Java设计模式——原型模式
原型模式是一种创建模式,它在考虑性能的同时创建重复对象。
当直接创建对象成本高时,使用原形模式。它定义一个原型接口,这个接口会帮助返回克隆对象。
例如,一个对象将在一个代价高昂的数据库操作之后创建。我们可以缓存对象,在下一次请求时返回其克隆,并在需要时更新数据库,从而减少数据库调用。
举例说明:
- 创建一个抽象类Shape以及它的子类(Circle、Rectangle、Square);
- 创建ShapeCache类,它将shape对象存放在哈希表中,并在得到请求时返回一个克隆对象。
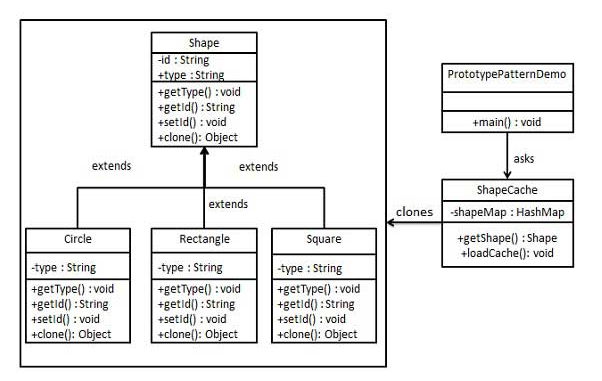
1、创建抽象类Shape,需要实现Clonable接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | public abstract class Shape implements Cloneable { private String id; protected String type; abstract void draw(); public String getType(){ return type; } public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public Object clone() { Object clone = null; try { clone = super.clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return clone; }} |
2、创建子类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | public class Rectangle extends Shape { public Rectangle(){ type = "Rectangle"; } @Override public void draw() { System.out.println("Inside Rectangle::draw() method."); }}public class Square extends Shape { public Square(){ type = "Square"; } @Override public void draw() { System.out.println("Inside Square::draw() method."); }}public class Circle extends Shape { public Circle(){ type = "Circle"; } @Override public void draw() { System.out.println("Inside Circle::draw() method."); }} |
3、创建ShapeCache类,用于将对象存放到哈希表中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | import java.util.Hashtable;public class ShapeCache { private static Hashtable<String, Shape> shapeMap = new Hashtable<String, Shape>(); public static Shape getShape(String shapeId) { Shape cachedShape = shapeMap.get(shapeId); return (Shape) cachedShape.clone(); } // for each shape run database query and create shape // shapeMap.put(shapeKey, shape); // for example, we are adding three shapes public static void loadCache() { Circle circle = new Circle(); circle.setId("1"); shapeMap.put(circle.getId(),circle); Square square = new Square(); square.setId("2"); shapeMap.put(square.getId(),square); Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(); rectangle.setId("3"); shapeMap.put(rectangle.getId(), rectangle); }} |
4、通过ShapeCache,返回克隆对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | public class PrototypePatternDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { ShapeCache.loadCache(); Shape clonedShape = (Shape) ShapeCache.getShape("1"); System.out.println("Shape : " + clonedShape.getType()); Shape clonedShape2 = (Shape) ShapeCache.getShape("2"); System.out.println("Shape : " + clonedShape2.getType()); Shape clonedShape3 = (Shape) ShapeCache.getShape("3"); System.out.println("Shape : " + clonedShape3.getType()); }} |
5、结果
Shape : Circle
Shape : Square
Shape : Rectangle



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律