基于python的鸢尾花二分类
前言
也算是自己接触的第一个实例化的完整实现的小项目了吧(以前的的作业之类的都是没完全弄懂就交了不算哈),本此分享为简易鸢尾花的分类,实现语言是python 3.7,实现环境就是jupyter notebook。
1.数据集简介
本次数据集是从sklearn库中导入的load_iris()数据集,数据分四列,分别代表花萼长度、花萼宽度、花瓣长度、花瓣宽度,标签列或者说是target列有三种花种的类别数据表示分别是:'setosa', 'versicolor', 'virginica';在数据集中以0,1,2 的形式展示。在本次实验中选择的是二分类任务这就要求我们对数据集进行一定的划分(这点的代码方面给了我很大的提升,个人觉得受益匪浅,我入坑的前进道路进了一大步)
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.datasets import load_iris from pylab import mpl iris = load_iris() iris.feature_names, iris.target_names,iris.target,iris,data # 显示你需要看的所有数据
2.看看数据
下面我们来看看数据集的具体数字,如下图所示,四列是feature_names的数据,也就是花萼的有关数据,中间一行是target 也就是标签--花的种类,可以看到有50个0、50个1、50个2。
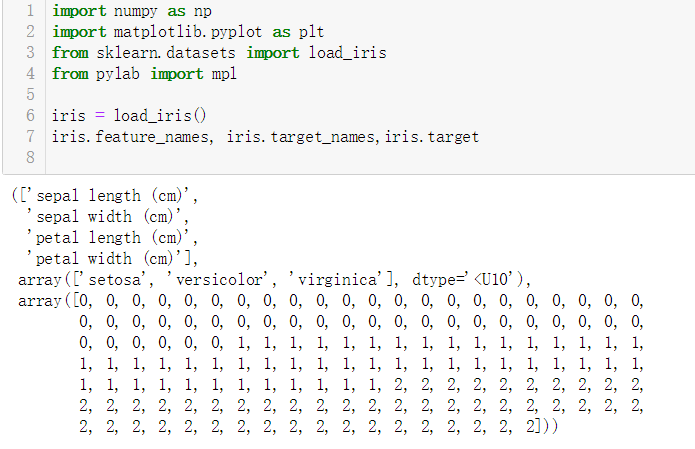
3.筛选数据并可视化
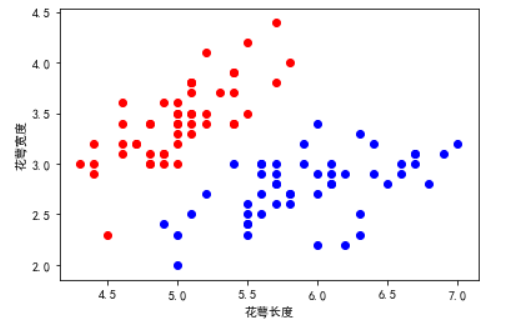
接下来就是数据筛选,我们选择二分类需要的数据,在这里决定对0和1进行分类,数据选择为前一百个。利用花萼长度和花萼宽度进行一个预测,四个数据的以此类推大致输出就是z = sigmoid(w1x1 + w2x2),w是权重值,x是特征。
1 x = iris.data[0:100,0:2] # 数据选择0到100行。前两列的标签数据,也就是0与1的花萼花瓣的数据 2 y = iris.target[0:100] # 这是选中对应的前100个标签数据 3 samples_0 = x[y == 0,:] # samples-0 是标签 y==0的集合 4 samples_1 = x[y == 1,:] # samples-1 是标签 y==1的集合 5 plt.scatter(samples_0[:,0],samples_0[:,1],marker ='o',color = 'r') 6 plt.scatter(samples_1[:,0],samples_1[:,1],marker ='o',color = 'b') #画出散点图 7 mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 没有这行代码,画出的图的xy轴标签数据会乱码没发现显示 8 plt.xlabel("花萼长度") 9 plt.ylabel("花萼宽度")
显示的图像如下:
接下来就是划分训练集和测试集;由于原始数据排列得很好所以我们要有预谋的进行打乱
xtrain = np.vstack([x[0:40,:],x[60:100,:]]) # 选中X的前40行和60到99行的数据,列数为X的所有列虽然只有2列 ytrain = np.concatenate([y[0:40],y[60:100]]) #把x对应的标签数据对应挑出来 xtest = x[40:60,:] # 把剩下的当作数据集 ytest = y[40:60] # 剩下的标签当作数据集 xtest.shape,ytest.shape
4.设计函数模型并输出
接下来就是定义Logistic类和各种函数了:
class LR(): def __init__(self): self.w = None # w就是我们要训练的权重值 def sigmoid(self,z): a = 1/(1+ np.exp(-z)) # 也可以用lambda函数进行设置 return a def output(self,x): # 输出嘛,肯定是经过sigmoid激活函数进行转换 z = np.dot(self.w,x.T) a = self.sigmoid(z) return a def comloss(self,x,y): numtrain = x.shape[0] # x 是数据 y是标签 输出的是x的行数,将0变成1就是列数 a = self.output(x) loss = np.sum(-y * np.log(a) - (1-y)*np.log(1-a))/numtrain # 自定义的损失函数,可以在这里进行调试 dw = np.dot((a-y),x) / numtrain # dot就是向量之间点乘的函数,dw是导数,这里用了梯度下降法 return loss,dw def train(self,x,y,learningrate = 0.1,num_interations = 10000 ): # 学习率就是梯度下降的直接影响步长的量,10000是迭代次数 numtrain,numfeatures = x.shape self.w = 0.001 * np.random.randn(1,numfeatures) loss = [] for i in range(num_interations): error,dw = self.comloss(x,y) loss.append(error) self.w -= learningrate * dw # 更新权重 if i % 200 == 0: # 每200次进行一次损失输出 print('steps:[%d/%d],loss: %f' % (i,num_interations,error)) return loss def predict(self,x): a = self.output(x) ypred = np.where(a >= 0.5,1,0) return ypred LR = LR() loss = LR.train(xtrain,ytrain) plt.plot(loss) 输出: steps:[0/10000],loss: 0.692566 steps:[200/10000],loss: 0.237656 steps:[400/10000],loss: 0.155935 steps:[600/10000],loss: 0.121161 steps:[800/10000],loss: 0.101404 steps:[1000/10000],loss: 0.088442 steps:[1200/10000],loss: 0.079171 steps:[1400/10000],loss: 0.072148 steps:[1600/10000],loss: 0.066605 steps:[1800/10000],loss: 0.062095 steps:[2000/10000],loss: 0.058337 steps:[2200/10000],loss: 0.055146 steps:[2400/10000],loss: 0.052395 steps:[2600/10000],loss: 0.049991 steps:[2800/10000],loss: 0.047869 steps:[3000/10000],loss: 0.045979 steps:[3200/10000],loss: 0.044280 steps:[3400/10000],loss: 0.042744 steps:[3600/10000],loss: 0.041346 steps:[3800/10000],loss: 0.040068 steps:[4000/10000],loss: 0.038892 steps:[4200/10000],loss: 0.037806 steps:[4400/10000],loss: 0.036800 steps:[4600/10000],loss: 0.035864 steps:[4800/10000],loss: 0.034990 steps:[5000/10000],loss: 0.034173 steps:[5200/10000],loss: 0.033405 steps:[5400/10000],loss: 0.032683 steps:[5600/10000],loss: 0.032002 steps:[5800/10000],loss: 0.031358 steps:[6000/10000],loss: 0.030749 steps:[6200/10000],loss: 0.030170 steps:[6400/10000],loss: 0.029621 steps:[6600/10000],loss: 0.029097 steps:[6800/10000],loss: 0.028599 steps:[7000/10000],loss: 0.028122 steps:[7200/10000],loss: 0.027667 steps:[7400/10000],loss: 0.027231 steps:[7600/10000],loss: 0.026813 steps:[7800/10000],loss: 0.026413 steps:[8000/10000],loss: 0.026028 steps:[8200/10000],loss: 0.025657 steps:[8400/10000],loss: 0.025301 steps:[8600/10000],loss: 0.024958 steps:[8800/10000],loss: 0.024627 steps:[9000/10000],loss: 0.024308 steps:[9200/10000],loss: 0.023999 steps:[9400/10000],loss: 0.023701 steps:[9600/10000],loss: 0.023413 steps:[9800/10000],loss: 0.023134
损失表达图像:
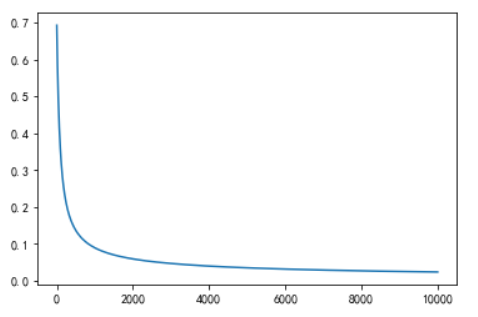
可以看出来经过梯度下降法的不断迭代其损失不断下降。
经过训练,权重值已经算出来了,接下来对其进行一个可视化;
plt.scatter(samples_0[:,0],samples_0[:,1],marker ='o',color = 'r') plt.scatter(samples_1[:,0],samples_1[:,1],marker ='o',color = 'b') mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] plt.xlabel("花萼长度") plt.ylabel("花萼宽度") x1 = np.arange(4,7.5,0.05) # 数据都是根据 数据集合理设置的 目的是为了不留太多空白 x2 = (-LR.w[0][0]* x1)/LR.w[0][1] # plt.plot(x1,x2,'-',color = 'black')
输出图像为;
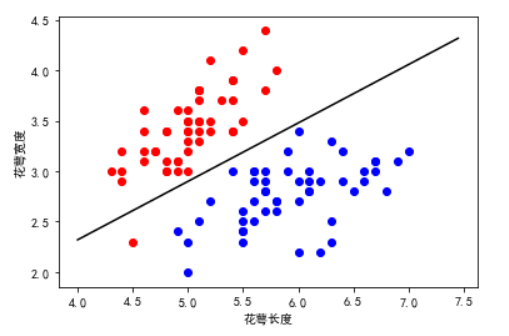
为了便于读者理解,在这里加两行代码进行分析:
numtest = xtest.shape[0] prediction = LR.predict(xtest) acc = np.sum(prediction == ytest)/numtest print("准确率",acc) LR.w # 输出最终预测的权重值
输出:
好了 到此为止,预测,损失,训练的权重值,准确率都出来了,本次实验比较简单,但是折射出很多细节问题,还是值得小白入手训练的。
贴一下完整代码(其实上面就是完整了,为了减少学生白嫖党的烦恼还是总结一下吧,毕竟我也是这么过来的哈哈):
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.datasets import load_iris from pylab import mpl iris = load_iris() iris.feature_names, iris.target_names x = iris.data[0:100,0:2] y = iris.target[0:100] samples_0 = x[y == 0,:] # samples-0 是标签 y==0的集合 samples_1 = x[y == 1,:] # samples-1 是标签 y==1的集合 plt.scatter(samples_0[:,0],samples_0[:,1],marker ='o',color = 'r') plt.scatter(samples_1[:,0],samples_1[:,1],marker ='o',color = 'b') mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] plt.xlabel("花萼长度") plt.ylabel("花萼宽度") # 划分数据集 xtrain = np.vstack([x[0:40,:],x[60:100,:]]) # 原始x 定义的是两列数据 ytrain = np.concatenate([y[0:40],y[60:100]]) #原始y 是标签值 xtest = x[40:60,:] ytest = y[40:60] xtest.shape,ytest.shape class LR(): def __init__(self): self.w = None def sigmoid(self,z): a = 1/(1+ np.exp(-z)) return a def output(self,x): z = np.dot(self.w,x.T) a = self.sigmoid(z) return a def comloss(self,x,y): numtrain = x.shape[0] # x 是数据 y是标签 输出的是x的行数,1就是列数 a = self.output(x) loss = np.sum(-y * np.log(a) - (1-y)*np.log(1-a))/numtrain dw = np.dot((a-y),x) / numtrain return loss,dw def train(self,x,y,learningrate = 0.1,num_interations = 10000 ): numtrain,numfeatures = x.shape self.w = 0.001 * np.random.randn(1,numfeatures) loss = [] for i in range(num_interations): error,dw = self.comloss(x,y) loss.append(error) self.w -= learningrate * dw # 更新权重 if i % 200 == 0: print('steps:[%d/%d],loss: %f' % (i,num_interations,error)) return loss def predict(self,x): a = self.output(x) ypred = np.where(a >= 0.5,1,0) return ypred LR = LR() loss = LR.train(xtrain,ytrain) plt.plot(loss) plt.scatter(samples_0[:,0],samples_0[:,1],marker ='o',color = 'r') plt.scatter(samples_1[:,0],samples_1[:,1],marker ='o',color = 'b') mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] plt.xlabel("花萼长度") plt.ylabel("花萼宽度") x1 = np.arange(4,7.5,0.05) x2 = (-LR.w[0][0]* x1)/LR.w[0][1] plt.plot(x1,x2,'-',color = 'black') numtest = xtest.shape[0] prediction = LR.predict(xtest) acc = np.sum(prediction == ytest)/numtest print("准确率",acc) LR.w # 输出最终预测的权重值
建议从上而下依次复现才会理解。



