java NIO 随笔
一,NIO入门
NIO 是new io的缩写,说实话,nio api比较难用,所用大家需要采用网络通信的时候,普通首先想到的是netty,不直接使用NIO,但是你不了解NIO,说实话,你也理解不了netty
好多人不理解socket 是干啥的,只知道socket是Java 用来通信的。应用层协议(HTTP 协议)如何发送数据,这个协议使我们自己定义的,我们需要和其他机器通信,就必须通过
TCP协议来完成数据传输。你可以理解socket就是应用层和传输层的适配器,负责将应用层的数据转换为TCP协议需要的数据。
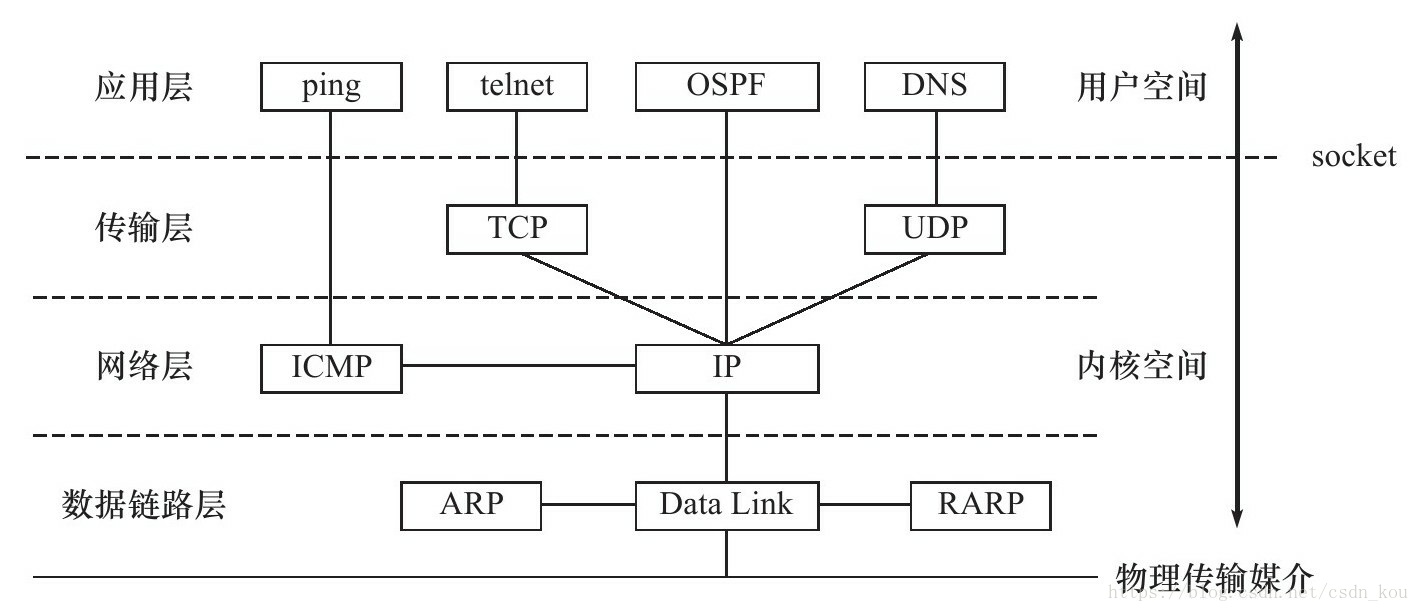
我们先来一个demo,通过TCP 协议发送一个文件 我们先学会用,在来考虑细节。
package com.ppdai.user.weixin.controller.test;
import com.ppdai.common.collect.Lists;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.core.Constants;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* Created by huxuhong on 2020/3/11.
*/
@Slf4j
public class TcpClient {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
startClient("localhost",8080);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void startClient(String serverIp, int serverPort) throws IOException{
log.info("创建一个SocketChannel,指定为非阻塞模式");
/*
* 创建一个SocketChannel,指定为非阻塞模式
* A selectable channel for stream-oriented connecting sockets.
*/
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
/*
* 创建一个事件选择器Selector
*/
Selector selector = Selector.open();
/*
* 将创建的SocketChannel注册到指定的Selector上,并指定关注的事件类型为OP_CONNECT
*/
SelectionKey selectionKey = socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
/*
* 连接到指定的服务地址,这里有坑socketChannel.connect 异步接口,但是有可能理解返回为true,这里不引申怎么处理啦,等分析kafka-client源码的时候在做解析
* (具体啥时候返回false,true,请看API说明),此时不会触发监控(即selector.select(),此方法可能返回0)
*/
Boolean connection = socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(serverIp, serverPort));
System.out.println("链接结果:"+connection);
/**
* 顾名思义,针对文件的一种channel,类似IO中的FileInputStream,
* 这个类很重要,kafak broker的顺序存储,查找,以及数据推送的客户端都是通过类似的技术mmap(内存映射),sendfile实现的
* java 方式的内存映射(kafka broker 是scala写的)
* fileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 5);
* 有兴趣的话,可以去扩展开研究一下
* fileChannel 写入的操作 不一定比FileInputStream 快,它的优势在于如果大数据写入,每次写入4KB和pageCache大小一致,此时速度最快
* 想知道fileChannel mmap 普通IO 读写速度,以及啥时候能够最大利用他们的优势可以看看下面2篇文章
* https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/673567
* https://blog.csdn.net/alex_xfboy/article/details/90174840
*/
FileChannel inputChannel = new FileInputStream(new File("E:\\huhu\\hudad.txt")).getChannel();
int sendCount = 0;
/*
* 发送文件
*/
while(true){
if(socketChannel.isConnected() && sendCount < 1){
++sendCount;
/**
* 这里在linux环境下采用零拷贝技术(send_file)
*/
inputChannel.transferTo(0,inputChannel.size(),socketChannel);
log.info("connect就绪");
}
/*
* 设置1sec的超时时间,进行IO事件选择操作
*/
int nSelectedKeys = selector.select();
if(nSelectedKeys > 0){
for(SelectionKey skey: selector.selectedKeys()){
/*
* 判断检测到的channel是不是可连接的,将对应的channel注册到选择器上,指定关心的事件类型为OP_READ
*/
if(skey.isConnectable()){
log.info("key connect就绪");
SocketChannel connChannel = (SocketChannel) skey.channel();
connChannel.configureBlocking(false);
/**
* 这里connection成功,直接监控OP_READ,其实一种偷懒方法,应该是先监控OP_WRITE,然后在OP_WRITE处理方法中监控OP_READ
* OP_WRITE 是指channel对应的ByteBuffer 还有空间可以写入
* OP_READ 是指channel对应的ByteBuffer 还存在数据可以读
*/
connChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
/**
* 目的是为了校验是否和服务器连接成功
* SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT触发条件是链接成功或者链接失败抛出异常,所以需要通过finishConnect校验,如果失败,此方法会抛出异常
*/
connChannel.finishConnect();
}
/*
* 若检测到的IO事件是读事件,则处理相关数据的读相关的业务逻辑
*/
else if(skey.isReadable()){
log.info("key read就绪");
SocketChannel readChannel = (SocketChannel) skey.channel();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
/*
* 定义一个ByteBuffer的容器,容量为1k
*/
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readBytes = 0;
int ret = 0;
/*
* 注意,对ByteBuffer的操作,需要关心的是flip,clear等。
*/
while ((ret = readChannel.read(byteBuffer)) > 0) {
readBytes += ret;
byteBuffer.flip();
sb.append(Charset.forName("UTF-8").decode(byteBuffer).toString());
byteBuffer.clear();
}
if (readBytes == 0) {
System.err.println("handle opposite close Exception");
readChannel.close();
}
System.out.println("服务器返回信息"+sb.toString());
}
}
/*
* 一次监听的事件处理完毕后,需要将已经记录的事件清除掉,准备下一轮的事件标记
*/
selector.selectedKeys().clear();
}else{
System.err.println("handle select timeout Exception");
}
}
}
}
package com.ppdai.user.weixin.controller.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* Created by hxh on 2020/3/11.
*/
@Slf4j
public class TcpServer {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
startServer(8080);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/* Set<String> key = new HashSet<String>();
key.add("11");
key.add("22");
Set<String> publicKey = new HashSet<String>();
publicKey = key;
key.add("33");
publicKey.stream().forEach(keyName->{
System.out.println(keyName);
});
//key.clear();
publicKey.stream().forEach(keyName->{
System.out.println("+"+keyName);
});*/
}
public static void startServer(int port) throws IOException {
log.info("开启一个服务channel");
/*
*开启一个服务channel,
*A selectable channel for stream-oriented listening sockets.
*/
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
/*
* 创建一个selector
*/
Selector selector = Selector.open();
/*
* 将创建的serverChannel注册到selector选择器上,指定这个channel只关心OP_ACCEPT事件
*/
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
/*
* select()操作,默认是阻塞模式的,即,当没有accept或者read时间到来时,将一直阻塞不往下面继续执行。
*/
int readyChannels = selector.select();
if (readyChannels <= 0) {
continue;
}
/*
* 从selector上获取到了IO事件,可能是accept,也有可能是read
*/
Set<SelectionKey> SelectonKeySet = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = SelectonKeySet.iterator();
/*
* 循环遍历SelectionKeySet中的所有的SelectionKey
*/
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
if (key.isAcceptable()) { //处理OP_ACCEPT事件
log.info("OP_ACCEPT事件就绪");
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if (key.isReadable()) { //处理OP_READ事件
log.info("OP_READ事件就绪");
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readBytes = 0;
int ret = 0;
/*
* 注意读数据的时候,ByteBuffer的操作,需要flip,clear进行指针位置的调整
*/
while ((ret = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer)) > 0) {
readBytes += ret;
byteBuffer.flip();
sb.append(Charset.forName("UTF-8").decode(byteBuffer).toString());
byteBuffer.clear();
}
if (readBytes == 0) {
System.err.println("handle opposite close Exception");
socketChannel.close();
}
String message = sb.toString();
System.out.println("Message from client: " + message);
if ("client_close".equalsIgnoreCase(message.toString().trim())) {
System.out.println("Client is going to shutdown!");
socketChannel.close();
} else if ("server_close".equalsIgnoreCase(message.trim())) {
System.out.println("Server is going to shutdown!");
socketChannel.close();
serverChannel.close();
selector.close();
System.exit(0);
} else {
String outMessage = "Server response:我已收到";
socketChannel.write(Charset.forName("UTF-8").encode(outMessage));
}
}
/*
* 将selector上当前已经监听到的且已经处理了的事件标记清除掉。
*/
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
上面是一个简单的利用TCP协议,发送一个文件的demo,代码基本上都有注释,就不过多解释
二,理论知识
NIO必然存在2个元素,channel,byteBuffer。他们和stream 有啥区别,或者说NIO和IO的区别。channel有很多种
IO和NIO区别
https://www.cnblogs.com/aspirant/p/8630283.html(理论参考这篇文章)
文件NIO(FileChannle 标准文件channel 不可以设置为非阻塞)
stream,底层是一个一个从磁盘读取字节,然后上层封装起来进行业务处理,而且分为inputstream和outputStream,也就说是单向的。
文件NIO channel 和ByteBuffer 的效果,就像,在目的地和磁盘直接开了一个通道(channel)然后利用卡车(ByteBuffer)一次性传送大量数据,双向,可读可写。
网络NIO
SocketChannel 是一个连接到TCP网络套接字的通道
ServerSocketChannel 可以监听新进来的TCP连接, 就像标准IO中的ServerSocket一样。
DatagramChannel 是一个能收发UDP包的通道
下面以SocketChannel为例,给大家列出来SocketChannel 的上下文,然后熟悉一下每个interface的作用,对后面的kafka-client 发送报文很有帮助

GatheringByteChannel,将多个ByteBuffer 聚合到一个channel中
ScatteringByteChannel 将从channel读初数据,按此存储到多个ByteBuffer中
AbstractSelectableChannel 这个类是用来管理channel的注册,注销和close,主要是配合selector才有效果
ByteChannel 用来实现channel读写ByteBuffer的interface
ByteBuffer 是NIO另外一个最重要的接口
https://blog.csdn.net/mrliuzhao/article/details/89453082(ByteBuffer用法小结,很详细,看完写个demo,你就入门啦)
PS:NIO没用过没关系,现在学习起来也不迟,熟悉一下主要的类,写个demo就入门啦。学无之境,一天不进步就是退步。
PS:NIO使用TCP发送报文会出现沾包和黏包具体原因以及解决方法(https://blog.csdn.net/fgx_123456/article/details/80031821)
posted on 2020-09-23 14:54 柠檬糖大人你尽然盗号 阅读(304) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报





