cf div2 236 D
You have an array of positive integers a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] and a set of bad prime numbers b1, b2, ..., bm. The prime numbers that do not occur in the set b are considered good. The beauty of array a is the sum 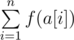 , where function f(s) is determined as follows:
, where function f(s) is determined as follows:
- f(1) = 0;
- Let's assume that p is the minimum prime divisor of s. If p is a good prime, then
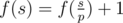 , otherwise
, otherwise 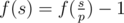 .
.
You are allowed to perform an arbitrary (probably zero) number of operations to improve array a. The operation of improvement is the following sequence of actions:
- Choose some number r (1 ≤ r ≤ n) and calculate the value g = GCD(a[1], a[2], ..., a[r]).
- Apply the assignments:
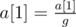 ,
,  , ...,
, ..., 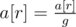 .
.
What is the maximum beauty of the array you can get?
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 5000) showing how many numbers are in the array and how many bad prime numbers there are.
The second line contains n space-separated integers a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) — array a. The third line contains m space-separated integers b1, b2, ..., bm (2 ≤ b1 < b2 < ... < bm ≤ 109) — the set of bad prime numbers.
Print a single integer — the answer to the problem.
5 2
4 20 34 10 10
2 5
-2
4 5
2 4 8 16
3 5 7 11 17
10
贪心,从右往左扫gcd,若遇到好的质因子少于坏的质因子则可以更新使答案增加

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <cmath> 6 #include <set> 7 8 using namespace std; 9 10 #define maxn 40005 11 #define INF (1 << 30) 12 13 bool prime[maxn]; 14 int ele[maxn],a[5005],g[5005],b[5005]; 15 int len = 0,n,m,ans = 0; 16 17 int gcd(int x,int y) { 18 return y ? gcd(y,x % y) : x; 19 } 20 21 int cal(int x) { 22 int sum = 0; 23 for(int i = 2; i * i <= x; ++i) { 24 if(x % i == 0) { 25 int v,pos; 26 pos = lower_bound(b + 1,b + m + 1,i) - b; 27 v = b[pos] == i ? -1 : 1; 28 while(x % i == 0) { 29 sum += v; 30 x /= i; 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 35 if(x != 1) { 36 int pos = lower_bound(b + 1,b + m + 1,x) - b; 37 sum += b[pos] == x ? -1 : 1; 38 } 39 return sum; 40 } 41 42 void solve() { 43 //printf("cal = %d\n",cal(4)); 44 for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { 45 ans += cal(a[i]); 46 } 47 48 g[1] = a[1]; 49 for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) { 50 g[i] = gcd(g[i - 1],a[i]); 51 } 52 53 int t = 1; 54 for(int i = n; i >= 1; --i) { 55 int v; 56 if((v = cal(g[i] / t)) < 0) { 57 //printf("g = %d v = %d\n",g[i],v); 58 ans += (-v) * i; 59 t *= g[i] / t; 60 } 61 } 62 63 64 printf("%d\n",ans); 65 } 66 int main() { 67 68 //freopen("sw.in","r",stdin); 69 70 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 71 for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%d",&a[i]); 72 for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { 73 scanf("%d",&b[i]); 74 } 75 b[m + 1] = INF; 76 77 solve(); 78 return 0; 79 }



