JsonCpp学习-C++中处理Json
JsonCpp
了解何为Json 参考资料如下.
本节参考资料 jsoncpp的简易教程 - Tudou_Blog - 博客园
一丶简介
Json作为一种文件格式,可以作为配置文件使用.也可以作为网络传输使用. 而一些C/c++库.
rapidjson jsoncpp cJSON等都是来解析这种文件的库. 还有其它各种库.都是大同小异.
这里作为学习贴来简单的学习一下jsoncpp.
二丶JsonCpp环境配置.
首先先去 github下载jsoncpp的源码 jsoncpp
下载后在本地显示如下.
其中,我们想使用json的话,需要先进行 cmake编译
jsoncpp是需要cmake编译的.但是在高版本vs系列中.已经集成的cmake,不需要我们单独下载.
需要打开各个编译的器的命令行交叉编译工具.
如: Vs xxx的 x64_86 交叉工具命令提示符.
打开后索引到jsoncpp的源码目录. 只需要执行命令.
cmake F:\xxx\jsoncpp\ 即可. 执行完毕之后在本层就会看到生成的cmake 文件夹.
打开后则可以看到有生成 jsoncpp.sln工程. 打开此工程. 图片如下.
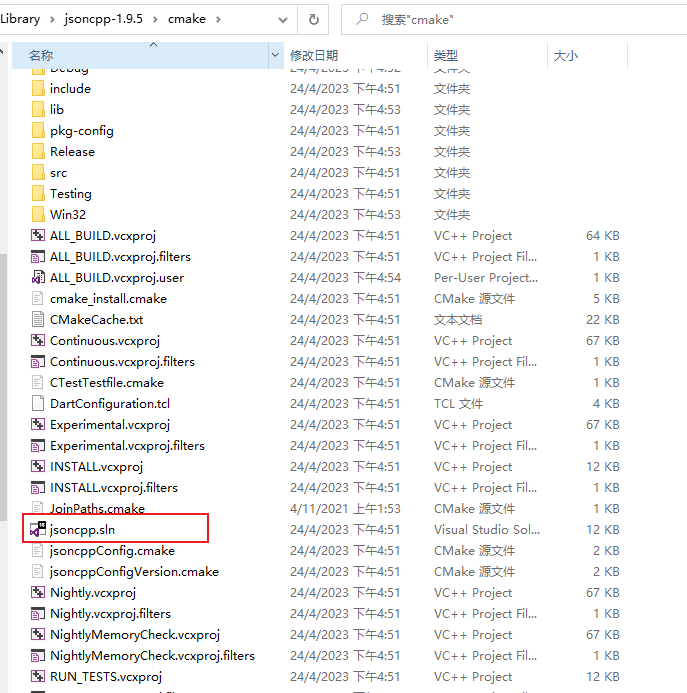
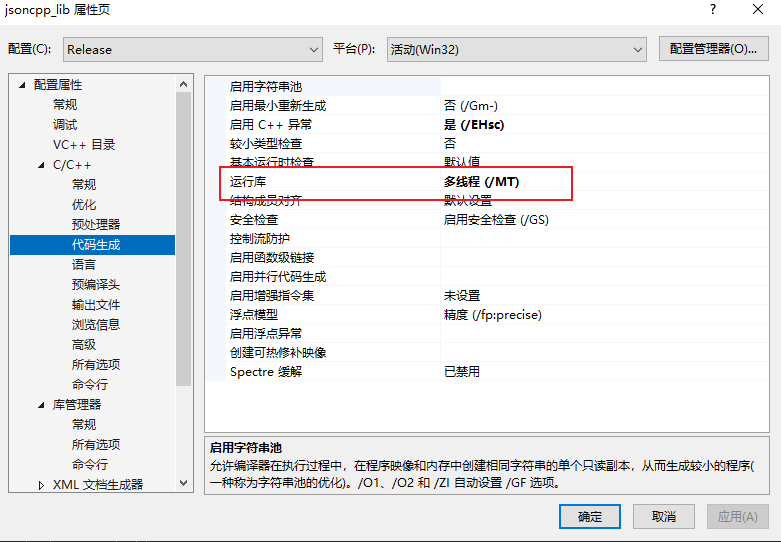
在里面找到 jsoncpp_lib 工程. 可以按照自己需要将其编译为 静态lib文件.或者dll文件. 默认是编译的dll文件.且编译方式是 MDD 和 MD 我们需要将其改为. Realse(MT) Debug(MTD) 否则编译出的DLL或者库在别人电脑上用则会用不起来.别人电脑上会提示缺少DLL或者缺少xxx.
注意在编译的时候,如果你要编译为lib.那么需要 将配置类型改为 静态库(.lib) 方式,且 目标文件扩展名要设置为父类继承,或者自己设置为.lib. 这样编译的库才是正常的lib.
配置图片.

三丶JsonCpp核心知识
3.1 JsonCpp的三个核心类
在JsonCpp中.提供了三个类.
| 类 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Json::Value | 类型支持类,此类可以解析所有Json支持的类型.如: bool 字符串 浮点数 对象,以及 数组. 针对这些类型,还支持 isxxx来判断.以及类型转换.可以将类型里面的值,按照json字段格式,转为相应的值. 如 value表示的是string节点.那么asString则可以拿到此节点里面的记录的值. |
| Json::Reader | 可以将文件,文件流,字符串内存,进行解析.解析的结果放到Json::Value中.剩下的时间我们就可以解析Json::Value了. 在JsonCpp新特性中,还允许用户使用Features来定义Json的严格等级.这关乎到值解析失败函数应该怎么返回. |
| Json::Write | 将数据转化为字符串流.也就是内存. 可以将内存写入到文件. 此类是基类,我们必须使用它的实现子类,Json::FastWrite. 子类可以将Json进行压缩.压缩后写入到文件.也可以使用 Json::StyledWrite子类. 可以指定自己喜爱的格式进行输出. |
3.2 Json::Value的引用和Json::Value
如果你使用 Json::Value& 接受的值. 那么如果修改里面的值.则其内存的json值会被修改.且其它代码位置会被同步修改.
如果你使用的是 Json::Value. 那么相当于只是一份副本. 修改副本里面的值不会影响到其它位置.
只需要知道一点,引用使用的是同一块内存.一个地方改.那么任何其它地方用到此块内存的Json::Value都会被修改. 然 Json::Value值是副本.修改不会影响原始值.
3.3 使用JsonCpp
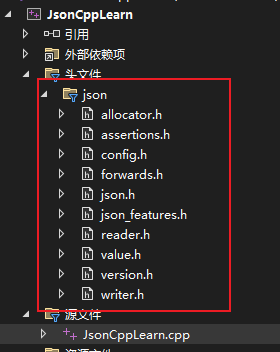
JsonCpp使用之前,需要从源码文件中将Include拷贝出来.然后按照需要配置到自己的项目工程中. 如果是编译的进程库.那么需要引入静态库.
配置方式有多种.
1.直接将Include放到自己项目文件夹下.将其Lib也是放到自己项目文件夹下.然后添加头文件,将所有的头文件加入到自己工程中.
2.可以在项目工程中的 Vc++目录中指定要包含的目录,以及引用的目录.
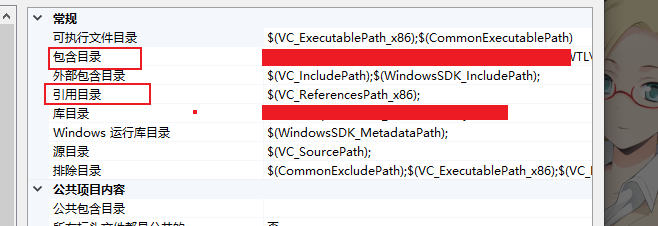
lib库的引用可以配置在 连接器里面的引用库目录中. (这属于Vs项目基础知识.不懂可以百度搜索)
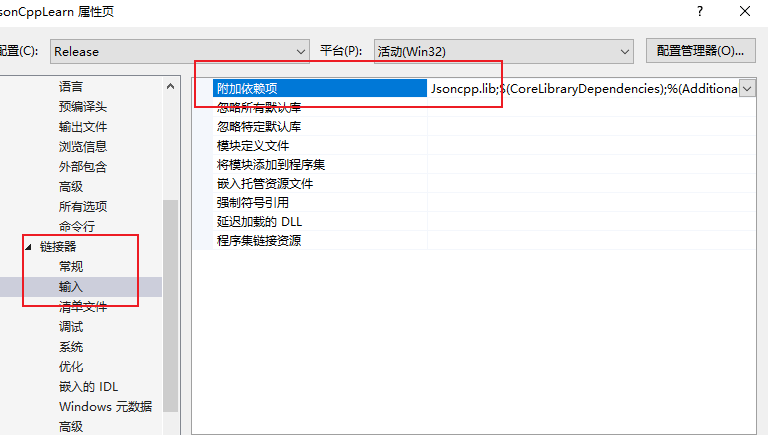
四丶学习JsonCpp中Value类中的函数.
3.1 JsonCpp值获取函数.
asxxx是JsonCpp中的类型值获取函数.如 Json字段如果是 字符串.那么则可以使用 asString将其转换为std::string.
const char* asCString() const;
unsigned getCStringLength() const;
String asString() const;
bool getString(char const** begin, char const** end) const;
Int asInt() const;
UInt asUInt() const;
#if defined(JSON_HAS_INT64)
Int64 asInt64() const;
UInt64 asUInt64() const;
#endif // if defined(JSON_HAS_INT64)
LargestInt asLargestInt() const;
LargestUInt asLargestUInt() const;
float asFloat() const;
double asDouble() const;
bool asBool() const;
3.2 JsonCpp值类型判断函数
isxxx 可以判断当前值是否是对应类型.
bool isNull() const;
bool isBool() const;
bool isInt() const;
bool isInt64() const;
bool isUInt() const;
bool isUInt64() const;
bool isIntegral() const;
bool isDouble() const;
bool isNumeric() const;
bool isString() const;
bool isArray() const;
bool isObject() const;
3.3 JsonCpp中数组操作函数
ArrayIndex = unsigned int.
Value get(ArrayIndex index, const Value& defaultValue) const; 传入index获取数组元素
bool isValidIndex(ArrayIndex index) const;//判断指定index是否有效
Value& append(const Value& value); //添加数组元素
Value& append(Value&& value);
bool insert(ArrayIndex index, const Value& newValue); //传入index插入数组元素
bool insert(ArrayIndex index, Value&& newValue);
bool removeIndex(ArrayIndex index, Value* removed);//删除指定index,删除的元素会通过参数2返回
bool empty() const; //数组为空 对象为空 或者是 null 返回true
void clear(); 如果是数组则清空所有元素,如是对象,则删除所有对象members.
void resid(ArrayIndex newSize); 将数组元素扩充至N
3.4 JsonCpp中的对象操作
Members = vector<string>
Members getMemberNames() const; //获取对象下面记录的所有key,返回值是一个vector<string)
bool isMember(const char* key) const; //三个重载函数,判断值是否是member
bool isMember(const String& key) const;
bool isMember(const char* begin, const char* end) const;
重载函数,删除对象里面的执行member. 根据重载函数,可以接受返回的值.
void removeMember(const char* key);
void removeMember(const String& key);
bool removeMember(const char* key, Value* removed);
bool removeMember(String const& key, Value* removed);
bool removeMember(const char* begin, const char* end, Value* removed);
获取和查找
根据c字符串的key 查找 value
Value get(const char* key, const Value& defaultValue) const;
//根据迭代器查找value
Value get(const char* begin, const char* end,
const Value& defaultValue) const;
//根据C++的string key获取
Value get(const String& key, const Value& defaultValue) const;
//进行查找
Value const* find(char const* begin, char const* end) const;
3.5 JsonCpp中的 运算符重载.
在JsonCpp中重载了[] .使我们可以在解析Json的时候可以按照数组方式解析. 当然还进行了增强.可以输入字符串.则JsonCpp会访问此节点.
示例伪代码如下
Value& operator[](ArrayIndex index);
Value& operator[](int index);
const Value& operator[](ArrayIndex index) const;
const Value& operator[](int index) const;
//示例
Json::Value& settings = root["A"]["B"]["C"];
Json::Value& settings = root[1][2]["C"].asString();
其它重载还有很多. .如 < <= > >= == !=
3.6 JsonCpp中的迭代器.
迭代器使我们可以去遍历 Json::Value. 而Json::Value存储的是Json数据.相当于我们可以直接按照自己喜欢的方式去遍历Json数据.
提供的迭代器如下
const_iterator begin() const; //常量迭代器 只能遍历值,而不能修改里面的值
const_iterator end() const;
iterator begin(); //迭代器,可以修改里面的值.
iterator end();
3.7 JsonCpp的Json串转化
可以将字符串转为Json串.主要使用Value类中的一个函数.可以将一个Value值转为一个格式化的字符串.
如果想将字符串压缩.或者只是想获取压缩的字符串.那么请使用 第五节所讲的 Json::Write的实现类.
String Value::toStyledString() const
五丶学习JsonCpp中的Json::Reader和Json::Write类
5.1 反序列化 - 解析函数
bool parse(const std::string& document, Value& root,
bool collectComments = true);
bool parse(const char* beginDoc, const char* endDoc, Value& root,
bool collectComments = true);
bool parse(IStream& is, Value& root, bool collectComments = true);
解析函数有三个重载, 可以解析 字符串流. 可以解析文件流. 也可以解析begindoc以及enddoc(我未用过) 解析的结果保存在 Jsn::Value中.
示例:
std::string json_data = 从文件中读取的数据.为了代码简介省去文件读写.
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value root;
reader.parse(json_data, root);
5.2 序列化-写入
Json::Write有许多实现的子类.常用的子类如下.
Json::StyledWriter styled_write;//格式化json
Json::FastWriter pack_write; //只是将value转化为压缩的内存数据
用法.
pack_writ.write(root);
//结果:
{"a":1,"b":2}
styled_write.write(root);
//结果
{
"a":1,
"b":2
}
六丶JsonCpp的实战操作.
6.1 JsonCpp 对象操作.
设Json值 = 如下.
{
"active_bit": false,
"active_permissions": {
"api": ["activeTab", "contextMenus", "storage"],
"explicit_host": [],
"manifest_permissions": [],
"scriptable_host": ["\u003Call_urls>"]
},
"granted_permissions": {
"api": ["activeTab", "contextMenus", "storage"],
"explicit_host": [],
"manifest_permissions": [],
"scriptable_host": ["\u003Call_urls>"]
},
"last_update_time": "13324124641142852",
"lastpingday": "13324114818159590",
"location": 1,
"state": 1,
"was_installed_by_default": false,
"was_installed_by_oem": false,
"withholding_permissions": false
}
代码如下.
void ParseJsonObject(Json::Value& root)
{
//1. 获取对象里面的所有 key值. 也就是name
//auto member = xxx 也是可以的.
//member其实是一个 std::vector<string>类型.可以按照自己喜欢的迭代方式进行迭代.
Json::Value::Members member = root.getMemberNames();
for (int i = 0; i < member.size(); i++)
{
cout << member[i].c_str() << endl;
}
//2.获取指定key值. 并且获取实际值.
Json::Value last_update_time = root["last_update_time"];
std::string last_update_time_str = last_update_time.asString();
//3.通过遍历方式,找到指定key值.并且修改里面的值.
for (int i = 0; i < member.size(); i++)
{
if (member[i].compare("location") != std::string::npos)
{
root[member[i]] = 3;
}
}
cout << root["location"].toStyledString() << endl;
//4.创建一个对象
Json::Value object;
object["a"] = "1";
object["b"] = "2";
object["c"] = 3;
object["d"] = true;
object["f"] = 3.14;
std::string test = object.toStyledString();
cout << test << endl;
}
int main()
{
//JsonCppObj jsoncppobj;
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value root;
std::string json_data = R"({
"active_bit": false,
"active_permissions": {
"api": ["activeTab", "contextMenus", "storage"],
"explicit_host": [],
"manifest_permissions": [],
"scriptable_host": ["\u003Call_urls>"]
},
"granted_permissions": {
"api": ["activeTab", "contextMenus", "storage"],
"explicit_host": [],
"manifest_permissions": [],
"scriptable_host": ["\u003Call_urls>"]
},
"last_update_time": "13324124641142852",
"lastpingday": "13324114818159590",
"location": 1,
"state": 1,
"was_installed_by_default": false,
"was_installed_by_oem": false,
"withholding_permissions": false
}
)";
reader.parse(json_data, root);
ParseJsonObject(root);
return 1;
}
输出结果如下
active_bit
active_permissions
granted_permissions
last_update_time
lastpingday
location
state
was_installed_by_default
was_installed_by_oem
withholding_permissions
3
{
"a" : "1",
"b" : "2",
"c" : 3,
"d" : true,
"f" : 3.1400000000000001
}
*/
6.2 JsonCpp中的数组操作.
void ParseJsonArray(Json::Value& root)
{
//1.创建对象数组
Json::Value array;
Json::Value array_item;
array_item.append(1);
array_item.append(2);
array_item.append(3);
array_item.append(4);
array_item.append(5);
array["test_ary"] = array_item;
std::string test = array.toStyledString();
cout << test << endl;
//2.第二种方式创建数组
//
Json::Value array_two;
array_two[0] = "z";
array_two[1] = 2;
array_two[2] = true;
array_two[3] = false;
array_two[4] = 3.14f; //float
array_two[5] = 7.23; //double
cout << array_two.toStyledString() << endl;
//3.遍历数组 解析数组
Json::Value api_array = root["active_permissions"]["api"];
for (int i = 0; i < api_array.size(); i++)
{
if (api_array[i].isString())
{
cout << api_array[i].asString().c_str() << endl;
}
}
}
输出结果如下:
{
"test_ary" :
[
1,
2,
3,
4,
5
]
}
[
"z",
2,
true,
false,
3.1400001049041748,
7.2300000000000004
]
activeTab
contextMenus
storage
6.3 其它.
其实json中大部分都是 Object嵌套基础类型.或者嵌套 Array. 只需要我们一层一层解析即可.
所以熟悉6.1 6.2小结完全够用.其它都是基础Value类型. 其中对于Object和Array还应有增删改查例子.其实还是函数的使用. 了解了JsonCpp的大体设计思想之后.只需要学习函数即可.
我也是花了半天时间熟悉了下JsonCpp写出了此篇文章. 而已经能解决复杂Json.
坚持两字,简单,轻便,但是真正的执行起来确实需要很长很长时间.当你把坚持两字当做你要走的路,那么你总会成功. 想学习,有问题请加群.群号:725864912(收费)群名称: 逆向学习小分队 群里有大量学习资源. 以及定期直播答疑.有一个良好的学习氛围. 涉及到外挂反外挂病毒 司法取证加解密 驱动过保护 VT 等技术,期待你的进入。
详情请点击链接查看置顶博客 https://www.cnblogs.com/iBinary/p/7572603.html
本文来自博客园,作者:iBinary,未经允许禁止转载 转载前可联系本人.对于爬虫人员来说如果发现保留起诉权力.https://www.cnblogs.com/iBinary/p/17352712.html
欢迎大家关注我的微信公众号.不定期的更新文章.更新技术. 关注公众号后请大家养成 不白嫖的习惯.欢迎大家赞赏. 也希望在看完公众号文章之后 不忘 点击 收藏 转发 以及点击在看功能. QQ群:
QQ群:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号