一张图彻底搞定 explain
explain的用途
1. 表的读取顺序如何 2. 数据读取操作有哪些操作类型 3. 哪些索引可以使用 4. 哪些索引被实际使用 5. 表之间是如何引用 6. 每张表有多少行被优化器查询 ......
explain的执行效果
mysql> explain select * from subject where id = 1 \G
******************************************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: subject
partitions: NULL
type: const
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 4
ref: const
rows: 1
filtered: 100.00
Extra: NULL
******************************************************
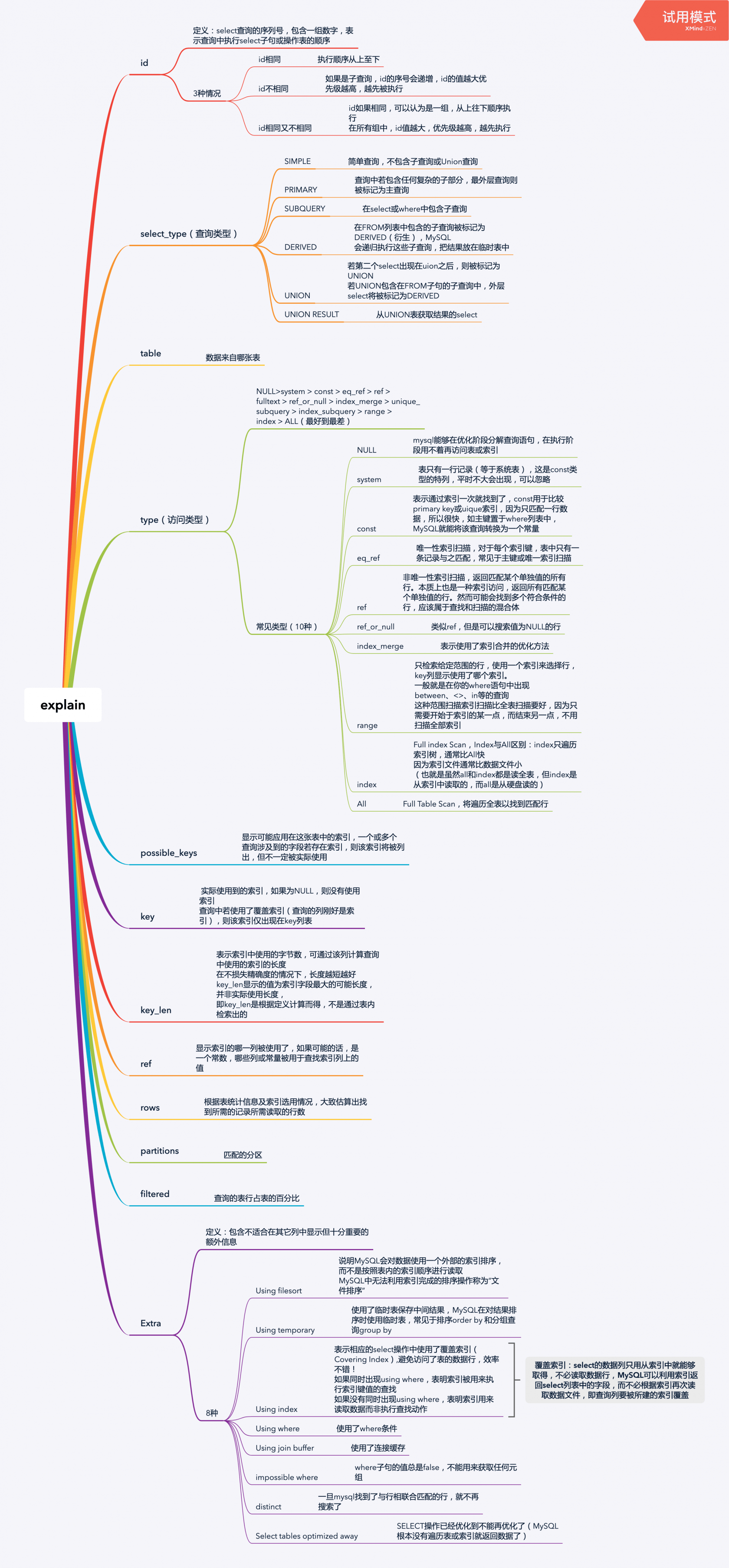
explain包含的字段
1. id //select查询的序列号,包含一组数字,表示查询中执行select子句或操作表的顺序 2. select_type //查询类型 3. table //正在访问哪个表 4. partitions //匹配的分区 5. type //访问的类型 6. possible_keys //显示可能应用在这张表中的索引,一个或多个,但不一定实际使用到 7. key //实际使用到的索引,如果为NULL,则没有使用索引 8. key_len //表示索引中使用的字节数,可通过该列计算查询中使用的索引的长度 9. ref //显示索引的哪一列被使用了,如果可能的话,是一个常数,哪些列或常量被用于查找索引列上的值 10. rows //根据表统计信息及索引选用情况,大致估算出找到所需的记录所需读取的行数 11. filtered //查询的表行占表的百分比 12. Extra //包含不适合在其它列中显示但十分重要的额外信息
图片版
文字版
id字段
1. id相同
执行顺序从上至下 例子: explain select subject.* from subject,student_score,teacher where subject.id = student_id and subject.teacher_id = teacher.id; 读取顺序:subject > teacher > student_score

2. id不同
如果是子查询,id的序号会递增,id的值越大优先级越高,越先被执行 例子: explain select score.* from student_score as score where subject_id = (select id from subject where teacher_id = (select id from teacher where id = 2)); 读取顺序:teacher > subject > student_score

3. id相同又不同
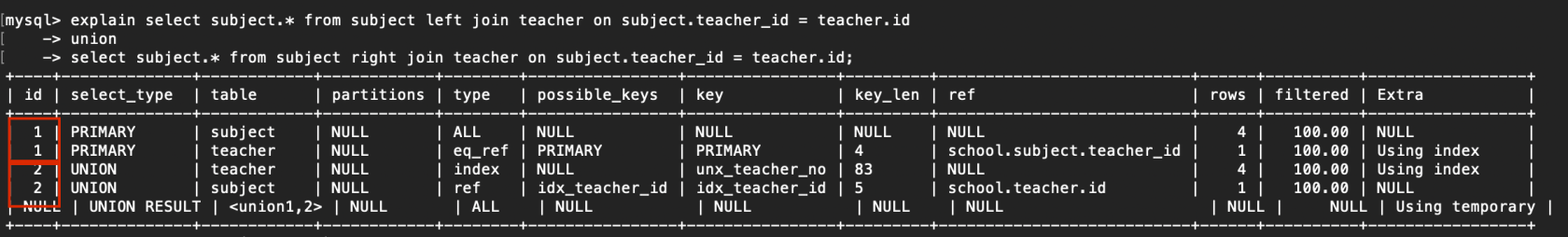
id如果相同,可以认为是一组,从上往下顺序执行 在所有组中,id值越大,优先级越高,越先执行 例子: explain select subject.* from subject left join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id -> union -> select subject.* from subject right join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id; 读取顺序:2.teacher > 2.subject > 1.subject > 1.teacher
select_type字段
1. SIMPLE
简单查询,不包含子查询或Union查询 例子: explain select subject.* from subject,student_score,teacher where subject.id = student_id and subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;

2. PRIMARY
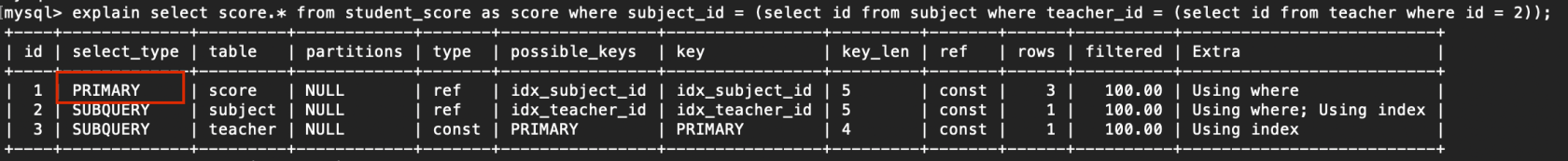
查询中若包含任何复杂的子部分,最外层查询则被标记为主查询 例子: explain select score.* from student_score as score where subject_id = (select id from subject where teacher_id = (select id from teacher where id = 2));
3. SUBQUERY
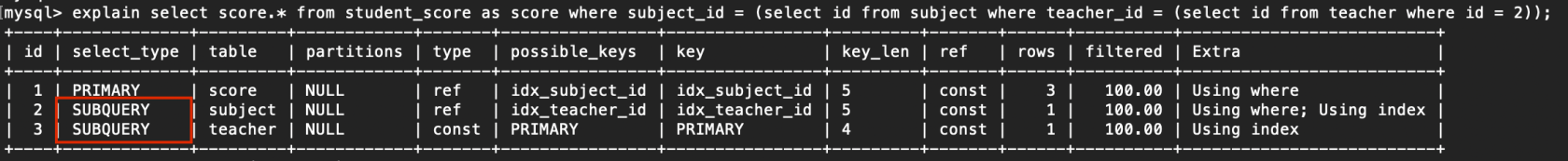
在select或where中包含子查询 例子: explain select score.* from student_score as score where subject_id = (select id from subject where teacher_id = (select id from teacher where id = 2));
详细explain语句知识,请查看原文:https://developer.aliyun.com/article/741250?utm_content=g_1000097577


