
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Q群:315858410. 此群用于关注DylanTongXue者交流!群成员职业不限,程序员居多,讨论主题不限:技术分享,生活感悟,职场心得,时事分析...


 ,需要执行下拉动作,才可以查看整个状态栏具体信息。
,需要执行下拉动作,才可以查看整个状态栏具体信息。

