64位内核开发第十一讲,内核下的进程操作
64位内开发第十一讲,内核下的进程操作
一丶进程的遍历
1.1 内核中的进程简介
在内核中 进程(Process) 其实就是一个结构体, 这个结构体称为 EPROCESS 这个结构体很巨大. 一般就记录了这个进程的一些信息. 比如: 进程名 进程的PID(编号) 进程路径 父进程PID 等等. 在 RING3直接使用进程快照 方式就可以遍历进程了. 而在内核中并没有给你提供一键遍历的方式,换句话来说就是并没有给你提供 API让你一键进行遍历. 而他提供了很多API. 很多API分别有不同的作用. 比如 有直接获取进程名的. 有获取进程PID的. 如果你想使用.那么你就要自己去封装出这些API来进行使用.
1.2 标准的遍历进程
标准方式是使用 ZwQuerySystemInformation 配合里面的SystemProcessInformation功能号来进行遍历的. 使用这个函数遍历进程 无法获得进程的 EPROCESS 结构. 也就相当于变相的帮你隐藏掉了直接操作 EPROCESS 的权限. 那么看下代码怎么操作的.
声明所需要的结构
typedef struct _SYSTEM_MODULE
{
HANDLE Section; // Not filled in
PVOID MappedBase;
PVOID ImageBase;
ULONG ImageSize;
ULONG Flags;
USHORT Index;
USHORT Unknown;
USHORT LoadCount;
USHORT ModuleNameOffset;
CHAR ImageName[256];
} SYSTEM_MODULE, *PSYSTEM_MODULE;
typedef struct _SYSTEM_MODULE_INFORMATION
{
ULONG ulModuleCount;
SYSTEM_MODULE Modules[1];
} SYSTEM_MODULE_INFORMATION, *PSYSTEM_MODULE_INFORMATION;
typedef enum _SYSTEM_INFORMATION_CLASS
{
SystemBasicInformation = 0x0,
SystemProcessorInformation = 0x1,
SystemPerformanceInformation = 0x2,
SystemTimeOfDayInformation = 0x3,
SystemPathInformation = 0x4,
SystemProcessInformation = 0x5,
SystemCallCountInformation = 0x6,
SystemDeviceInformation = 0x7,
SystemProcessorPerformanceInformation = 0x8,
SystemFlagsInformation = 0x9,
SystemCallTimeInformation = 0xa,
SystemModuleInformation = 0xb,
SystemLocksInformation = 0xc,
SystemStackTraceInformation = 0xd,
SystemPagedPoolInformation = 0xe,
SystemNonPagedPoolInformation = 0xf,
SystemHandleInformation = 0x10,
SystemObjectInformation = 0x11,
SystemPageFileInformation = 0x12,
SystemVdmInstemulInformation = 0x13,
SystemVdmBopInformation = 0x14,
SystemFileCacheInformation = 0x15,
SystemPoolTagInformation = 0x16,
SystemInterruptInformation = 0x17,
SystemDpcBehaviorInformation = 0x18,
SystemFullMemoryInformation = 0x19,
SystemLoadGdiDriverInformation = 0x1a,
SystemUnloadGdiDriverInformation = 0x1b,
SystemTimeAdjustmentInformation = 0x1c,
SystemSummaryMemoryInformation = 0x1d,
SystemMirrorMemoryInformation = 0x1e,
SystemPerformanceTraceInformation = 0x1f,
SystemObsolete0 = 0x20,
SystemExceptionInformation = 0x21,
SystemCrashDumpStateInformation = 0x22,
SystemKernelDebuggerInformation = 0x23,
SystemContextSwitchInformation = 0x24,
SystemRegistryQuotaInformation = 0x25,
SystemExtendServiceTableInformation = 0x26,
SystemPrioritySeperation = 0x27,
SystemVerifierAddDriverInformation = 0x28,
SystemVerifierRemoveDriverInformation = 0x29,
SystemProcessorIdleInformation = 0x2a,
SystemLegacyDriverInformation = 0x2b,
SystemCurrentTimeZoneInformation = 0x2c,
SystemLookasideInformation = 0x2d,
SystemTimeSlipNotification = 0x2e,
SystemSessionCreate = 0x2f,
SystemSessionDetach = 0x30,
SystemSessionInformation = 0x31,
SystemRangeStartInformation = 0x32,
SystemVerifierInformation = 0x33,
SystemVerifierThunkExtend = 0x34,
SystemSessionProcessInformation = 0x35,
SystemLoadGdiDriverInSystemSpace = 0x36,
SystemNumaProcessorMap = 0x37,
SystemPrefetcherInformation = 0x38,
SystemExtendedProcessInformation = 0x39,
SystemRecommendedSharedDataAlignment = 0x3a,
SystemComPlusPackage = 0x3b,
SystemNumaAvailableMemory = 0x3c,
SystemProcessorPowerInformation = 0x3d,
SystemEmulationBasicInformation = 0x3e,
SystemEmulationProcessorInformation = 0x3f,
SystemExtendedHandleInformation = 0x40,
SystemLostDelayedWriteInformation = 0x41,
SystemBigPoolInformation = 0x42,
SystemSessionPoolTagInformation = 0x43,
SystemSessionMappedViewInformation = 0x44,
SystemHotpatchInformation = 0x45,
SystemObjectSecurityMode = 0x46,
SystemWatchdogTimerHandler = 0x47,
SystemWatchdogTimerInformation = 0x48,
SystemLogicalProcessorInformation = 0x49,
SystemWow64SharedInformationObsolete = 0x4a,
SystemRegisterFirmwareTableInformationHandler = 0x4b,
SystemFirmwareTableInformation = 0x4c,
SystemModuleInformationEx = 0x4d,
SystemVerifierTriageInformation = 0x4e,
SystemSuperfetchInformation = 0x4f,
SystemMemoryListInformation = 0x50,
SystemFileCacheInformationEx = 0x51,
SystemThreadPriorityClientIdInformation = 0x52,
SystemProcessorIdleCycleTimeInformation = 0x53,
SystemVerifierCancellationInformation = 0x54,
SystemProcessorPowerInformationEx = 0x55,
SystemRefTraceInformation = 0x56,
SystemSpecialPoolInformation = 0x57,
SystemProcessIdInformation = 0x58,
SystemErrorPortInformation = 0x59,
SystemBootEnvironmentInformation = 0x5a,
SystemHypervisorInformation = 0x5b,
SystemVerifierInformationEx = 0x5c,
SystemTimeZoneInformation = 0x5d,
SystemImageFileExecutionOptionsInformation = 0x5e,
SystemCoverageInformation = 0x5f,
SystemPrefetchPatchInformation = 0x60,
SystemVerifierFaultsInformation = 0x61,
SystemSystemPartitionInformation = 0x62,
SystemSystemDiskInformation = 0x63,
SystemProcessorPerformanceDistribution = 0x64,
SystemNumaProximityNodeInformation = 0x65,
SystemDynamicTimeZoneInformation = 0x66,
SystemCodeIntegrityInformation = 0x67,
SystemProcessorMicrocodeUpdateInformation = 0x68,
SystemProcessorBrandString = 0x69,
SystemVirtualAddressInformation = 0x6a,
SystemLogicalProcessorAndGroupInformation = 0x6b,
SystemProcessorCycleTimeInformation = 0x6c,
SystemStoreInformation = 0x6d,
SystemRegistryAppendString = 0x6e,
SystemAitSamplingValue = 0x6f,
SystemVhdBootInformation = 0x70,
SystemCpuQuotaInformation = 0x71,
SystemNativeBasicInformation = 0x72,
SystemErrorPortTimeouts = 0x73,
SystemLowPriorityIoInformation = 0x74,
SystemBootEntropyInformation = 0x75,
SystemVerifierCountersInformation = 0x76,
SystemPagedPoolInformationEx = 0x77,
SystemSystemPtesInformationEx = 0x78,
SystemNodeDistanceInformation = 0x79,
SystemAcpiAuditInformation = 0x7a,
SystemBasicPerformanceInformation = 0x7b,
SystemQueryPerformanceCounterInformation = 0x7c,
SystemSessionBigPoolInformation = 0x7d,
SystemBootGraphicsInformation = 0x7e,
SystemScrubPhysicalMemoryInformation = 0x7f,
SystemBadPageInformation = 0x80,
SystemProcessorProfileControlArea = 0x81,
SystemCombinePhysicalMemoryInformation = 0x82,
SystemEntropyInterruptTimingInformation = 0x83,
SystemConsoleInformation = 0x84,
SystemPlatformBinaryInformation = 0x85,
SystemThrottleNotificationInformation = 0x86,
SystemHypervisorProcessorCountInformation = 0x87,
SystemDeviceDataInformation = 0x88,
SystemDeviceDataEnumerationInformation = 0x89,
SystemMemoryTopologyInformation = 0x8a,
SystemMemoryChannelInformation = 0x8b,
SystemBootLogoInformation = 0x8c,
SystemProcessorPerformanceInformationEx = 0x8d,
SystemSpare0 = 0x8e,
SystemSecureBootPolicyInformation = 0x8f,
SystemPageFileInformationEx = 0x90,
SystemSecureBootInformation = 0x91,
SystemEntropyInterruptTimingRawInformation = 0x92,
SystemPortableWorkspaceEfiLauncherInformation = 0x93,
SystemFullProcessInformation = 0x94,
SystemKernelDebuggerInformationEx = 0x95,
SystemBootMetadataInformation = 0x96,
SystemSoftRebootInformation = 0x97,
SystemElamCertificateInformation = 0x98,
SystemOfflineDumpConfigInformation = 0x99,
SystemProcessorFeaturesInformation = 0x9a,
SystemRegistryReconciliationInformation = 0x9b,
MaxSystemInfoClass = 0x9c,
} SYSTEM_INFORMATION_CLASS;
//方式一的声明 二者选其一即可.另一个注释掉
extern "C" NTSTATUS NTAPI ZwQuerySystemInformation(
DWORD32 systemInformationClass,
PVOID systemInformation,
ULONG systemInformationLength,
PULONG returnLength);
//方式二的声明
NTSYSAPI
NTSTATUS
NTAPI ZwQuerySystemInformation(
IN ULONG SystemInformationClass,
IN OUT PVOID SystemInformation,
IN ULONG SystemInformationLength,
OUT PULONG ReturnLength
);
在内核中 ZwQuerySystemInformation 是导出的. 所以我们只需要声明一下即可. 也就是使用 extern "C" 如果你想动态使用的话 那么就需要配合 MmGetSystemRoutineAddress 函数来进行动态调用 MmGetSystemRoutineAddress 跟我们Ring3常用的 GetProcAddress函数一样.
其中每种功能号对应的结构是不一样的. 如我们使用的 SystemProcessInformation(5)它所 对应的结构名称则为 SYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION 这个结构可以在官网找到. 而这个结构有三种写法.分别为如下. 怎么使用都是可以的.
其中结构如下:
//第一种方式
typedef struct _SYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION
{
ULONG NextEntryOffset; //因次结构是链表结构,所以此成员记录了下一此结构的偏移
ULONG NumberOfThreads;
LARGE_INTEGER SpareLi1;
LARGE_INTEGER SpareLi2;
LARGE_INTEGER SpareLi3;
LARGE_INTEGER CreateTime;
LARGE_INTEGER UserTime;
LARGE_INTEGER KernelTime;
UNICODE_STRING ImageName; //记录的进程名
KPRIORITY BasePriority;
HANDLE UniqueProcessId; //记录的进程ID
HANDLE InheritedFromUniqueProcessId; //父进程ID
ULONG HandleCount;
ULONG SessionId; //会话ID
ULONG_PTR PageDirectoryBase;
SIZE_T PeakVirtualSize;
SIZE_T VirtualSize; //记录了虚拟大小
ULONG PageFaultCount; //记录了错误页的个数
SIZE_T PeakWorkingSetSize;
SIZE_T WorkingSetSize;
SIZE_T QuotaPeakPagedPoolUsage;
SIZE_T QuotaPagedPoolUsage;
SIZE_T QuotaPeakNonPagedPoolUsage;
SIZE_T QuotaNonPagedPoolUsage;
SIZE_T PagefileUsage;
SIZE_T PeakPagefileUsage;
SIZE_T PrivatePageCount;
LARGE_INTEGER ReadOperationCount;
LARGE_INTEGER WriteOperationCount;
LARGE_INTEGER OtherOperationCount;
LARGE_INTEGER ReadTransferCount;
LARGE_INTEGER WriteTransferCount;
LARGE_INTEGER OtherTransferCount;
} SYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION, *PSYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION;
//第二种方式
typedef struct _SYSTEM_THREAD
{
LARGE_INTEGER KernelTime;
LARGE_INTEGER UserTime;
LARGE_INTEGER CreateTime;
ULONG WaitTime;
PVOID StartAddress;
CLIENT_ID ClientId;
KPRIORITY Priority;
LONG BasePriority;
ULONG ContextSwitchCount;
ULONG State;
KWAIT_REASON WaitReason;
} SYSTEM_THREAD, *PSYSTEM_THREAD; //
typedef struct _SYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION
{
ULONG NextEntryOffset; // 下一个结构的偏移
ULONG NumberOfThreads; //线程个数
LARGE_INTEGER Reserved[3];
LARGE_INTEGER CreateTime; //创建时间
LARGE_INTEGER UserTime; //用户模式(Ring 3)的CPU时间
LARGE_INTEGER KernelTime; //内核模式(Ring 0)的CPU时间
UNICODE_STRING ImageName; //进程名称
KPRIORITY BasePriority; //进程优先权
HANDLE ProcessId; // ULONG UniqueProcessId 进程标识符
HANDLE InheritedFromProcessId; //父进程的标识符
ULONG HandleCount; //句柄数目
ULONG Reserved2[2];
ULONG PrivatePageCount;
VM_COUNTERS VirtualMemoryCounters; //虚拟存储器的结构
IO_COUNTERS IoCounters; // IO计数结构
SYSTEM_THREAD Threads[1]; //进程相关线程的结构数组
} SYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION, *PSYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION;
//第三种方式
typedef struct _SYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION
{
ULONG NextEntryDelta;
ULONG ThreadCount;
ULONG Reserved[6];
LARGE_INTEGER CreateTime;
LARGE_INTEGER UserTime;
LARGE_INTEGER KernelTime;
UNICODE_STRING ProcessName;
KPRIORITY BasePriority;
ULONG ProcessId;
ULONG InheritedFromProcessId;
ULONG HandleCount;
ULONG Reserved2[2];
VM_COUNTERS VmCounters;
IO_COUNTERS IoCounters;
} SYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION, *PSYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION;
遍历代码如下:
BOOLEAN EnumProcess()
{
ULONG res_len = 0;
BOOLEAN result = FALSE;
NTSTATUS status = STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL;
PSYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION psi = NULL;
ULONG next_offset = 0;
PVOID save_start_addr = NULL;
// step1: 第一步获取所使用的的大小.但是第一次有可能获取的大小并不对.所以需要循环获取.
status = ZwQuerySystemInformation(SystemProcessInformation, 0, NULL, &res_len);
while (status == STATUS_INFO_LENGTH_MISMATCH)
{
// Setp2: 为其申请内存,申请内存之前先释放之前的内存
if (psi != NULL)
{
ExFreePoolWithTag(psi, 'abcd');
psi = NULL;
}
psi = (PSYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION)ExAllocatePoolWithTag(PagedPool, res_len, 'abcd');
RtlZeroMemory(psi, res_len);
// Check
if (psi == NULL)
{
// Memory failed
return FALSE;
}
//继续获取或取出实际的大小
status = ZwQuerySystemInformation(SystemProcessInformation, psi, res_len, &res_len);
}
save_start_addr = psi; //最后内存释放要从首地址进行释放.所以记录一下.
// Step4: 获取出来的内容是一个SYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION结构.它是一个链表组成.第一个成员指向了下一个成员的偏移位置
while (psi->NextEntryOffset != 0)
{
if (psi != NULL)
{
//输出遍历到的进程PID
DbgPrint("[hex-PID] = %p [dec-pid] = %d [PPID] = %p [PName] = %wZ \r\n",
psi->UniqueProcessId,
(ULONG)psi->UniqueProcessId,
psi->InheritedFromUniqueProcessId,
psi->ImageName);
}
psi = (PSYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION)((PUCHAR)psi + psi->NextEntryOffset);
}
if (save_start_addr != NULL)
{
ExFreePoolWithTag(save_start_addr, 'abcd');
save_start_addr = NULL;
}
return TRUE;
}
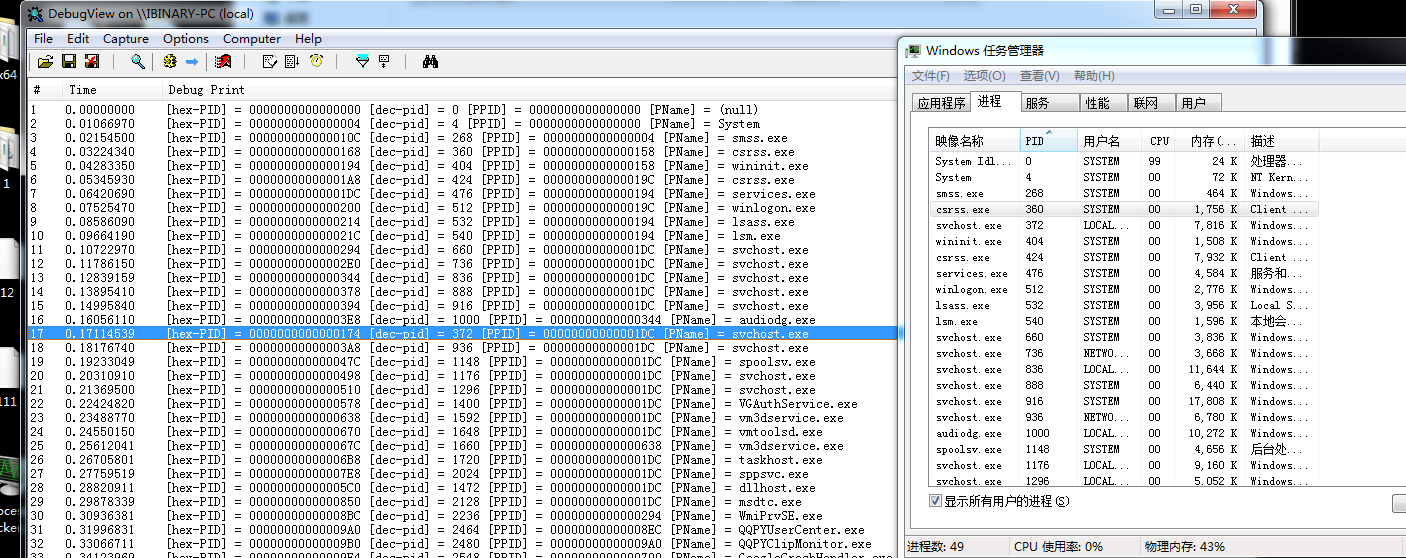
实现效果.
在Win7下都可以正常遍历(64) 在win10 64下也可以正常遍历. 至于使用上面那个结构体.自己选择自己喜爱的即可.32位没有试,如果 PSYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION 结构不变的情况下,那么也可以遍历出相同的信息.
1.3 Ps函数遍历进程
在Windows内核中 遍历进程还可以使用 微软提供的API. 其实我们枚举进程的时候都会 枚举 PspCidTable 这个表(句柄表) 而这个不是一个公开的变量,虽然枚举它可以有效的遍历出 隐藏的进程(针对断链隐藏) 但是毕竟太底层. 而我们使用的API.在内核它的函数内部则间接的枚举了这个表. 所以我们就是用此API即可.
NTSTATUS PsLookupProcessByProcessId(
[in] HANDLE ProcessId,
[out] PEPROCESS *Process
);
extern "C" NTKERNELAPI UCHAR *PsGetProcessImageFileName(IN PEPROCESS Process); //未公开的进行导出即可 16字节方式获取EPROCESS中子域记录的进程名
extern "C" NTKERNELAPI HANDLE PsGetProcessInheritedFromUniqueProcessId(IN PEPROCESS Process); //未公开进行导出 获取父进程Pid
直接使用此函数可以直接枚举出进程ID所对应的EPROCESS 所以很强大.获得了EPROCESS 我们则可以做好多事情. 比如还可以获取它对应的句柄. 变向的相当于通过 Pid获取进程的句柄. 也就相当于自己实现了 RING3的 OpenProcess
需要注意的是此函数只是获取 进程PID与之对应的EPROCESS. 所以想要获取EPROCESS中的其它想要的成员(父进程ID,进程名)那么就需要其它函数了,下面会说.如果观察进程PID的增量来则可以看到它是按照+4方式来管理PID的. 所以最高可以获取的PID为 2^32-1.
还需要注意的是,按照Windows 以引用计数方式来管理结构的方式.使用完此函数之后会对获取到的 Process 的引用计数+1 所以不使用的时候需要对其解引用.
解引用如下:
ObDereferenceObject(ppEprocess);
遍历代码如下:
//未公开的进行导出即可 16字节方式获取EPROCESS中子域记录的进程名
extern "C" NTKERNELAPI UCHAR *PsGetProcessImageFileName(IN PEPROCESS Process);
//未公开进行导出 获取父进程Pid
extern "C" NTKERNELAPI HANDLE PsGetProcessInheritedFromUniqueProcessId(IN PEPROCESS Process);
BOOLEAN EnumProcess2()
{
PEPROCESS ppEprocess = NULL;
int pid_index = 0;
NTSTATUS status = STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL;
//缺点,不知道进程Pid有多少.所以遍历 2^31-1(2147483647). 但是其实遍历到3W (30000)即可.很少有这么多进程
for (pid_index = 0; pid_index < 30000; pid_index += 4)
{
status = PsLookupProcessByProcessId((HANDLE)pid_index, &ppEprocess);
if (NT_SUCCESS(status))
{
DbgPrint("[Pid] = %p [Ppid] = %p [ImageFileName]: %s \t\r\n",
PsGetProcessId(ppEprocess),
PsGetProcessInheritedFromUniqueProcessId(ppEprocess),
PsGetProcessImageFileName(ppEprocess));
}
if (ppEprocess != NULL)
{
ObDereferenceObject(ppEprocess);
ppEprocess = NULL;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
效果:
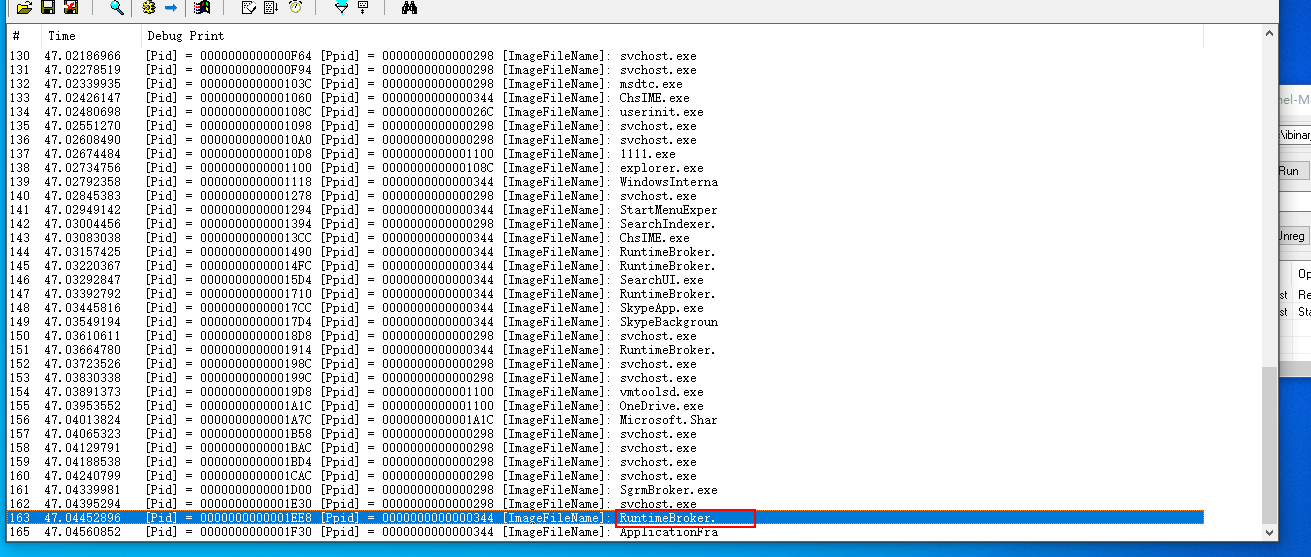
虽然获取出来了.但是文件名超出了16个字节. 那么解决方法在下面说. 先放过.
1.4 通过PspCidTable
涉及句柄表.后面再说.
1.5 遍历进程总结
遍历进程分为三种方式:
-
ZwQuerySystemInformation的五号功能(SystemProcessInformation)可以获取,优点是标准.缺点是结构体比较多可能要定义一下. 还有不能直接获取和操作EPROCESS -
PsLookupProcessByProcessId方式可以直接返回出PID所对应的EPROCESS,可以通过EPROCESS直接获取要操作的句柄也是可以的. 缺点是 PID不知道有多少.所以需要盲目遍历. 但是如果封装好第一种方式和这种方式. 那么潜力无限. 那么都可以实现自己的PsGetProcessNameByProcessId PsOpenProcess PsGetEprocessByProcessId... -
PspCidTable这种方式最牛.甚至于可以遍历出隐藏的进程但是在PG的年代没必要再去遍历PspCidTable了,因为断链隐藏有可能PG都会检测了. 如果想使用这种方法.那么每出一个系统.都要去适配. 而且写得程序大多数是Ark程序. 如果你在工作中使用(除非特殊需求)是没有必要的. 可以选择第一第二种方式.
二丶 句柄 pid 对象的互相转化
2.1 简介
这一讲尤为重要.明白了这一讲,才能在内核编程中写代码变得游刃有余.
2.2 进程PID转变为进程的Handle
原理就是 跟ring3一样. 使用打开进程(OpenProcess)的函数来获取HANDLE
核心原理就是在内核中使用 ZwOpenProcess 传入PID 传出一个HANDLE.
ULONG pid;
HANDLE hProcessHandle;
OBJECT_ATTRIBUTES obj;
CLIENT_ID clientid;
//必须初始化
pid = 2378;
clientid.UniqueProcess = (HANDLE)pid;
clientid.UniqueThread = 0;
InitializeObjectAttributes(&obj, 0, OBJ_CASE_INSENSITIVE | OBJ_KERNEL_HANDLE, 0, 0);
ZwOpenProcess(&hProcessHandle, PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS, &obj, &clientid);
2.3 Handle(句柄)转化为Pid
Handle转化为PID就要使用跟进程相关的特有API.
可以使用 未声明但是内核导出的函数 也就是 ZwQueryInformationProcess
凡是未声明但是内核导出的函数.我们都可以 进行动态调用. 亦或者是直接声明一下.
如下:
extern "C" NTSYSAPI
NTSTATUS
NTAPI
ZwQueryInformationProcess(
IN HANDLE ProcessHandle,
IN PROCESSINFOCLASS ProcessInformationClass,
OUT PVOID ProcessInformation,
IN ULONG ProcessInformationLength,
IN PULONG ReturnLength);
在遍历的时候我们需要传递一个 ProcessInformationClass 来告诉他查询啥. 而这个数组是个枚举. 其中这个结构会在 ntddk.h 中定义. 而BlackBone 代码中也为其进行了声明.
如下:
typedef enum _PROCESSINFOCLASS {
ProcessBasicInformation = 0, //查询进程基础信息,必须Pid
ProcessQuotaLimits = 1,
ProcessIoCounters = 2,
ProcessVmCounters = 3,
ProcessTimes = 4,
ProcessBasePriority = 5,
ProcessRaisePriority = 6,
ProcessDebugPort = 7,
ProcessExceptionPort = 8,
ProcessAccessToken = 9,
ProcessLdtInformation = 10,
ProcessLdtSize = 11,
ProcessDefaultHardErrorMode = 12,
ProcessIoPortHandlers = 13, // Note: this is kernel mode only
ProcessPooledUsageAndLimits = 14,
ProcessWorkingSetWatch = 15,
ProcessUserModeIOPL = 16,
ProcessEnableAlignmentFaultFixup = 17,
ProcessPriorityClass = 18,
ProcessWx86Information = 19,
ProcessHandleCount = 20,
ProcessAffinityMask = 21,
ProcessPriorityBoost = 22,
ProcessDeviceMap = 23,
ProcessSessionInformation = 24,
ProcessForegroundInformation = 25,
ProcessWow64Information = 26, //查询是否是64位
ProcessImageFileName = 27, //查询名字 查询结果可能是 \\Device\\ha...
ProcessLUIDDeviceMapsEnabled = 28,
ProcessBreakOnTermination = 29,
ProcessDebugObjectHandle = 30,
ProcessDebugFlags = 31,
ProcessHandleTracing = 32,
ProcessIoPriority = 33,
ProcessExecuteFlags = 34,
ProcessTlsInformation = 35,
ProcessCookie = 36,
ProcessImageInformation = 37,
ProcessCycleTime = 38,
ProcessPagePriority = 39,
ProcessInstrumentationCallback = 40,
ProcessThreadStackAllocation = 41,
ProcessWorkingSetWatchEx = 42,
ProcessImageFileNameWin32 = 43,//查询Nt名字: C:\\xx
ProcessImageFileMapping = 44,
ProcessAffinityUpdateMode = 45,
ProcessMemoryAllocationMode = 46,
ProcessGroupInformation = 47,
ProcessTokenVirtualizationEnabled = 48,
ProcessOwnerInformation = 49,
ProcessWindowInformation = 50,
ProcessHandleInformation = 51,
ProcessMitigationPolicy = 52,
ProcessDynamicFunctionTableInformation = 53,
ProcessHandleCheckingMode = 54,
ProcessKeepAliveCount = 55,
ProcessRevokeFileHandles = 56,
ProcessWorkingSetControl = 57,
ProcessHandleTable = 58,
ProcessCheckStackExtentsMode = 59,
ProcessCommandLineInformation = 60,
ProcessProtectionInformation = 61,
ProcessMemoryExhaustion = 62,
ProcessFaultInformation = 63,
ProcessTelemetryIdInformation = 64,
ProcessCommitReleaseInformation = 65,
ProcessReserved1Information = 66,
ProcessReserved2Information = 67,
ProcessSubsystemProcess = 68,
ProcessInPrivate = 70,
ProcessRaiseUMExceptionOnInvalidHandleClose = 71,
ProcessSubsystemInformation = 75,
ProcessWin32kSyscallFilterInformation = 79,
ProcessEnergyTrackingState = 82,
MaxProcessInfoClass // MaxProcessInfoClass should always be the last enum
} PROCESSINFOCLASS;
其中我们要查询的是 Basic信息,这个结构体在Ntddk中有定义.所以列出来看一下即可. 里面的UniqueProcessId则为所求. 结构如下.
typedef struct _PROCESS_BASIC_INFORMATION {
NTSTATUS ExitStatus;
PPEB PebBaseAddress;
ULONG_PTR AffinityMask;
KPRIORITY BasePriority;
ULONG_PTR UniqueProcessId;
ULONG_PTR InheritedFromUniqueProcessId;
} PROCESS_BASIC_INFORMATION,*PPROCESS_BASIC_INFORMATION;
代码如下:
PROCESS_BASIC_INFORMATION ProcessBasicInfor;
//动态获取.
UNICODE_STRING UtrZwQueryInformationProcessName =
RTL_CONSTANT_STRING(L"ZwQueryInformationProcess");
ZwQueryInformationProcess =
(PfnZwQueryInformationProcess)MmGetSystemRoutineAddress(&UtrZwQueryInformationProcessName);
//check...
//核心代码
/*
1.利用PID
*/
PROCESS_BASIC_INFORMATION ProcessBasicInfor;
ZwQueryInformationProcess(
ProcessHndle,
ProcessBasicInformation,
(PVOID)&ProcessBasicInfor,
sizeof(ProcessBasicInfor),
NULL);
/*
ProcessBasicInfor.UniqueProcessId; 则为你所求
*/
2.4 Pid转化为对象(EPROCESS)
原理就是通过 PsLookUpProcessByProcessId 传入PID.传出EPROCESS.
在上面已经说过了.不再赘述.
PEPROCESS pEpro;
PsLookUpProcessByProcessId((HANDLE)pid,&pEpro);
ObDereferenceObject(pEpro);
2.5 句柄(Handle)转对象(EPROCESS)
原理是使用内核函数. 有了进程的HANDLE 第一时间就要想着获取它的对象指针.
HANDLE 不仅限于进程. 例如线程 File Event等等.
ObReferenceObjectByHandle(ProcessHandle, GENERIC_ALL,*PsProcessType,KernelMode,&pEprocess,NULL);
2.6 EPROCESS转化为Pid
在EPROCESS对象中直接有一个成员域记录着Pid. 也就是 eprocess.UniqueProcessId
但是直接获取并不行.所以还是使用内核函数.
PsGetProcessId(PEPROCESS eprocess);
2.7 EPROCESS转化为HANDLE
这个也很常用 也是使用内核Api. 有了 对象则可以获取对象对应的HANDLE. 不仅限于 EPROCESS
ObOpenObjectByPoint(Process,attributes,&AccessState,0,*PsProcessType,PreviousMode,&Handle);
//例子
HANDLE hProcessHandle = (HANDLE)-1;
Status = ObOpenObjectByPointer(
pEprocess, //传递的是EPROCES的对象
OBJ_KERNEL_HANDLE,
0,
0,
*PsProcessType, //想要从对象中获取的类型是 EPROCESS
KernelMode,
&hProcessHandle //如果成功则 hProcessHandle即为所求.
);
if (!NT_SUCCESS(Status))
{
Status = STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL;
goto RELEASE;
}
三丶进程名的操作
3.1 16字节方式获取进程名
通过使用导出函数,可以获取EPROCESS中的域,这个域记录着进程名. 但是它是一个16字节数组. 且是0结尾的. 所以存储有效的名字只有15个字符.
所以一般常用的代码不考虑名字的前提下可以使用它.
此函数是导出的,所以声明即可. 如果你在.cpp文件中声明,请一定加上 extern "C" 如果是在.c文件中声明.那么去掉 extern "C" 即可. 其它函数同理.
extern "C" NTKERNELAPI UCHAR *PsGetProcessImageFileName(IN PEPROCESS Process);
此方式的效果观看一下第二种方式遍历进程. 里面有图片有画出来的问题所在.
3.2 Zw方式获取完成进程名
Zw方式其实还是使用 2.3小姐所说的函数 ZwQueryInformationProcess
此函数原型如下:
extern "C" NTSYSAPI
NTSTATUS
NTAPI
ZwQueryInformationProcess(
IN HANDLE ProcessHandle,
IN PROCESSINFOCLASS ProcessInformationClass,
OUT PVOID ProcessInformation,
IN ULONG ProcessInformationLength,
IN PULONG ReturnLength);
在这里 我们要查询的 ProcessInformationClass 则为 27功能号(ProcessImageFileName) 亦或者是 43(ProcessImageFileNameWin32)的功能号. 她们查询的信息都是UNICODE_STRING的结构. 所以我们解析的时候解析为UNICODE_STRING即可.
使用 此函数的第一个参数是一个句柄 也就是代表你要查询的句柄是那个. 我们可以通过第二小节所讲的内容. 进行 pid -->Handle 亦或者是 pid->EPROCESS->handle 这里采用两种方式. 增强转化能力.
43号功能遍历的代码如下:
BOOLEAN GetFullFileName(ULONG upid)
{
ULONG need_size = 0;
// ProcessImageFileName
NTSTATUS status = STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL;
PUNICODE_STRING ucd_image_name_ptr = NULL;
PEPROCESS ppeprocess = NULL;
HANDLE hProcessHandle = (HANDLE)0;
status = PsLookupProcessByProcessId((HANDLE)upid, &ppeprocess);
if (!NT_SUCCESS(status))
{
return FALSE;
}
status = ObOpenObjectByPointer(
ppeprocess,
OBJ_KERNEL_HANDLE,
0,
0,
*PsProcessType,
KernelMode,
&hProcessHandle);
if (!NT_SUCCESS(status))
{
if (ppeprocess != NULL)
{
ObDereferenceObject(ppeprocess);
ppeprocess = NULL;
}
return FALSE;
}
status = ZwQueryInformationProcess(hProcessHandle, ProcessImageFileNameWin32, NULL, 0, &need_size);
while (status == STATUS_INFO_LENGTH_MISMATCH)
{
if (ucd_image_name_ptr != NULL)
{
ExFreePoolWithTag(ucd_image_name_ptr, 'abcd');
ucd_image_name_ptr = NULL;
}
ucd_image_name_ptr = (PUNICODE_STRING)ExAllocatePoolWithTag(PagedPool, need_size, 'abcd');
if (ucd_image_name_ptr != NULL)
{
RtlZeroMemory(ucd_image_name_ptr, need_size);
}
else
{
if (ppeprocess != NULL)
{
ObDereferenceObject(ppeprocess);
ppeprocess = NULL;
}
if (hProcessHandle != NULL)
{
ZwClose(hProcessHandle);
hProcessHandle = NULL;
}
return FALSE;
}
status = ZwQueryInformationProcess(hProcessHandle, ProcessImageFileNameWin32, ucd_image_name_ptr, need_size, &need_size);
}
if (ucd_image_name_ptr == NULL)
{
if (ppeprocess != NULL)
{
ObDereferenceObject(ppeprocess);
ppeprocess = NULL;
}
if (hProcessHandle != NULL)
{
ZwClose(hProcessHandle);
hProcessHandle = NULL;
}
return FALSE;
}
DbgPrint("[name] = %wZ \r\n", ucd_image_name_ptr);
if (ucd_image_name_ptr != NULL)
{
ExFreePoolWithTag(ucd_image_name_ptr, 'abcd');
ucd_image_name_ptr = NULL;
}
if (ppeprocess != NULL)
{
ObDereferenceObject(ppeprocess);
ppeprocess = NULL;
}
if (hProcessHandle != NULL)
{
ZwClose(hProcessHandle);
hProcessHandle = NULL;
}
return TRUE;
}
其中我要获取的是 DbgView的全路径 调用时则传递 Dbgview进程的Pid. 效果如下.
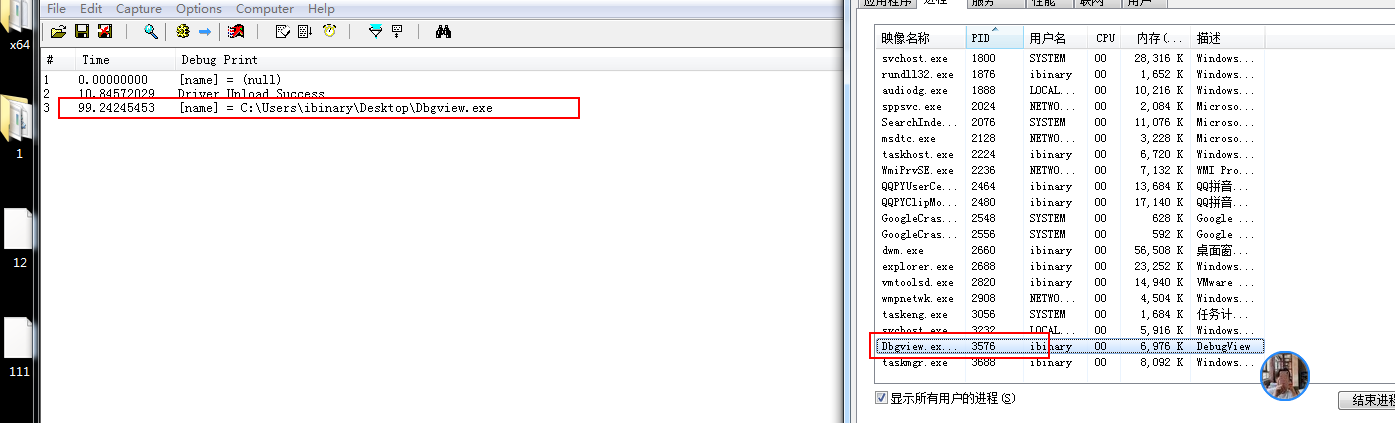
结果输出的则是NT路径
C:\Users\ibinary\DeskTop\DbgView.exe
经过尝试,使用27的功能遍历出的结果跟上面一样. 但是注意,27的功能很可能遍历出来的路径不是 Nt路径. 而是 \Device\ha....
3.3 Zw方式Attach模式下的操作
如果我们使用 KeStackAttachProcess 函数附加到某一进程空间内. 那么此时使用此函数的时候其句柄 也就是参数一 我们直接传 ZwCurrentProcess() 即可.
伪代码:
ZwQueryInformationProcess(ZwCurrentProcess(),
ProcessImageFileName,
NULL,
0,
&need_size);
如果我们附加到进程的空间中. 那么其它类似函数是一样的. 必须内存的申请. 释放. 等等.都可以传递 ZwCurrentProcess() 来操作
四丶进程PID,句柄,EPROCESS的操作
4.1 获取父进程的Pid
获取父进程Pid
导出的函数,但是没有声明. 自己声明下即可.
extern "C" NTKERNELAPI HANDLE PsGetProcessInheritedFromUniqueProcessId(IN PEPROCESS Process);
4.2 获取进程的Pid
使用Api直接获取EPROCESS的Pid即可.
PsGetProcessId(ppEprocess); //参数是EPROCESS 可以直接根据对象获取自己的Pid
4.3 通过EPRCESS获取PEB32
此函数返回的是EPROCESS所对应的32位PEB.
其实也是未文档化的Api.
网上有一段说明:
PsGetProcessWow64Process 是 Windows 内核导出的例程,但 Microsoft 也没有记录它。 该例程使用起来很稳定,至少从 64 位版本的 Windows XP 内核开始就存在了——而且该例程很快就会过时的可能性极小,同样适用于 PsGetProcessPeb 。 PsGetProcessPeb 和 PsGetProcessWow64Process 是检索指向属于目标进程的 进程环境块 (PEB) ,但是后一个例程仅在目标进程是 WOW64 进程时才有效。
NTKERNELAPI
PVOID
NTAPI
PsGetProcessWow64Process( IN PEPROCESS Process );
例子:
typedef struct _PEB32
{
UCHAR InheritedAddressSpace;
UCHAR ReadImageFileExecOptions;
UCHAR BeingDebugged;
UCHAR BitField;
ULONG Mutant;
ULONG ImageBaseAddress;
ULONG Ldr;
ULONG ProcessParameters;
ULONG SubSystemData;
ULONG ProcessHeap;
ULONG FastPebLock;
ULONG AtlThunkSListPtr;
ULONG IFEOKey;
ULONG CrossProcessFlags;
ULONG UserSharedInfoPtr;
ULONG SystemReserved;
ULONG AtlThunkSListPtr32;
ULONG ApiSetMap;
} PEB32, *PPEB32;
PEB32 peb = PsGetProcessWow64Process(Process );
4.4 获取EPROCESS的64位PEB
网上的说明:
PsGetProcessPeb 是由 Windows 内核导出的例程,但 Microsoft 没有记录它。 从至少从 Windows 2000 开始就已经存在的意义上,该例程使用起来很稳定。
这个也是使用的API如下.
NTKERNELAPI
PPEB
NTAPI
PsGetProcessPeb( IN PEPROCESS Process );
4.5 判断进程是否是Wow64
未文档化的Api
NTKERNELAPI
PVOID
NTAPI
PsGetCurrentProcessWow64Process( );
返回值不是NULL 则代表是Wow64的进程(也就是32位)
观看 BlackBone 发现它判断是否是Wow64还直接对其获取32的PEB
如果不是就代表是Wow64
代码如下:
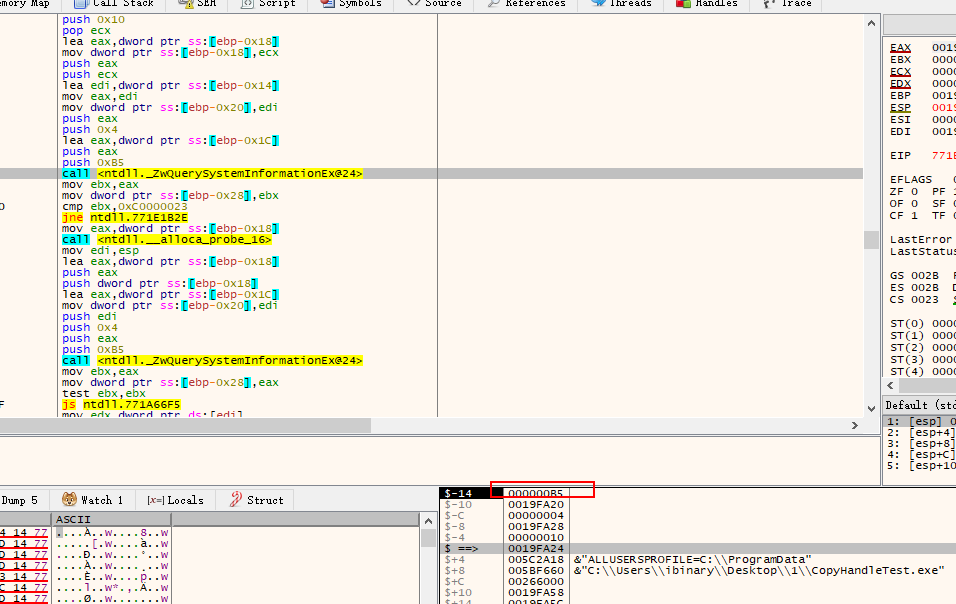
BOOLEAN isWow64 = (PsGetProcessWow64Process( pProcess ) != NULL) ? TRUE : FALSE;
当时还有查询法.
查询法则是使用 ZwQuerySystemInformationEx 配合0xE6 功能号来进行查询的.
通过逆向分析 IsWow64Process
发现其底层调用的是 ZwQuerySystemInformationEx (Win11下) 然后此函数原型如下:
NTSTATUS
ZwQuerySystemInformationEx (
SYSTEM_INFORMATION_CLASS SystemInformationClass,
PVOID InputBuffer,
ULONG InputBufferLength,
PVOID SystemInformation,
ULONG SystemInformationLength,
ULONG *ReturnLength);
逆向分析时的缓冲区如下:
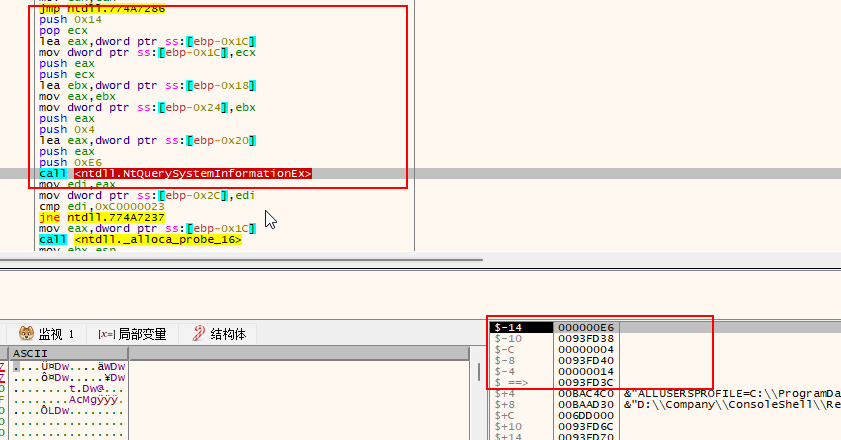
大概伪代码为:
ZwQuerySystemInformationEx(0xE6,inbuf,4,outbuf,0x14,&need_size);
但是分析win7下的实现.发现它是使用的
ZwQueryInformationProcess的26(ProcessWow64Information)号功能进行查询的.
逆向分析截图如下:
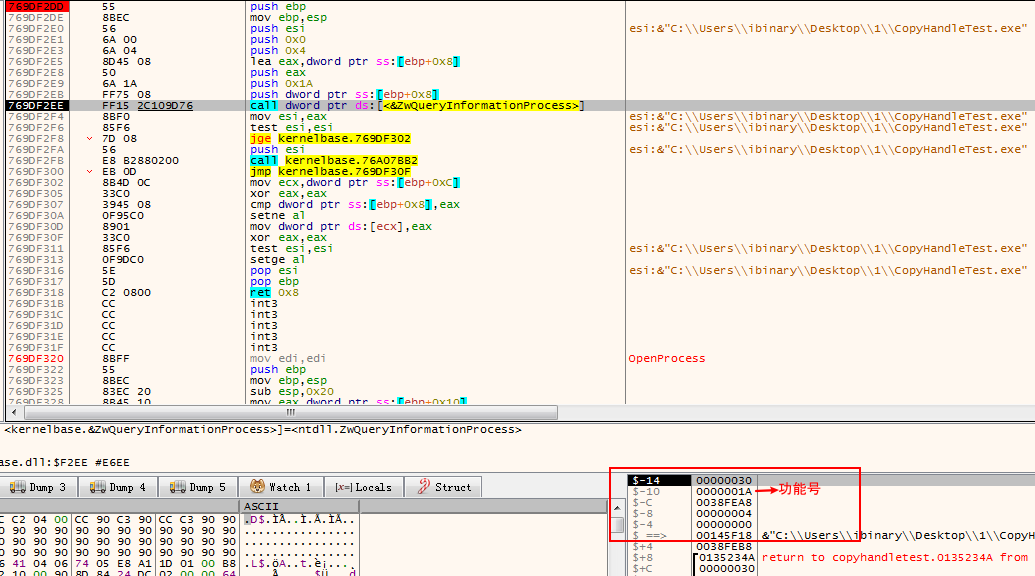
伪代码:
DWORD isWow64 = 0;
DWORD need_size = 0;
ZwQueryInformationProcess(handle,ProcessWow64Information,&isWow64 ,sizeof(DWORD),&need_size);
win10下和Win11使用的函数一样,唯一不同的就是功能号不同.
五丶进程的挂起和恢复
5.1 挂起进程(暂停进程)
挂起进程在内核中已经给我们导出了函数进行使用. 但是并没有声明.我们声明一下即可使用.
extern "C" NTKERNELAPI NTSTATUS PsSuspendProcess(PEPROCESS Proc);
未挂起前效果:
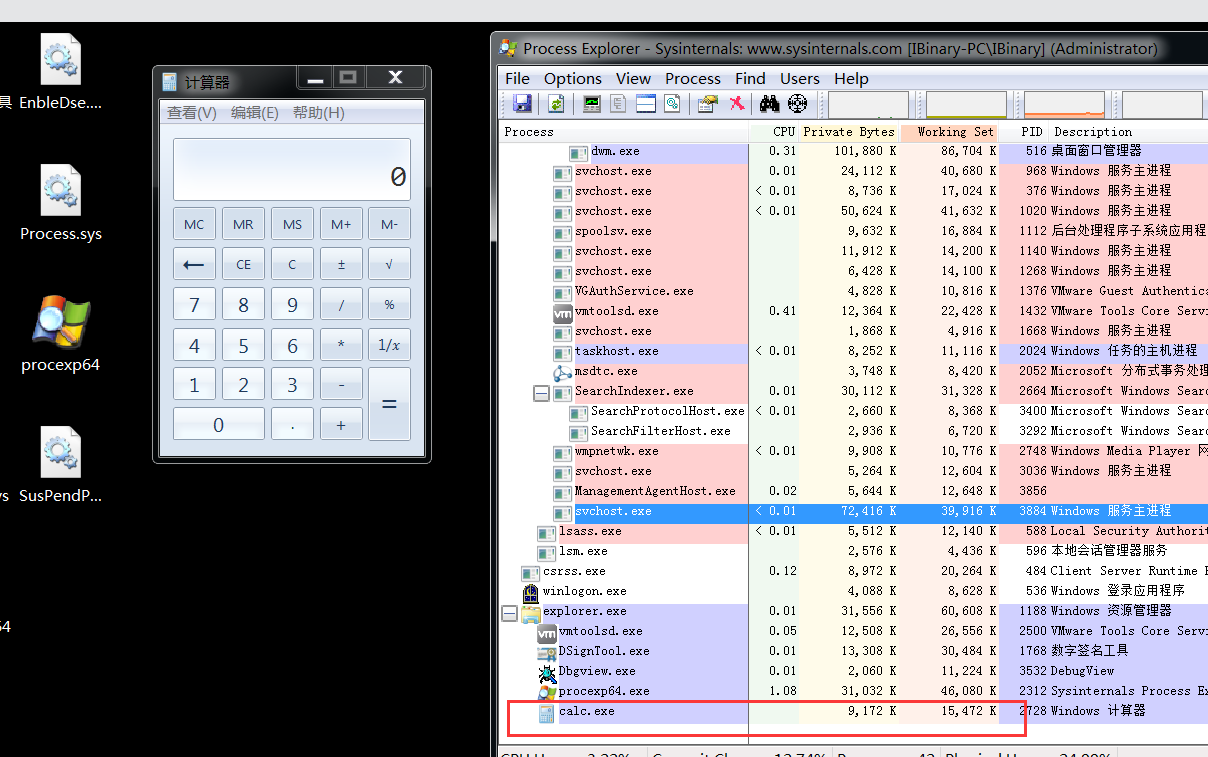
驱动挂起代码
```c
#include <ntifs.h>
extern "C" NTKERNELAPI NTSTATUS PsSuspendProcess(PEPROCESS proc); //暂停进程
extern "C" NTKERNELAPI NTSTATUS PsResumeProcess(PEPROCESS proc); //恢复进程
void DriverUnLoad(PDRIVER_OBJECT pDriverObj)
{
KdPrint(("驱动卸载成功"));
}
/*
1.枚举所有进程. 2^31方
*/
PEPROCESS GetEprocessByPid(HANDLE pid)
{
//根据PID 返回PEPROCESS
PEPROCESS pEpro = NULL;
NTSTATUS ntStatus = STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL;
ntStatus = PsLookupProcessByProcessId(pid, &pEpro);
if (NT_SUCCESS(ntStatus))
{
return pEpro;
}
return NULL;
}
void TestSusPendProcess(ULONG pid)
{
PEPROCESS pCurrentEprocess = NULL;
pCurrentEprocess = GetEprocessByPid((HANDLE)pid);
if (pCurrentEprocess != NULL)
{
PsSuspendProcess(pCurrentEprocess);
DbgPrint("挂起进程成功\r\n");
ObDereferenceObject(pCurrentEprocess);
}
}
NTSTATUS DriverEntry(PDRIVER_OBJECT pDriverObj, PUNICODE_STRING pRegPath)
{
ULONG iCount = 0;
NTSTATUS ntStatus;
pDriverObj->DriverUnload = DriverUnLoad;
//IteratorProcess(); //遍历进程
TestSusPendProcess(2728); //挂起进程,传入指定PID
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
### 5.2 恢复进程(恢复暂停的进程)
跟挂起进程一样,我们声明一下恢复挂起的函数即可.
```cpp
extern "C" NTKERNELAPI NTSTATUS PsResumeProcess(PEPROCESS proc); //恢复进程
六丶结束进程的操作
6.1 标准方式结束
标准方式结束进程则是 使用 ZwOpenProcess打开进程获取进程句柄. 然后使用 ZwTerminateProcess来结束. 最后把打开的句柄使用 ZwClose关闭掉.
代码示例:
void ZwKillProcess(ULONG pid)
{
HANDLE ProcessHandle = NULL;
OBJECT_ATTRIBUTES obj;
CLIENT_ID cid = { 0 };
NTSTATUS ntStatus = STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL;
InitializeObjectAttributes(&obj,NULL,OBJ_KERNEL_HANDLE|OBJ_CASE_INSENSITIVE,NULL,NULL);
cid.UniqueProcess = (HANDLE)pid;
cid.UniqueThread = 0;
ntStatus = ZwOpenProcess(&ProcessHandle, GENERIC_ALL, &obj, &cid);
if (NT_SUCCESS(ntStatus))
{
ZwTerminateProcess(ProcessHandle, 0);
ZwClose(ProcessHandle);
}
ZwClose(ProcessHandle);
}
6.2 内存清零方式结束
上面当时有说过,当我们 附加到某一进程的时候.我们就是这个进程的一部分.那么自然的我们就可以操作内存了. 因为上下文都是我们进程的. 所以我们可以使用 内存清零法进行结束进程
原理就是把内存,包括代码执行的内存都给Free掉. 这样程序就会自己出现异常.进而崩溃. 崩溃了就会退出了.
void MemKillProcess(HANDLE pid)
{
PEPROCESS proc = NULL;
NTSTATUS ntStatus = STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL;
PKAPC_STATE pApcState = NULL;
PsLookupProcessByProcessId((HANDLE)pid,&proc);
if (proc == 0)
{
return;
}
//KeAttachProcess(proc);
//KeDetachProcess() 等都已经过时.所以使用新的
pApcState = (PKAPC_STATE)ExAllocatePoolWithTag(NonPagedPool, sizeof(PKAPC_STATE), '1111');
if (NULL == pApcState)
{
ObDereferenceObject(proc);
return;
}
__try{
KeStackAttachProcess(proc, pApcState);
//KeAttachProcess(proc);
for (int i = 0x10000; i < 0x20000000; i += PAGE_SIZE)
{
__try
{
memset((PVOID)i, 0, PAGE_SIZE);
}
__except (1)
{
; //内部处理异常
}
}
KeUnstackDetachProcess(pApcState);
//KeDetachProcess();
ObDereferenceObject(proc);
return;
}
__except (1)
{
DbgPrint("强杀出错\r\n");
KeUnstackDetachProcess(pApcState);
ObDereferenceObject(proc);
}
return;
}
坚持两字,简单,轻便,但是真正的执行起来确实需要很长很长时间.当你把坚持两字当做你要走的路,那么你总会成功. 想学习,有问题请加群.群号:725864912(收费)群名称: 逆向学习小分队 群里有大量学习资源. 以及定期直播答疑.有一个良好的学习氛围. 涉及到外挂反外挂病毒 司法取证加解密 驱动过保护 VT 等技术,期待你的进入。
详情请点击链接查看置顶博客 https://www.cnblogs.com/iBinary/p/7572603.html
本文来自博客园,作者:iBinary,未经允许禁止转载 转载前可联系本人.对于爬虫人员来说如果发现保留起诉权力.https://www.cnblogs.com/iBinary/p/11704838.html
欢迎大家关注我的微信公众号.不定期的更新文章.更新技术. 关注公众号后请大家养成 不白嫖的习惯.欢迎大家赞赏. 也希望在看完公众号文章之后 不忘 点击 收藏 转发 以及点击在看功能. QQ群:
QQ群:


