Tarjan
强连通分量
前置知识
- 强连通 :一张有向图的节点两两互相可达。
- 连通分量 : 若
Tarjan求强连通分量
DFS生成树
(用的OI-wiki的图)
- 树边 : 图中的黑边,每次搜索找到一个还没有访问过的结点的时候就形成了一条树边。
- 返祖边/回边 : 图中的红色边,指向父亲节点。
- 横叉边 : 图中的蓝边,搜索时访问到一个已经访问过的节点,但这个节点不是当前节点的祖先。
- 前向边 : 图中的绿边,搜索时访问到子树的节点
那么这个有什么用呢?
如果结点
证明
假如有一个节点
考虑用这个结论,得出Tarjan求强连通分量的算法
Tarjan求强连通分量
基于对图进行深度优先搜索。
先定义两个数组,对于每个节点
有两个非常显然的结论,一个节点子树内的虽然到现在为止没用过
算法流程 :
深度优先搜索,维护每个节点的
根据强连通分量的根为强连通分量中第一个被搜索到的节点,所以其
时间复杂度
点此查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<bits/extc++.h> // using namespace __gnu_pbds; // using namespace __gnu_cxx; using namespace std; #define infile(x) freopen(x,"r",stdin) #define outfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stdout) #define errfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stderr) #define rep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i <= t; i += p) #define drep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i >= t; i -= p) #ifdef LOCAL FILE *InFile = infile("in.in"),*OutFile = outfile("out.out"); // FILE *ErrFile=errfile("err.err"); #else FILE *Infile = stdin,*OutFile = stdout; //FILE *ErrFile = stderr; #endif using ll=long long;using ull=unsigned long long; using db = double;using ldb = long double; const int N = 1e4 + 10; vector<int> edge[N]; #define eb emplace_back inline void add(int u,int v){edge[u].eb(v);} int n,m,dfn[N],low[N],sta[N],top,tot,num,bel[N]; bitset<N> insta,out; vector<int> scc[N]; void Tarjan(int x){ dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tot; sta[++top] = x;insta[x] = true; for(int y:edge[x]){ if(!dfn[y]){ Tarjan(y); low[x] = min(low[x],low[y]); } else if(insta[y]) low[x] = min(low[x],dfn[y]); } if(dfn[x] == low[x]){ num++;int y; do{ y = sta[top--]; bel[y] = num; scc[num].eb(y),insta[y] = false; }while(y != x); } } inline void solve(){ cin>>n>>m; rep(i,1,m,1){ int u,v;cin>>u>>v; add(u,v); } rep(i,1,n,1) if(!dfn[i]) Tarjan(i); rep(i,1,num,1) sort(scc[i].begin(),scc[i].end()); cout<<num<<'\n'; rep(i,1,n,1){ if(out[bel[i]]) continue; for(int j:scc[bel[i]]) cout<<j<<' '; cout<<'\n'; out[bel[i]] = true; } } signed main(){ cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); cout.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); solve(); }
例题 :
就是求强连通分量,然后看每个强连通分量的出度,如果出度为0的强连通分量有一个以上,那么无解,反之答案就是出度为0的那个强连通分量的大小
点此查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<bits/extc++.h> // using namespace __gnu_pbds; // using namespace __gnu_cxx; using namespace std; #define infile(x) freopen(x,"r",stdin) #define outfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stdout) #define errfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stderr) #define rep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i <= t; i += p) #define drep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i >= t; i -= p) #ifdef LOCAL FILE *InFile = infile("in.in"),*OutFile = outfile("out.out"); // FILE *ErrFile=errfile("err.err"); #else FILE *Infile = stdin,*OutFile = stdout; //FILE *ErrFile = stderr; #endif using ll=long long;using ull=unsigned long long; using db = double;using ldb = long double; const int N = 1e4 + 10; vector<int> edge[N]; #define eb emplace_back inline void add(int u,int v){edge[u].eb(v);} int n,m,dfn[N],low[N],sta[N],top,tot,num,bel[N],out[N],len[N]; bitset<N> insta; void Tarjan(int x){ dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tot; sta[++top] = x;insta[x] = true; for(int y:edge[x]){ if(!dfn[y]){ Tarjan(y); low[x] = min(low[x],low[y]); } else if(insta[y]) low[x] = min(low[x],dfn[y]); } if(dfn[x] == low[x]){ num++;int y; do{ y = sta[top--]; bel[y] = num; insta[y] = false; len[num]++; }while(y != x); } } inline void solve(){ cin>>n>>m; rep(i,1,m,1){ int u,v;cin>>u>>v; add(u,v); } rep(i,1,n,1) if(!dfn[i]) Tarjan(i); int ans = 0,ok = 0; rep(x,1,n,1) for(int y:edge[x]) if(bel[x] != bel[y]) out[bel[x]]++; rep(i,1,num,1) if(!out[i])ans = len[i],ok++; if(ok > 1) cout<<0; else cout<<ans; } signed main(){ cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); cout.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); solve(); }
先缩点,第一问的答案就是缩完点后入度为0的点的个数,第二问的答案就是缩完点后
点此查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<bits/extc++.h> // using namespace __gnu_pbds; // using namespace __gnu_cxx; using namespace std; #define infile(x) freopen(x,"r",stdin) #define outfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stdout) #define errfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stderr) #define rep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i <= t; i += p) #define drep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i >= t; i -= p) #ifdef LOCAL FILE *InFile = infile("in.in"),*OutFile = outfile("out.out"); // FILE *ErrFile=errfile("err.err"); #else FILE *Infile = stdin,*OutFile = stdout; //FILE *ErrFile = stderr; #endif using ll=long long;using ull=unsigned long long; using db = double;using ldb = long double; const int N = 1e4 + 10; #define eb emplace_back vector<int> edge[N]; inline void add(int u,int v){edge[u].eb(v);} int n,dfn[N],low[N],tim,tot,sta[N],top,bel[N],in[N],out[N]; bitset<N> insta; void Tarjan(int x){ dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tim; sta[++top] = x;insta[x] = true; for(int y:edge[x]){ if(!dfn[y]){ Tarjan(y); low[x] = min(low[x],low[y]); } else if(insta[y]) low[x] = min(low[x],dfn[y]); } if(dfn[x] == low[x]){ tot++;int y; do{ y = sta[top--]; bel[y] = tot; insta[y] = false; }while(y != x); } } inline void solve(){ cin>>n; rep(i,1,n,1){int x; while(cin>>x&&x) add(i,x);} rep(i,1,n,1) if(!dfn[i]) Tarjan(i); rep(x,1,n,1) for(int y:edge[x]) if(bel[x] != bel[y]) in[bel[y]]++,out[bel[x]]++; if(tot == 1) return cout<<"1\n0",void(); int ans1 = 0,ans2 = 0; rep(i,1,tot,1) if(!in[i]) ans1++; rep(i,1,tot,1) if(!out[i]) ans2++; ans2 = max(ans1,ans2); cout<<ans1<<'\n'<<ans2<<'\n'; } signed main(){ cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); cout.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); solve(); }
缩完点后跑最长路就没了
点此查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<bits/extc++.h> // using namespace __gnu_pbds; // using namespace __gnu_cxx; using namespace std; #define infile(x) freopen(x,"r",stdin) #define outfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stdout) #define errfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stderr) #define rep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i <= t; i += p) #define drep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i >= t; i -= p) #ifdef LOCAL FILE *InFile = infile("in.in"),*OutFile = outfile("out.out"); // FILE *ErrFile=errfile("err.err"); #else FILE *Infile = stdin,*OutFile = stdout; //FILE *ErrFile = stderr; #endif using ll=long long;using ull=unsigned long long; using db = double;using ldb = long double; const int N = 5e5 + 10; struct node{int to,w;node(int To,int W):to(To),w(W){}};vector<node> e2[N]; #define eb emplace_back vector<int> e1[N]; int n,m,s,p,ed[N],a[N],dfn[N],low[N],tim,sta[N],top,g[N],num[N],tot; int dist[N]; bitset<N> insta,vis; void Tarjan(int x){ dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tim; sta[++top] = x;insta[x] = true; for(int y:e1[x]){ if(!dfn[y]) Tarjan(y),low[x] = min(low[x],low[y]); else if(insta[y]) low[x] = min(low[x],dfn[y]); } if(dfn[x] == low[x]){ tot++;int y; do{ y = sta[top--]; insta[y] = false; g[y] = tot; num[tot] += a[y]; }while(y != x); } } inline void spfa(int s){ queue<int> q;q.push(s);vis[s] = true; while(q.size()){ int x = q.front();q.pop();vis[x] = false; for(node i:e2[x]){ int y = i.to,w = i.w; if(dist[y] < dist[x] + w){ dist[y] = dist[x] + w; if(!vis[y]) q.push(y),vis[y] = true; } } } } inline void solve(){ cin>>n>>m; rep(i,1,m,1){int u,v;cin>>u>>v;e1[u].eb(v);} rep(i,1,n,1) cin>>a[i]; rep(i,1,n,1) if(!dfn[i]) Tarjan(i); rep(x,1,n,1) for(int y:e1[x]) if(g[x] != g[y]) e2[g[x]].eb(node(g[y],num[g[y]])); cin>>s>>p;rep(i,1,p,1) cin>>ed[i]; spfa(g[s]); int ans = 0; rep(i,1,p,1) ans = max(ans,dist[g[ed[i]]]); cout<<ans+num[g[s]]<<'\n'; } signed main(){ cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); cout.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); solve(); }
双连通分量
这里的连通图均指无向连通图
前置知识
割点
对于一个连通图
容易发现,孤立点不是割点,孤立边的两个端点也不是割点。
点双连通 : 没有割点的连通图。
点双连通分量(V-BCC) : 一张图的极大点双连通子图,简称点双。
桥
类比割点的定义即可。
对于一个连通图
容易发现,孤立边是割边。
边双连通 : 没有桥的连通图。
边双连通分量(E-BCC) : 一张图的极大边双连通子图,简称边双。
割点和桥
既然已经知道了割点和桥是什么,那么如何求呢?
Tarjan求割点
和强连通分量一样,还是维护两个数组
开始进行
但是这对于搜索的起点并不成立,所以特殊考虑起点。考虑在搜索树上,如果起点只有一个儿子,那么说明删去这个点并不影响其搜索树子树内的连通性,所以其不是割点。而如果有两个及以上的儿子,那么说明删去以后这个儿子便不连通,所以此时起点也是割点。
就比如这张图,容易发现2为图中唯一的一个割点。
如果以1为起点搜索,画出来的搜索树就是这样的
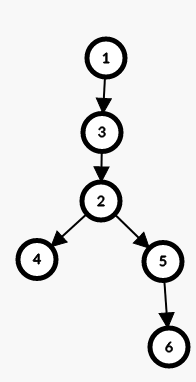
而以2为起点搜索,画出来的搜索树是这样的
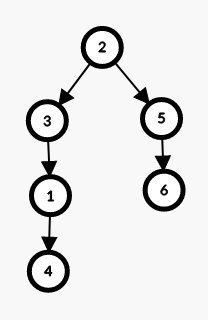
看,很符合上面说的。
点此查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<bits/extc++.h> // using namespace __gnu_pbds; // using namespace __gnu_cxx; using namespace std; #define infile(x) freopen(x,"r",stdin) #define outfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stdout) #define errfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stderr) #define rep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i <= t; i += p) #define drep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i >= t; i -= p) #ifdef LOCAL FILE *InFile = infile("in.in"),*OutFile = outfile("out.out"); // FILE *ErrFile=errfile("err.err"); #else FILE *Infile = stdin,*OutFile = stdout; //FILE *ErrFile = stderr; #endif using ll=long long;using ull=unsigned long long; using db = double;using ldb = long double; const int N = 2e4 + 10; int n,m,rt,dfn[N],low[N],tim; vector<int> edge[N]; bitset<N> vis,cut; #define eb emplace_back void Tarjan(int x,int f){ dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tim; vis[x] = true; int son = 0; for(int y:edge[x]){ if(y == f) continue; if(!vis[y]){ Tarjan(y,x);son++; low[x] = min(low[x],low[y]); if(x == rt && son > 1) cut[x] = true; if(low[y] >= dfn[x] && x != rt) cut[x] = true; } else low[x] = min(low[x],dfn[y]); } } inline void solve(){ cin>>n>>m; rep(i,1,m,1){int u,v;cin>>u>>v;edge[u].eb(v);edge[v].eb(u);} rep(i,1,n,1) if(!dfn[i]) rt = i,Tarjan(i,0); cout<<cut.count()<<'\n'; rep(i,1,n,1) if(cut[i]) cout<<i<<' '; } signed main(){ cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); cout.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); solve(); }
Tarjan求割边
和求割点差不多的,就是将
点此查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<bits/extc++.h> // using namespace __gnu_pbds; // using namespace __gnu_cxx; using namespace std; #define infile(x) freopen(x,"r",stdin) #define outfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stdout) #define errfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stderr) #define rep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i <= t; i += p) #define drep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i >= t; i -= p) #ifdef LOCAL FILE *InFile = infile("in.in"),*OutFile = outfile("out.out"); // FILE *ErrFile=errfile("err.err"); #else FILE *Infile = stdin,*OutFile = stdout; //FILE *ErrFile = stderr; #endif using ll=long long;using ull=unsigned long long; using db = double;using ldb = long double; const int N = 1e5 + 10; int n,m,dfn[N],low[N],tim,cnt; vector<int> edge[N]; bitset<N> vis; #define eb emplace_back void Tarjan(int x,int f){ dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tim; vis[x] = true; int son = 0; for(int y:edge[x]){ if(y == f) continue; if(!vis[y]){ Tarjan(y,x);son++; low[x] = min(low[x],low[y]); if(low[y] > dfn[x]) cnt++; } else low[x] = min(low[x],dfn[y]); } } inline void solve(){ cin>>n>>m; rep(i,1,m,1){int u,v;cin>>u>>v;edge[u].eb(v);edge[v].eb(u);} rep(i,1,n,1) if(!dfn[i]) Tarjan(i,0); cout<<cnt; } signed main(){ cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); cout.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); solve(); }
双连通分量
边双连通分量
综合了一下,还是选择了先找出桥后dfs找边双的做法,较为好理解而且不是很容易写挂。
直接写就可以了。建议还是链式前向星建图,比较好判割边。
点此查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<bits/extc++.h> // using namespace __gnu_pbds; // using namespace __gnu_cxx; using namespace std; #define infile(x) freopen(x,"r",stdin) #define outfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stdout) #define errfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stderr) #define rep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i <= t; i += p) #define drep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i >= t; i -= p) #ifdef LOCAL FILE *InFile = infile("in.in"),*OutFile = outfile("out.out"); // FILE *ErrFile=errfile("err.err"); #else FILE *Infile = stdin,*OutFile = stdout; //FILE *ErrFile = stderr; #endif using ll=long long;using ull=unsigned long long; using db = double;using ldb = long double; const int N = 5e5 + 10,M = 4e6 + 10; struct EDGE{int to,next;}edge[M]; int head[N],cnt = 1; inline void add(int u,int v){edge[++cnt] = {v,head[u]};head[u] = cnt;} vector<int> vdcc[N];int tot; bitset<M> bri; bitset<N> vis; int n,m,dfn[N],low[N],tim; void Tarjan(int x,int f){ dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tim; vis[x] = true; for(int i = head[x]; i;i = edge[i].next){ int y = edge[i].to; if(y == f) continue; if(!vis[y]){ Tarjan(y,x); low[x] = min(low[x],low[y]); if(low[y] > dfn[x]) bri[i] = bri[i^1] = true; } else low[x] = min(low[x],dfn[y]); } } void dfs(int x,int f){ vis[x] = true; vdcc[tot].emplace_back(x); for(int i = head[x]; i;i = edge[i].next){ int y = edge[i].to; if(bri[i] || y == f || vis[y]) continue; dfs(y,x); } } inline void solve(){ cin>>n>>m; rep(i,1,m,1){int u,v;cin>>u>>v;add(u,v);add(v,u);} rep(i,1,n,1) if(!dfn[i]) Tarjan(i,0); vis.reset(); rep(i,1,n,1) if(!vis[i]) tot++,dfs(i,0); cout<<tot<<'\n'; rep(i,1,tot,1){cout<<vdcc[i].size()<<' ';for(int j:vdcc[i]) cout<<j<<' ';cout<<'\n';} } signed main(){ cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); cout.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); solve(); }
点双连通分量
对于一个点双,它在
分类讨论:
- 这个点为割点,那么它就是点双的根
- 这个点为树根
- 有两个及以上子树,为一个割点
- 只有一个子树,它是一个点双的根
- 没有子树,视为一个点双。
点此查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<bits/extc++.h> // using namespace __gnu_pbds; // using namespace __gnu_cxx; using namespace std; #define infile(x) freopen(x,"r",stdin) #define outfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stdout) #define errfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stderr) #define rep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i <= t; i += p) #define drep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i >= t; i -= p) #ifdef LOCAL FILE *InFile = infile("in.in"),*OutFile = outfile("out.out"); // FILE *ErrFile=errfile("err.err"); #else FILE *Infile = stdin,*OutFile = stdout; //FILE *ErrFile = stderr; #endif using ll=long long;using ull=unsigned long long; using db = double;using ldb = long double; const int N = 5e5 + 10; vector<int> edge[N],vdcc[N]; #define eb emplace_back int n,m,rt,dfn[N],low[N],tim,sta[N],top,tot,d[N]; bitset<N> cut; void Tarjan(int x,int f){ dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tim; sta[++top] = x;int son = 0; for(int y:edge[x]){ if(!dfn[y]){ Tarjan(y,x);low[x] = min(low[x],low[y]); if(dfn[x] <= low[y]){ son++; if(x != rt || son > 1) cut[x] = true; tot++;int z; do{ z = sta[top--]; vdcc[tot].eb(z); }while(z != y); vdcc[tot].eb(x); } } else low[x] = min(low[x],dfn[y]); } if(x == rt && !son) return vdcc[++tot].eb(x),void(); } inline void solve(){ cin>>n>>m; rep(i,1,m,1){int u,v;cin>>u>>v;edge[u].eb(v);edge[v].eb(u);} rep(i,1,n,1) if(!dfn[i]) rt = i,Tarjan(i,0); cout<<tot<<'\n'; rep(i,1,tot,1){ cout<<vdcc[i].size()<<' '; for(int j:vdcc[i]) cout<<j<<' '; cout<<'\n'; } } signed main(){ cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); cout.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); solve(); }
2-SAT
定义
就是给出
解决方法
如果
然后跑一边缩点,判断是否有
输出方案时可以通过变量在图中的拓扑序确定该变量的取值。如果变量
分为四种情况讨论建图
然后对
反之,输出解,当
点此查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<bits/extc++.h> // using namespace __gnu_pbds; // using namespace __gnu_cxx; using namespace std; #define infile(x) freopen(x,"r",stdin) #define outfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stdout) #define errfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stderr) #define rep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i <= t; i += p) #define drep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i >= t; i -= p) #ifdef LOCAL FILE *InFile = infile("in.in"),*OutFile = outfile("out.out"); // FILE *ErrFile=errfile("err.err"); #else FILE *Infile = stdin,*OutFile = stdout; //FILE *ErrFile = stderr; #endif using ll=long long;using ull=unsigned long long; using db = double;using ldb = long double; const int N = 2e6 + 10; vector<int> edge[N]; #define eb emplace_back inline void add(int u,int v){edge[u].eb(v);} int n,m,dfn[N],low[N],tim,g[N],sta[N],top,num; bitset<N> insta; void Tarjan(int x){ dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tim; sta[++top] = x;insta[x] = true; for(int y:edge[x]){ if(!dfn[y]) {Tarjan(y);low[x] = min(low[x],low[y]);} else if(insta[y]) low[x] = min(low[x],dfn[y]); } if(dfn[x] == low[x]){ num++;int y; do{ y = sta[top--]; insta[y] = false; g[y] = num; }while(y != x); } } inline void solve(){ cin>>n>>m; rep(i,1,m,1){ int x,a,y,b; cin>>x>>a>>y>>b; if(a&&b) add(x+n,y),add(y+n,x); if(a&&!b) add(x+n,y+n),add(y,x); if(!a&&b) add(x,y),add(y+n,x+n); if(!a&&!b) add(x,y+n),add(y,x+n); } rep(i,1,n<<1,1) if(!dfn[i]) Tarjan(i); rep(i,1,n,1) if(g[i] == g[i+n]) cout<<"IMPOSSIBLE\n",exit(0); cout<<"POSSIBLE\n"; rep(i,1,n,1) cout<<(bool)(g[i] < g[i+n])<<' '; } signed main(){ cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); cout.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); solve(); }
练习 :
还是那么套路,直接套上就好啦。
点此查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<bits/extc++.h> // using namespace __gnu_pbds; // using namespace __gnu_cxx; using namespace std; #define infile(x) freopen(x,"r",stdin) #define outfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stdout) #define errfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stderr) #define rep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i <= t; i += p) #define drep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i >= t; i -= p) #ifdef LOCAL FILE *InFile = infile("in.in"),*OutFile = outfile("out.out"); // FILE *ErrFile=errfile("err.err"); #else FILE *Infile = stdin,*OutFile = stdout; //FILE *ErrFile = stderr; #endif using ll=long long;using ull=unsigned long long; using db = double;using ldb = long double; const int N = 210; vector<int> edge[N];//1~n 为满 #define eb emplace_back int n,m,dfn[N],low[N],sta[N],top,tim,tot,g[N]; bitset<N> insta; void Tarjan(int x){ dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tim; sta[++top] = x;insta[x] = true; for(int y:edge[x]){ if(!dfn[y]) Tarjan(y),low[x] = min(low[x],low[y]); else if(insta[y]) low[x] = min(low[x],dfn[y]); } if(dfn[x] == low[x]){ tot++;int y; do{ y = sta[top--]; insta[y] = false; g[y] = tot; }while(y != x); } } inline void solve(){ cin>>n>>m; tim = top = tot = 0; rep(i,1,n<<1,1) dfn[i] = low[i] = insta[i] = g[i] = false; rep(i,1,n<<1,1) vector<int> ().swap(edge[i]); rep(i,1,m,1){ char x,y;int id1,id2; cin>>x>>id1>>y>>id2; if(x == 'm'){ if(y == 'm') edge[id1+n].eb(id2),edge[id2+n].eb(id1); else edge[id1+n].eb(id2+n),edge[id2].eb(id1); } else{ if(y == 'm') edge[id1].eb(id2),edge[id2+n].eb(id1+n); else edge[id1].eb(id2+n),edge[id2].eb(id1+n); } } rep(i,1,n<<1,1) if(!dfn[i]) Tarjan(i); bool flag = false; rep(i,1,n,1) if(g[i] == g[i+n]){flag = true;break;} cout<<(flag?"BAD\n":"GOOD\n"); } signed main(){ cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); cout.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); int T;cin>>T;while(T--)solve(); }
还是建反边跑Tarjan
点此查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<bits/extc++.h> // using namespace __gnu_pbds; // using namespace __gnu_cxx; using namespace std; #define infile(x) freopen(x,"r",stdin) #define outfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stdout) #define errfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stderr) #define rep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i <= t; i += p) #define drep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i >= t; i -= p) #ifdef LOCAL FILE *InFile = infile("in.in"),*OutFile = outfile("out.out"); // FILE *ErrFile=errfile("err.err"); #else FILE *Infile = stdin,*OutFile = stdout; //FILE *ErrFile = stderr; #endif using ll=long long;using ull=unsigned long long; using db = double;using ldb = long double; const int N = 20010; #define eb emplace_back vector<int> edge[N]; inline void add(int u,int v){edge[u].eb(v);} int n,m,dfn[N],low[N],tim,num,g[N],sta[N],top; bitset<N> insta; void Tarjan(int x){ dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tim; sta[++top] = x;insta[x] = true; for(int y:edge[x]){ if(!dfn[y]) Tarjan(y),low[x] = min(low[x],low[y]); else if(insta[y]) low[x] = min(low[x],dfn[y]); } if(dfn[x] == low[x]){ num++;int y; do{ y = sta[top--]; insta[y] = false; g[y] = num; }while(y != x); } } inline void solve(){ cin>>n>>m; auto opp = [](int x){return (x&1)?x+1:x-1;}; rep(i,1,m,1){ int a,b;cin>>a>>b; add(a,opp(b));add(b,opp(a)); } rep(i,1,n<<1,1) if(!dfn[i]) Tarjan(i); rep(i,1,n<<1,2) if(g[i] == g[i+1]) cout<<"NIE\n",exit(0); rep(i,1,n<<1,2) cout<<(g[i]<g[i+1]?i:i+1)<<'\n'; } signed main(){ cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); cout.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); solve(); }
好题。
考虑到选了第
考虑到选人最好的方法就是选择一个没有出度的强连通分量,这样就可以保证直接选人即可,不用再考虑其它的限制。
深入理解一下Tarjan算法,发现找到的第一个强连通分量便没有出度。因为如果有出度的话,那么Tarjan算法就会递归进入到下一个强连通分量中,直到一个没有出度的强连通分量为止。
选的人的个数就是第一个强连通分量的个数,人就是强连通分量中的人,剩下的猫都是选手。
特判只有一个强连通分量时,无解。
点此查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<bits/extc++.h> // using namespace __gnu_pbds; // using namespace __gnu_cxx; using namespace std; #define infile(x) freopen(x,"r",stdin) #define outfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stdout) #define errfile(x) freopen(x,"w",stderr) #define rep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i <= t; i += p) #define drep(i,s,t,p) for(int i = s;i >= t; i -= p) #ifdef LOCAL FILE *InFile = infile("in.in"),*OutFile = outfile("out.out"); // FILE *ErrFile=errfile("err.err"); #else FILE *Infile = stdin,*OutFile = stdout; //FILE *ErrFile = stderr; #endif using ll=long long;using ull=unsigned long long; using db = double;using ldb = long double; const int N = 1e6 + 10; #define eb emplace_back #define All(x) x.begin(),x.end() vector<int> edge[N]; inline void add(int u,int v){edge[u].eb(v);} int n,m,dfn[N],low[N],tim,num,g[N],sta[N],top,len[N]; bitset<N> insta; void Tarjan(int x){ dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tim; sta[++top] = x;insta[x] = true; for(int y:edge[x]){ if(!dfn[y]) Tarjan(y),low[x] = min(low[x],low[y]); else if(insta[y]) low[x] = min(low[x],dfn[y]); } if(dfn[x] == low[x]){ num++;int y; do{ y = sta[top--]; insta[y] = false; g[y] = num;len[num]++; }while(y != x); } } inline void solve(){ cin>>n>>m; rep(i,1,num,1) len[i] = 0; tim = top = num = 0; rep(i,1,n,1) vector<int>().swap(edge[i]),dfn[i] = low[i] = g[i] = insta[i] = false; rep(i,1,m,1){ int a,b;cin>>a>>b; if(a == b) continue; add(a,b); } rep(i,1,n,1) if(!dfn[i]) Tarjan(i); if(num == 1) return cout<<"No\n",void(); cout<<"Yes\n"<<len[1]<<' '<<n-len[1]<<'\n'; rep(i,1,n,1) if(g[i] == 1) cout<<i<<' '; cout<<'\n'; rep(i,1,n,1) if(g[i] != 1) cout<<i<<' '; cout<<'\n'; } signed main(){ cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); cout.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false); int T;cin>>T;while(T--) solve(); }
好像还有一个圆方树完了,到时候再开一个写
本文来自博客园,作者:CuFeO4,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/hzoi-Cu/p/18455109






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】