@Conditional注解
1.介绍@Conditional注解
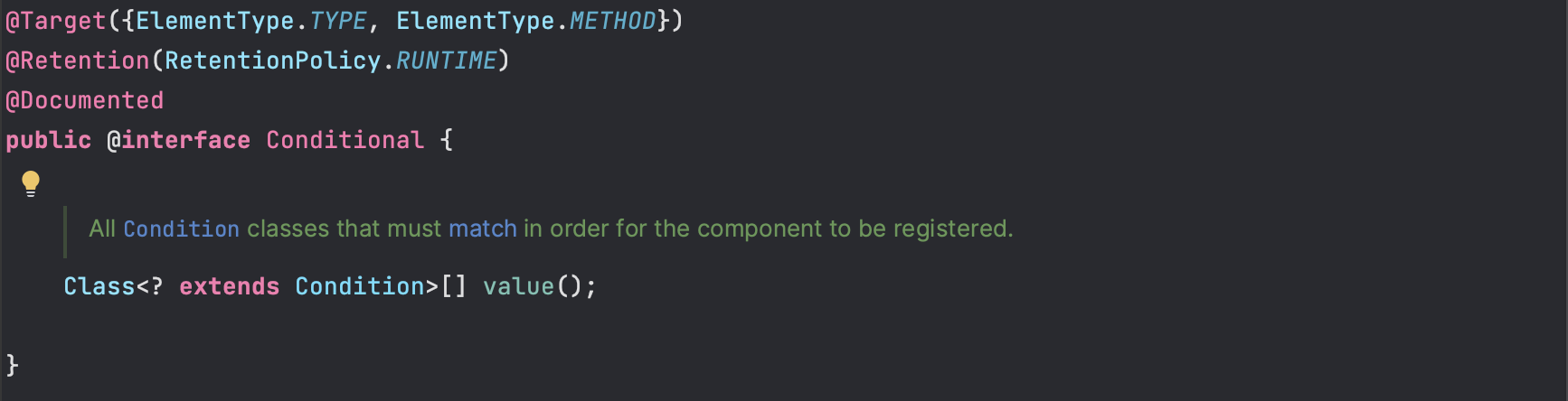
@Conditional注解源码
@Conditionl注解简单说明
@Conditional注解所属包
org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional
注解作用范围
{ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD}
类、接口、注解、枚举以及 方法
注解生命周期
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
代码编译为.class文件后,注解仍然存在,而且能被虚拟机识别,可以通过反射获取到
2.@Conditional注解的用法
Indicates that a component is only eligible for registration when all specified conditions match.
仅当所有条件被满足时组件才有资格被注册进容器中
The @Conditional annotation may be used in any of the following ways:
1.as a type-level annotation on any class directly or indirectly annotated with @Component, including @Configuration classes
2.as a meta-annotation, for the purpose of composing custom stereotype annotations
3.as a method-level annotation on any @Bean method
@Conditional注解可能用在以下这些场景中
1.作为一个type级别的注解,在任何被@Component注解包括@Configuration注解注解或者间接修饰的类上使用;
2.作为元注释,用于组合自定义构造型注释
3.作为method级别注解在任何被@Bean修饰的方法上
If a @Configuration class is marked with @Conditional, all of the @Bean methods, @Import annotations, and @ComponentScan annotations associated with that class will be subject to the conditions.
如果@Configuration类被标记为@Conditional,那么与该类关联的所有@Bean方法、@Import注解和@ComponentScan注解都将受这些条件的约束。
3.代码用例
创建类A,B,C以及TestCondition
class A extends AllNestedConditions { public A() { super(ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN); } public A(ConfigurationPhase configurationPhase) { super(configurationPhase); } @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = {C.class}) static class Son{ } }
public class B { }
@Component public class C { }
@Configuration public class TestCondition { @Bean @Conditional(value = {A.class}) public B b(){ System.out.println("B注入了!"); return new B(); } }
当C被注入到容器中时,@Conditional注解满足条件,B就被注入到容器中
当C不@Component注解时,@Conditional注解不满足条件,B无法被注入到容器中
4.原理简介
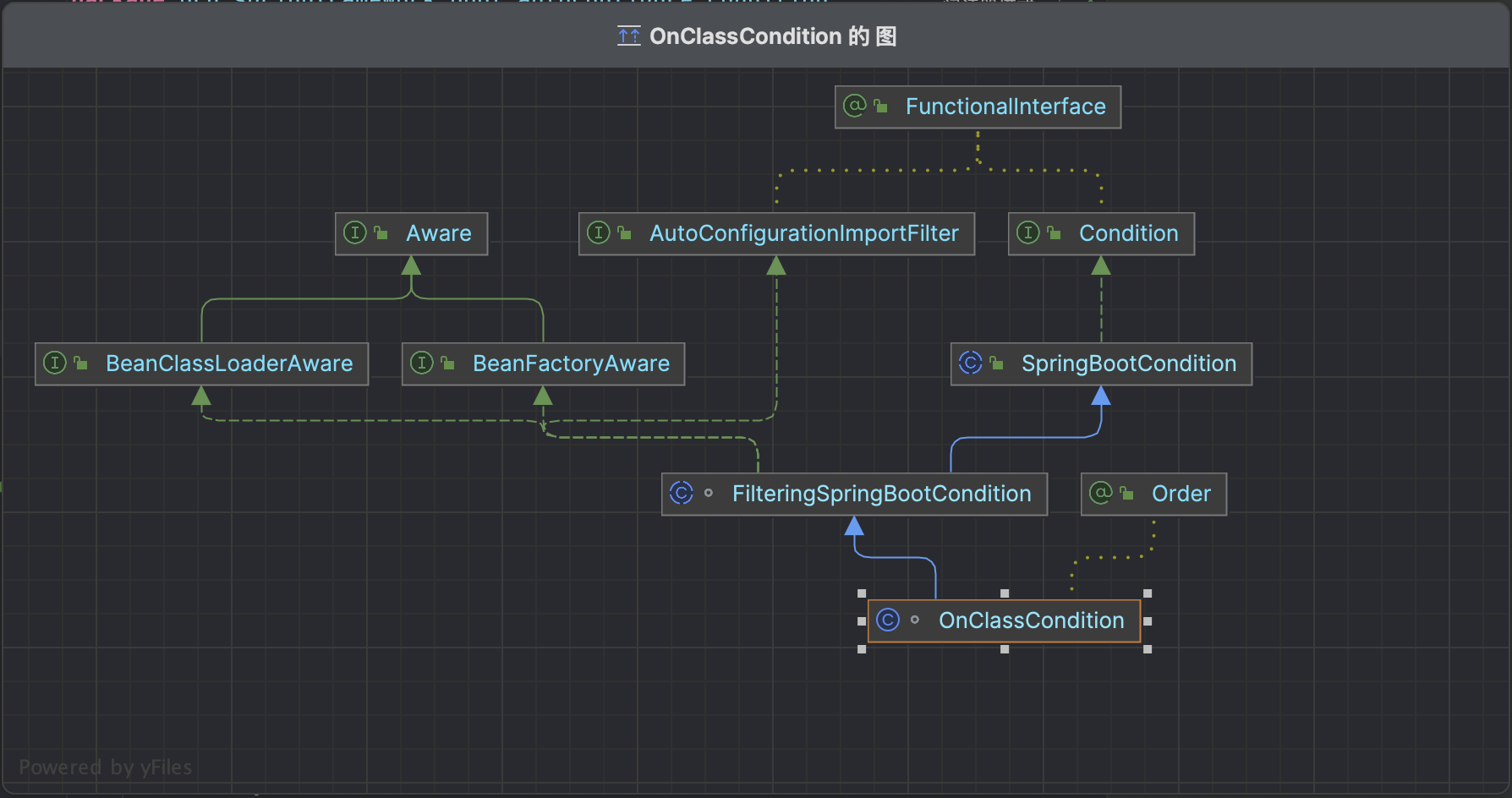
主要代码逻辑在
org/springframework/boot/autoconfigure/condition/FilteringSpringBootCondition.java中的match方法中
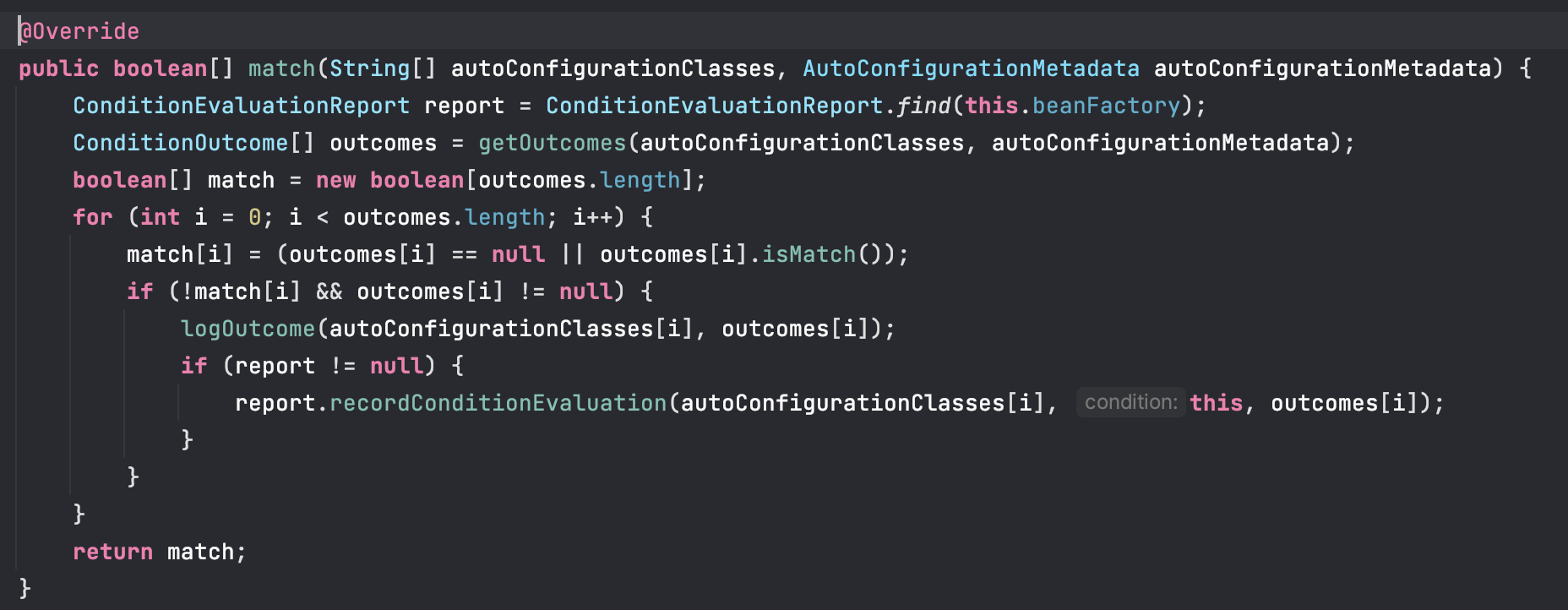
项目启动时,先在OnClassCondition类中的
方法中获取到条件输出
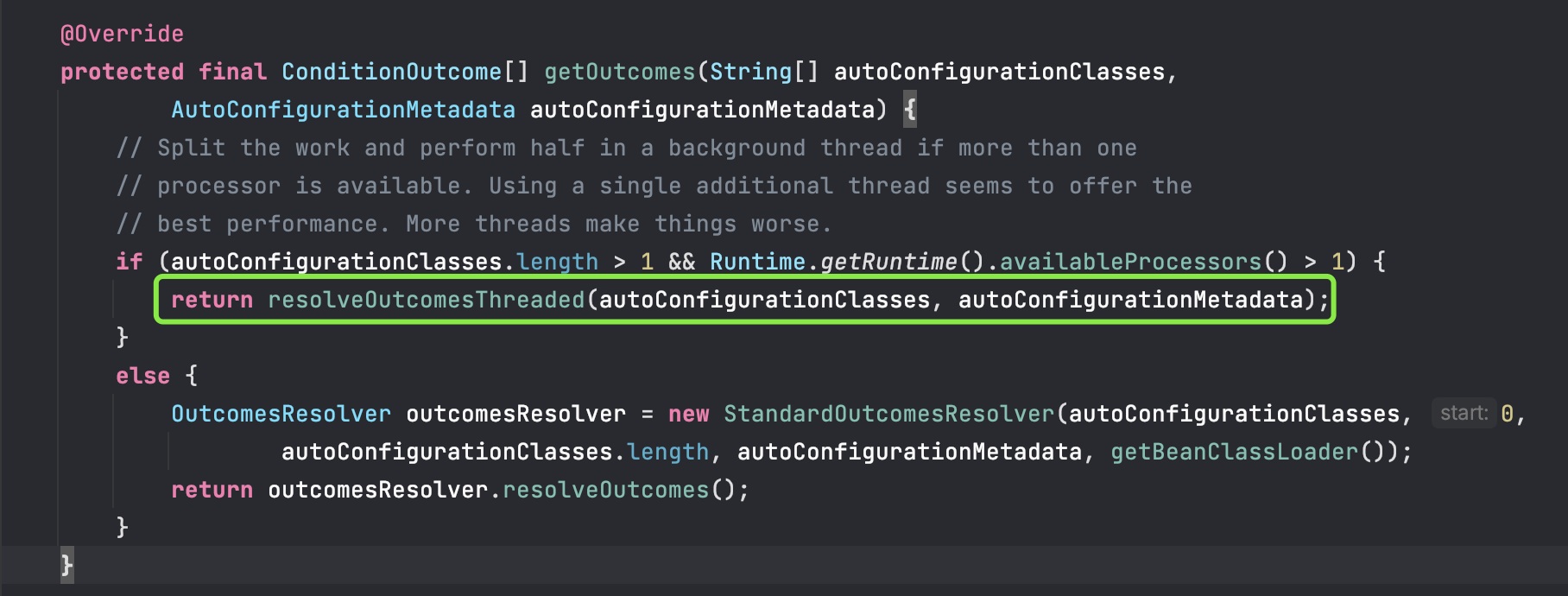
一个标准解析器一个线程解析器
当我们自动配置的类大于一个的时候,就会从中间分开用2个线程去处理返回条件输出
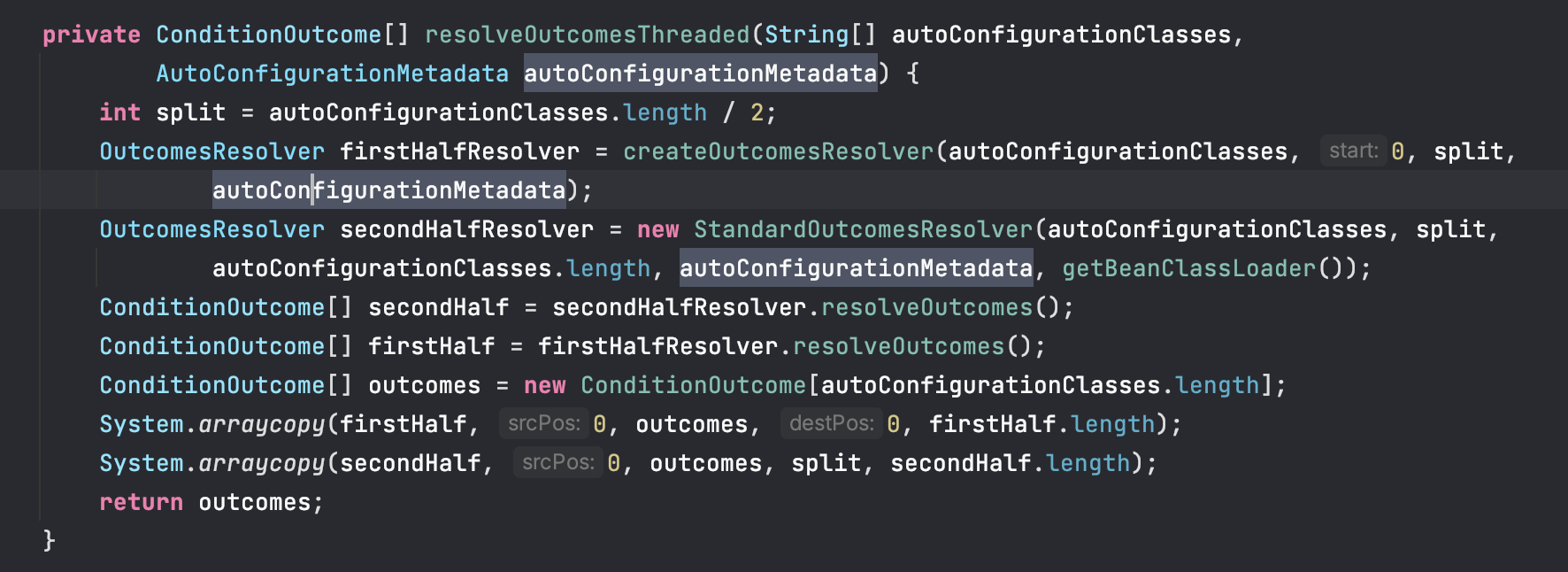
新开的线程调用join方法,新开线程执行完,主线程才会继续执行,最后才将2个线程获取的数据合并到新建的ConditionOutCome数组中





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律