C++ 友元类
 要是觉得内容枯燥,您可以点击左下角的播放按钮,让您在音乐的熏陶下愉快的阅读
要是觉得内容枯燥,您可以点击左下角的播放按钮,让您在音乐的熏陶下愉快的阅读
 本文总字数:2895
本文总字数:2895
•概念
类的友元函数是定义在类外部,但有权访问类的所有私有(private)成员和保护(protected)成员。
尽管友元函数的原型有在类的定义中出现过,但是友元函数并不是成员函数。
友元可以是一个函数,该函数被称为友元函数;友元也可以是一个类,该类被称为友元类,在这种情况下,整个类及其所有成员都是友元。
如果要声明函数为一个类的友元,需要在类定义中该函数原型前使用关键字 friend
•全局函数做友元
样例1
来看一个样例,如下所示:
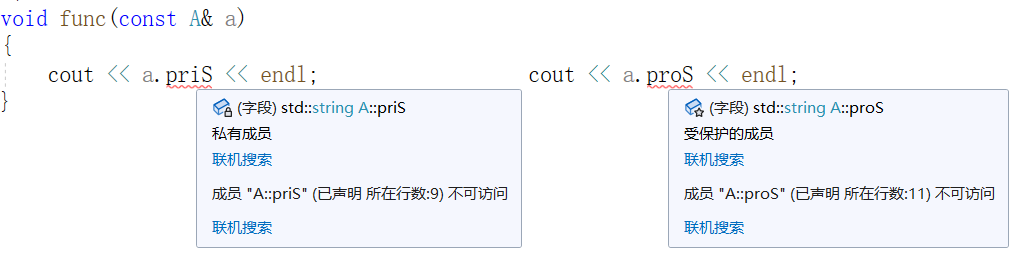
#pragma warning(disable:4996) #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; class A { private: string priS = "我是类A的私有成员";//私有成员 protected: string proS = "我是类A的受保护的成员";//受保护的成员 }; void func(A& a) { cout << a.priS << endl; cout << a.proS << endl; } int main() { A a; func(a); }分析
在该样例中,有一个类 A,A 中有两个属性,分别是 私有成员 priS , 受保护的成员 proS。
对于全局函数 func() 而言,A中的这两个属性都是不可访问的,若要强行访问,编译阶段就不会通过:
意思是,func() 不可以访问类A的私有成员和受保护的成员,那么,如何才能让 func() 访问到呢?
只需要将 func() 定义为类A的友元函数即可,定义如下:
friend void func(A& a);
将该定义放入类 A 中进行声明,你就可以在 func 中访问 A 的私有成员和受保护的成员了。
修改后的代码
#pragma warning(disable:4996) #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; class A { friend void func(A& a); private: string priS = "我是类A的私有成员";//私有成员 protected: string proS = "我是类A的受保护的成员";//受保护的成员 }; void func(A& a) { cout << a.priS << endl; cout << a.proS << endl; } int main() { A a; func(a); }
•类做友元
样例2
#pragma warning(disable:4996) #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; class A { friend class B;//声明B是A的友元类 private: string priS = "我是类A的私有成员";//私有成员 void priF() { cout << "我是类A的私有函数" << endl; } protected: string proS = "我是类A的受保护的成员";//受保护的成员 void proF() { cout << "我是类A的受保护函数" << endl; } }; class B { private: A a; public: void func() { cout << "func可访问A的所有成员和函数" << endl; a.priF(); a.proF(); puts(""); cout << a.priS << endl; cout << a.proS << endl; } }; int main() { B b; b.func(); }分析
在类A中,通过 friend class B; 语句,将B定义为A的友元类,那么,B中的任何成员和成员函数都可以访问A的私有的和受保护的成员或函数。
•成员函数做友元
样例3
#pragma warning(disable:4996) #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; class A;//B中使用了类A定义变量,所以要先声明类A class B { private: A* a;//此处的 a 必须是 A* 类型 public: B(); void func(); }; class A//因为类A中用到了类B中的func,所以类B的声明要在类A的前面 { friend void B::func();//声明B中的成员函数func作为A的友元函数 private: string priS = "我是类A的私有成员";//私有成员 void priF() { cout << "我是类A的私有函数" << endl; } protected: string proS = "我是类A的受保护的成员";//受保护的成员 void proF() { cout << "我是类A的受保护函数" << endl; } }; B::B() { a = new A();//对a进行初始化,必须要在A声明后才能进行,所以类B的构造函数要放在类A的下面 } void B::func()//因为该函数使用了类A中的成员,所以,要在类外定义该函数且要放到类A下面 { cout << "func可访问A的所有成员和函数" << endl; a->priF(); a->proF(); puts(""); cout << a->priS << endl; cout << a->proS << endl; } int main() { B b; b.func(); }注意
1. 注意类A和类B的声明顺序
2. 类B中的函数要在类外进行定义,且要放到类A的声明后
•参考资料
【1】:C++ 友元函数(菜鸟教程)
【2】:友元(黑马程序员)




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!