13 垃圾邮件分类2
读取
1 # 读取文件 2 sms = open(r'D:\机器学习\垃圾邮件分类\SMSSpamCollection','r',encoding = 'utf-8') 3 sms_label = [] # 字符串的列表 4 sms_data = [] # 数据 5 csv_reader = csv.reader(sms, delimiter = '\t') 6 for line in csv_reader: 7 sms_label.append(line[0]) 8 sms_data.append(preprocessing(line[1])) # 对每封邮件做预处理,生成有效词的字符串 9 sms.close()
数据预处理
1 # 定义词性还原的函数
2 def get_wordnet_pos(treebank_tag): # 还原参数pos
3 if treebank_tag.startswith('J'):
4 return nltk.corpus.wordnet.ADJ
5 elif treebank_tag.startswith('V'):
6 return nltk.corpus.wordnet.VERB
7 elif treebank_tag.startswith('N'):
8 return nltk.corpus.wordnet.NOUN
9 elif treebank_tag.startswith('R'):
10 return nltk.corpus.wordnet.ADV
11 else:
12 return nltk.corpus.wordnet.NOUN
13
14 # 预处理
15 def preprocessing(text):
16 tokens = [word for sent in nltk.sent_tokenize(text) for word in nltk.word_tokenize(sent)] # 分词
17 stops = stopwords.words('english') # 停用词类型为英文
18 tokens = [token for token in tokens if token not in stops] # 保留非停用词
19 tokens = [token.lower() for token in tokens if len(token)>=3] # 大写转小写,去掉长度短于3的词
20
21 tag = nltk.pos_tag(tokens) # 标注词性
22 lemmatizer = WordNetLemmatizer() # 词性还原
23 tokens = [lemmatizer.lemmatize(token, pos = get_wordnet_pos(tag[i][1])) for i, token in enumerate(tokens)] # 词性还原
24 preprocessed_text = ''.join(tokens)
25 return preprocessed_text
数据划分—训练集和测试集数据划分
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train,x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data, target, test_size=0.2, random_state=0, stratify=y_train)
代码:
1 # 划分训练集跟测试集
2 x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(sms_data, sms_label, test_size = 0.2, stratify = sms_label) # 测试集占20%
3 print('总数据量:',len(sms_label))
4 print('训练数据量:',len(x_train))
5 print('测试数据量:',len(y_test))
文本特征提取
sklearn.feature_extraction.text.CountVectorizer
sklearn.feature_extraction.text.TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
tfidf2 = TfidfVectorizer()
1 # 向量化 2 tfidf2 = TfidfVectorizer() 3 X_train = tfidf2.fit_transform(x_train) 4 X_test = tfidf2.transform(x_test) 5 print(X_train.toarray().shape) 6 print(X_test.toarray().shape)
模型选择
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
说明为什么选择这个模型?
1 mnb = MultinomialNB()
2 mnb.fit(X_train, y_train)
3 y_mnb = mnb.predict(X_test)
4 print('预测值:',y_mnb)
5 print('实际值:',y_test)
模型评价:混淆矩阵,分类报告
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
confusion_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_predict)
说明混淆矩阵的含义
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
说明准确率、精确率、召回率、F值分别代表的意义
1 # 混淆矩阵,分类报告 2 cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_mnb) 3 print(cm) 4 cr = classification_report(y_test, y_mnb) 5 print(cr)
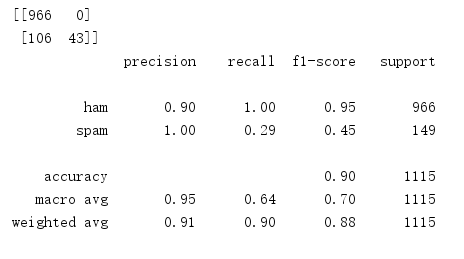
比较与总结
如果用CountVectorizer进行文本特征生成,与TfidfVectorizer相比,效果如何?
答:效果较差,因为用CountVectorizer进行文本特征生成,会出现正常邮件被划分为垃圾邮件的情况





