PYQT5:基于QsciScintilla的代码编辑器分析8--子菜单及对话框
这一篇介绍子菜单“example”、“recentProject”、“Chip”、“Port”;对话框“complier”、“download setting”、“Find”的实现思路和源代码。
1.example子菜单

在第1章说到:example子菜单在实现时,要求将文件夹《example》放在与软件相同的目录下。example里面有子文件夹,例如图中的《01BasicCode》《02display》等。《01BasicCode》下面又有子文件夹,例如图中的《01target001》,后者里面就有一个同名的.cbp的文件,也就是《01target001.cbp》。如果工程文件名和所在目录不同名,将会检测不到工程文件,不能添加到example菜单中。
#“fileMenu” 增加exampleMenu,再增加子菜单,example文件夹下面的每个子文件夹就是一个子菜单
#子菜单再增加Action,每个子子文件夹对应一个Action(就是工程名)
exampleMenu = QMenu('example', self)
fileMenu.addMenu(exampleMenu)
#0. exampleMenu 上的动作项触发信号链接到槽函数 OpenRecentProject
exampleMenu.triggered[QAction].connect(self.OpenRecentProject)
if os.path.exists(self.Code51_dir+'/example'):
#1. 遍历examp 文件夹下面的子文件夹
for dir in os.listdir(self.Code51_dir+'/example'):
if os.path.isfile(dir): #1.2 为文件 则忽略
continue
#2. 子文件夹也生成一个子子菜单
exampleSubMenu=QMenu(dir, self)
exampleMenu.addMenu(exampleSubMenu)
fulldir = self.Code51_dir+'/example'+'/'+dir
#3. 遍历子文件夹里面的子子文件夹,子子文件夹就是工程所在
for _dir in os.listdir(fulldir):
if os.path.isfile(_dir):
continue
# example dir _dir _dir.cbp
#3.1 举例 example/01BasicCode/01target001/01target001.cbp
sub_fulldir=fulldir+'/'+_dir+'/'+_dir+'.cbp'
#4. 将工程名创建为一个动作项Action。
if os.path.exists(sub_fulldir):
fileAction = self.createAction(sub_fulldir, None, None, None,
'Open an example project', checkable=False)
exampleSubMenu.addAction(fileAction)
然后在点击Action时,通过Action.text()获得工程的完整路径,就可以打开工程:
def OpenRecentProject(self, qaction):
#1. 已打开了工程,先关闭
if len(self.fullfile) !=0:
self.ProjectClose()
#2. 获取工程完整路径
self.fullfile = qaction.text()
if os.path.exists(self.fullfile)==None:
self.SetTipString("工程文件名不存在。打开失败。")
#3. 打开工程
self.OpenProjectByName()
OpenProjectByName()的源代码分析请参考第4章《xml格式的工程文件与树状列表部件》。
2.recentProject子菜单

本子菜单位于菜单Project的最后一项,记录了最近打开的10个工程路径。在打开软件时,从保存的初始化文件《Setting.ini》读入最近的10个工程路径。关闭软件时,当前的工程路径将保存回《Setting.ini》,且排在第1位。子菜单的动作项也是链接到上面的函数OpenRecentProject().
#1. 创建RecentProject 子菜单,依附在 Project 菜单的最后一项
self.RecentProject = QMenu('recent Project', self)
projectMenu.addMenu(self.RecentProject)
fileGroup = QActionGroup(self)
#2.从《setting.ini》读入10个工程路径
settings=QSettings("setting.ini",QSettings.IniFormat)
settings.setIniCodec(QTextCodec.codecForName("utf-8"))
filesize= settings.beginReadArray("recentProject")
#3. 每个 工程路径 就是一个动作项 Action
for i in range(filesize):
settings.setArrayIndex(i)
fileAction = self.createAction(settings.value("File_Name"), None, None, None,
'Open a project', checkable=True)
self.RecentProject.addAction(fileAction)
fileGroup.addAction(fileAction)
settings.endArray()
#4. 动作项触发信号链接到槽函数 OpenRecentProject
self.RecentProject.triggered[QAction].connect(self.OpenRecentProject)
与examp子菜单类似,点击Action时,通过Action.text()获得工程的完整路径,就可以打开工程。
3.Chip子菜单
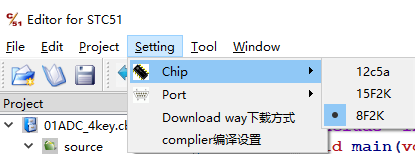
Chip子菜单用于选择目标芯片,实际就是告诉软件用什么下载协议。这里只提供3类芯片(4种具体型号):
1】STC12C5A08S2
2】STC15F2K60S2
3】STC8F2K32S2
4】STC8A8K64S4A12(与STC8F2K32S2相同协议)
因为手头只有这几种,其它的没有测试。详情在第9章讲解。打开本编辑器时,会从《setting.ini》读取上一次的设定,选择芯片时会触发对应的槽函数,将改动保存到《setting.ini》。
#创建setting——menu
# -----Chip-select 1]12C5A ; 2]15F2K; 3]8F2K
# -----Port-select
SettingMenu = self.menuBar().addMenu("&Setting")
self.ChipMenu = QMenu('Chip', self)
self.ChipMenu.setIcon(QIcon(":/{0}.png".format("chip")))
SettingMenu.addMenu(self.ChipMenu)
Chip1 = self.createAction(PROTOCOL_12C5A, self.ChangChip, None, None,
'STC12C5A08S2',checkable=True )
Chip2 = self.createAction(PROTOCOL_15F2K, self.ChangChip, None, None,
'STC15F2K60S2', checkable=True)
Chip3 = self.createAction(PROTOCOL_8F2K, self.ChangChip, None, None,
'STC8F2K32S2', checkable=True)
PortGroup = QActionGroup(self) #QActionGroup 里面的项是互斥的,只能有一个被选中
PortGroup.addAction(Chip1)
PortGroup.addAction(Chip2)
PortGroup.addAction(Chip3)
self.addActions(self.ChipMenu, (Chip1, Chip2, Chip3))
# 根据 保存的设置信息,将对应的芯片项打钩
actions = self.ChipMenu.actions()
self.Chipstr = settings.value("Download/Chip" )
for i in range(len(actions)):
if actions[i].text() == self.Chipstr:
actions[i].setChecked(True)
break
def ChangChip(self): #选择芯片就是选择下载协议
actions = self.ChipMenu.actions()
for i in range(len(actions)):
if actions[i].isChecked():
self.Chipstr = actions[i].text()
settings=QSettings("setting.ini",QSettings.IniFormat)
settings.setIniCodec(QTextCodec.codecForName("utf-8"))
settings.setValue("Download/Chip",self.Chipstr )
break
4.串口Port子菜单
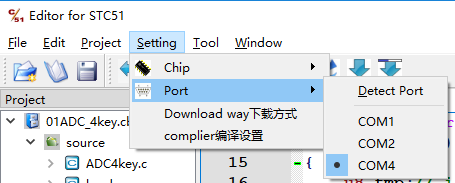
在打开本编辑器时,初始化过程读取上一次的保存信息来决定哪个串口打钩。如果串口有变动,点击“Detect Port”刷新串口列表。
#生成 串口子菜单
self.PortMenu = QMenu('Port', self)
self.PortMenu.setIcon(QIcon(":/{0}.png".format("com32")))
DetectAct = self.createAction("&Detect Port", self.DetectPort, None, None,
'Creat a project')
SettingMenu.addMenu(self.PortMenu)
self.addActions(self.PortMenu,(DetectAct, None) )
#检测有限串口
self.DetectPort()
# 根据 保存的设置信息,将对应的串口打钩
actions = self.PortMenu.actions()
self.Portstr = settings.value("Download/Port" )
for i in range(2, len(actions)):
if actions[i].text() == self.Portstr:
actions[i].setChecked(True)
break
def DetectPort(self):
#1]检测所有存在的串口,将信息存储在字典中
PortGroup = QActionGroup(self)
port_list = list(serial.tools.list_ports.comports())
actions = self.PortMenu.actions()
#2]self.PortMenu.保留前2项,其它清空
for i in range(2, len(actions)):
self.PortMenu.removeAction(actions[i])
#3]将port_list 添加到菜单中
for port in port_list:
portAction = self.createAction(port[0], self.ChangPort, None, None,
'选择下载口', checkable=True)
self.PortMenu.addAction(portAction)
PortGroup.addAction(portAction)
def ChangPort(self):
actions = self.PortMenu.actions()
for i in range(2, len(actions)):
if actions[i].isChecked():
self.Portstr = actions[i].text()
settings=QSettings("setting.ini",QSettings.IniFormat)
settings.setIniCodec(QTextCodec.codecForName("utf-8"))
settings.setValue("Download/Port", self.Portstr)
5.下载方式选择对话框

下载hex文件的方式:1】冷启动;2】发送[0x5a,0x3a,0x6c];3】自定义数据,输入时用空格隔开,2个十六进制数字对齐。
波特率是指目标芯片运行时的下载口的波特率。
#在设置菜单3中增加一个弹出对话框,用于选择下载方式:1]断电;2]默认指令;3]自定义指令
SettingAction = self.createAction("Download way下载方式", self.OpenSettingDlg, None, None,
'选择下载方式', checkable=False)
self.downloadWay = settings.value("Download/way" )
self.DIYString=settings.value("Download/baudrateIndex")
if self.DIYString is not None: #借用DIYString
self.baudIndex=int(self.DIYString)
self.DIYString = settings.value("Download/DIY_Data" )
#在设置菜单4中增加【编译设置】对话框,用于设置:1]编译路径;2]外部ram大小 --xdata 从工程文件中读取
complierSettingAction = self.createAction("complier编译设置", self.OpenComplierSettingDlg, None, None,
'设置编译器路径和外部ram大小', checkable=False)
self.addActions(SettingMenu,(SettingAction, complierSettingAction))
self.isComplierPathDefault=settings.value("Complier/Path/Default" )
if self.isComplierPathDefault != None and self.isComplierPathDefault == '1':
self.compilePath = self.Code51_dir
else:
self.compilePath =settings.value("Complier/Path/Input" )
self.isXdataDefault=settings.value("Complier/Xdata/Default" )
这里的代码包含了下一节的编译设置。调用对话框的函数OpenSettingDlg()d 源码:
def OpenSettingDlg(self):
SettingDlg = Setting()
#1. 初始化对话框参数
if self.downloadWay == '1' :
SettingDlg.radioButton_1.setChecked(True)
elif self.downloadWay == '2' :
SettingDlg.radioButton_2.setChecked(True)
else :
SettingDlg.radioButton_3.setChecked(True)
SettingDlg.lineEdit.setText(self.DIYString)
SettingDlg.comboBox.setCurrentIndex(self.baudIndex)
#2.显示对话框
ret = SettingDlg.exec_()
#3. 对话框按下 OK 时,保存设置改动
if ret:
settings=QSettings("setting.ini",QSettings.IniFormat)
if SettingDlg.radioButton_1.isChecked():
self.downloadWay = '1'
settings.setValue("Download/way" , self.downloadWay)
elif SettingDlg.radioButton_2.isChecked():
self.downloadWay = '2'
settings.setValue("Download/way" , self.downloadWay)
else :
self.downloadWay = '3'
settings.setValue("Download/way" , self.downloadWay)
self.DIYString=SettingDlg.lineEdit.text()
self.baudIndex=SettingDlg.comboBox.currentIndex()
settings.setValue("Download/DIY_Data" ,self.DIYString)
settings.setValue("Download/baudrateIndex", self.baudIndex)
6.编译器设置对话框

编译器路径选择后保存在软件目录下的《setting.ini》文件中;外部ram则保存于工程文件《xxx.cbp》中。
def OpenComplierSettingDlg(self):
settings=QSettings("setting.ini",QSettings.IniFormat)
SettingDlg = complierSetting(self)
#1.初始化设置,xdata的参数不是通用的,每个工程都可以不同,要保存在工程文件中。
if self.isComplierPathDefault == '1':
SettingDlg.rdb_pathDefault.setChecked(True)
else:
SettingDlg.rdb_pathSelect.setChecked(True)
SettingDlg.lineEdit_path.setText(settings.value("Complier/Path/Input" ))
if self.isXdataDefault == '1':
SettingDlg.rdb_xdataDefault.setChecked(True)
SettingDlg.lineEdit_xdata.setEnabled(False)
else:
SettingDlg.radioButton.setChecked(True)
SettingDlg.lineEdit_xdata.setText(self.XdataLen)
#2.打开对话框
ret = SettingDlg.exec_()
if not ret :
return
#3.保存设置
if SettingDlg.rdb_pathDefault.isChecked():
self.isComplierPathDefault = '1'
else:
self.isComplierPathDefault = '0'
settings.setValue("Complier/Path/Default",self.isComplierPathDefault)
self.compilePath=SettingDlg.lineEdit_path.text()
settings.setValue("Complier/Path/Input",self.compilePath)
if SettingDlg.rdb_xdataDefault.isChecked():
self.isXdataDefault = '1'
SettingDlg.lineEdit_xdata.setText('8192')
else:
self.isXdataDefault = '0'
self.XdataLen = SettingDlg.lineEdit_xdata.text()
settings.setValue("Complier/Xdata/Default",self.isXdataDefault)
#settings.setValue("Complier/Xdata/Input",SettingDlg.lineEdit_xdata.text())
#写人工程文件
self.mycbp.SetOptionOfXram(self.XdataLen)
7.查找对话框
通过菜单Edit–>Find 或者 快捷键 Ctrl + F打开查找对话框。如果打开查找窗口时已有选择文字, 所选文字将自动传入;当然也可以复制粘贴,手动输入。查找后的结果显示在“built output”窗口。双击窗口将读取鼠标所在行的文字对应的文件名和行数,进行跳转。实现跳转的代码看回第7章《编译器命令与信息输出视图》第2节信息输出视图的源代码。

主窗口MainWindow对应菜单动作的槽函数源代码:
def editFind(self):
#1. 获取Mdi的焦点窗口
textEdit = self.mdi.activeSubWindow()
if textEdit is None :
return
#2. 获取窗口里面的 SciTextEdit
textEdit=textEdit.widget()
if textEdit is None :
return
#3. 初始化 查找窗口,传入SciTextEdit 中选中的文字
FindDlg = FindText(self)
FindDlg.lineEdit_destText.setText(textEdit.selectedText())
#4. 显示查找窗口
FindDlg.exec_()
查找对话框FindText类的源代码:
class FindText(QDialog, Ui_Dialog):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
super(FindText, self).__init__(parent)
self.setupUi(self)
#1.主窗口作为父窗口
self.parent = parent
#2. 点击查找按钮的信号的槽函数
self.ButtonFind.clicked.connect(self.FineTextInFiles)
self.rdb_cbpDir.setChecked(True)
def FineTextInFiles(self):
self.parent.text_browser.clear()
if os.path.isdir(self.parent.ProjectDir) == False:
self.parent.text_browser.append("工程目录出错。")
return
text_file_list = []
#1. 仅仅查找当前的文件
if self.rdb_currentFile.isChecked():
text_file_list.append(self.parent.mdi.activeSubWindow().widget().filename)
#2. 扫描整个工程目录的c、h文件,并存放到 text_file_list
else:
walk_tree = os.walk(self.parent.ProjectDir)
#"walk" through the directory tree and save the readable files to a list
for root, subFolders, files in walk_tree:
for file in files:
full_with_path = os.path.join(root, file)
if os.path.exists(full_with_path) != None:
endChar = full_with_path[-1]
if 'h' == endChar or 'H' == endChar or 'c' == endChar or 'C' == endChar:
full_with_path = full_with_path.replace("\\", "/")
text_file_list.append(full_with_path)
#3. 开始查找
destCount=0
for file in text_file_list:
fin = open(file, "r", encoding='utf-8', errors="ignore")
input_file = fin.read()
input_str = input_file.splitlines(False)
for i in range(len(input_str) ) :
if self.lineEdit_destText.text() in input_str[i]:
destCount += 1
self.parent.text_browser.append("%s:%d:%s"%(file, i+1, input_str[i]))
#4. 在信息输出窗口中显示结果
self.parent.text_browser.append("在 %d 个文件中找到 %d 处。"%(len(text_file_list), destCount))
#5. 发送一个 QCloseEvent,窗口自杀
e = QCloseEvent()
QApplication.postEvent(self, e)




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?