JSP标准标签库(JSTL)之核心标签(上)
在myeclipse中新建web项目时,会自动为我们安装JSTL库,如下图:
核心标签是我们最常用的JSTL标签。在JSP页面中引用核心标签库的语法如下:
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
一、<c:out>标签
<c:out>标签用来显示一个表达式的结果,与jsp中的<%= %>作用相似,语法格式:
<c:out value="要输出的内容" default="输出的默认值" escapeXml="是否忽略XML特殊字符"/>
其中,value属性是必需的,其它两个属性不是必需的,escapeXml的默认值是true。
如果为escapeXml="false",则将其中的html、xml解析出来。
如value="<font size=16>java</font>",会显示为大小为16的”java“ ,
如果为escapeXml="true",则显示<font size=16>java</font>。
如果value中的值是空值,则输出default中的值,如下例子(单标签),网页会输出:默认值
<c:out value="${null}" default="默认值" escapeXml="false" />
上面的写法等价于下面的写法(双标签):
<c:out value="${null}" escapeXml="false">默认值</c:out>
从上面的例子可以看出,value属性值可以是一个EL表达式,这样就可以很方便的输出一个某个值了。如下的例子:输出今天的日期
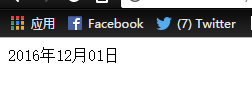
1 <%@page import="java.text.SimpleDateFormat"%> 2 <%@page import="java.text.DateFormat"%> 3 <%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> 4 <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %> 5 6 <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> 7 <html> 8 <head> 9 <title>c:out 标签举例</title> 10 <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> 11 <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> 12 <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> 13 <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> 14 <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> 15 </head> 16 17 <body> 18 <% 19 Date date = new Date(); 20 DateFormat f=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日");//设置时间格式 21 String dayDate=f.format(date); 22 pageContext.setAttribute("date", dayDate);//设置本页范围内的属性 23 %> 24 <c:out value="${pageScope.date }" escapeXml="true"> 这是默认值</c:out> 25 </body> 26 </html>
输出:
二、<c:set>标签
<c:set>标签用于设置变量值和对象属性。语法格式:
<c:set var="存储信息的变量" value="要存储的值" target="要修改的属性所属的对象" property="要修改的属性" scope="var属性的作用域"/>
设置一个在page范围内属性名为info的属性,如下:
<c:set var="info" value="www.cnblogs.com" scope="page" />
然后就可以通过<c:out>标签来输出,但是只能在本页面中获取到info ,因为上面标明范围是在本页面中:
<c:out value="${info }"></c:out>
<c:set>标签中的target、property属性是对一个具体对象进行操作的。举个栗子:
首先,需要建一个java类(Student.java):
1 package cn.cqvie; 2 3 public class Student { 4 private String name; 5 private int age; 6 public String getName() { 7 return name; 8 } 9 public void setName(String name) { 10 this.name = name; 11 } 12 public int getAge() { 13 return age; 14 } 15 public void setAge(int age) { 16 this.age = age; 17 } 18 }
然后建一个jsp页面,用<c:set>标签来给一个student对象设置属性值,最后<c:out>标签来输出:
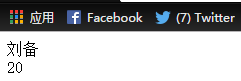
1 <%@page import="cn.cqvie.*" %> 2 <%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> 3 <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %> 4 5 <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> 6 <html> 7 <head> 8 <title>c:out 标签举例2</title> 9 <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> 10 <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> 11 <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> 12 <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> 13 <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> 14 </head> 15 16 <body> 17 <% 18 Student s=new Student(); 19 pageContext.setAttribute("stu", s); 20 %> 21 <c:set var="sname" value="刘备" target="${stu }" property="name" scope="page"></c:set> 22 <c:set var="sage" value="20" target="${stu }" property="age" scope="page"></c:set> 23 <c:out value="${pageScope.sname }" escapeXml="true"> 这是默认值</c:out><br> 24 <c:out value="${pageScope.sage }" escapeXml="true"> 这是默认值</c:out> 25 </body> 26 </html>
运行web页面后显示:
三、<c:remove>标签
<c:remove>标签用于移除一个变量,可以指定这个变量的作用域,若未指定,则默认为变量第一次出现的作用域。这个标签不是特别有用,不过可以用来确保JSP完成清理工作。
语法格式:
<c:remove var="要移除的变量名称" scope="变量所属的作用域"/>
我们将上个例子中的sage(即年龄属性)移除,核心代码块如下:
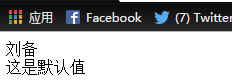
<body> <% Student s=new Student(); pageContext.setAttribute("stu", s); %> <c:set var="sname" value="刘备" target="${stu }" property="name" scope="page"></c:set> <c:set var="sage" value="20" target="${stu }" property="age" scope="page"></c:set> <c:remove var="sage" scope="page"/> <c:out value="${pageScope.sname }" escapeXml="true"> 这是默认值</c:out><br> <c:out value="${pageScope.sage }" escapeXml="true"> 这是默认值</c:out> </body>
网页显示效果:
四、<c:catch>标签
<c:catch> 标签主要用来处理产生错误的异常状况,并且将错误信息储存起来。语法格式:
<c:catch var="用来储存错误信息的变量"> 可能存在异常的代码 </c:catch>
举个栗子:
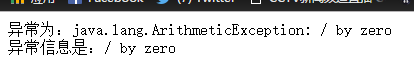
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <title>c:catch 举例</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> </head> <body> <c:catch var="errorMsg"> <% int result = 10/0; %> </c:catch> 异常为:${errorMsg }<br> 异常信息是:${errorMsg.message } </body> </html>
网页显示:
五、<c:if>标签
<c:if>标签判断表达式的值,如果表达式的值为 true 则执行其主体内容。语法格式:
<c:if test="条件" var="用于存储条件结果的变量" scope="var属性的作用域"> 当test条件为真(var中变量值为true),执行的代码块 </c:if>
举例:
<body> <c:if test="${param.name=='xiaosongshu' }" var="result"> <h3>欢迎${param.name}光临</h3> </c:if> 看一看result的值:${result} </body>
在网页中请求页面时需要传一个name属性,如:http://localhost:5200/JSTLtest/if.jsp?name=xiaosongshu
看到结果:

六、<c:choose>, <c:when>, <c:otherwise> 标签
<c:choose>标签与Java中的switch语句的功能一样,用于在众多选项中做出选择。
switch语句中有case,而<c:choose>标签中对应有<c:when>,switch语句中有default,而<c:choose>标签中有<c:otherwise>。
语法格式:
<c:choose> <c:when test="条件1"/> 当条件1成立时执行的代码块 </c:when> <c:when test="条件2"/> 当条件2成立时执行的代码块 </c:when> ... <c:when test="条件n"/> 当条件n成立时执行的代码块 </c:when> <c:otherwise> 当条件1-条件n都不成立执行的代码块 </c:otherwise> </c:choose>
举例如下:
<body> <c:set var="num" value="30"></c:set> <c:choose> <c:when test="${num==10 }"> <h3>num的值是10</h3> </c:when> <c:when test="${num==20 }"> <h3>num的值是20</h3> </c:when> <c:otherwise> <h3>以上条件都不成立</h3> </c:otherwise> </c:choose> </body>
在<c:choose>, <c:when>, <c:otherwise> 三个标签中,只有<c:when>标签有一个条件(test)属性,其它两个标签都没有属性。




