1086 再次树遍历
通过使用栈可以以非递归方式实现二叉树的中序遍历。
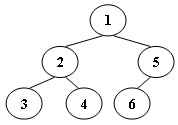
例如,假设遍历一个如下图所示的 6 节点的二叉树(节点编号从 1 到 6)。
则堆栈操作为:push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop()。
我们可以从此操作序列中生成唯一的二叉树。
你的任务是给出这棵树的后序遍历。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 N,表示树中节点个数。
树中节点编号从 1 到 N。
接下来 2N 行,每行包含一个栈操作,格式为:
Push X,将编号为 X 的节点压入栈中。Pop,弹出栈顶元素。
输出格式
输出这个二叉树的后序遍历序列。
数据保证有解,数和数之间用空格隔开,末尾不能有多余空格。
数据范围
1≤N≤30
输入样例:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop输出样例:
3 4 2 6 5 1代码实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int N=55;
stack<int>s1;
vector<int>v;
int pre[N],middle[N],idx,idx1,l[N],r[N];
unordered_map<int,int>mp;
int buildTree(int l1,int r1,int l2,int r2){
if(l1>r1||l2>r2)return 0;
int t=pre[l2];
int k=mp[t];
if(l1<k)l[t]=buildTree(l1,k-1,l2+1,l2+k-l1);
if(r1>k)r[t]=buildTree(k+1,r1,l2+k-l1+1,r2);
return t;
}
void dfs(int x){
if(x==0)return;
dfs(l[x]);
dfs(r[x]);
v.push_back(x);
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<2*n;i++){
string s;
cin>>s;
if(s=="Push"){
int x;
cin>>x;
s1.push(x);
pre[idx++]=x;
}else{
middle[idx1++]=s1.top();
mp[s1.top()]=idx1-1;
s1.pop();
}
}
int root=buildTree(0,n-1,0,n-1);
dfs(root);
for(int i=0;i<v.size();i++){
if(i==0)cout<<v[i];
else cout<<" "<<v[i];
}
return 0;
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人