codeforces 633D - Fibonacci-ish 离散化 + 二分查询
Yash has recently learnt about the Fibonacci sequence and is very excited about it. He calls a sequence Fibonacci-ish if
- the sequence consists of at least two elements
- f0 and f1 are arbitrary
- fn + 2 = fn + 1 + fn for all n ≥ 0.
You are given some sequence of integers a1, a2, ..., an. Your task is rearrange elements of this sequence in such a way that its longest possible prefix is Fibonacci-ish sequence.
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 1000) — the length of the sequence ai.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (|ai| ≤ 109).
Print the length of the longest possible Fibonacci-ish prefix of the given sequence after rearrangement.
3
1 2 -1
3
5
28 35 7 14 21
4
In the first sample, if we rearrange elements of the sequence as - 1, 2, 1, the whole sequence ai would be Fibonacci-ish.
In the second sample, the optimal way to rearrange elements is 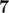 ,
,  ,
, 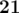 ,
, 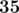 , 28.
, 28.
思路:由于斐波那契数列数值成指数型增长(称为斐波那契数列的收敛性),所以实际可选的长度不会超过100(实际上增长速度比2的幂次方要慢,若是正整数的斐波那契数列,要从0 1增长到1e9只需40位左右,所以题解给出的长度最大也是接近90的);那么只需离散出全部的不同的数值及其个数,枚举前两位即可;特例是前两位为0,这时长度可能达到1000,但只会出现一次;
实现细节:用stk记录下路径上的序号,为了方便每次枚举时,初始化每个数的个数;同时也可递推出当前两位的和;
没使用map,使用map的话,插入和查询都是log(n),总时间复杂度为O(n^2*log(n)*len)len为每次搜索的长度,且常数较大;用数组模拟,时间复杂度中少了log(n)与map带来的额外的常数,只需46ms 0k

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<string.h> #include<algorithm> #include<vector> #include<cmath> #include<stdlib.h> #include<time.h> #include<stack> #include<set> #include<map> #include<queue> using namespace std; #define rep0(i,l,r) for(int i = (l);i < (r);i++) #define rep1(i,l,r) for(int i = (l);i <= (r);i++) #define rep_0(i,r,l) for(int i = (r);i > (l);i--) #define rep_1(i,r,l) for(int i = (r);i >= (l);i--) #define MS0(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a)) #define MS1(a) memset(a,-1,sizeof(a)) #define MSi(a) memset(a,0x3f,sizeof(a)) #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define lson l, m, rt << 1 #define rson m+1, r, rt << 1|1 typedef __int64 ll; template<typename T> void read1(T &m) { T x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} m = x*f; } template<typename T> void read2(T &a,T &b){read1(a);read1(b);} template<typename T> void read3(T &a,T &b,T &c){read1(a);read1(b);read1(c);} template<typename T> void out(T a) { if(a>9) out(a/10); putchar(a%10+'0'); } int v[1010],num[1010],stk[1010];//stk长度也要为1000,因为前面两个为0时,len可能为最大值 int main() { int n; read1(n); rep0(i,0,n) read1(v[i]); sort(v,v + n); int ans = 0,cnt = 0; rep0(i,0,n){ int t = i; while(i < n - 1 && v[i] == v[i + 1]) i++; num[cnt] = i - t + 1; v[cnt++] = v[i];//压缩 } v[cnt] = 2e9; rep0(i,0,cnt){ rep0(j,0,cnt){ if(i != j || num[j] > 1){ stk[1] = i;stk[2] = j; int len = 2,val = v[i] + v[j]; num[i]--,num[j]--; int down = lower_bound(v,v+cnt,val) - v; while(v[down] == val && num[down]){ num[down]--; val -= v[stk[len-1]]; val += v[down]; stk[++len] = down; down = lower_bound(v,v+cnt,val) - v; } ans = max(ans,len); rep1(i,1,len) num[stk[i]]++; } } } out(ans); return 0; }



