实验二 类和对象_基础编程1
1. 实验任务1
验证性实验:简单类T的定义和测试。实践、阅读代码,回答问题。
这个简单任务覆盖以下内容:
类的定义(封装)
类的使用:对象的创建、访问
数据共享机制
在同一个对象的所有操作之间共享数据 —— 实现机制:封装
在同一个类的所有对象之间共享数据 —— 实现机制:类的static成员
在不同模块(类、函数)之间共享数据 —— 实现机制:友元
数据保护机制
const对象
const引用作为形参
const成员数据/函数
代码组织方式:多文件结构
代码组织方式:
t.h 内容:类T的声明、友元函数声明
t.cpp 内容:类T的实现、友元函数实现
task1.cpp 内容:测试模块、main函数
t.h

1 #pragma once 2 3 #include <string> 4 5 // 类T: 声明 6 class T { 7 // 对象属性、方法 8 public: 9 T(int x = 0, int y = 0); // 普通构造函数 10 T(const T &t); // 复制构造函数 11 T(T &&t); // 移动构造函数 12 ~T(); // 析构函数 13 14 void adjust(int ratio); // 按系数成倍调整数据 15 void display() const; // 以(m1, m2)形式显示T类对象信息 16 17 private: 18 int m1, m2; 19 20 // 类属性、方法 21 public: 22 static int get_cnt(); // 显示当前T类对象总数 23 24 public: 25 static const std::string doc; // 类T的描述信息 26 static const int max_cnt; // 类T对象上限 27 28 private: 29 static int cnt; // 当前T类对象数目 30 31 // 类T友元函数声明 32 friend void func(); 33 }; 34 35 // 普通函数声明 36 void func();
t.cpp

1 // 类T: 实现 2 // 普通函数实现 3 4 #include "t.h" 5 #include <iostream> 6 #include <string> 7 8 using std::cout; 9 using std::endl; 10 using std::string; 11 12 // static成员数据类外初始化 13 const std::string T::doc{"a simple class sample"}; 14 const int T::max_cnt = 999; 15 int T::cnt = 0; 16 17 18 // 对象方法 19 T::T(int x, int y): m1{x}, m2{y} { 20 ++cnt; 21 cout << "T constructor called.\n"; 22 } 23 24 T::T(const T &t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} { 25 ++cnt; 26 cout << "T copy constructor called.\n"; 27 } 28 29 T::T(T &&t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} { 30 ++cnt; 31 cout << "T move constructor called.\n"; 32 } 33 34 T::~T() { 35 --cnt; 36 cout << "T destructor called.\n"; 37 } 38 39 void T::adjust(int ratio) { 40 m1 *= ratio; 41 m2 *= ratio; 42 } 43 44 void T::display() const { 45 cout << "(" << m1 << ", " << m2 << ")" ; 46 } 47 48 // 类方法 49 int T::get_cnt() { 50 return cnt; 51 } 52 53 // 友元 54 void func() { 55 T t5(42); 56 t5.m2 = 2049; 57 cout << "t5 = "; t5.display(); cout << endl; 58 }
task1.cpp

1 #include "t.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::endl; 6 7 void test(); 8 9 int main() { 10 test(); 11 cout << "\nmain: \n"; 12 cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl; 13 } 14 15 void test() { 16 cout << "test class T: \n"; 17 cout << "T info: " << T::doc << endl; 18 cout << "T objects'max count: " << T::max_cnt << endl; 19 cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl << endl; 20 21 22 T t1; 23 cout << "t1 = "; t1.display(); cout << endl; 24 25 T t2(3, 4); 26 cout << "t2 = "; t2.display(); cout << endl; 27 28 T t3(t2); 29 t3.adjust(2); 30 cout << "t3 = "; t3.display(); cout << endl; 31 32 T t4(std::move(t2)); 33 cout << "t3 = "; t4.display(); cout << endl; 34 35 cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl; 36 37 func(); 38 }
运行结果截图

阅读代码,结合运行结果,理解使用C++封装类涉及的关联知识点。
问题1: t.h中,普通函数 func 作为类X的友元,在类的内部声明了友元关系。在类外部,去掉line36,重 新编译,是否能正确运行。如果能,回答说明可以去掉line36。如果不能,以截图形式给出编译报 错信息,分析可能的原因。
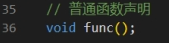
答:不能。

全部重新编译后,编译器报错显示没有找到“func”,这可能与友元函数的函数表示有关。
问题2: t.h中,line9-12给出了各种构造函数、析构函数。总结各种构造函数的功能,以及它们与析构函数 的调用时机。
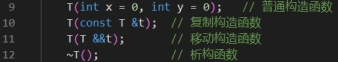
答:普通构造函数:用于创建对象并通过其接收到的参数初始化对象的成员变量。
复制构造函数:用于创建对象,并通过另一个对象参数来初始化成员变量。
移动构造函数:用一个临时对象来初始化另一个同类型的新对象。相比于复制构造函数复制资源的方式,移动构造函数直接将临时对象的资源占有权转移给新对象,临时对象会进入一个可以被安全析构的状态。
析构函数的调用时机:1、对于栈上的对象,当对象的作用域结束时(函数返回、代码块结束),其析构函数会被自动调用。
2、对于堆上通过new创建的对象,需要手动用delete来销毁对象,否则会造成内存泄漏。
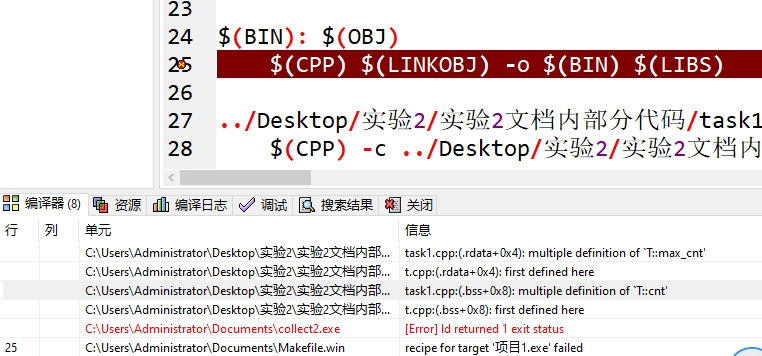
问题3: t.cpp中,line13-15,调整到t.h,重新编译,程序能否正确编译运行。
不能。
2. 实验任务2
不使用C++标准库提供的复数模板类,设计并实现一个简化版的复数类Complex。要求如下:
类属性
用于对自定义复数类Complex做描述说明的doc,用 string 类型,常量,公有
描述信息为: a simplified complex class
对象属性
用于表示复数的实部real和虚部imag, 均为小数形式,私有
对象方法
构造函数
要求支持以下方式构造复数对象
接口
get_real() 返回复数实部
get_imag() 返回复数虚部
add() 用于把一个复数加到自身,如 c1.add(c2) , 相当于 c1 += c2
友元函数 a
dd() 用于实现两个复数相加,返回复数。比如 c3 = add(c1, c2)
is_equal() 用于判断两个复数是否相等,相等返回 true , 否则,返回 false
is_not_equal() 用于判断两个复数是否相等,不相等返回 true , 否则,返回 false
output() 用于输出一个复数,以a+bi的形式。比如3 + 4i
abs() 用于对复数进行取模运算。比如, Complex c(3, 4); 对其取模运算后 abs(c) 结果为 5.0
代码要求
要求采用多文件方式组织代码。
Complex.h
类Complex声明、友元函数声明
Complex.cpp
类Complex实现、友元函数实现
task2.cpp
测试代码、main()函数 (测试代码已经在task2.cpp给出)
类设计及编码风格要求
设计并实现类时,合理利用数据的共享和保护机制,尽可能在数据共享和保护之间达到平衡
关注编码风格,可读性、易维护性
根据描述和测试代码,设计的Complex UML类图如下。
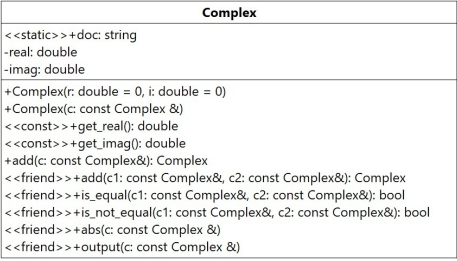
Complex.h

1 #pragma once 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 #include<cmath> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 class Complex 9 { 10 public: 11 12 //类的属性 13 static const string doc; 14 15 //构造函数声明 16 Complex(); 17 Complex(double r, double i = 0); 18 Complex(const Complex& other); 19 20 //外部接口 21 double get_real()const; 22 double get_imag()const; 23 void add(const Complex& other); 24 25 //友元函数声明 26 friend Complex add(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2); 27 friend bool is_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2); 28 friend bool is_not_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2); 29 friend void output(const Complex& c); 30 friend double abs(const Complex& c); 31 32 private: 33 double real; 34 double imag; 35 };
Complex.cpp

1 //用于对Complex类的实现 2 3 #include"Complex.h" 4 //类的属性实现 5 const string Complex::doc{ "a simplified Complex class" }; 6 7 //类的构造函数的实现 8 Complex::Complex() :real{ 0 }, imag{ 0 } {}; 9 Complex::Complex(double r, double i ) :real{ r }, imag{i} {}; 10 Complex::Complex(const Complex& other) :real(other.get_real()), imag(other.get_imag()) {}; 11 12 //外部接口实现 13 double Complex::get_real() const{ return real; } 14 double Complex::get_imag() const{ return imag; } 15 void Complex::add(const Complex& other) { real += other.get_real(), imag = other.get_imag(); } 16 17 //友元函数实现 18 Complex add(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2) 19 { 20 return Complex(c1.real + c2.real, c1.imag + c2.imag); 21 } 22 23 bool is_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2) 24 { 25 return (c1.real == c2.real) && (c1.imag==c2.imag); 26 } 27 28 bool is_not_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2) 29 { 30 return (c1.real != c2.real) || (c1.imag!=c2.imag); 31 } 32 33 void output(const Complex& c) 34 { 35 cout << c.real; 36 if (c.imag >= 0) { cout << '+'; } 37 cout << c.imag << "i"; 38 } 39 40 double abs(const Complex& c) 41 { 42 return sqrt(c.real * c.real + c.imag * c.imag); 43 }
main.cpp

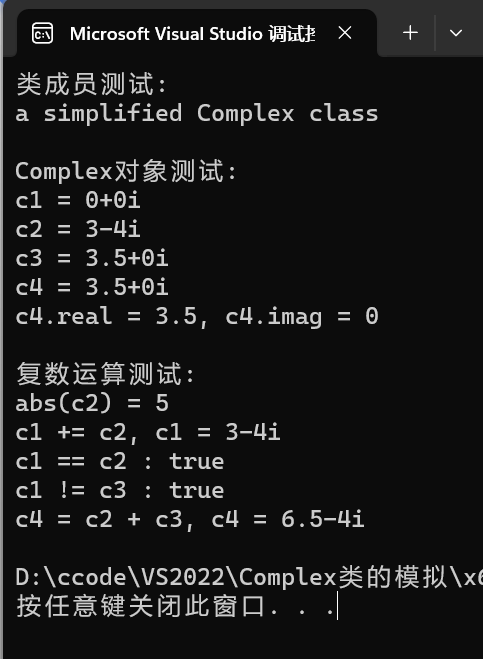
1 #include"Complex.h" 2 void test() { 3 cout << "类成员测试: " << endl; 4 cout << Complex::doc << endl; 5 6 cout << endl; 7 8 cout << "Complex对象测试: " << endl; 9 Complex c1; 10 Complex c2(3, -4); 11 const Complex c3(3.5); 12 Complex c4(c3); 13 14 cout << "c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl; 15 cout << "c2 = "; output(c2); cout << endl; 16 cout << "c3 = "; output(c3); cout << endl; 17 cout << "c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl; 18 cout << "c4.real = " << c4.get_real() << ", c4.imag = " << c4.get_imag() << endl; 19 20 cout << endl; 21 22 cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl; 23 cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl; 24 c1.add(c2); 25 cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl; 26 cout << boolalpha; 27 cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl; 28 cout << "c1 != c3 : " << is_not_equal(c1, c3) << endl; 29 c4 = add(c2, c3); 30 cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl; 31 } 32 33 int main() { 34 test(); 35 }
3. 实验任务3
验证性实验。使用标准库模板类complex实现复数运算。
complex 是C++标准库中提供的复数模板类,提供了关于复数类型的丰富计算接口。
complex模板类的丰富用法可参考:https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/numeric/complex
在C++编码环境中,输入以下代码。
task3.cpp

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <complex> 3 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::endl; 6 using std::boolalpha; 7 using std::complex; 8 9 void test() { 10 cout << "标准库模板类comple测试: " << endl; 11 complex<double> c1; 12 complex<double> c2(3, -4); 13 const complex<double> c3(3.5); 14 complex<double> c4(c3); 15 16 cout << "c1 = " << c1 << endl; 17 cout << "c2 = " << c2 << endl; 18 cout << "c3 = " << c3 << endl; 19 cout << "c4 = " << c4 << endl; 20 cout << "c4.real = " << c4.real() << ", c4.imag = " << c4.imag() << endl; 21 cout << endl; 22 23 cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl; 24 cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl; 25 c1 += c2; 26 cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = " << c1 << endl; 27 cout << boolalpha; 28 cout << "c1 == c2 : " << (c1 == c2) << endl; 29 cout << "c1 != c3 : " << (c1 != c3) << endl; 30 c4 = c2 + c3; 31 cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = " << c4 << endl; 32 } 33 34 int main() { 35 test(); 36 }
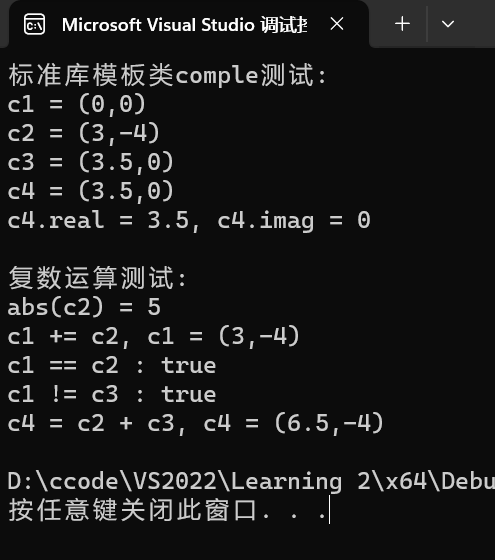
阅读代码,结合运行结果,分析代码中使用了标准库complex模板类提供的哪些接口。
接口:1.通过real()和image()函数获取对象real和imag。
2.通过abs(const complex& other)函数求模。
3.直接通过算式的+-运算进行复数的+-运算并且可以直接通过==与!=判断两个复数是否相等。
对比任务2:
1. 观察使用标准库模板类进行复数运算与输出时,代码比任务2的测试代码,哪些地方代码写法 不同/代码更简洁
1、输出不同,模板类是(real,imag)输出,手写类是real+/-imagi输出。
2、不同对象间的加减运算不同,模板类可直接对对象进行加减,手写类需要用外部接口或友元函数进行加减运算。
3、两个对象是否相等的判断不同。
2. 思考标准库模板类Complex的设计,与任务2对比,你是否有所启发
1、complex类重载了多种运算符如+-*/,使得复数运算看起来像普通基础数据运算看起来一样自然。
2、模板类可以通过<type>使得程序员自定义实部虚部的类型,更加方便。
4. 实验任务4
设计并实现一个分数类Fraction. 要求如下:
类属性
对分数类Fraction做描述说明的doc,用 string 类型,常量,公有
描述信息为: Fraction类 v 0.01版. 目前仅支持分数对象的构造、输出、加/减/乘/除运算.
对象属性
用于表示分数的分子up和分母down, 均为整数形式,私有
对象接口
对象方法
构造函数
要求支持以下方式构造分数对象

接口
get_up() 返回分子
get_down() 返回分母
negative() 用于求负,支持 Fraction f2 = f1.negative(); 这样的操作,形如的 f2 = -f1
求负运算,分数对象f1本身不变,返回值是求负后的分数对象
友元函数
output() 用于输出一个分数,以形如2/3或-2/3这样的形式 (输出化简后的形式,比如-4/10,输出时化简后的-2/5)
add() 用于实现两个分数相加,返回分数。比如 f3 = add(f1, f2)
sub() 用于实现两个分数相减,返回分数。比如 f3 = sub(f1, f2)
mul() 用于实现两个分数相乘,返回分数。比如 f3 = mul(f1, f2)
div() 用于实现两个分数相除法,返回分数。比如 f3 = div(f1, f2)
代码要求
要求采用多文件方式组织代码。
Fraction.h 类Fraction声明、友元函数声明
Fraction.cpp 类Fraction实现、友元函数实现
task4.cpp 测试代码、main()函数 (测试代码已经在task4.cpp给出)
类设计及编码风格要求
设计并实现类时,可以设计必要的内部工具函数辅助分数计算;合理利用数据的共享和保护机 制
关注编码风格,可读性、易维护性
Fraction.h

1 #pragma once 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 #include<cstdlib> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 class Fraction 9 { 10 public: 11 //类的属性 12 static const string doc; 13 14 //构造函数 15 Fraction(int _up = 0,int _dowm = 1); 16 Fraction(const Fraction& other); 17 18 //外部接口 19 int get_up() const; 20 int get_down() const; 21 Fraction negative(); 22 23 //友元函数 24 friend void output(const Fraction& f); 25 friend Fraction add(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); 26 friend Fraction sub(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); 27 friend Fraction mul(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); 28 friend Fraction div(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); 29 30 private: 31 //内部私有函数 32 static int fac(int a,int b); 33 void adjust(); 34 35 private: 36 int up; 37 int down; 38 39 };
Fraction.cpp

1 //Fraction类的实现 2 3 #include"Fraction.h" 4 5 //类的属性 6 const string Fraction::doc{ "Fraction类 v 0.01版. \n目前仅支持分数对象的构造、输出、加 / 减 / 乘 / 除运算.\n" }; 7 8 //构造函数 9 Fraction::Fraction(int _up, int _down) :up{ _up }, down{ _down } { Fraction::adjust(); }; 10 Fraction::Fraction(const Fraction& other) :up{ other.get_up() }, down{ other.get_down() } { }; 11 12 //外部接口 13 int Fraction::get_up()const { return up; } 14 int Fraction::get_down()const { return down; } 15 Fraction Fraction::negative() { return Fraction(-up, down); } 16 17 //内部私有函数 18 int Fraction::fac(int a,int b) 19 { 20 if (!b) { return a; } 21 return fac(b, a % b); 22 } 23 void Fraction::adjust() 24 { 25 int factor = fac(abs(up), abs(down)); 26 if (up * down > 0) { up = abs(up)/factor; down = abs(down)/factor; } 27 else if (up * down < 0) { up = -abs(up)/factor; down = abs(down)/factor; } 28 } 29 30 //友元函数 31 void output(const Fraction& f) 32 { 33 Fraction pf{f}; 34 if (pf.down == 0) { cout << "分母不能为0"; } 35 else 36 { 37 pf.adjust(); 38 if (pf.down == 1) { cout << pf.up; } 39 else if (pf.up == 0) { cout << pf.up; } 40 else { cout << pf.up << "/" << pf.down; } 41 } 42 } 43 Fraction add(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) 44 { 45 Fraction pf1{ f1 }, pf2{ f2 }; 46 int factor = Fraction::fac(pf1.down, pf2.down); 47 int lcm = (pf1.down * pf2.down / factor); 48 pf1.up *= (lcm / pf1.down); 49 pf2.up *= (lcm / pf2.down); 50 return Fraction(pf1.up + pf2.up, lcm); 51 } 52 Fraction sub(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) 53 { 54 Fraction pf1{ f1 }, pf2{ f2 }; 55 int factor = Fraction::fac(pf1.down, pf2.down); 56 int lcm = (pf1.down * pf2.down / factor); 57 pf1.up *= (lcm / pf1.down); 58 pf2.up *= (lcm / pf2.down); 59 return Fraction(pf1.up - pf2.up, lcm); 60 } 61 Fraction mul(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) 62 { 63 return Fraction(f1.up * f2.up, f1.down * f2.down); 64 } 65 Fraction div(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) 66 { 67 return Fraction(f1.up * f2.down, f2.up * f1.down); 68 }
main.cpp

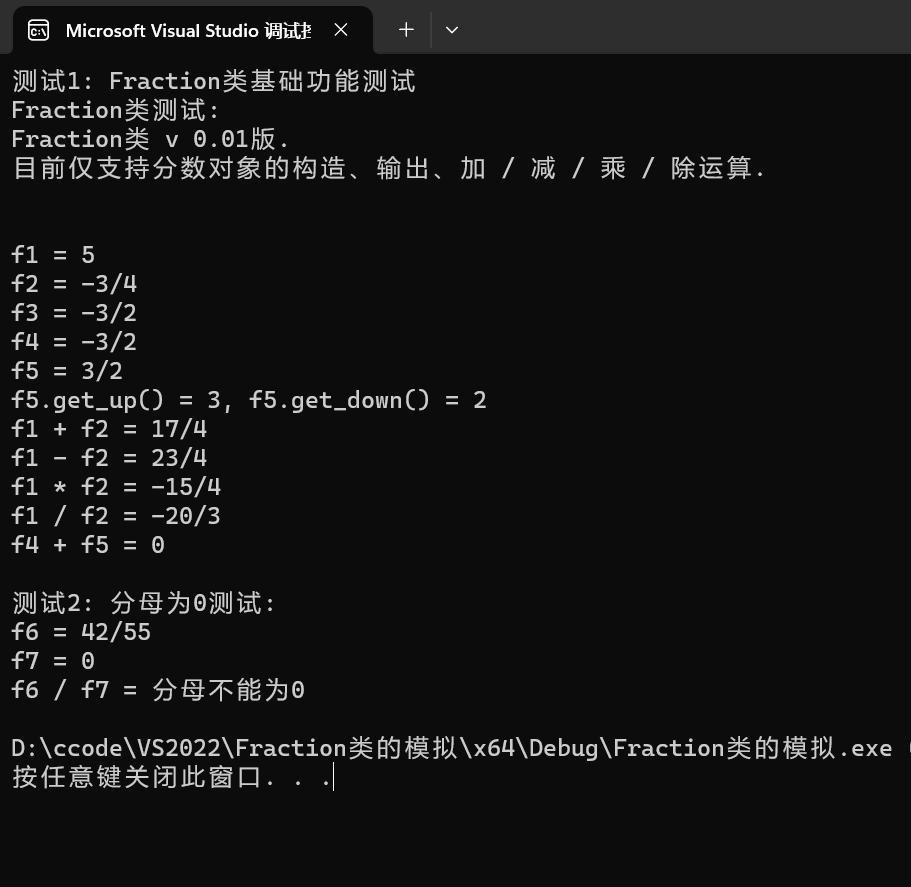
1 #include"Fraction.h" 2 3 void test1() { 4 cout << "Fraction类测试: " << endl; 5 cout << Fraction::doc << endl << endl; 6 7 Fraction f1(5); 8 Fraction f2(3, -4), f3(-18, 12); 9 Fraction f4(f3); 10 cout << "f1 = "; output(f1); cout << endl; 11 cout << "f2 = "; output(f2); cout << endl; 12 cout << "f3 = "; output(f3); cout << endl; 13 cout << "f4 = "; output(f4); cout << endl; 14 15 Fraction f5(f4.negative()); 16 cout << "f5 = "; output(f5); cout << endl; 17 cout << "f5.get_up() = " << f5.get_up() << ", f5.get_down() = " << f5.get_down() << endl; 18 19 cout << "f1 + f2 = "; output(add(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 20 cout << "f1 - f2 = "; output(sub(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 21 cout << "f1 * f2 = "; output(mul(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 22 cout << "f1 / f2 = "; output(div(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 23 cout << "f4 + f5 = "; output(add(f4, f5)); cout << endl; 24 } 25 26 void test2() { 27 Fraction f6(42, 55), f7(0, 3); 28 cout << "f6 = "; output(f6); cout << endl; 29 cout << "f7 = "; output(f7); cout << endl; 30 cout << "f6 / f7 = "; output(div(f6, f7)); cout << endl; 31 } 32 33 int main() { 34 cout << "测试1: Fraction类基础功能测试\n"; 35 test1(); 36 37 cout << "\n测试2: 分母为0测试: \n"; 38 test2(); 39 }
运行结果截图:
5. 实验任务5
在C++编码环境中录入教材第5章5.7节例5-11源码(个人银行账户管理程序),编译、运行、测试程序。 结合第4-5章所学内容,理解代码,体会用面向对象思维思考、设计业务场景问题,理解面向对象的封装 特性、数据的共享、保护。
说明*:
个人银行账户管理程序是教材提供的一个面向对象设计与编程的综合实例。第4章4.8节是最初版本 的设计与实现。其后,是逐步迭代改进的版本。建议你从第4章的版本开始,关注在银行业务场景 下,类的抽象与设计,以及,其后每章的迭代改进。系统、连贯地阅读和分析这个实例代码,会更 有助于你理解和体会面向对象设计与编程。
结合当下你使用银行业务(线下/银行app)的经历,分析教材上这个教学型实例目前的问题,思 考,如果由你来重构这个程序,你会如何抽象、设计。
account.h

1 #pragma once 2 //储蓄账户类 3 class SavingAccount 4 { 5 private: 6 int id; //账号 7 double balance; //余额 8 double rate; //存款年利率 9 int lastDate; //上次变更余额时期 10 double accumulation; //余额按日累加和 11 static double total; //所有账户总金额 12 void record(int date, double amount); 13 double accumulate(int date)const 14 { 15 return accumulation + balance * (date - lastDate); 16 } 17 public: 18 SavingAccount(int date, int id, double rate); 19 int getId()const { return id; } 20 double getBalance()const { return balance; } 21 double getRate()const { return rate; } 22 static double getTotal() { return total; } 23 void deposit(int date, double amount); 24 void withdraw(int date, double amount); 25 void settle(int date); 26 void show()const; 27 };
account.cpp

1 #include"account.h" 2 #include<cmath> 3 #include<iostream> 4 using namespace std; 5 double SavingAccount::total = 0; 6 SavingAccount::SavingAccount(int date, int id, double rate) 7 :id(id),balance(0),rate(rate),lastDate(lastDate),accumulation(0) 8 { 9 cout << date << "\t#" << id << "is created" << endl; 10 } 11 void SavingAccount::record(int date, double amount) 12 { 13 accumulation = accumulate(date); 14 lastDate = date; 15 amount = floor(amount * 100 + 0.5) / 100; 16 balance += amount; 17 total += amount; 18 cout << date << "\t#" << id << "\t" << amount << "\t" << balance << endl; 19 } 20 void SavingAccount::deposit(int date, double amount) 21 { 22 record(date, amount); 23 } 24 void SavingAccount::withdraw(int date, double amount) 25 { 26 if (amount > getBalance()) { cout << "Error: not enough money" << endl; } 27 else 28 { 29 record(date, -amount); 30 } 31 } 32 void SavingAccount::settle(int date) 33 { 34 double interest = accumulate(date) * rate / 365; 35 if (interest != 0) 36 { 37 record(date, interest); 38 } 39 accumulation = 0; 40 } 41 void SavingAccount::show()const 42 { 43 cout << "#" << id << "\tBalance:" << balance; 44 }
main.cpp

1 #include"account.h" 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() 5 { 6 SavingAccount sa0(1, 21325302, 0.015); 7 SavingAccount sa1(1, 58320212, 0.015); 8 sa0.deposit(5, 5000); 9 sa1.deposit(25, 10000); 10 sa0.deposit(45, 5500); 11 sa1.withdraw(60, 4000); 12 sa0.settle(90); 13 sa1.settle(90); 14 sa0.show(); 15 sa1.show(); 16 cout << "Total: " << SavingAccount::getTotal() << endl; 17 }
运行结果截图:
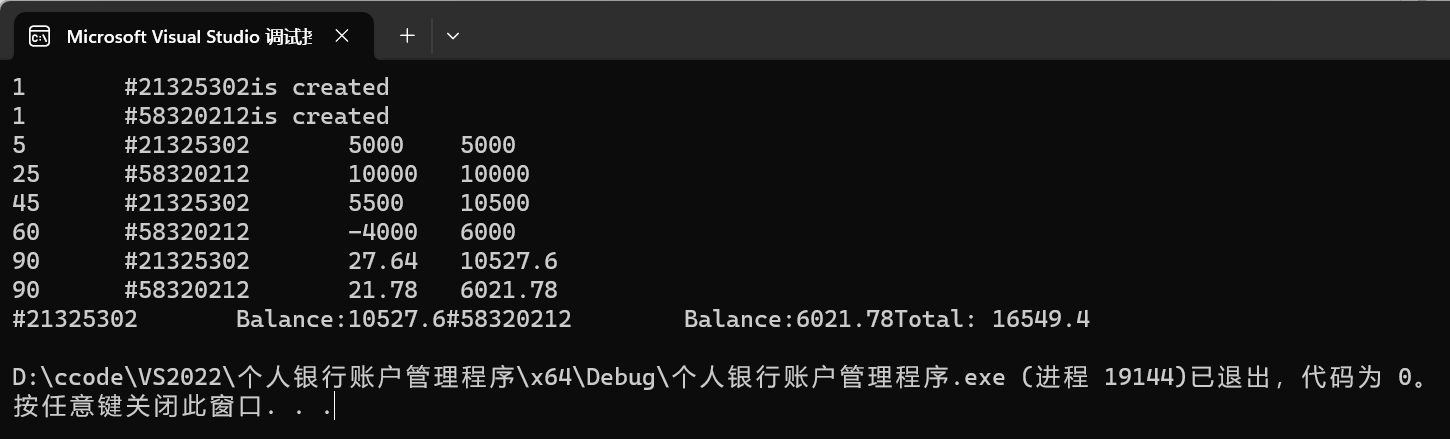
1、日期处理上可以用专门的日期时间库,使日期处理更规范。
2、在record函数中对金额进行了四舍五入的处理,但不够灵活且小数点后的位数过少。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号