python自动化之UI自动化框架搭建三(关键字驱动)
十二、util中新建一个ParseExcel.py,用于实现读取Excel数据文件代码封装
# ending-utf-8 import openpyxl from openpyxl.styles import Border, Side, Font import time class ParseExcel(object): def __init__(self): self.workbook = None self.excelFile = None self.font = Font(color=None) # 设置字体颜色 # 颜色对应的RGB值 self.RGBDict = {'red': 'FFFF3030', 'green': 'FF008B00'} # 将Excel文件加载到内存, 并获取期workbook对象 def loadWordBook(self, excelPathAndName): try: self.workbook = openpyxl.load_workbook(excelPathAndName) except Exception as e: raise e self.excelFile = excelPathAndName return self.workbook # 根据sheet名获取该sheet对象 def getSheetByName(self, sheetName): try: sheet = self.workbook[sheetName] return sheet except Exception as e: raise e # 根据sheet索引号获取该sheet对象 def getSheetByIndex(self, sheetIndex): try: sheet = self.workbook.worksheets[0] return sheet except Exception as e: raise e # 获取sheet中有数据区域的结束行号 def getRowsNumber(self, sheet): return sheet.max_row # 获取sheet中有数据区域的结束列号 def getColsNumber(self, sheet): return sheet.max_column # 获取sheet中有数据区域的开始的行号 def getStartRowsNumber(self, sheet): return sheet.min_row # 获取sheet中有数据区域的开始的列号 def getStartColsNumber(self, sheet): return sheet.min_column # 获取sheet中某一行,返回这一行所有数据内容组成的tuple # 下标从1开始,sheet.rows[1]表示第一行 def get_row_value(self, sheet, row, max_col): try: # return sheet.rows[rowNo-1] # 最新版本sheet.rows 返回的为一个生成器,所以不能采用此方法 row_data = [] for num in range(1, max_col+1): cell_value = sheet.cell(row=row, column=num).value row_data.append(cell_value) return row_data except Exception as e: raise e # 获取sheet中某一列,返回这一列所有数据组成的tuple # 下标从1开始,sheet.columns[1]表示第一列 def get_col_value(self, sheet, row, col): try: col_data = [] for num in range(1, row+1): cell_value = sheet.cell(row=num, column=col).value col_data.append(cell_value) return col_data except Exception as e: raise e # 获取某个单元格的值 def get_cell_value(self, sheet, row, col): try: cell_value = sheet.cell(row=row, column=col).value return cell_value except Exception as e: raise e # 获取某个单元的对象,可以根据单元格所在位置的数字索引,也可以根据Excel中单元格的编码及坐标 def getCellOfObject(self, sheet, coordinate=None, rowNo=None, colNo=None): if coordinate is not None: try: return sheet.cell(coordinate=coordinate) except Exception as e: raise e elif coordinate is None and rowNo is not None and colNo is not None: try: return sheet.cell(row=rowNo, column=colNo) except Exception as e: raise e else: raise Exception('Insufficient Coordinates of cell!') # 根据单元格在Excel中的编码坐标或者数字索引坐标向单元格中写入数据,参数style表示颜色 def writeCell(self, sheet, content, coordinate=None, rowNo=None, colNo=None, style=None): if coordinate is not None: try: sheet.cell(coordinate=coordinate).value = content if style is not None: sheet.cell(coordinate=coordinate).font \ = Font(color=self.RGBDict[style]) self.workbook.save(self.excelFile) except Exception as e: raise e elif coordinate is None and rowNo is not None and colNo is not None: try: sheet.cell(row=rowNo, column=colNo).value = content if style is not None: sheet.cell(row=rowNo, column=colNo).font = \ Font(color=self.RGBDict[style]) self.workbook.save(self.excelFile) except Exception as e: raise e else: raise Exception('Insufficient Coordinates of cell!') # 写入当前的时间,下标从1开始 def writeCellCurrentTime(self, sheet, coordinate=None, rowNo=None, colNo=None): now = int(time.time()) timeArray = time.localtime(now) currentTime = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H:%M:%S", timeArray) if coordinate is not None: try: sheet.cell(coordinate=coordinate).value=currentTime self.workbook.save(self.excelFile) except Exception as e: raise e elif coordinate is None and rowNo is not None and colNo is not None: try: sheet.cell(row=rowNo, column=colNo).value = currentTime self.workbook.save(self.excelFile) except Exception as e: raise e else: raise Exception('Insufficient Coordinates of cell!') if __name__ == '__main__': pe = ParseExcel() # 测试使用的Excel文件 pe.loadWordBook('******.xlsx') print("通过名称获取sheet对象的名字:%s" % pe.getSheetByName("测试").title) print("通过index序号获取sheet对象的名字:%s" % pe.getSheetByIndex(0).title) sheet = pe.getSheetByIndex(0) print(type(sheet)) maxRow = pe.getRowsNumber(sheet) # 获取最大行号 maxCol = pe.getColsNumber(sheet) # 获取最大列号 rows = pe.get_row_value(sheet, 3, maxCol) # 获取某一行内容 print(rows) cols = pe.get_col_value(sheet, 1, maxRow) # 获取某一列内容 pe.writeCell(sheet, '测试用', rowNo=26, colNo=1) pe.writeCellCurrentTime(sheet, rowNo=26, colNo=2)
十三、在testData目录中新建一个楼宇测试.xlsx的Excel文件,并在此Excel文件中新建三个工作表(根据实际测试用例情况添加),分别命名为"测试用例"、"登录"、"新建"
测试用例:

登录:
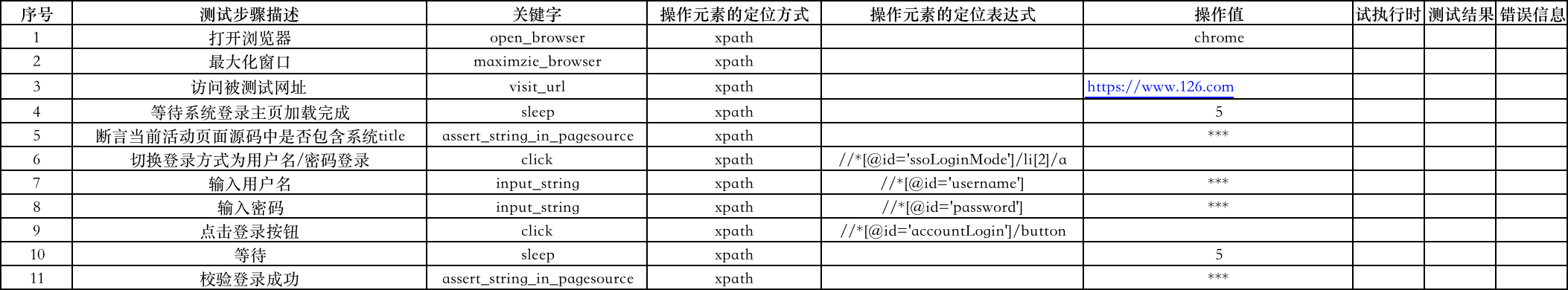
新建:
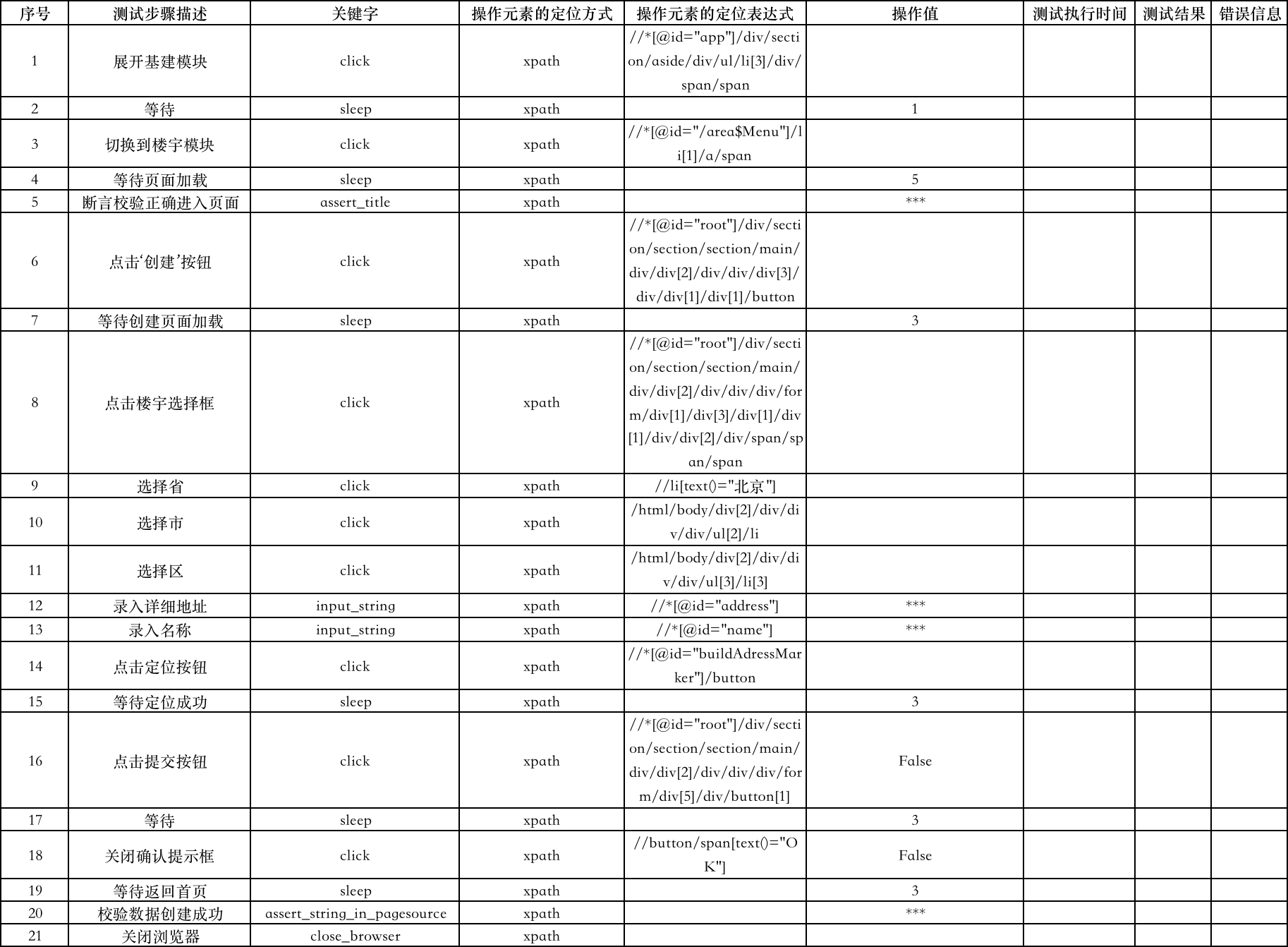
说明:
登录 和 新建工作表中关键字列内容对应 action包中 PageAction.py文件中的函数名;“操作元素定位方式”列表示定位元素所使用的定位方式;“表达式”列表示元素定位方式对应表达式;“操作值”列,表示需要输入的内容
十四、修改config包中的VarConfig.py文件
# encoding=utf-8 import os # 获取当前文件所在目录的父目录的绝对路径 parenthDirPath = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) # 异常截图存放目录绝对路径 screenPicturesDir = parenthDirPath + "/exceptionpictures" # 测试数据文件存放绝对路径 dataFilePath = parenthDirPath + "/testData/楼宇测试" # 测试数据文件中,测试用例表中部分列对应的数字序号 testCase_testCaseName = 2 testCase_testStepSheetName = 4 testCase_testisExecute = 5 testCase_runTime = 6 testCase_testResult = 7 # 用例步骤中,部分列对应的数字序号 testStep_testStepDescribe = 2 testStep_keyWords = 3 testStep_locationType = 4 testStep_locatorExpression = 5 testStep_operateValue = 6 testStep_runTime = 7 testStep_testResult = 8 testStep_errorInfo = 9 testStep_errorPic = 10
十五、修改testScripts包中的TestCreatBuilding.py文件
# encoding=utf-8 from KeyWordsFrameWork.action.PageAction import * from KeyWordsFrameWork.util.ParseExcel import ParseExcel from KeyWordsFrameWork.config.VarConfgi import * import time import traceback # 创建解析Excel对象 excelObj = ParseExcel() # 将Excel数据文件加载到内存 excelObj.loadWordBook(dataFilePath) # 用例或用例步骤执行结束后,向Excel中写入执行结果 def writeTestResult(sheetObj, rowNo, colNo, testResult, errorInfo=None, picPath=None): # 测试通过结果信息未绿色,失败为红色 colorDict = {"pass": "green", "fail": "red"} # 因为测试用例工作表和用例步骤sheet表中都有测试执行时间和测试结果列, # 定义此字典对象是为了区分具体应该写哪个工作表 colsDict = { "testCase": [testCase_runTime, testCase_testResult], "caseStep": [testStep_runTime, testStep_testResult] } try: # 在测试步骤sheet中写入测试时间 excelObj.writeCellCurrentTime(sheetObj, rowNo=rowNo, colNo=colsDict[colNo][0]) # 在测试步骤sheet中写入测试结果 excelObj.writeCell(sheetObj, content=testResult, rowNo=rowNo, colNo=colsDict[colNo][1], style=colorDict[testResult]) if errorInfo and picPath: # 在测试步骤sheet中,写入异常信息 excelObj.writeCell(sheetObj, content=errorInfo, rowNo=rowNo, colNo=testStep_errorInfo) # 在测试步骤sheet中写入异常截图路径 excelObj.writeCell(sheetObj, content=picPath, rowNo=rowNo, colNo=testStep_errorPic) else: # 在测试步骤sheet中,清空异常信息单元格 excelObj.writeCell(sheetObj, content='', rowNo=rowNo, colNo=testStep_errorInfo) # 在测试步骤sheet中,清空异常信息单元格 excelObj.writeCell(sheetObj, content='', rowNo=rowNo, colNo=testStep_errorPic) except Exception: print("写Excel出错,%s" % traceback.print_exc()) def TestCreatBuild(): try: # 根据Excel文件中的sheet名称获取sheet对象 caseSheet = excelObj.getSheetByName("测试用例") # 获取测试用例sheet中是否执行列对象 maxRow = excelObj.getRowsNumber(caseSheet) # 获取最大行号 maxCol = excelObj.getColsNumber(caseSheet) # 获取最大列号 isExecuteCol = excelObj.getColumn(caseSheet, maxRow, testCase_testisExecute) # print(isExecuteCol) # 记录执行成功的测试用例个数 successfulCase = 0 # 记录需要执行的测试用例个数 requiredCase = 0 for idx, i in enumerate(isExecuteCol[1:]): # 因为用例sheet中第一行为标题行,无需执行 # 循环遍历测试用例表中的测试用例,执行被设置为执行的用例 if i.lower() == "y": requiredCase += 1 # 获取测试用例中第idx+2行数据 caseRow = excelObj.getRow(caseSheet, idx+2, maxCol) # 获取第idx+2行的步骤sheet单元格内容 caseStepName = caseRow[testCase_testStepSheetName-1] # 根据用例步骤名获取步骤sheet对象 stepSheet = excelObj.getSheetByName(caseStepName) # 获取步骤sheet中的步骤数 stepNum = excelObj.getRowsNumber(stepSheet) # 获取最大行数和列数 maxstepRow = excelObj.getRowsNumber(caseSheet) # 获取最大行号 maxstepCol = excelObj.getColsNumber(caseSheet) # 获取最大列号 # 记录用例i的步骤成功数 successfulSteps = 0 print("开始执行用例 %s" % caseStepName) for step in range(2, stepNum+1): # 获取步骤sheet中第step行内容 stepRow = excelObj.getRow(stepSheet, step, maxstepCol) # 获取关键字作为调用的函数名 keyWord = stepRow[testStep_keyWords-1] # 获取操作元素定位方式作为调用的函数的参数 locationType = stepRow[testStep_locationType-1] # 获取操作元素的定位表达式作为调用函数的参数 locatorExpression = stepRow[testStep_locatorExpression-1] # 获取操作值作为调用函数的参数 operateValue = stepRow[testStep_operateValue-1] # 构造需要执行的python语句 # 对应PageAction.py文件中的页面动作函数调用的字符串表示 if keyWord and operateValue and locationType is None \ and locatorExpression is None: expressionStr = keyWord.strip() + '("' + str(operateValue) + '")' elif keyWord and operateValue is None and locationType is None\ and locatorExpression is None: expressionStr = keyWord.strip() + '()' elif keyWord and locationType and locatorExpression \ and operateValue: expressionStr = keyWord.strip() + '("' + locationType.strip() \ + '","' + locatorExpression.strip() + '","' \ + str(operateValue) + '")' elif keyWord and locationType and locatorExpression \ and operateValue is None: expressionStr = keyWord.strip() + '("' + locationType.strip() \ + '","' + locatorExpression.strip() + '")' try: # 通过eval函数,将拼接的页面动作函数调用的字符串表示当成有效的python表达式执行, # 从而执行测试步骤的sheet中关键字在PageAction.py文件中对应的映射方法 # 完成对页面元素的操作 eval(expressionStr) # 测试执行时间列写入执行时间 excelObj.writeCellCurrentTime( stepSheet, rowNo=step, colNo=testStep_runTime ) except Exception as e: # 截取异常屏幕图片 capturePic = capture_screen() # 获取详细的异常信息 errorInfo = traceback.format_exc() # 测试步骤sheet中写入失败信息 writeTestResult( stepSheet, step, "caseStep", "fail", errorInfo, capturePic ) print("步骤%s执行失败" % stepRow[testStep_testStepDescribe-1]) else: # 在测试步骤sheet中写入成功信息 writeTestResult(stepSheet, step, "caseStep", "pass") # 每成功一步,successfulSteps变量+1 successfulSteps += 1 print(("步骤 %s 执行成功" % stepRow[testStep_testStepDescribe-1])) if successfulSteps == stepNum - 1: # 当测试用例步骤sheet中所有的步骤都执行成功,方认为此测试用例执行 # 通过,然后将成功信息写入测试用例工作表中,否则写入失败信息 writeTestResult(caseSheet, idx+2, "testCase", "pass") successfulCase += 1 else: writeTestResult(caseSheet, idx+2, "testCase", "fail") print("共%d条测试用,%d条需要被执行,本次执行通过%d条。" % (len(isExecuteCol)-1, requiredCase, successfulCase)) except Exception as e: print(traceback.print_exc()) if __name__ == "__main__": TestCreatBuild()



