线段树 Segment Tree
2018-03-12 16:25:04
一、线段树
线段树(英语:Segment tree)是一种二叉树形数据结构,1977年由Jon Louis Bentley发明,用以储存区间或线段,并且允许快速查询结构内包含某一点的所有区间。
线段树是一棵二叉树,树中的每一个结点表示了一个区间[a,b]。a,b通常是整数。每一个叶子节点表示了一个单位区间。对于每一个非叶结点所表示的结点[a,b],其左儿子表示的区间为[a, (a+b)/2],右儿子表示的区间为[(a+b)/2 + 1, b]。
线段:树上的每个节点对应于一个线段(还是叫“区间”更容易理解,区间的起点和终点通常为整数)。
线段树的一些性质:
- 同一层的节点所代表的区间,相互不会重叠。
- 叶子节点的区间是单位长度,不能再分了。
- 线段树的深度不超过logL(L是最长区间的长度)。
- 线段树把区间上的任意一条线段都分成不超过2logL条线段。
线段树的构建:
关于构建时数组大小:有理论证明对于大小为N的数组开大小为4N的数组来表示线段树完全足够。

线段树的基本用途:线段树适用于和区间统计有关的问题。比如某些数据可以按区间进行划分,按区间动态进行修改,而且还需要按区间多次进行查询,那么使用线段树可以达到
较快查询速度。
举个例子:
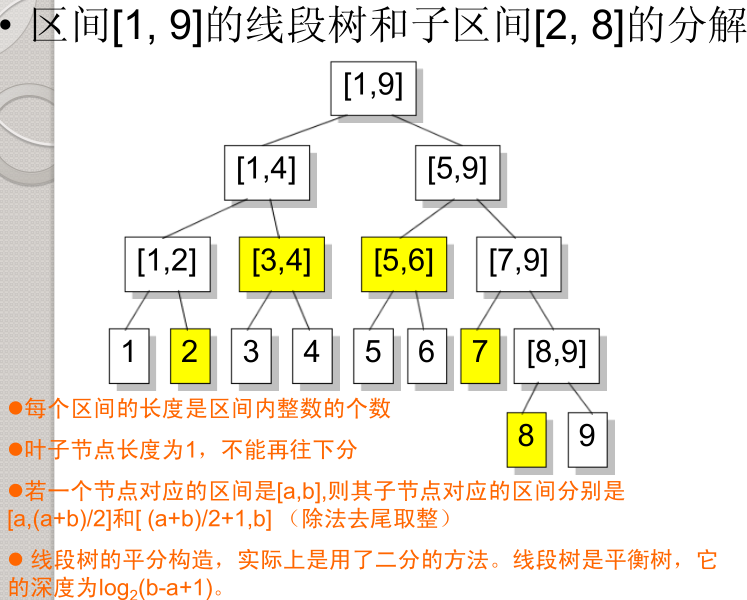
二、线段树在求解RMQ问题上的应用
使用线段树可以在O(n)的时间复杂度内完成预处理,然后在O(logn)的时间复杂度内完成查询操作。
使用ST表也是可以完成RMQ问题的,其时间复杂度为<O(nlogn),O(1)>。
线段树的查询效率似乎和ST表比起来要逊色一些,然而,线段树的有点并不仅仅在于其预处理的高效性,还体现在其动态处理问题的能力,在ST表中是无法完成数据的实时修改的(除非重新使用O(nlogn)建立一个ST表),但是在线段树中可以在O(logn)的时间复杂度内完成修改操作,在动态操作方面线段树有极大的优势。
void initialize(int[] T, int index, int[] nums, int L, int R) {
if (L == R) {
T[index] = L;
}
else {
int mid = (R - L) / 2 + L;
initialize(T, index * 2, nums, L, mid);
initialize(T, index * 2 + 1, nums, mid + 1, R);
if (nums[T[index * 2]] < nums[T[index * 2 + 1]]) {
T[index] = T[index * 2];
}
else {
T[index] = T[index * 2 + 1];
}
}
}
int query(int[] T, int index, int L, int R, int[] nums, int i, int j) {
if (R < i || L > j) {
return -1;
}
if (i <= L && j >= R) {
return T[index];
}
int mid = (R - L) / 2 + L;
int tmpL = query(T, index * 2, L, mid, nums, i, j);
int tmpR = query(T, index * 2 + 1, mid + 1, R, nums, i, j);
if (tmpL == -1) {
return tmpR;
}
if (tmpR == -1) {
return tmpL;
}
else {
if (nums[tmpL] < nums[tmpR]) return tmpL;
else return tmpR;
}
}
void change(int[] T, int index, int L, int R, int[] nums, int i, int val) {
if (L == R) {
nums[i] = val;
return;
}
int mid = (R - L) / 2 + L;
if (i >= L && i <= mid) change(T, index * 2, L, mid, nums, i, val);
if (i >= mid + 1 && i <= R) change(T, index * 2 + 1, mid + 1, R, nums, i, val);
if (nums[T[index * 2]] < nums[T[index * 2 + 1]]) {
T[index] = T[index * 2];
}
else {
T[index] = T[index * 2 + 1];
}
}
int RMQ(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int[] T = new int[nums.length * 4];
initialize(T, 1, nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
change(T, 1, 0, nums.length - 1, nums, 5, 1);
return query(T, 1, 0, nums.length - 1, nums, i, j);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SegmentTree st = new SegmentTree();
System.out.println(st.RMQ(new int[]{2, 4, 3, 1, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1, 7}, 4, 7));
}
三、线段树的应用
线段树有很多扩展和应用,在实际使用过程中,可以对原定义进行部分修改,比如,原定义是完全二分的,实际问题中往往不是这样完全二分的情况,另外实际问题范围也可以设定为前闭后开,方便编程实现。
-
732. My Calendar III
问题描述:
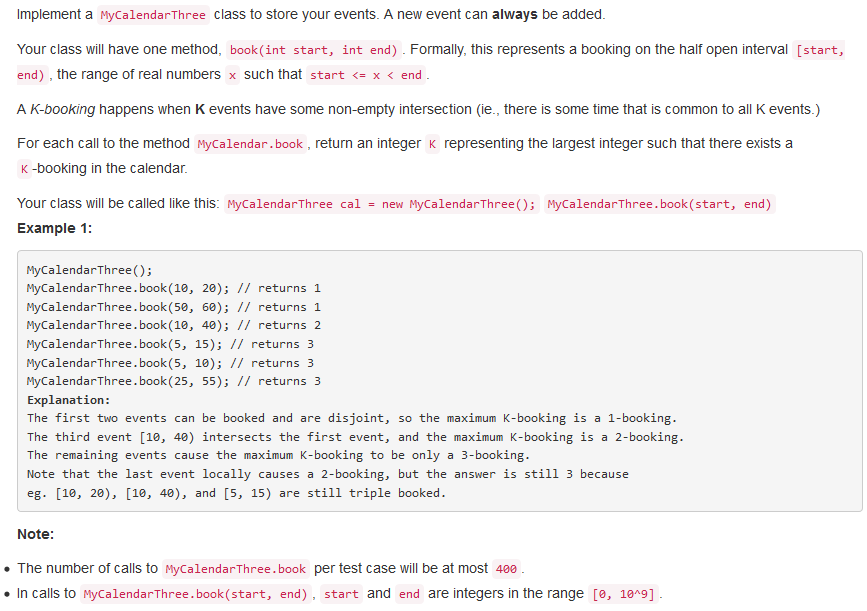
问题求解:
本题显然可以使用线段树来进行解决。当然,本题的解法不止一种,还可以通过记录端点值来进行计算。
public class MyCalendarThree {
SegmentTree root;
int res;
public MyCalendarThree() {
root = new SegmentTree(0, 1000000000, 0);
res = 0;
}
public int book(int start, int end) {
add(start, end, root);
return res;
}
private void add(int start, int end, SegmentTree root) {
if (root.m != -1) {
if (start >= root.m) add(start, end, root.right);
else if (end <= root.m) add(start, end, root.left);
else {
add(start, root.m, root.left);
add(root.m, end, root.right);
}
return;
}
if (start == root.l && end == root.r) {
root.cnt++;
res = Math.max(res, root.cnt);
}
else if (start == root.l) {
root.m = end;
root.left = new SegmentTree(start, root.m, root.cnt + 1);
root.right = new SegmentTree(root.m, root.r, root.cnt);
res = Math.max(res, root.cnt + 1);
}
else if (end == root.r) {
root.m = start;
root.left = new SegmentTree(root.l, root.m, root.cnt);
root.right = new SegmentTree(root.m, root.r, root.cnt + 1);
res = Math.max(res, root.cnt + 1);
}
else {
root.m = start;
root.left = new SegmentTree(root.l, root.m, root.cnt);
root.right = new SegmentTree(root.m, root.r, root.cnt);
add(start, end, root.right);
}
}
}
class SegmentTree {
int l;
int r;
int m;
int cnt;
SegmentTree left;
SegmentTree right;
SegmentTree(int l, int r, int cnt) {
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
this.m = -1;
this.cnt = cnt;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}



