使用K-means和高斯混合模型对图像进行聚类
导入图片
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | %matplotlib inlineimport numpy as np import skimage.io as SKimg import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.cluster import KMeansfrom sklearn.mixture import GaussianMixturefrom skimage import io,data,colorfrom scipy.ndimage import gaussian_filterfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D # noqa: F401 unused importimport time<br>import matplotlib.cm as cmimgpath=r"H:\02Course\pics\35049.jpg"img =SKimg.imread(imgpath)io.imshow(img)print(type(img)) #显示类型print(img.shape) #显示尺寸print('图片高度:',img.shape[0]) #图片高度print('图片宽度:',img.shape[1]) #图片宽度print('图片通道数:',img.shape[2]) #图片通道数print('总像素个数:',img.size) #显示总像素个数print('最大像素值:',img.max()) #最大像素值print('最小像素值:',img.min()) #最小像素值print('像素平均值:',img.mean()) #像素平均值print('图像的像素值:',img[0][0])#图像的像素值 |

1 2 3 4 5 6 | image_height, image_width, image_channels = img.shapeimage_pixels = np.reshape(img, (-1, image_channels))#将三维矩阵转为通道特征矩阵 每列代表R G B值_mean = np.mean(image_pixels,axis=0,keepdims=True)_std = np.std(image_pixels,axis=0,keepdims=True)image_pixels_ = (image_pixels - _mean) / _std # 归一化X=image_pixels_ #特征矩阵 |
1 2 3 | #绘制每个通道的直方图Kwars=dict(histtype='stepfilled',alpha=0.4,bins=np.arange(0,255))#,normed=Trueintervals=plt.hist(image_pixels,color=[ "red","green","blue"],**Kwars) |
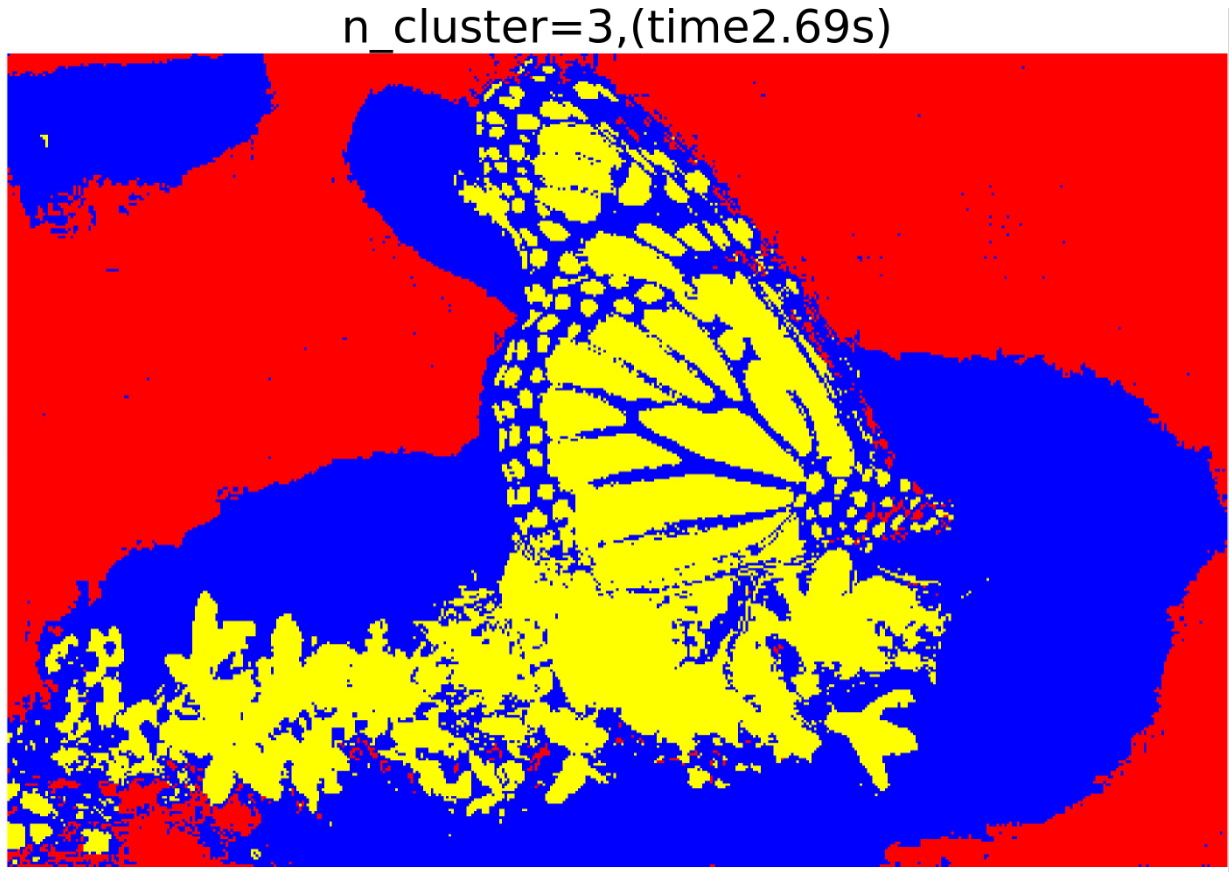
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 | #聚类个数从3递增至8for ncomp in range(3,9): fig =plt.figure(figsize=(12,10)) plt.axis('off') t0 = time.time() gmm = GaussianMixture(n_components=ncomp,covariance_type='full').fit(X)#调用GMM算法,设置聚类的目标类别数 Clus_Centers=gmm.means_#每个类别的聚类中心 Labels=gmm.predict(X) elapsed_time = time.time() - t0 Labels_show=np.reshape(Labels,(image_height, image_width))#把分类标签展开为二维数组 dst=color.label2rgb(Labels_show)#将标签转为RGB plt.title('n_cluster=%i,(time%.2fs)'%(ncomp,elapsed_time), size=25) plt.imshow(dst) fig.savefig('pics/gmm_cluster_%i.jpg'%(ncomp), format='jpg', dpi=300,bbox_inches = 'tight',pad_inches = 0)#保存聚类结果图 Labels_arr=np.reshape(Labels_show, (-1, 1)) combine=np.append(image_pixels, Labels_arr, 1) fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10)) ax = plt.axes(projection='3d') xs = combine[:,0] ys = combine[:,1] zs = combine[:,2] ax.scatter(xs, ys, zs,c=combine[:,3],edgecolors='none',s=1) ax.set_xlabel('R channel') ax.set_ylabel('G channel') ax.set_zlabel('B channel') plt.show() fig.savefig('pics/gmm_cluster3d_%i.jpg'%(ncomp), format='jpg', dpi=300,bbox_inches = 'tight',pad_inches = 0)#保存RGB通道三维特征空间图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,5)) plt.xlabel('R channel') plt.ylabel('G channel') plt.axis('equal') plt.xlim(0, 255) plt.ylim(0, 255) plt.scatter(combine[:, 0], combine[:, 1], c=combine[:,3],s=.2) plt.colorbar() plt.show() fig.savefig('pics2/gmm_clusterR&G_%i.jpg'%(ncomp), format='jpg', dpi=300,bbox_inches = 'tight',pad_inches = 0)#保存RG通道二维特征空间图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,5)) plt.xlabel('R channel') plt.ylabel('B channel') plt.axis('equal') plt.xlim(0, 255) plt.ylim(0, 255) plt.scatter(combine[:, 0], combine[:, 2], c=combine[:,3],s=.2) plt.colorbar() plt.show() fig.savefig('pics/gmm_clusterR&B_%i.jpg'%(ncomp), format='jpg', dpi=300,bbox_inches = 'tight',pad_inches = 0)#保存RB通道二维特征空间图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,5)) plt.xlabel('G channel') plt.ylabel('B channel') plt.axis('equal') plt.xlim(0, 255) plt.ylim(0, 255) plt.scatter(combine[:, 1], combine[:, 2], c=combine[:,3],s=.2) plt.colorbar() plt.show() fig.savefig('pics/gmm_clusterG&B_%i.jpg'%(ncomp), format='jpg', dpi=300,bbox_inches = 'tight',pad_inches = 0)#保存GB通道二维特征空间图 |


聚类算法换位K-means,只需将聚类部分代码换为:
1 2 | kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=ncomp,random_state=0)Labels = kmeans.fit_predict(X) |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | #高斯滤波 可平滑噪声 #替换即可img =SKimg.imread(imgpath)img[:,:,0] = gaussian_filter(img[:,:,0], sigma=1)img[:,:,1] = gaussian_filter(img[:,:,1], sigma=1)img[:,:,2] = gaussian_filter(img[:,:,2], sigma=1)plt.axis('off')plt.imshow(img)plt.savefig('pics/gausfilter.jpg', format='jpg', dpi=300,bbox_inches = 'tight',pad_inches = 0) |
参考:
https://jakevdp.github.io/PythonDataScienceHandbook/05.12-gaussian-mixtures.html
https://scikit-learn.org/0.15/modules/generated/sklearn.mixture.GMM.html





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 一文读懂知识蒸馏
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下