React入门
自从有了Node.js后,JAVASCRIPT已经变成了一个与JavaEE不相上下的企业级语言了。React 是一个用于构建用户界面的 JAVASCRIPT 库,通常也运行在Node.js的平台之下。React主要用于构建UI,很多人认为 React 是 MVC 中的 V(视图)。React 起源于 Facebook 的内部项目,用来架设 Instagram 的网站,并于 2013 年 5 月开源。React 拥有较高的性能,代码逻辑非常简单,越来越多的人已开始关注和使用它。结合个人使用JavaEE多年的体会,React就象当年sun主推的JSF框架的作用有类似之处,是一个组件型的V端 框架。作为入门,必须先要去React官网看一下 ,官网地址:https://reactjs.org , 源码地址:https://github.com/facebook/react/ ,编译好的React版本的下载地址:https://github.com/facebook/react/releases
目前个人的理解是React可以基于Node.js进行使用(这是主流的应用方式)。也可以基于浏览器的使用,这种形式则跟传统js项目的形式差不多。下面将分别演示这两种项目的形式,同时也通过代码熟悉一下React的一些概念。
一、先来体验传统的方式,即仅基于浏览器使用React的方式:( 在官网上正好有这样的例子 https://reactjs.org/docs/add-react-to-a-website.html)
代码只有两个文件,一个index.html和like_button.js ,在这个项目上我们仅用了 react.development.js 和 react-dom.development.js
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Add React in One Minute</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Add React in One Minute</h2>
<p>This page demonstrates using React with no build tooling.</p>
<p>React is loaded as a script tag.</p>
<!-- 将放置React组件在这个div中 -->
<div id="like_button_container"></div>
<!-- 加载React. -->
<!-- 注意: 在生产环境部署时, 需要替换 "development.js" 为"production.min.js". -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@16/umd/react.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@16/umd/react-dom.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<!-- 加载我们的 React组件. -->
<script src="like_button.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
like_button.js
'use strict'; const e = React.createElement; //创建React Element的一种简写形式 class LikeButton extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { liked: false }; } render() { if (this.state.liked) { return 'You liked this.'; } return e( 'button', { onClick: () => this.setState({ liked: true }) }, 'Like' ); } } const domContainer = document.querySelector('#like_button_container'); ReactDOM.render(e(LikeButton), domContainer);
通过浏览器访问index.html页面即可看到效果。
二. 结合node.js进行使用
执行命令npx create-react-app my-app创建一个基于Node.js的React项目,其中my-app是项目名,执行后会在项目的目录下创建以my-app命名的目录,进入my-app目录后,项目结构如下:

启动项目,默认会启动服务监听3000端口:
cd my-app
npm start
访问 http://127.0.0.1:3000,即会触发src/index.js的代码,只不过此时是由Node.js来执行该代码,在浏览器上展示界面如下:

项目运行说明:
npm start命令实示是启动了项目下的package.json文件中定义的脚本,如图:
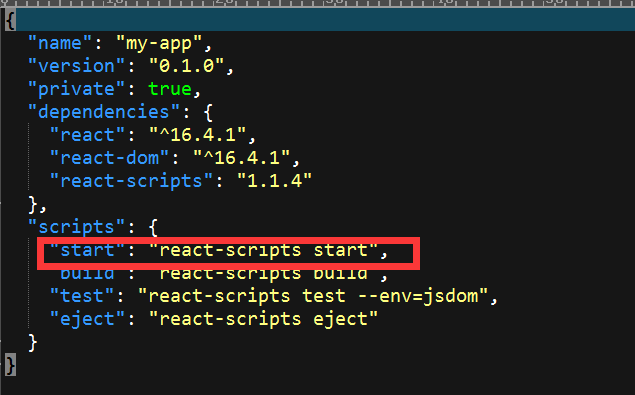
即react-scripts模块下的start脚本,在项目下的node_modules/scripts/目录下的start.js 代码有引用到路径配置的一段代码:
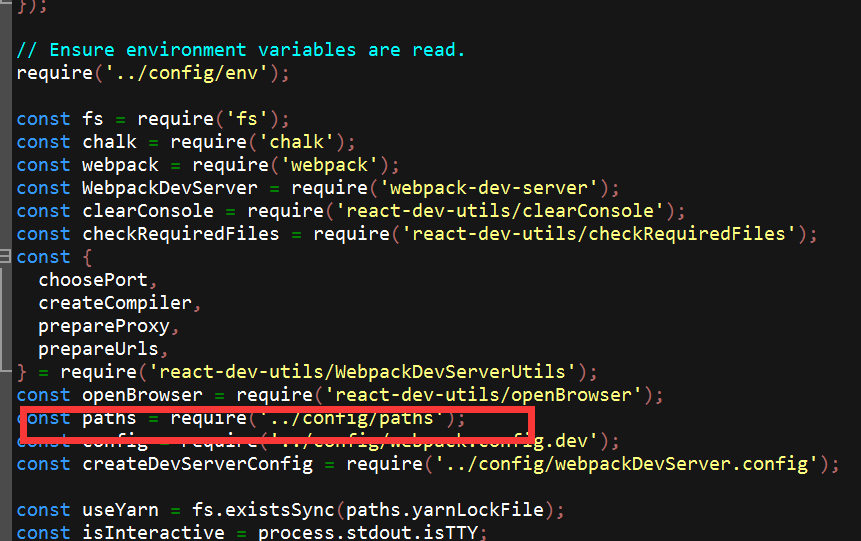
然后打开config/paths.js文件,可以看到项目内的相关文件的设置:
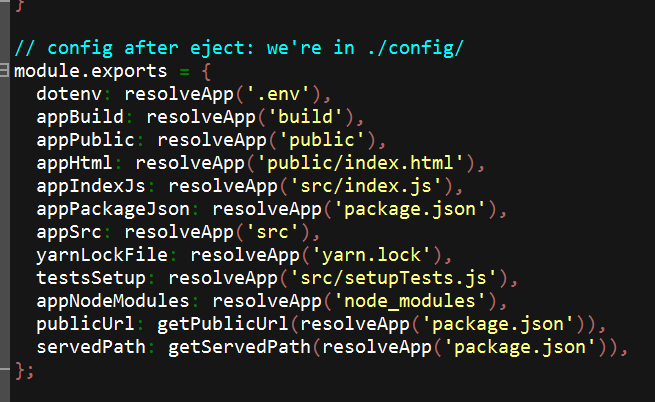
这样也就大致能理解项目下生成的这些文件和目录的作用了。
再打开src/index.js文件,如下:
import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'; import './index.css'; import App from './App'; import registerServiceWorker from './registerServiceWorker'; ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root')); registerServiceWorker();
再打开src/registerServiceWorker.js文件,如下:
// In production, we register a service worker to serve assets from local cache. // This lets the app load faster on subsequent visits in production, and gives // it offline capabilities. However, it also means that developers (and users) // will only see deployed updates on the "N+1" visit to a page, since previously // cached resources are updated in the background. // To learn more about the benefits of this model, read https://goo.gl/KwvDNy. // This link also includes instructions on opting out of this behavior. const isLocalhost = Boolean( window.location.hostname === 'localhost' || // [::1] is the IPv6 localhost address. window.location.hostname === '[::1]' || // 127.0.0.1/8 is considered localhost for IPv4. window.location.hostname.match( /^127(?:\.(?:25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)){3}$/ ) ); export default function register() { if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' && 'serviceWorker' in navigator) { // The URL constructor is available in all browsers that support SW. const publicUrl = new URL(process.env.PUBLIC_URL, window.location); if (publicUrl.origin !== window.location.origin) { // Our service worker won't work if PUBLIC_URL is on a different origin // from what our page is served on. This might happen if a CDN is used to // serve assets; see https://github.com/facebookincubator/create-react-app/issues/2374 return; } window.addEventListener('load', () => { const swUrl = `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/service-worker.js`; if (isLocalhost) { // This is running on localhost. Lets check if a service worker still exists or not. checkValidServiceWorker(swUrl); // Add some additional logging to localhost, pointing developers to the // service worker/PWA documentation. navigator.serviceWorker.ready.then(() => { console.log( 'This web app is being served cache-first by a service ' + 'worker. To learn more, visit https://goo.gl/SC7cgQ' ); }); } else { // Is not local host. Just register service worker registerValidSW(swUrl); } }); } } function registerValidSW(swUrl) { navigator.serviceWorker .register(swUrl) .then(registration => { registration.onupdatefound = () => { const installingWorker = registration.installing; installingWorker.onstatechange = () => { if (installingWorker.state === 'installed') { if (navigator.serviceWorker.controller) { // At this point, the old content will have been purged and // the fresh content will have been added to the cache. // It's the perfect time to display a "New content is // available; please refresh." message in your web app. console.log('New content is available; please refresh.'); } else { // At this point, everything has been precached. // It's the perfect time to display a // "Content is cached for offline use." message. console.log('Content is cached for offline use.'); } } }; }; }) .catch(error => { console.error('Error during service worker registration:', error); }); } function checkValidServiceWorker(swUrl) { // Check if the service worker can be found. If it can't reload the page. fetch(swUrl) .then(response => { // Ensure service worker exists, and that we really are getting a JS file. if ( response.status === 404 || response.headers.get('content-type').indexOf('javascript') === -1 ) { // No service worker found. Probably a different app. Reload the page. navigator.serviceWorker.ready.then(registration => { registration.unregister().then(() => { window.location.reload(); }); }); } else { // Service worker found. Proceed as normal. registerValidSW(swUrl); } }) .catch(() => { console.log( 'No internet connection found. App is running in offline mode.' ); }); } export function unregister() { if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) { navigator.serviceWorker.ready.then(registration => { registration.unregister(); }); } }
可以看到start.js启动了http服务在监听3000端口,node.js以package.json文件中的入口index.js上面的React代码来渲染组件,通过public/index.html作为模板,最终返回给浏览器进行展示。



