001-SpringMVC和Spring的结合
SpringMVC 全体系图
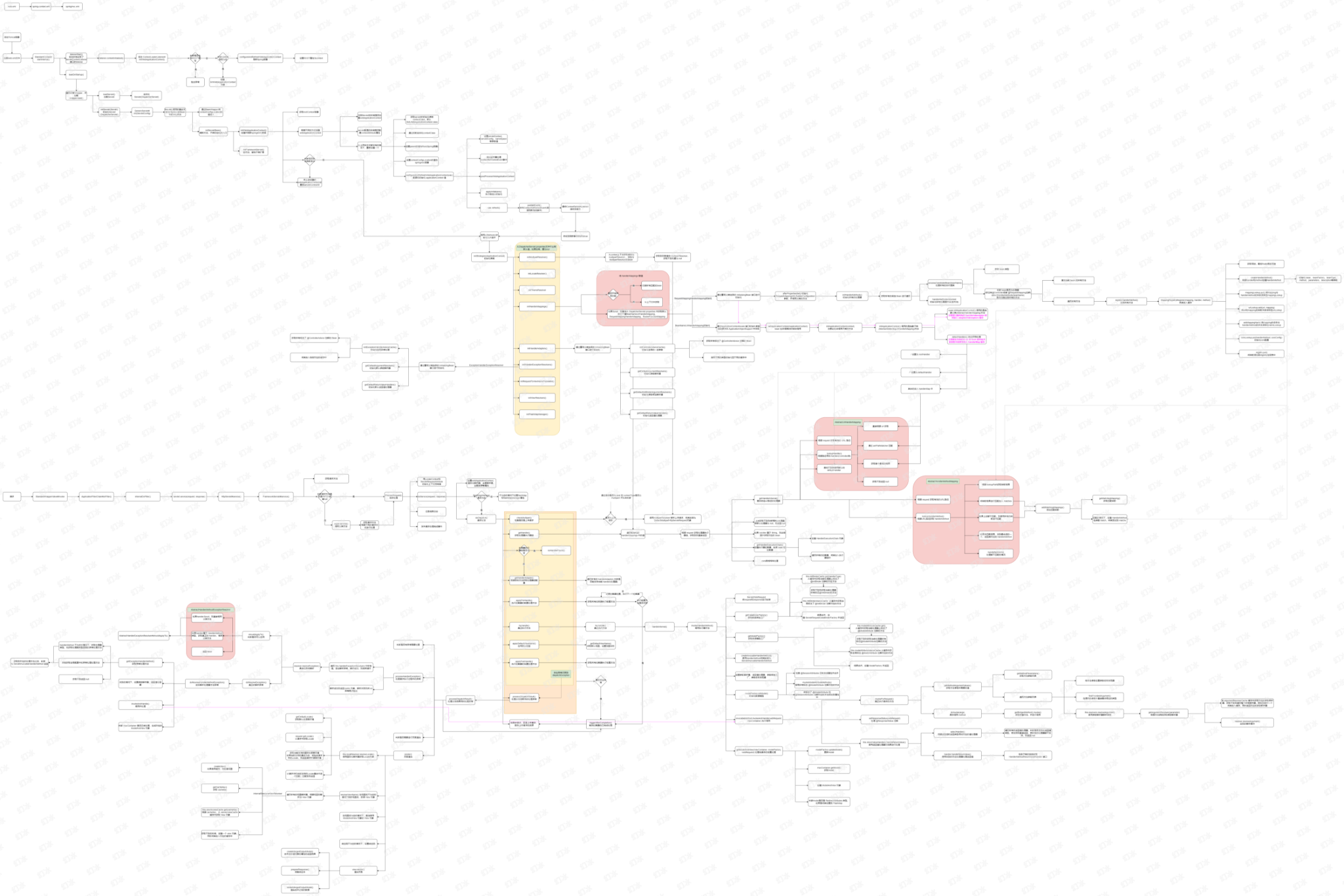
SpringMVC配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-config.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc-test</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!--SpringMVC配置文件-->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
<async-supported>true</async-supported>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mvc-test</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
</web-app>
整体启动流程
在启动Spring容器之前,需要启动Tomcat等Web服务器,由Tomcat等Web服务器根据配置文件web.xml,中配置的ContextLoaderListener监听器来启动Spring容器,启动Spring 容器之后,再由Tomcat等Web服务器根据配置文件web.xml 中配置的 DispatcherServlet 来启动 SpringMVC 容器,然后以Spring容器做为父容器将两个容器关联起来,最后由事件通知机制来初始化 SpringMVC 的九大内置组件。
启动 Spring 容器
如上述所说,由 Web 服务器根据配置文件中 ContextLoaderListener 来启动 Spring 容器,contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event)。
initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext)
初始化context,获取到一个 Root webApplicationContext,同时刷新容器,最后将其记录到servlet上下文中,方便后续在SpringMVC容器中获取,将其关联到一块。
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
// web.xml中存在多次ContextLoader定义
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
// 初始化context,第一次执行的时候获取到一个root webApplicationcontext
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
// 将创建的context对象记录在servletContext中,创建并且准备好了spring容器
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
}
createWebApplicationContext(servletContext)
获取上下文类对象,实例化上下文对象
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
// 获取contextClass的Class对象
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
// 如果是自定义的contextClass对象,那么必须要实现ConfigurableWebApplicationContext此接口,否则无法直接运行
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
determineContextClass(sc)
从上下文中获取上下文类名称,如果没有获取到,从默认的配置文件 ContextLoader.properties 中获取
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext)
设置一些基本属性,加载全局配置文件中 contextConfigLocation 的值,将其设置 Spring 容器上下文中,方便其后续进行上下文刷新,加载和实例化 Bean。
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
wac.setServletContext(sc);
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
customizeContext(sc, wac);
wac.refresh();
}
启动 SpringMVC 容器
如上述所说,由 Web 容器根据配置文件,来启动 Servlet,由 Servlet 的生命周期来控制,init、service、destroy,在 init 方法中进行各种参数的初始化,同时启动 SpringMVC 容器等。
init()
将 servlet 中配置的 init-param 参数封装到 PropertyValues 变量中,方便后续将其填充到 DispatcherServlet 中。
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
// 将servlet中配置的init-param参数封装到pvs变量中
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
// 将当前的servlet对象转化成BeanWrapper对象,从而能够以spring的方法来将pvs注入到该beanWrapper中
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
// 注册自定义属性编辑器,一旦有Resource类型的属性,将会使用ResourceEditor进行解析
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
// 模板方法,可以在子类调用,做一些初始化工作,bw代表的是DispatcherServlet
initBeanWrapper(bw);
// 以spring的方式来将pvs注入到该beanWrapper对象中,将配置的初始化值(contextConfigLocation)设置到DispatcherServlet
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
// 模板方法,子类初始化的入口方法,查看FrameworkServlet#initServletBean方法
initServletBean();
}
initServletBean()
主要用于创建并刷新 applicationContext,同时对其用到的变量进行初始化,包括九大组件。
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
// 记录开启时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 创建或刷新WebApplicationContext实例并对servlet功能所使用的变量进行初始化
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
// 模板方法,空实现,留给子类扩展
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
}
initWebApplicationContext()
获取根 WebApplicationContext,然后创建一个 webApplicationContext,
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 获得根webApplicationContext对象
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
// 获得webApplicationContext wac对象
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
// 如果构造方法中已经传入webApplicationContext属性,则直接使用
// 此方式主要用于servlet3.0之后的环境,也就是说可以通过ServletContext.addServlet的方法注册servlet,此时就可以在创建FrameworkServlet和
// 其子类的时候通过构造方法传递已经准备好的webApplicationContext
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
// 如果是ConfigurationWebApplicationContext类型,并且未激活,则进行初始化
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
// 未激活
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
// 配置和刷新上下文环境
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
// 从servletContext获取对应的webApplicationContext对象
// 此方式需要在配置Servlet的时候将servletContext中的webApplicationContext的name配置到contextAttribute属性就可以
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
// 当前面两种方式都无效的情况下会创建一个webApplicationContext对象,一般情况下都是使用这样的方式
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
// 将contextRefreshedEvent事件没有触发时调用此方法,模板方法,可以在子类重写
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
// 将applicationContext设置到servletContext中
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
createWebApplicationContext(rootContext)
获取 servlet 的初始化参数值 contextClass,默认值为 XmlWebApplicationContext,通过反射的方式实例化 contextClass,设置各种初始化参数。
createWebApplicationContext((ApplicationContext) parent)
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
// 获取servlet的初始化参数contextClass,如果没有配置默认为XmlWebApplicationContext.class
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
// 如果非ConfigurableWebApplicationContext类型,抛出ConfigurableWebApplicationContext异常
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
// 通过反射方式实例化contextClass
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
// 设置environment
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
// parent为在ContextLoaderListener中创建的实例,在ContextLoaderListener加载的时候初始化的WebApplicationContext类型实例
wac.setParent(parent);
// 获取contextConfigLocation属性,配置在servlet初始化参数中
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
// 将设置的contextConfigLocation参数传给wac,默认传入WEB-INFO/servletName-servlet.xml
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
// 配置和初始化wac
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac)
配置和初始化 SpringMVC 容器,设置 容器的 servletContext、servletConfig、namespace 等属性,添加监听器,监听 ContextRefreshedEvent 事件,当接收到消息的时候会调用 onApplicationEvent 方法。
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
// 如果wac使用了默认编号,则重新设置id属性
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
// 使用contextId属性
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
// 自动生成
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
// 设置wac的servletContext、servletConfig、namespace属性
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
// 添加监听器sourceFilteringListener到wac中,实际监听的是ContextRefreshListener所监听的事件,监听ContextRefreshedEvent事件,
// 当接收到消息之后会调用onApplicationEvent方法,调用onRefresh方法,并将refreshEventReceived标志设置为true,表示已经refresh过
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
// 获取环境对象并且添加相关的属性
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
// 执行处理完WebApplicationContext后的逻辑,此处为空方法,不做任何实现
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
// 执行自定义初始化context
applyInitializers(wac);
// 刷新wac,从而初始化wac
wac.refresh();
}
ContextRefreshListener
wac.refresh() 刷新容器的时候会在最后发出上下文刷新完成 ContextRefreshedEvent 事件,最后会调用 onApplicationEvent 来进行九大内置组件的初始化。
private class ContextRefreshListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
FrameworkServlet.this.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
}
FrameworkServlet.this.onApplicationEvent(event)
将收到刷新事件的标志置为 true,防止后续进行重复刷新。
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
// 标记 refreshEventReceived 为true
this.refreshEventReceived = true;
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
// 处理事件中的 ApplicationContext 对象,空实现,子类DispatcherServlet会实现
onRefresh(event.getApplicationContext());
}
}
onRefresh(event.getApplicationContext())
初始化九大内置组件。
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
// 初始化 MultipartResolver:主要用来处理文件上传.如果定义过当前类型的bean对象,那么直接获取,如果没有的话,可以为null
initMultipartResolver(context);
// 初始化 LocaleResolver:主要用来处理国际化配置,基于URL参数的配置(AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver),基于session的配置(SessionLocaleResolver),基于cookie的配置(CookieLocaleResolver)
initLocaleResolver(context);
// 初始化 ThemeResolver:主要用来设置主题Theme
initThemeResolver(context);
// 初始化 HandlerMapping:映射器,用来将对应的request跟controller进行对应
initHandlerMappings(context);
// 初始化 HandlerAdapter:处理适配器,主要包含Http请求处理器适配器,简单控制器处理器适配器,注解方法处理器适配器
initHandlerAdapters(context);
// 初始化 HandlerExceptionResolver:基于HandlerExceptionResolver接口的异常处理
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
// 初始化 RequestToViewNameTranslator:当controller处理器方法没有返回一个View对象或逻辑视图名称,并且在该方法中没有直接往response的输出流里面写数据的时候,spring将会采用约定好的方式提供一个逻辑视图名称
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
// 初始化 ViewResolver: 将ModelAndView选择合适的视图进行渲染的处理器
initViewResolvers(context);
// 初始化 FlashMapManager: 提供请求存储属性,可供其他请求使用
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
initHandlerMappings(context);
初始化处理器映射器,看是否开启了探测功能,如果开启,则扫描所有已注册的 HandlerMapping 的 Bean,添加到 handlerMappings 中,如果没有开启,则获取名称为 handlerMapping 类型的Bean,将其添加到handlerMappings中;最后如果上述未获取到,则获取默认配置的 handlerMapping 类。
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
// 将handlerMappings置空
this.handlerMappings = null;
// 如果开启探测功能,则扫描已注册的HandlerMapping的bean,添加到handlerMappings中
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
// 扫描已注册的handlerMapping的bean
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
// 添加到handlerMappings中,并进行排序
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
// 如果关闭探测功能,则获取Bean名称为handlerMapping对应的bean,将其添加到handlerMappings
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
// 如果未获得到,则获得默认配置的handlerMapping类
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet_test.properties");
}
}
}
getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
从默认的 DispatcherServlet.properties 中加载配置,文件位置位于 org.springframework.web.servlet 下,
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "DispatcherServlet.properties";
private static final Properties defaultStrategies;
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, DispatcherServlet.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load '" + DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH + "': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) {
// 获得strategyInterface对应的value值
String key = strategyInterface.getName();
// 创建value对应的对象们,并返回
String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key);
if (value != null) {
// 基于","分隔,创建classNames数组
String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value);
// 创建strategyInterface集合
List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<>(classNames.length);
// 遍历classNames数组,创建对应的类,添加到strategyInterface中
for (String className : classNames) {
try {
// 获得className类
Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader());
// 创建className对应的类,并添加到strategies中
Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz);
strategies.add((T) strategy);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(
"Could not find DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className +
"] for interface [" + key + "]", ex);
}
catch (LinkageError err) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(
"Unresolvable class definition for DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" +
className + "] for interface [" + key + "]", err);
}
}
return strategies;
}
else {
return new LinkedList<>();
}
}


