C++ Run-time type information
static binding和dynamic binding
Binding一般指的将一个物体绑定到另外一个物体上,C++编译时指的Binding是,将函数调用和函数具体的定义连接到一起。在C++里,当函数被调用时,程序会把对应函数的定义部分链接到函数的声明处。

Binding分为static和dynamic binding两种,区别为:
- static binding位于编译期,后者位于运行期,所以也叫early binding和late binding。
- 如果一个函数被调用时的参数能在编译期决定,那么就属于static binding,否则是dynamic binding。
- 函数重载,运算符重载和普通的函数调用都是static binding,而dynamic binding只能通过virtual functions
- static binding更快,但dynamic binding更灵活
RTTI
run-time type information or run-time type identification (RTTI),可以用于在运行时知道Object的类型,需要添加头文件typeinfo,具体用法如下:
//The typeid operator retrieves a std::type_info object describing the most derived type of an object:
// typeid返回的类型为std::type_info
if (typeid(Person) == typeid(*obj)) {
serialize_person( obj );
}
举一个例子,代码如下所示:
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
class Person {
public:
virtual ~Person() = default;
};
class Employee : public Person {};
int main() {
Person person;
Employee employee;
Person* ptr = &employee;
Person& ref = employee;
// The string returned by typeid::name is implementation-defined.
std::cout << typeid(person).name()
<< std::endl; // Person (statically known at compile-time).
std::cout << typeid(employee).name()
<< std::endl; // Employee (statically known at compile-time).
std::cout << typeid(ptr).name()
<< std::endl; // Person* (statically known at compile-time).
std::cout << typeid(*ptr).name()
<< std::endl; // Employee (looked up dynamically at run-time
// because it is the dereference of a
// pointer to a polymorphic class).
std::cout << typeid(ref).name()
<< std::endl; // Employee (references can also be polymorphic)
}
输出如下:
class Person
class Employee
class Person *
class Employee
class Employee
普通的数据类型也可以输出:
std::cout << typeid(6.0f).name() << std::endl; // 输出float
std::cout << typeid(6).name() << std::endl; // 输出int
RTII可以在Runtime得知类的类型,可以用于dynamic_cast函数,不过RTII会造成性能开销,相关链接参考https://stackoverflow.com/questions/579887/how-expensive-is-rtti
dynamic_cast
dynamic_cast用于基类对象和派生类对象之间的转换,尤其是用于基类对象向派生类对象的转换
正常的如果直接进行强转,如果转错了会报错,而用dynamic_cast进行转换,如果转换错误,不会报错,而是会返回一个空指针,从而可以进行条件判断,举个例子:
class Entity{} // Entity是基类
class Enemy : public Enity{} // 子类
class Player : public Enity{} // 子类
如果输入一个对象A,A的类型为Entity,但是我不知道具体是Enemy还是Player类型,如果正常的(Player)A,是不行的,这个时候就通过dynamic_cast<Player>来进行转换。注意dynamic_cast必须用于运行时,也就是说转换的对象里必须包含多态属性,基类里需要有虚函数,一般的基类都会有虚函数(虚析构函数)。
那么dynamic_cast怎么判断对象A是Enemy对象还是Player对象呢,它就是通过RTTI来判断的,在VS2017里,可以对其进行设置,如下图所示:
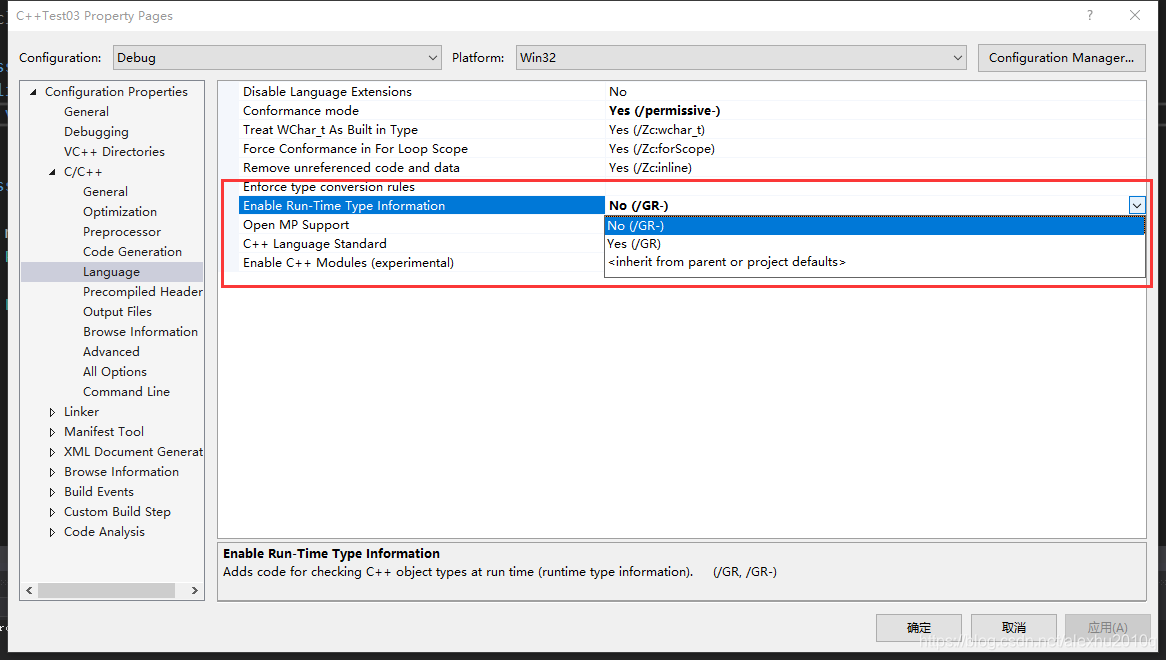
如果我们关掉RTTI的功能,原本可以成功运行的代码就会报错,代码如下所示:
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
class Person {
public:
virtual ~Person() = default;
};
class Employee : public Person {};
int main() {
Person *p = new Employee();
Employee* p0 = dynamic_cast<Employee*>(p);
}
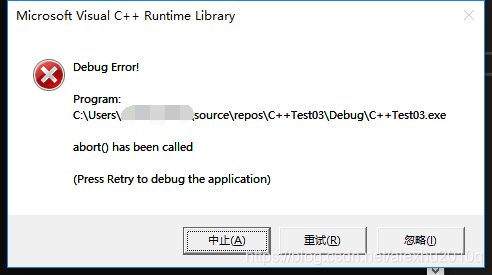
关掉RTII后会报错,如下图所示:




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本