Java wait和notify
wait和notify作用
wait和notify是定义在Object类中的,而且是final的。因此会被所有的Java类继承并且无法重写。这两个方法要求在调用时所处的线程已经获取了对象monitor锁,因此对这两个方法的调用需要在synchronized方法或者代码块中。比如wait方法的Java Doc中也有对此的说明:
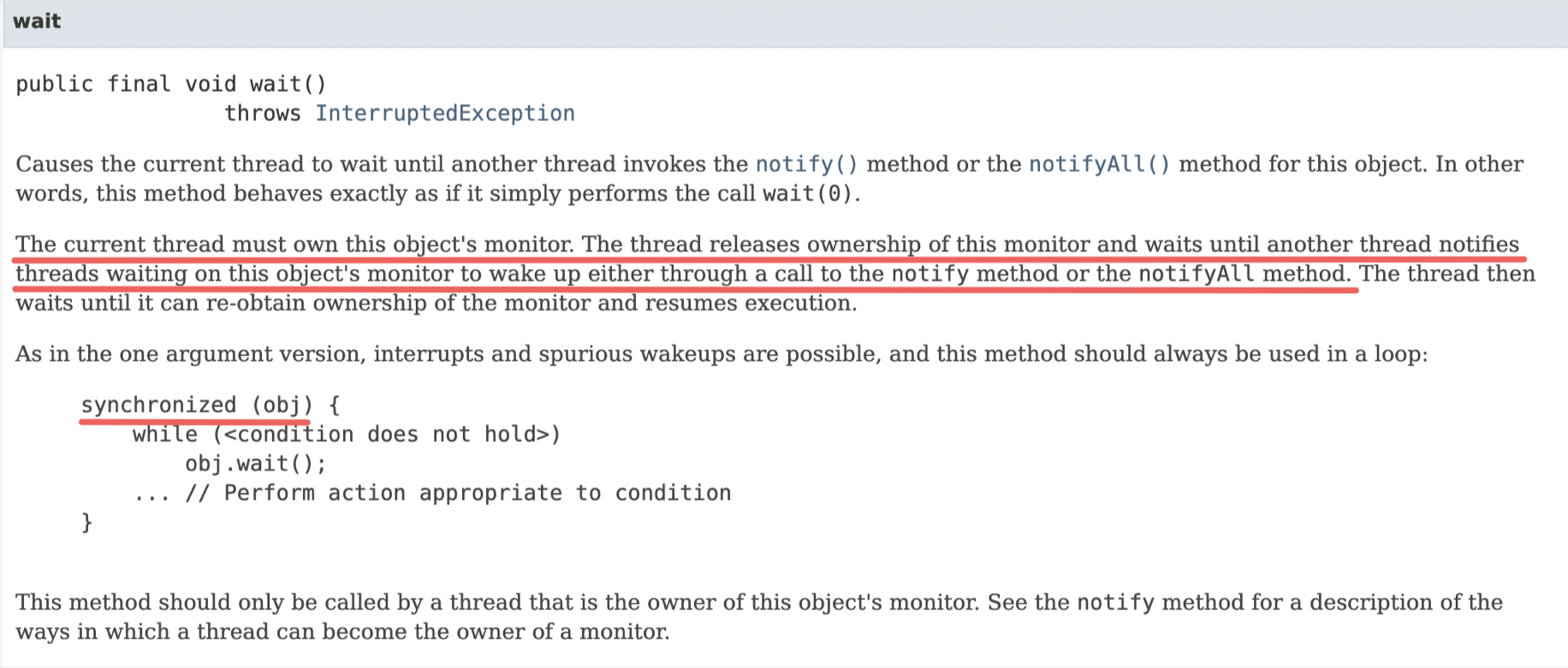
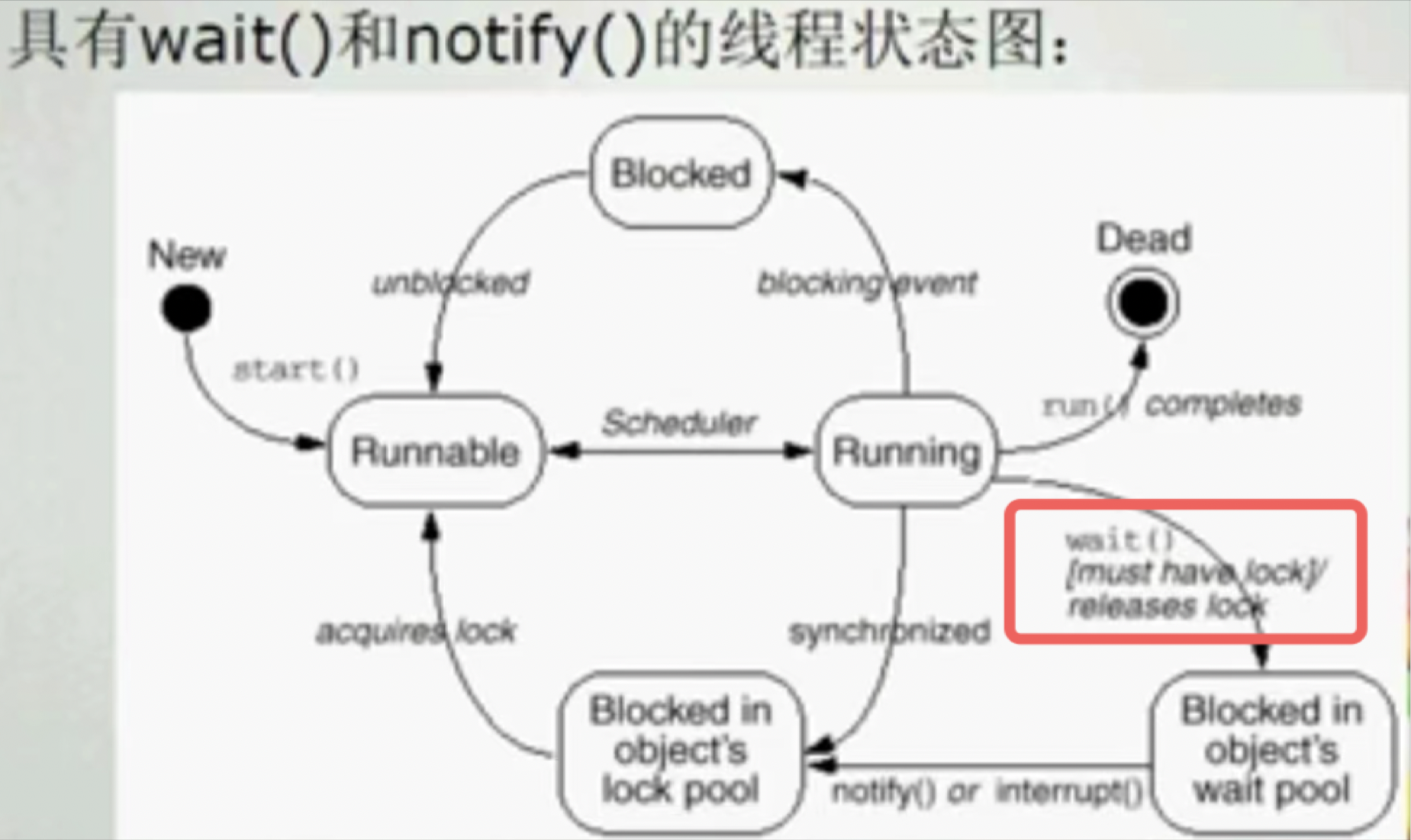
当线程执行了wait方法时,会释放掉前面synchronized获取的monitor锁。
举例说明
下面举个两个线程通过wait和notify进行通信的例子:通过两个线程,实现一个将int num在0-1-0-1之间不断加1和减1的功能。
Sample类
public class Sample {
// 成员变量 持有num
int num = 0;
// 加1
synchronized public void increase() {
while (num != 0) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
this.num ++;
notify();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--" + this.num);
}
// 减1
synchronized public void decrease() {
while (num == 0) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
this.num --;
notify();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--" + this.num);
}
}
IncreaseRunnable类
public class IncreaseRunnable implements Runnable {
Sample sample;
public IncreaseRunnable(Sample sample) {
this.sample = sample;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
sample.increase();
}
}
}
DecreaseRunnable类
public class DecreaseRunnable implements Runnable{
Sample sample;
public DecreaseRunnable(Sample sample) {
this.sample = sample;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
sample.decrease();
}
}
}
主测试类
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sample sample = new Sample();
IncreaseRunnable increaseRunnable = new IncreaseRunnable(sample);
DecreaseRunnable decreaseRunnable = new DecreaseRunnable(sample);
Thread t1 = new Thread(increaseRunnable);
t1.setName("increase-thread-1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(increaseRunnable);
t2.setName("increase-thread-2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(decreaseRunnable);
t3.setName("decrease-thread-1");
Thread t4 = new Thread(decreaseRunnable);
t4.setName("decrease-thread-2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
}
}



