css小知识
1.什么是css?
中文名:层叠样式表
英文名:Cascading Style Sheets
英文缩写:CSS
其他称呼:级联样式表
2.css选择器种类
- 通配选择器
- 类型选择器
- ID选择器
- 类选择器
- 包含选择器
- 子元素选择器
- 相邻兄弟选择器
- 属性选择器
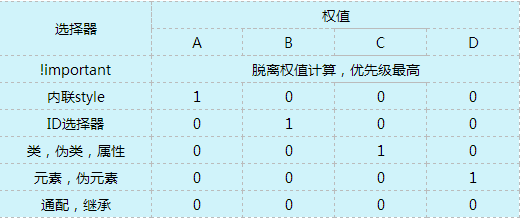
3.css选择器权值计算:
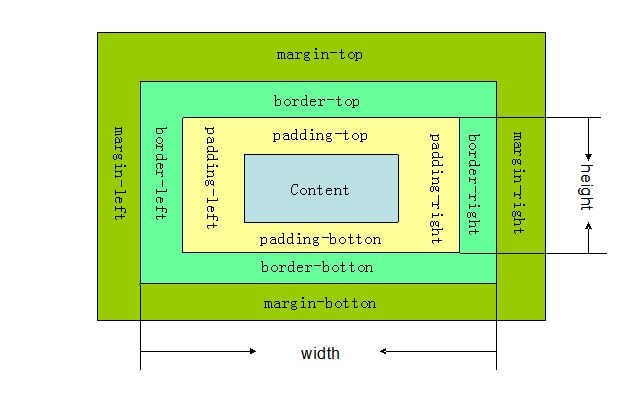
4.css盒子模型:
css盒子模型就是在网页设计中经常用到的CSS技术所使用的一种思维模型
css盒子模型具有属性:内容(content)、填充(padding)、边框(border)、边界(margin)
5.css3动画
@-webkit/o/ms/moz-keyframes bgMove{
from{
background-position:
0 center;
}
to{
background-position:
-1920px center;
}
}
-webkit/o/ms/moz-animation:
animation-name(动画名), animation-duration(动画时间),
animation-timing-function(动画播放方式,默认为ease平滑过度,linear线性),
animation-delay(延长多少时间执行),animation-iteration-count(播放次数,infinite为无限循环),
animation-direction(normal:正常方向alternate:正常与反向交替 );
6.css定位:
static:对象遵循常规流。top,right,bottom,left等属性不会被应用。
relative:对象遵循常规流,并且依据自身在正常流中的位置通过top,right,bottom,left属性进行偏移时不影响常规流中的任何元素。层叠通过z-index属性定义。
absolute:对象脱离常规流,使用top,right,bottom,left等属性进行绝对定位,盒子的偏移位置不影响常规流中的任何元素,其margin不与其他任何margin折叠,其层叠通过z-index属性定义。
fixed:对象脱离常规流,使用top,right,bottom,left等属性以窗口为参考点进行定位,当出现滚动条时,对象不会随着滚动
7.css过渡:
transition:过渡属性(style),过渡时间(S),过渡方式(linear | ease | ease-in | ease-out | ease-in-out),延时执行时间(s);
8.css继承和不可继承属性:
css不可继承属性:
display、margin、border、padding、background、height、min-height、max- height、width、min-width、max-width、overflow、position、left、right、top、 bottom、z-index、float、clear、table-layout、vertical-align。
css可继承属性:
所有元素可继承:visibility和cursor。
内联元素可继承:letter-spacing、word-spacing、white-space、line-height、color、font、 font-family、font-size、font-style、font-variant、font-weight、text- decoration、text-transform、direction。
块状元素可继承:text-indent和text-align。
列表元素可继承:list-style、list-style-type、list-style-position、list-style-image。
表格元素可继承:border-collapse。
9.css3属性选择器
[att=value]
该属性有指定的确切的值。
[att~=value] 该属性的值必须是一系列用空格隔开的多个值,(比如,class=”title featured home”),而且这些值中的一个必须是指定的值”value”。
[att|=value] 属性的值就是“value”或者以“value”开始并立即跟上一个“-”字符,也就是“value-”。(比如lang=”zh-cn”)
[att^=value] 该属性的值以指定值开始。
[att$=value] 该属性的值包含指定的值(而无论其位置)。
[att*=value] 该属性的值以指定的值结束
10.css3否定选择器
input:not([type="submit"]) { width: 200px; padding: 3px; border: 1px solid #000000; }
11.css3兄弟选择器
(1).临近兄弟组合
该选择器使用加号“+”来链接前后两个选择器。选择器中的元素有同一个父亲,而且第二个必须紧紧的跟着第一个。
p + h2 { margin-top: 10px; }
(2).普通兄弟组合
普通兄弟组合和临近兄弟组合的工作原理很像,不同的是第二个选择其无需紧紧跟随第一个。
.post h1 ~ p { font-size: 13px; }


