Springboot+shiro配置笔记+错误小结
软件152 尹以操
springboot不像springmvc,它没有xml配置文件,那该如何配置shiro呢,其实也不难,用java代码+注解来解决这个问题。仅以此篇记录我对shiro的学习,如有对过客造成不便,实在抱歉!
一、加入jar包
既然要用到shiro,当然要加入它的jar包咯,在pom.xml中jar包依赖中加入:
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId> <version>1.2.2</version> </dependency>
二、写实体类
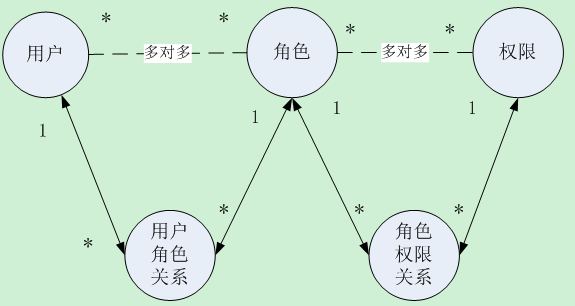
这需要三个实体类,hibernate自动生成5个表
User实体(用户):
package com.cy.coo.bean; import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.FetchType; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.JoinColumn; import javax.persistence.JoinTable; import javax.persistence.ManyToMany; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonBackReference; @Entity public class User { @Id @GeneratedValue private Integer user_id;//用户序号 @Column(unique=true) private String name;//账户 private String password;//密码 private String salt;//盐 private Integer state;//用户状态 private String createtime;//创建时间 @ManyToMany(fetch=FetchType.EAGER)//立即从数据库中进行加载数据; @JoinTable(name="User_Role",joinColumns={@JoinColumn(name="user_id")}, inverseJoinColumns={@JoinColumn(name="role_id")}) private List<Role> roleList; @JsonBackReference public List<Role> getRoleList(){ return roleList; } public void setRoleList(List<Role> roleList){ this.roleList=roleList; } 注:其它getter和setter省略 }
关于为什么要在getRolelist这个方法上加上@JsonBackReference注解,可以查看这篇文章http://blog.csdn.net/maxu12345/article/details/45538157
Role实体(角色):
package com.cy.coo.bean; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.FetchType; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.JoinColumn; import javax.persistence.JoinTable; import javax.persistence.ManyToMany; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonBackReference; @Entity public class Role implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @Id @GeneratedValue private Integer role_id;//角色序号 private String role_name;//角色名称 private String role_description;//角色描述 @ManyToMany @JoinTable(name = "User_Role", joinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "role_id") }, inverseJoinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "user_id") }) private List<User> userList=new ArrayList<>(); @ManyToMany(fetch=FetchType.EAGER) @JoinTable(name="Role_Function",joinColumns={@JoinColumn(name="role_id")},inverseJoinColumns={ @JoinColumn(name="function_id")}) private List<Function> functionList=new ArrayList<>(); @JsonBackReference public List<Function> getFunctionList(){ return functionList; } public void setFunctionList(List<Function> functionList){ this.functionList=functionList; } @JsonBackReference public List<User> getUserList() { return userList; } public void setUserList(List<User> userList) { this.userList = userList; } public Integer getRole_id() { return role_id; } public void setRole_id(Integer role_id) { this.role_id = role_id; } public String getRole_name() { return role_name; } public void setRole_name(String role_name) { this.role_name = role_name; } public String getRole_description() { return role_description; } public void setRole_description(String role_description) { this.role_description = role_description; } }
Function实体(权限):
package com.cy.coo.bean; import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.JoinColumn; import javax.persistence.JoinTable; import javax.persistence.ManyToMany; @Entity public class Function { @Id @GeneratedValue private Integer function_id;//功能序号 private String permission;//权限字符串 @ManyToMany @JoinTable(name = "Role_Function", joinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "function_id") }, inverseJoinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "role_id") }) private List<Role> roleList; public List<Role> getRoleList() { return roleList; } public void setRoleList(List<Role> roleList) { this.roleList = roleList; } public Integer getFunction_id() { return function_id; } public void setFunction_id(Integer function_id) { this.function_id = function_id; } public String getPermission() { return permission; } public void setPermission(String permission) { this.permission = permission; } }
这几个实体类的具体关系如下图,也完美的解释了为什么会生成5张表:
三、写一个与前端交互的controller方法,service层的具体逻辑的方法
@PostMapping(value = "/logon") public Object logon(@RequestBody Login user) { return userService.login(user); }
这个方法就是将前端传来的username和password封装到Login类中,Login类也只有这两个属性,然后调用Service层的login方法来处理。下面是service的login方法:
/** * 用户登录 create by yyc 2017年5月12日下午4:31:26 */ @Override public Object login(Login user) { String username = user.getUsername().trim(); String password = user.getPassword().trim(); // 检查空值 if (!CheckObjectField.CheckField(user)) { throw new ResultException(CheckObjectField.FieldName + "为空!"); } // 检查用户状态 Integer userState = userRepository.findUserState(username); if (new Integer("1").equals(userState)) { throw new ResultException("该用户已锁定"); } // 1、获取Subject实例对象 Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); // 2、判断当前用户是否登录 if (currentUser.isAuthenticated() == false) { // 3、将用户名和密码封装到UsernamePasswordToken UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password); // 4、认证 try { currentUser.login(token);// 传到MyAuthorizingRealm类中的方法进行认证 Session session = currentUser.getSession(); session.setAttribute("username", username); } catch (AuthenticationException e) { throw new ResultException("密码或用户名错误"); } } // 根据用户名查询角色信息 List<String> RoleNames = roleService.findRoleName(username); return new LoginReturn(username, RoleNames); }
service中主要是将用户名和密码封装到shiro的UsernamePasswordToken中,然后将token对象放到SecurityUtils.getSubject()的login方法中,以便shiro认证登录使用。认证失败就会抛出AuthenticationException这个异常,就对异常进行相应的操作,这里的处理是抛出一个自定义异常ResultException。
四、写我认为的shiro的核心类
package com.cy.coo.shiro; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken; import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken; import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm; import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection; import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import com.cy.coo.bean.Function; import com.cy.coo.bean.Role; import com.cy.coo.bean.User; import com.cy.coo.service.UserService; /** * * * @author E-mail:34782655@qq.com * @version 创建时间:2017年5月8日 上午10:50:50 * 类说明: * -- */ public class MyAuthorizingRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { private final static Logger logger=LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyAuthorizingRealm.class); @Autowired private UserService userService; //shiro的权限配置方法 @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) { logger.info("权限配置-->doGetAuthorizationInfo"); SimpleAuthorizationInfo authorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(); logger.info("----------------------------->"+principals.getPrimaryPrincipal()); User user=(User) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal(); for(Role role:user.getRoleList()){ authorizationInfo.addRole(role.getRole_name()); for(Function function:role.getFunctionList()){ authorizationInfo.addStringPermission(function.getPermission()); } } logger.info("用户"+user.getName()+"具有的角色:"+authorizationInfo.getRoles()); logger.info("用户"+user.getName()+"具有的权限:"+authorizationInfo.getStringPermissions()); return authorizationInfo; } //shiro的身份验证方法 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { logger.info("正在验证身份..."); SimpleAuthenticationInfo info=null; //将token转换成UsernamePasswordToken UsernamePasswordToken upToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) token; //从转换后的token中获取用户名 String username= upToken.getUsername(); logger.info("----->"+username); //查询数据库,得到用户 User user=userService.findByName(username); if(user==null){ return null; } //得到加密密码的盐值 ByteSource salt = ByteSource.Util.bytes(user.getSalt()); // logger.info("加密密码的盐:"+salt); // //得到盐值加密后的密码:只用于方便数据库测试,后期不会用到。 // Object md = new SimpleHash("MD5",upToken.getPassword(),salt,1024); // logger.info("盐值加密后的密码:"+md); info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo( user, //用户名 user.getPassword(), //密码 salt, //加密的盐值 getName() //realm name ); return info; } }
这个类继承shiro的AuthorizingRealm ,主要有两个方法,一个是权限配置,一个是身份认证,权限配置:当我们要用到权限时shiro会回调doGetAuthorizationInfo这个方法,对当前的用户分配权限,这个方法中的嵌套for循环是怎么回事呢,其实就是将数据库中的对应角色、权限放进shiro中,让他来管理,这需要实体类User中有getRoleList()、getRole_name()和getFunctionList()、getPermission这几个方法,这几个个方法就是设计数据库和实体类时的东西了,关于shiro权限相关的实体类在前面已经给出了。身份认证:在用户登录认证的时候回调,认证失败就抛出AuthenticationException。
五、shiro配置类
package com.cy.coo.shiro; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher; import org.apache.shiro.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManager; import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager; import org.apache.shiro.spring.security.interceptor.AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor; import org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean; import org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.CookieRememberMeManager; import org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager; import org.apache.shiro.web.servlet.SimpleCookie; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManagerFactoryBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource; @Configuration // 等价于beans public class ShiroConfig { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ShiroFilterFactoryBean.class); @Bean(name = "securityManager") public SecurityManager securityManager(@Qualifier("authRealm") MyAuthorizingRealm authRealm, @Qualifier("cookieRememberMeManager") CookieRememberMeManager cookieRememberMeManager) { log.info("securityManager()"); DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager(); // 设置realm. securityManager.setRealm(authRealm); // 设置rememberMe管理器 securityManager.setRememberMeManager(cookieRememberMeManager); return securityManager; } /** * realm * * @return */ @Bean(name = "authRealm") public MyAuthorizingRealm myAuthRealm( @Qualifier("hashedCredentialsMatcher") HashedCredentialsMatcher matcher, @Qualifier("ehCacheManager") EhCacheManager ehCacheManager) { log.info("myShiroRealm()"); MyAuthorizingRealm myAuthorizingRealm = new MyAuthorizingRealm(); // 设置密码凭证匹配器 myAuthorizingRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(matcher); // myShiroRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(hashedCredentialsMatcher()); // 设置缓存管理器 myAuthorizingRealm.setCacheManager(ehCacheManager); return myAuthorizingRealm; } /** * 缓存管理器 * @return */ @Bean(value="ehCacheManager") public EhCacheManager ehCacheManager(@Qualifier("ehCacheManagerFactoryBean") EhCacheManagerFactoryBean bean) { log.info("ehCacheManager()"); EhCacheManager cacheManager = new EhCacheManager(); cacheManager.setCacheManagerConfigFile("classpath:ehcache-shiro.xml"); return cacheManager; } /** * cookie对象; * * @return */ @Bean public SimpleCookie rememberMeCookie() { log.info("rememberMeCookie()"); // 这个参数是cookie的名称,对应前端的checkbox 的name = rememberMe SimpleCookie simpleCookie = new SimpleCookie("rememberMe"); // <!-- 记住我cookie生效时间30天(259200) ,单位秒;--> simpleCookie.setMaxAge(259200); return simpleCookie; } /** * 记住我管理器 cookie管理对象; * * @return */ @Bean(name = "cookieRememberMeManager") public CookieRememberMeManager rememberMeManager() { System.out.println("rememberMeManager()"); CookieRememberMeManager cookieRememberMeManager = new CookieRememberMeManager(); cookieRememberMeManager.setCookie(rememberMeCookie()); return cookieRememberMeManager; } /** * 密码匹配凭证管理器 * * @return */ @Bean(name = "hashedCredentialsMatcher") public HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher() { log.info("hashedCredentialsMatcher()"); HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher(); hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("MD5");// 散列算法:这里使用MD5算法; hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);// 散列的次数,比如散列两次,相当于 // md5(md5("")); return hashedCredentialsMatcher; } /** * 开启shiro aop注解支持. 使用代理方式;所以需要开启代码支持; Controller才能使用@RequiresPermissions * * @param securityManager * @return */ @Bean public AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor( @Qualifier("securityManager") SecurityManager securityManager) { log.info("authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor()"); AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor = new AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(); authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor.setSecurityManager(securityManager); return authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor; } @Bean public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilter(@Qualifier("securityManager") SecurityManager securityManager) { log.info("shirFilter()"); ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); // 必须设置 SecurityManager shiroFilterFactoryBean.setSecurityManager(securityManager); // 拦截器. Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>(); map.put("/logout", "logout"); map.put("/login", "anon"); map.put("/logon", "anon"); map.put("/**", "authc"); // 如果不设置默认会自动寻找Web工程根目录下的"/login.jsp"页面 shiroFilterFactoryBean.setLoginUrl("/login"); // 登录成功后要跳转的链接 shiroFilterFactoryBean.setSuccessUrl("/index"); // 未授权界面; shiroFilterFactoryBean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/unauthorized"); shiroFilterFactoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map); return shiroFilterFactoryBean; } }
这个没什么好说的,最后一个类是shiro的过滤器配置。可以看到我在每个方法上面加了一个@Bean(name="..."),其实这是spring的注解,将这个类放到spring容器中管理,在方法形参中使用@Qualifier(...)来使用它,以致于我们在方法体中调用某个方法时就方面多了。
在这里,关于shiro在springboot中的基础配置就完成了。下面是期间遇到的错误解决方案:






