RabbitMQ简介
-
同步调用
- 基于OpenFeign的调用都属于是同步调用,等待上一个需求结束,开始下一个需求。
- 有缺点:
- 拓展性差:每次有新的需求,现有支付逻辑都要跟着变化,代码经常变动,不符合开闭原则,拓展性不好。
- 性能下降:每次远程调用,调用者都是阻塞等待状态。
- 级联失败:当某一个服务出现故障时,整个事务都会回滚,交易失败。
-
异步调用:消息发送者,消息Broker,消息接收者
-
异步调用的优势包括:
- 耦合度更低
- 性能更好
- 业务拓展性强
- 故障隔离,避免级联失败
-
缺点:
- 完全依赖于Broker的可靠性、安全性和性能
- 架构复杂,后期维护和调试麻烦
-
-
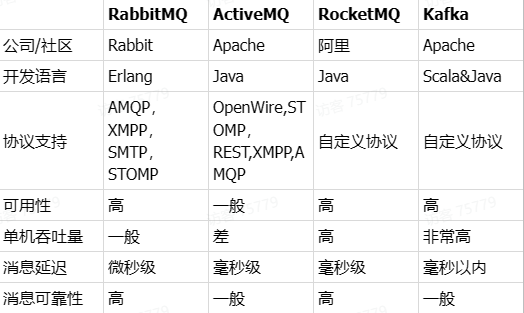
技术选型
![]()
目前国内消息队列使用最多的还是RabbitMQ,再加上其各方面都比较均衡,稳定性也好。 -
RabbitMQ是基于Erlang语言开发的开源消息通信中间件。
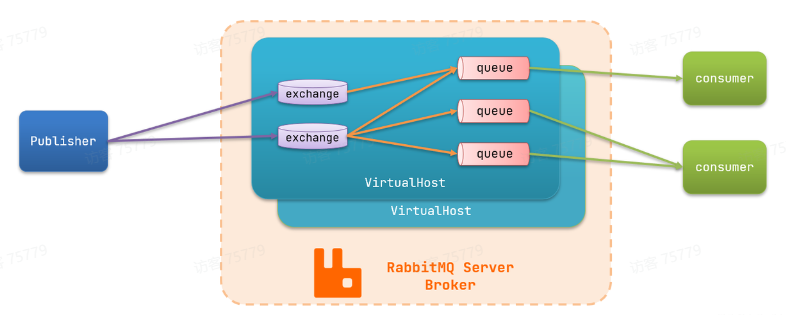
RabbitMQ对应的架构如图:
![]()
- publisher:生产者,也就是发送消息的一方
- consumer:消费者,也就是消费消息的一方
- queue:队列,存储消息。生产者投递的消息会暂存在消息队列中,等待消费者处理
- exchange:交换机,负责消息路由。生产者发送的消息由交换机决定投递到哪个队列。
- virtual host:虚拟主机,起到数据隔离的作用。每个虚拟主机相互独立,有各自的exchange、queue
-
SpringAMQP:由于RabbitMQ采用了AMQP协议,因此它具备跨语言的特性。任何语言只要遵循AMQP协议收发消息,都可以与RabbitMQ交互。并且RabbitMQ官方也提供了各种不同语言的客户端。但是,RabbitMQ官方提供的Java客户端编码相对复杂,一般生产环境下我们更多会结合Spring来使用。而Spring的官方刚好基于RabbitMQ提供了这样一套消息收发的模板工具:SpringAMQP。并且还基于SpringBoot对其实现了自动装配,使用起来非常方便。
-
SpringAMQP提供了三个功能:
- 自动声明队列、交换机及其绑定关系
- 基于注解的监听器模式,异步接收消息
- 封装了RabbitTemplate工具,用于发送消息
-
-
快速使用
- 引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId> </dependency>- 添加配置
spring: rabbitmq: host: 192.168.150.101 # 你的虚拟机IP port: 5672 # 端口 virtual-host: /hmall # 虚拟主机 username: hmall # 用户名 password: 123 # 密码- 进行测试,消息发送
@SpringBootTest public class SpringAmqpTest { @Autowired private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; @Test public void testSimpleQueue() { // 队列名称 String queueName = "simple.queue"; // 消息 String message = "hello, spring amqp!"; // 发送消息 rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName, message); } }- 消息接收
package com.itheima.consumer.listener; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class SpringRabbitListener { // 利用RabbitListener来声明要监听的队列信息 // 将来一旦监听的队列中有了消息,就会推送给当前服务,调用当前方法,处理消息。 // 可以看到方法体中接收的就是消息体的内容 @RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue") public void listenSimpleQueueMessage(String msg) throws InterruptedException { System.out.println("spring 消费者接收到消息:【" + msg + "】"); } } -
WorkQueues模型: 让多个消费者绑定到一个队列,共同消费队列中的消息,能够提高消息处理的速度。但是这是消息是平均分配给每个消费者的,并没有考虑到消费者的处理能力。
- 修改consumer服务的application.yml文件,添加配置
spring: rabbitmq: listener: simple: prefetch: 1 # 每次只能获取一条消息,处理完成才能获取下一个消息这样充分利用了每一个消费者的处理能力,可以有效避免消息积压问题。
Work模型的使用:
- 多个消费者绑定到一个队列,同一条消息只会被一个消费者处理
- 通过设置prefetch来控制消费者预取的消息数量
-
Fanout交换机:广播,FanoutExchange的会将消息路由到每个绑定的队列
- 可以有多个队列
- 每个队列都要绑定到Exchange(交换机)
- 生产者发送的消息,只能发送到交换机
- 交换机把消息发送给绑定过的所有队列
- 订阅队列的消费者都能拿到消息
-
Direct交换机:不同的消息被不同的队列消费
- 队列与交换机的绑定,不能是任意绑定了,而是要指定一个RoutingKey(路由key)
- 消息的发送方在 向 Exchange发送消息时,也必须指定消息的 RoutingKey。
- Exchange不再把消息交给每一个绑定的队列,而是根据消息的Routing Key进行判断,只有队列的Routingkey与消息的 Routing key完全一致,才会接收到消息
-
Topic交换机:可以让队列在绑定BindingKey 的时候使用通配符
通配符规则:
'#':匹配一个或多个词
*:匹配不多不少恰好1个词 -
Java代码的形式声明队列和交换机
- fanout示例
package com.itheima.consumer.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding; import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder; import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class FanoutConfig { /** * 声明交换机 * @return Fanout类型交换机 */ @Bean public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){ return new FanoutExchange("hmall.fanout"); } /** * 第1个队列 */ @Bean public Queue fanoutQueue1(){ return new Queue("fanout.queue1"); } /** * 绑定队列和交换机 */ @Bean public Binding bindingQueue1(Queue fanoutQueue1, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue1).to(fanoutExchange); } /** * 第2个队列 */ @Bean public Queue fanoutQueue2(){ return new Queue("fanout.queue2"); } /** * 绑定队列和交换机 */ @Bean public Binding bindingQueue2(Queue fanoutQueue2, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue2).to(fanoutExchange); } }- direct示例:direct模式由于要绑定多个KEY,会非常麻烦,每一个Key都要编写一个binding
package com.itheima.consumer.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.*; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class DirectConfig { /** * 声明交换机 * @return Direct类型交换机 */ @Bean public DirectExchange directExchange(){ return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange("hmall.direct").build(); } /** * 第1个队列 */ @Bean public Queue directQueue1(){ return new Queue("direct.queue1"); } /** * 绑定队列和交换机 */ @Bean public Binding bindingQueue1WithRed(Queue directQueue1, DirectExchange directExchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue1).to(directExchange).with("red"); } /** * 绑定队列和交换机 */ @Bean public Binding bindingQueue1WithBlue(Queue directQueue1, DirectExchange directExchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue1).to(directExchange).with("blue"); } /** * 第2个队列 */ @Bean public Queue directQueue2(){ return new Queue("direct.queue2"); } /** * 绑定队列和交换机 */ @Bean public Binding bindingQueue2WithRed(Queue directQueue2, DirectExchange directExchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue2).to(directExchange).with("red"); } /** * 绑定队列和交换机 */ @Bean public Binding bindingQueue2WithYellow(Queue directQueue2, DirectExchange directExchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue2).to(directExchange).with("yellow"); } }- 基于注解声明
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue1"), exchange = @Exchange(name = "hmall.direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT), key = {"red", "blue"} )) public void listenDirectQueue1(String msg){ System.out.println("消费者1接收到direct.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】"); } @RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue2"), exchange = @Exchange(name = "hmall.direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT), key = {"red", "yellow"} )) public void listenDirectQueue2(String msg){ System.out.println("消费者2接收到direct.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】"); } -
消息转换器:Spring的消息发送代码接收的消息体是一个Object,而在数据传输时,它会把你发送的消息序列化为字节发送给MQ,接收消息的时候,还会把字节反序列化为Java对象。
默认情况下Spring采用的序列化方式是JDK序列化。众所周知,JDK序列化存在下列问题:
-
数据体积过大:JDK 序列化会将对象转换为字节流进行传输,但这种方式可能导致序列化后的数据体积远大于原始对象的大小
-
有安全漏洞:JDK 序列化在处理对象时存在一些安全漏洞,主要是由于它对反序列化的输入信任过度,可能导致恶意代码注入、远程代码执行等安全问题。
-
可读性差:序列化后的数据通常是以字节流的形式存在的
-
配置JSON转换器
-
在publisher和consumer两个服务中都引入依赖,如果项目中引入了spring-boot-starter-web依赖,则无需再次引入Jackson依赖。
<dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId> <version>xxx</version> </dependency>- 配置消息转换器,在publisher和consumer两个服务的启动类中添加一个Bean即可:
@Bean public MessageConverter messageConverter(){ // 1.定义消息转换器 Jackson2JsonMessageConverter jackson2JsonMessageConverter = new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter(); // 2.配置自动创建消息id,用于识别不同消息,也可以在业务中基于ID判断是否是重复消息 jackson2JsonMessageConverter.setCreateMessageIds(true); return jackson2JsonMessageConverter; } -
-
业务改造
-
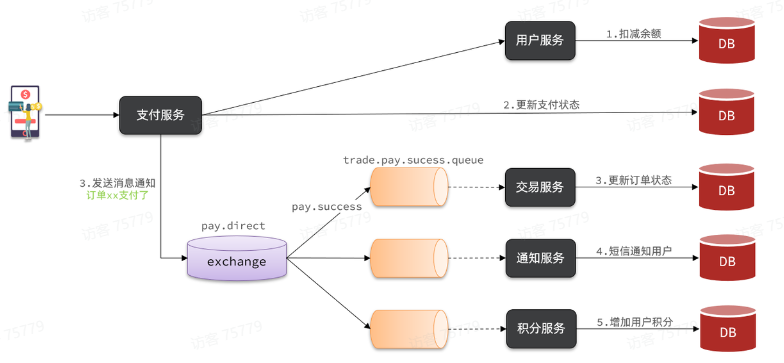
案例需求:改造余额支付功能,将支付成功后基于OpenFeign的交易服务的更新订单状态接口的同步调用,改为基于RabbitMQ的异步通知。
![]()
-
定义direct类型交换机,命名为pay.direct
-
定义消息队列,命名为trade.pay.success.queue
-
将trade.pay.success.queue与pay.direct绑定,BindingKey为pay.success
-
支付成功时不再调用交易服务更新订单状态的接口,而是发送一条消息到pay.direct,发送消息的RoutingKey 为pay.success,消息内容是订单id
-
交易服务监听trade.pay.success.queue队列,接收到消息后更新订单状态为已支付
-
配置MQ,添加依赖
<!--消息发送--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId> </dependency>- 配置MQ地址
spring: rabbitmq: host: 192.168.150.101 # 你的虚拟机IP port: 5672 # 端口 virtual-host: /hmall # 虚拟主机 username: hmall # 用户名 password: 123 # 密码- 在trade-service服务中定义一个消息监听类
package com.hmall.trade.listener; import com.hmall.trade.service.IOrderService; import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor; import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeTypes; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @RequiredArgsConstructor public class PayStatusListener { private final IOrderService orderService; @RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue(name = "trade.pay.success.queue", durable = "true"), exchange = @Exchange(name = "pay.topic"), key = "pay.success" )) public void listenPaySuccess(Long orderId){ orderService.markOrderPaySuccess(orderId); } }- 修改pay-service服务下的com.hmall.pay.service.impl.PayOrderServiceImpl类中的tryPayOrderByBalance方法
private final RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; @Override @Transactional public void tryPayOrderByBalance(PayOrderDTO payOrderDTO) { // 1.查询支付单 PayOrder po = getById(payOrderDTO.getId()); // 2.判断状态 if(!PayStatus.WAIT_BUYER_PAY.equalsValue(po.getStatus())){ // 订单不是未支付,状态异常 throw new BizIllegalException("交易已支付或关闭!"); } // 3.尝试扣减余额 userClient.deductMoney(payOrderDTO.getPw(), po.getAmount()); // 4.修改支付单状态 boolean success = markPayOrderSuccess(payOrderDTO.getId(), LocalDateTime.now()); if (!success) { throw new BizIllegalException("交易已支付或关闭!"); } // 5.修改订单状态 // tradeClient.markOrderPaySuccess(po.getBizOrderNo()); try { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("pay.direct", "pay.success", po.getBizOrderNo()); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("支付成功的消息发送失败,支付单id:{}, 交易单id:{}", po.getId(), po.getBizOrderNo(), e); } } -


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号