day69:Vue:组件化开发&Vue-Router&Vue-client
目录
组件化开发
1.什么是组件?
2.而在网页中实现一个功能,需要使用html定义功能的内容结构,使用css声明功能的外观样式,还要使用js来定义功能的特效,因此就产生了把一个功能相关的[HTML、css和javascript]代码封装在一起组成一个整体的代码块封装模式,我们称之为“组件”。
3.所以,组件就是一个html网页中的功能,一般就是一个标签,标签中有自己的html内容结构,css样式和js特效。
4.这样,前端人员就可以在开发时,只需要书写一次代码,随处引入即可使用。
5.我们在进行vue开发的时候,还记得我们自己创建的vm对象吗,这个vm对象我们称为一个大组件,根组件(页面上叫Root),在一个网页的开发中,根据网页上的功能区域我们又可以细分成其他组件,或称为子组件

2.局部组件
局部组件三步走:声子、挂子、用子,即声明子组件、挂载子组件、使用子组件
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <title>html</title> <meta charset="UTF-8"> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <div class="header"> 这是头部{{ appmsg }} </div> <Sonapp/> <!-- 3.使用子组件 --> </div> </body> <script src="vue.js"></script> <script> let Sonapp = { data(){ // 注意:组件中必须写成函数形式 return { 'sonappmsg':'hello Sonapp!' } }, template:` <div class="content"> 内容部分{{sonappmsg}} </div> ` };
let vm = new Vue({ el:'#app', data(){ return{ 'appmsg':'hello app!', } }, components:{ Sonapp, // 2.挂载子组件 } }) </script> </html>
3.全局组件
局部组件使用时需要挂载,全局组件使用时不需要挂载。
局部组件就在某个局部使用的时候,全局组件是大家公用的,或者说每个页面都有这么一个功能的时候,在哪里可能都会用到的时候。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <title>html</title> <meta charset="UTF-8"> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <Addnum></Addnum> <!-- 使用全局组件 --> </div> </body> <script src="vue.js"></script> <script>
Vue.component("Addnum",{ data(){ return{ num:1 } }, template:` <div><input type="text" v-model="num"><button @click="num+=1">点击</button></div> ` })
let vm =new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ // 全局组件不需要挂载 } }) </script> </html>
4.父组件向子组件传值
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <title>html</title> <meta charset="UTF-8"> </head> <body> <div id="show"> <h1>hello !</h1> <Father></Father> </div> </body> <script src="vue.js"></script> <script> let Son = { data(){ return{ sonmsg:'这是子组件信息' } }, template:` <div class="Son"> <h1>{{sonmsg}}</h1> <h2>子组件Template</h2> <h2>{{ xx }}</h2> </div> `, props:['xx'] // 1.在子组件中使用prop属性声明 }; let Father ={ data(){ return{ msg:'这是father组件', num:100, } }, template:` <div class="nav"> <h1 style="color:blue;">{{Msg}}---{{num}}</h1> <!-- <Naver xx="xiaobei"></Naver> 静态传值 <Naver :xx="num"></Naver> 动态传值 --> <Son :xx="num"></Son> </div> `, components:{ Son, } }; let vm = new Vue({ el:'#show', data(){ return{ } }, components: { Father, } }) </script> </html>
父组件向子组件传值,其实大致可以分为两步:
1
声明了prop属性有xx之后,在子组件就可以使用xx了
let Son = { data(){ return{ sonmsg:'这是子组件信息' } }, template:` <div class="Son"> <h1>{{sonMsg}}</h1> <h2>子组件Template</h2> <h2>{{ xx }}</h2> </div> `, props:['xx'] // 1.在子组件中使用prop属性声明
2.父组件要定义自定义的属性
let father ={ data(){ return{ msg:'这是father组件', num:100, } }, template:` <div class="nav"> <h1 style="color:blue;">{{Msg}}---{{num}}</h1> <Son xx="xiaobei"></Son> // 静态传值 <Son :xx="num"></Son> // 动态传值 </div> ` }
5.子组件往父组件传值
子组件往父组件传值,分三步。
第一步:
所以第一步就是在父组件使用子组件的地方加上自定义事件
第二步:在父组件中定义自定义事件对应的方法。方法需要写参数,用来接收子组件传递过来的参数
第三步:
step1.就是在父组件使用子组件的地方加上自定义事件
let App = { ...... //1. 父组件使用子组件的地方加上自定事件 // <Naver @fatherHandler="fuckSon"></Naver> template: ` <div class="nav"> <h1 style="color:blue;">{{Msg}}---子组件的num为:{{xx}}</h1> <Naver @fatherHandler="fuckSon"></Naver> </div> `, ......
step2.在父组件中定义自定义事件对应的方法
let App = { ...... // 2 在父组件中定义自定义事件对应的方法,方法需要写参数,用来接收子组件传递过来的数据 fuckSon(val){ this.xx = val; } ...... } };
step3.子组件中调用方法来实现传值动作emit
let Naver = { ...... methods:{ zouni(){ // console.log(this); // 3 子组件中调用$emit方法,来实现传值动作 $emit(父组件自定义事件名称,数据) this.$emit('fatherHandler',this.sonNum); ...... } } };
所有代码如下所示:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>你好</h1>
<App></App>
</div>
</body>
<script src="vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 1 声明子组件 声子
let Naver = {
data(){
return {
navMsg:'这是顶部导航栏',
sonNum:80,
}
},
template:
`
<div class="Naver">
<h1>{{navMsg}}</h1>
<button @click="zouni">走你</button>
</div>
`,
methods:{
zouni(){
//
console.log(this);
// 3 子组件中调用$emit方法,来实现传值动作 $emit(父组件自定义事件名称,数据)
this.$emit('fatherHandler',this.sonNum);
}
}
};
let App = {
data(){
return {
Msg:'这是App组件',
num:100,
xx:'',
}
},
//1. 父组件使用子组件的地方加上自定事件
// <Naver @fatherHandler="fuckSon"></Naver>
template:
`
<div class="nav">
<h1 style="color:blue;">{{Msg}}---子组件的num为:{{xx}}</h1>
<Naver @fatherHandler="fuckSon"></Naver>
</div>
`,
components:{
Naver,
},
methods:{
// 2 在父组件中定义自定义事件对应的方法,方法需要写参数,用来接收子组件传递过来的数据
fuckSon(val){
this.xx = val;
}
}
};
let vm = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data(){
return {
}
},
// 2 挂载子组件 挂子
components:{
// 挂载组件的简写形式
App,
// Naver,
}
})
</script>
</html>
6.平行组件传值
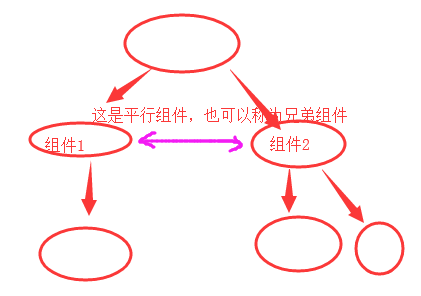
平行组件传值,需要在最外层声明一个公交车bus,通过上车和下车的动作来进行平行组件的传值功能。
平行组件传值,大致分为三步:
第一步:声明一个bus的Vue对象
第二步:假设是T1组件往T2组件传值,那么在T1的method中需要执行一个bus.$emit('name',this.t1num)
第三步:在T2组件中需要执行一个bus.$on('name',(val))=>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>你好</h1>
<App></App>
<div class="t1"></div>
</div>
</body>
<script src="vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 1.声明公交车对象
let bus = new Vue();
Vue.component('T1',{
data(){
return {
t1Msg:'我是t1组件',
t1Num:120,
}
},
template:`
<div class="t1">
<h3>{{t1Msg}}</h3>
<button @click="zouni">走你</button>
</div>
`,
methods:{
zouni(){
// 2.通过公交车将t1的值传送出去
bus.$emit('kkk',this.t1Num);
}
}
});
Vue.component('T2',{
data(){
return {
t2Msg:'我是t2组件',
t2Num:130,
t1msg:'',
}
},
template:`
<div class="t1">
<h3>{{t2Msg}}</h3>
<h3>t1组件传递过来的数据:{{t1msg}}</h3>
</div>
`,
created(){
// 3.通过公交车将t1传送的值接收过来
bus.$on('kkk', (val) => {
console.log(this);
this.t1msg = val;
});
},
});
let App = {
data(){
return {
Msg:'这是App组件',
num:100,
xx:'',
}
},
template:
`
<div class="nav">
<h1 style="color:blue;">{{Msg}}---子组件的num为:{{xx}}</h1>
<T1></T1>
<T2></T2>
</div>
`,
methods:{
}
}
};
let vm = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data(){
return {
}
},
components:{
App,
}
});
console.log(vm);
</script>
</html>
Vue-Router的使用
1.Vue-Router的介绍
为什么要使用单页面应用呢?因为传统的路由跳转,如果后端资源过多,会导致页面出现'白屏现象',所以我们希望让前端来做路由,
在某个生命周期的钩子函数中,发送ajax来请求数据,进行数据驱动,之前比如我们用django的MTV模式,我们是将后端的数据全部渲染给了模板,然后模板再发送给前端进行浏览器页面的渲染,一下将所有的数据都给了页面,
而我们现在使用vue,我可以在组件的钩子函数中发送对应的ajax请求去获取对应的数据,而不是一下子就把数据都放到页面上了,单页面应用给我们提供了很多的便利。
那么解释一下什么是单页应用,看下图:(react、angular也都是做单页面应用,很多大型的网站像网易云音乐,豆瓣等都是react写的单页面应用)
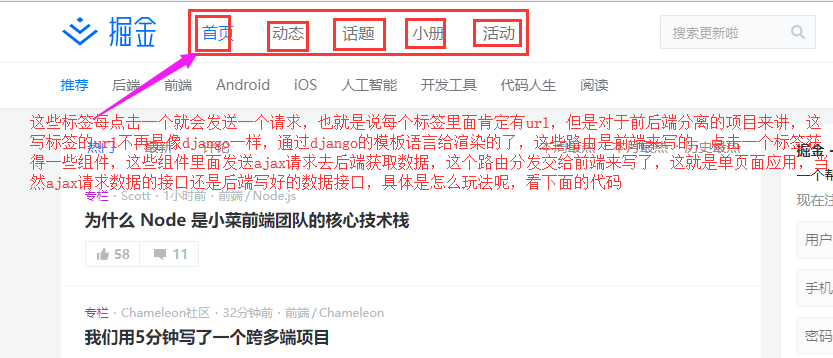
2.Vue-Router的简单操作
一共分五步
0.在HTML中写router-link和router-view
router-link相当于a href
router-view:<router-view> 是用来渲染通过路由映射过来的组件,当路径更改时,<router-view> 中的内容也会发生更改
1.定义组件。
2.定义路由routes.将路径和组件联系起来。
3.创建 VueRouter对象,然后将routes配置传到对象中
4.创建和挂载根实例。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h1>你好</h1> <App></App> </div> </body> <script src="vue.js"></script> <script src="vue-router.js"></script> <script> // 1.定义两个路由组件 let Home = { data(){ return { msg:'这是home页面' } }, template:` <div class="home"> <h1>{{msg}}</h1> </div> ` }; let Course = { data(){ return { msg:'这是Course页面' } }, template:` <div class="course"> <h1>{{msg}}</h1> </div> ` }; let App = { data(){ return { Msg:'这是App组件', num:100, xx:'', } }, template: ` <div class="nav"> // 0.在html中定义router-link和router-view <router-link to="/home">首页</router-link> <router-link to="/course">课程页</router-link> <router-view></router-view> </div> `, methods:{ } } }; // 2.定义路由 const routes = [ {path:'/home', component:Home}, {path:'/course', component:Course}, ]; // 3.创建VueRouter对象,然后传routes配置 let router = new VueRouter({ routes, }) let vm = new Vue({ el:'#app', router, // 4.挂载router data(){ return { } }, components:{ App, } }); console.log(vm); </script> </html>
Vue自动化工具:Vue-Client(脚手架)
1.Vue-Client的安装
1.安装nvm
nvm是一个开源的node版本管理器,通过它,你可以下载任意版本的node.js,还可以在不同版本之间切换使用。
sudo apt-get update sudo apt install curl curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/creationix/nvm/v0.34.0/install.sh | bash source ~/.bashrc
2.安装node.js
使用nvm的相关命令安装node。
安装命令
# 查看官方提供的可安装node版本 nvm ls-remote # 安装执行版本的node,例如:nvm install v10.15.2 nvm install <version> # 卸载node版本,例如:nvm uninstall v10.15.2 nvm uninstall <version> # 查看已安装的node列表 nvm ls # 切换node版本,例如:nvm use v10.15.2 nvm use <version> # 设置默认版本,如果没有设置,则开机时默认node是没有启动的。 nvm alias default v10.15.2 # 查看当前使用的版本 nvm current
3.npm
npm(node package manager)是nodejs的包管理器,用于node插件管理(包括安装、卸载、管理依赖等)。
安装了node以后,就自动安装了npm[不一定是最新版本]
查看npm版本
npm --version
4.Vue-cli的安装
使用前面已经安装好的node版本,进行安装。注意一旦安装以后,以后这个vue-li最好契合当前node版本。
也就是说,运行接下来安装的vue-cli时,最好运行的就是本次跑的node版本。
如果回头切换到其他版本node来运行vue-cli,有可能因为版本不兼容出现不必要的bug。
安装命令
npm install -g @vue/cli npm install -g @vue/cli-init # vue2.x版本需要安装桥接工具 # 安装完成可以查看版本 vue -V
2.如何生成vue项目目录
// 生成一个基于 webpack 模板的新项目 vue init webpack 项目名 例如: vue init webpack myproject // 启动开发服务器 ctrl+c 停止服务 cd myproject npm run dev # 运行这个命令就可以启动node提供的测试http服务器
3.vue项目的目录结构
├── build/ # 项目部署时需要用到
├── config/ # 配置文件
├── index.html
├── node_modules/ # 项目运行的依赖库存储目录[非常大]
├── package.json # 项目运行需要的依赖库记录配置
├── src/
│ ├── App.vue # 父级组件
│ ├── assets/ # 静态资源目录,图片存放在这里
│ ├── components/ # 单文件组件保存目录
│ └── main.js # 项目入口文件
└── static/ # 静态资源目录,所有的测试时用的,但是不需要交给线上服务器的css,js等文件放在这个目录
4.vue项目的执行流程图
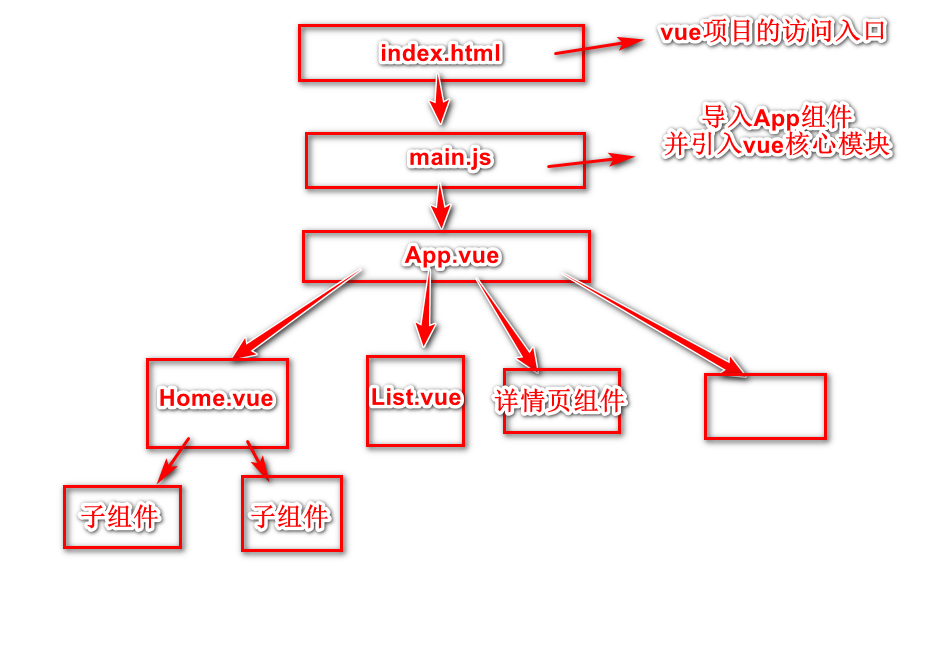
5.vue项目各个文件的内容详情
src/router/index.js
这个文件用来配置路由规则
import Vue from 'vue' // 引入vue对象 import Router from 'vue-router' // 导入包中的vue-router 接受vueRouter对象 import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld' // @代表src文件夹 Vue.use(Router) // 使用一下vueRouter对象 export default new Router({ // 抛出对象 以供后面的文件引入 routes: [ { path: '/', // 路径 component: HelloWorld // 路径所匹配的组件 } ] })
src/App.vue
app组件是所有你自己定义的组件的父组件,它起到一个代理的作用,我们将自己定义的组件都挂载到app组件上
app组件在template中要写router-view让渲染路由映射的组件显示在上边。
<template> <!-- 写html代码 -->
<div id="app">
<router-view/> <!-- 渲染路由映射的组件 -->
</div>
</template>
<script> // 写js代码
export default {
name: 'App'
}
</script>
<style> /* css代码 */
#app {
}
</style>
src/main.js
main.js为整个vue项目的入口文件
做的事情:
1.实例化vue对象
2.挂载父组件app
3.挂载路由规则router
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' import router from './router' Vue.config.productionTip = false /* eslint-disable no-new */ new Vue({ el: '#app', // 圈地,限定范围为app router,// 挂载路由规则 components: { App }, // 在Vue对象上挂载父组件app template: '<App/>' })
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>vueproday70</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"></div> <!-- 在vue中圈的那块地在这儿 --> <!-- built files will be auto injected --> </body> </html>
src/components/Helloworld.vue
所有自己定义的组件都写到components中,helloword.vue只是作为一个示例。
<template> <div class="hello"> </div> </template> <script> export default { // 抛出对象 供其他文件去调用 name: 'HelloWorld', data () { return { msg: 'Welcome to Your Vue.js App' } } } </script> <style scoped> /* 在style后添加scoped代表这个样式只能在这个组件中使用,如果不加的话代表这个样式在全局都可以使用 */ </style>
6.总结
index.js是 用来配置路由规则
index.html 圈地,圈的是App的那块地,div id =app 用户访问的界面就是这个界面
main.js 导入App组件,导入Vue对象,导入index.js已经定义好的路由规则
实例化vue对象,将父组件app挂载到vue对象上
将router路由规则挂载到vue对象上
helloworld.vue 自己定义的组件 里面是html css js 写完组件之后要挂载到父组件app上
App.vue 父组件App,将自己写的组件挂载到app组件上


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号