kubernetes API服务器的安全防护
kubernetes API服务器的安全防护
正文
12.1.了解认证机制
启动API服务器时,通过命令行选项可以开启认证插件。
12.1.1.用户和组
了解用户:
分为两种连接到api服务器的客户端:
1.真实的人
2.pod,使用一种称为ServiceAccount的机制
了解组:
认证插件会连同用户名,和用户id返回组,组可以一次性给用户服务多个权限,不用单次赋予,
system:unauthenticated组:用于所有认证插件都不会认证客户端身份的请求。
system:authenticated组:会自动分配给一个成功通过认证的用户。
system:serviceaccount组:包含 所有在系统中的serviceaccount。
system:serviceaccount:<namespace>组:包含了所有在特定命名空间中的serviceAccount。
12.1.2 ServiceAccount介绍
每个pod中都包含/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token文件,如下图所示,文件内容用于对身份进行验证,token文件持有serviceaccount的认证token。

应用程序使用token去连接api服务器时,认证插件会对serviceaccount进行身份认证,并将serviceaccount的用户名传回到api服务器内部。
serviceaccount的用户名格式如下:
system:serviceaccount:<namespace>:<service account name>
ServiceAccount是运行在pod中的应用程序,和api服务器身份认证的一中方式。
了解ServiceAccount资源
ServiceAcount作用在单一命名空间,为每个命名空间创建默认的ServiceAccount。
多个pod可以使用相同命名空间下的同一的ServiceAccount,
ServiceAccount如何与授权文件绑定
在pod的manifest文件中,可以指定账户名称的方式,将一个serviceAccount赋值给一个pod,如果不指定,将使用该命名空间下默认的ServiceAccount.
可以 将不同的ServiceAccount赋值给pod,让pod访问不同的资源。
12.1.3创建ServiceAccount
为了集群的安全性,可以手动创建ServiceAccount,可以限制只有允许的pod访问对应的资源。
创建方法如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
$ kubectl get saNAME SECRETS AGEdefault 1 21h$ kubectl create serviceaccount yaohongserviceaccount/yaohong created$ kubectl get saNAME SECRETS AGEdefault 1 21hyaohong 1 3s |
使用describe来查看ServiceAccount。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
$ kubectl describe sa yaohongName: yaohongNamespace: defaultLabels: <none>Annotations: <none>Image pull secrets: <none>Mountable secrets: yaohong-token-qhbxn //如果强制使用可挂载秘钥。那么使用这个serviceaccount的pod只能挂载这个秘钥Tokens: yaohong-token-qhbxnEvents: <none> |
查看该token,
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
$ kubectl describe secret yaohong-token-qhbxnName: yaohong-token-qhbxnNamespace: defaultLabels: <none>Annotations: kubernetes.io/service-account.name: yaohong kubernetes.io/service-account.uid: a3d0d2fe-bb43-11e9-ac1e-005056870b4dType: kubernetes.io/service-account-tokenData====ca.crt: 1342 bytesnamespace: 7 bytestoken: eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IiJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzL3NlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Iiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9uYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJkZWZhdWx0Iiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9zZWNyZXQubmFtZSI6Inlhb2hvbmctdG9rZW4tcWhieG4iLCJrdWJlcm5ldGVzLmlvL3NlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50L3NlcnZpY2UtYWNjb3VudC5uYW1lIjoieWFvaG9uZyIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXMuaW8vc2VydmljZWFjY291bnQvc2VydmljZS1hY2NvdW50LnVpZCI6ImEzZDBkMmZlLWJiNDMtMTFlOS1hYzFlLTAwNTA1Njg3MGI0ZCIsInN1YiI6InN5c3RlbTpzZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudDpkZWZhdWx0Onlhb2hvbmcifQ.BwmbZKoM95hTr39BuZhinRT_vHF-typH4anjkL0HQxdVZEt_eie5TjUECV9UbLRRYIqYamkSxmyYapV150AQh-PvdcLYPmwKQLJDe1-7VC4mO2IuVdMCI_BnZFQBJobRK9EdPdbZ9uxc9l0RL5I5WyWoIjiwbrQvtCUEIkjT_99_NngdrIr7QD9S5SxHurgE3HQbmzC6ItU911LjmxtSvBqS5NApJoJaztDv0cHKvlT67ZZbverJaStQdxr4yiRbpSycRNArHy-UZKbNQXuzaZczSjVouo5A5hzgSHEBBJkQpQ6Tb-Ko5XGjjCgV_b9uQvhmgdPAus8GdFTTFAbCBw |
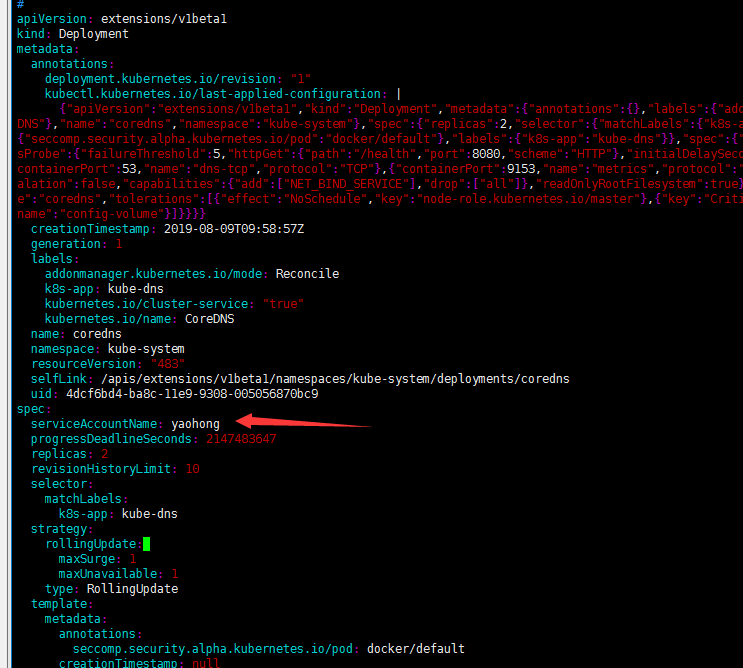
12.1.4将ServiceAccount分配给pod
在pod中定义的spec.serviceAccountName字段上设置,此字段必须在pod创建时设置后续不能被修改。
自定义pod的ServiceAccount的方法如下图
12.2通过基于角色的权限控制加强集群安全
12.2.1.介绍RBAC授权插件
RBAC授权插件将用户角色作为决定用户能否执行操作的关机因素。
12.2.2介绍RBAC授权资源
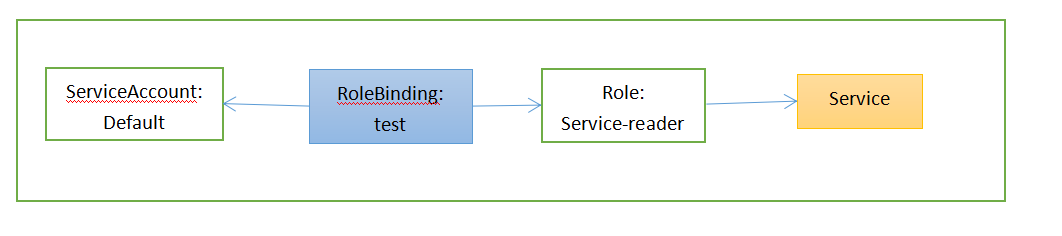
RBAC授权规则通过四种资源来进行配置的,他们可以分为两组:
Role和ClusterRole,他们决定资源上可执行哪些动词。
RoleBinding和ClusterRoleBinding,他们将上述角色绑定到特定的用户,组或者ServiceAccounts上。
Role和RoleBinding是namespace级别资源
ClusterRole和ClusterRoleBinding是集群级别资源
12.2.3使用Role和RoleBinding
Role资源定义了哪些操作可以在哪些资源上执行,
创建Role
service-reader.yml
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: Rolemetadata: namespace: kube-system name: service-readerrules:- apiGroups: [""] verbs: ["get", "list"] resources: ["services"] |
在kube-system中创建Role
|
1
|
#kubectl -n kube-system create -f service-reader.yml |
查看该namespace下的role
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
$ kubectl -n kube-system get roleNAME AGEextension-apiserver-authentication-reader 41hkube-state-metrics-resizer 41hservice-reader 2m17ssystem::leader-locking-kube-controller-manager 41hsystem::leader-locking-kube-scheduler 41hsystem:controller:bootstrap-signer 41hsystem:controller:cloud-provider 41hsystem:controller:token-cleaner 41h |
绑定角色到ServiceAccount
将service-reader角色绑定到default ServiceAccount
|
1
2
|
$ kubectl create rolebinding test --role=service-readerrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/test created |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
$ kubectl get rolebinding test -o yamlapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: RoleBindingmetadata: creationTimestamp: 2019-08-11T03:40:51Z name: test namespace: default resourceVersion: "239323" selfLink: /apis/rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1/namespaces/default/rolebindings/test uid: d0aff243-bbe9-11e9-ac1e-005056870b4droleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: Role name: service-reader |
12.2.4使用ClusterRole和ClusterRoleBinding
查看集群ClusterRole
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
# kubectl get clusterroleNAME AGEadmin 42hcluster-admin 42hedit 42hflannel 42hkube-state-metrics 42hsystem:aggregate-to-admin 42h... |
创建ClusterRole
|
1
|
kubectl create clusterrole flannel --verb=get,list -n kube-system |
查看yaml文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
# kubectl get clusterrole flannel -o yamlapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: ClusterRolemetadata: annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: | {"apiVersion":"rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1","kind":"ClusterRole","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"flannel"},"rules":[{"apiGroups":[""],"resources":["pods"],"verbs":["get"]},{"apiGroups":[""],"resources":["nodes"],"verbs":["list","watch"]},{"apiGroups":[""],"resources":["nodes/status"],"verbs":["patch"]}]} creationTimestamp: 2019-08-09T09:58:42Z name: flannel resourceVersion: "360" selfLink: /apis/rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1/clusterroles/flannel uid: 45100f6f-ba8c-11e9-8f57-005056870608rules:- apiGroups: - "" resources: - pods verbs: - get- apiGroups: - "" resources: - nodes verbs: - list - watch- apiGroups: - "" resources: - nodes/status verbs: - patch |
创建clusterRoleBinding
|
1
2
|
$ kubectl create clusterrolebinding cluster-tetst --clusterrole=pv-reader --serviceaccount=kuebsystem:yaohongclusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-tetst created |

12.2.5了解默认的ClusterRole和ClusterRoleBinding
如下所示使用kubectl get clusterroles和kubectl get clusterrolesbinding可以获取k8s默认资源。
用edit ClusterRole允许对资源进行修改
用admin ClusterRole赋予一个命名空间全部的权限
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
$ kubectl get clusterrolesNAME AGEadmin 44hcluster-admin 44hedit 44hflannel 44hkube-state-metrics 44hsystem:aggregate-to-admin 44hsystem:aggregate-to-edit 44hsystem:aggregate-to-view 44hsystem:auth-delegator 44hsystem:aws-cloud-provider 44hsystem:basic-user 44hsystem:certificates.k8s.io:certificatesigningrequests:nodeclient 44hsystem:certificates.k8s.io:certificatesigningrequests:selfnodeclient 44hsystem:controller:attachdetach-controller 44hsystem:controller:certificate-controller 44hsystem:controller:clusterrole-aggregation-controller 44h。。。 |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
$ kubectl get clusterrolebindingsNAME AGEclust-tetst 17mcluster-admin 44hcluster-tetst 13mflannel 44hkube-state-metrics 44hkubelet-bootstrap 44hsystem:aws-cloud-provider 44hsystem:basic-user 44hsystem:controller:attachdetach-controller 44hsystem:controller:certificate-controller 44h。。。 |



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?