任务管理、内存管理和文件系统是内核最为核心的部分。其中内存管理最为复杂,文件系统最为庞大。内核通过引入虚拟文件系统,从而支持数十种不同的文件系统,不得不让人感叹Linux以及它显示出的开源的力量的强大。
虚拟文件系统(Virtual Filesystem),也可以称为虚拟文件系统转换(Virual Filesystem Switch ,简称VFS),是Linux强大的集中体现。Linux通过VFS可以处理几十种特定的文件系统,它在内核中的位置如下:
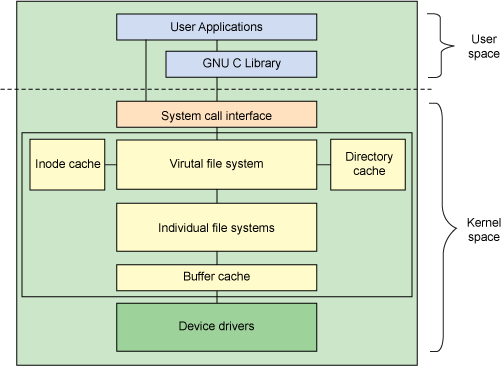
5.1、数据结构
虚拟文件系统所隐含的主要思想在于引入了一个通用的文件模型,这个模型能够表示所有支持的文件系统。该模型严格遵守传统Unix文件系统提供的文件模型。通用文件模型由下列关键对象组成:
(1) 超级块(superblock)对象:
存放系统中已安装文件系统的有关信息。对于基于磁盘的文件系统,这类对象通常对应于存放在磁盘上的文件系统控制块,也就是说,每个文件系统都有一个超级块对象。
(2) 索引节点(inode)对象:
存放关于具体文件的一般信息。对于基于磁盘的文件系统,这类对象通常对应于存放在磁盘上的文件控制块(FCB),也就是说,每个文件都有一个索引节点对象。每个索引节点对象都有一个索引节点号,这个号唯一地标识某个文件系统中的指定文件。
(3) 目录项(dentry)对象:
存放目录项与对应文件进行链接的信息。VFS把每个目录看作一个由若干子目录和文件组成的常规文件。
(4) 文件(file)对象:
存放打开文件与进程之间进行交互的有关信息。这类信息仅当进程访问文件期间存在于内存中。
进程与VFS之间的交互:
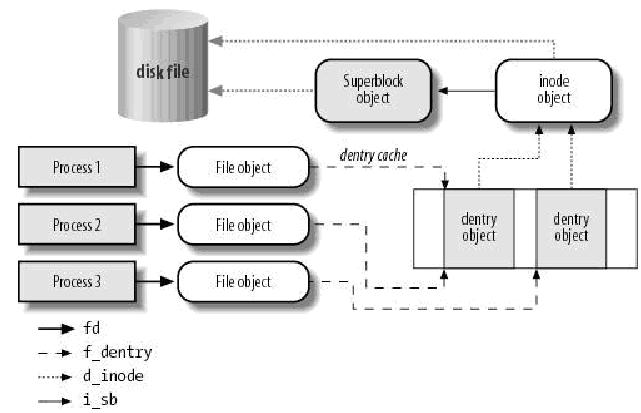
5.1.1、超级块对象

 Code
Code
//VFS超级块(fs/fs.h)
struct super_block {
struct list_head s_list; /* Keep this first,超级块链表*/
dev_t s_dev; /* search index; _not_ kdev_t,设备号*/
unsigned long s_blocksize; //块大小(以字节为单位)
unsigned long s_old_blocksize;
unsigned char s_blocksize_bits; //以位为单位的块大小
unsigned char s_dirt; /*脏位,若置该位,表明该超级块已被修改*/
unsigned long long s_maxbytes; /* Max file size, 文件的最大长度 */
struct file_system_type *s_type; //文件系统类型
struct super_operations *s_op; //超级块操作集合
struct dquot_operations *dq_op;
struct quotactl_ops *s_qcop;
struct export_operations *s_export_op;
unsigned long s_flags;
unsigned long s_magic;
struct dentry *s_root; /*指向该具体文件系统安装目录的目录项。*/
struct rw_semaphore s_umount;//卸载所用的信号量
struct semaphore s_lock; //超级块信号量
int s_count; //引用计数
int s_syncing; //索引节点同步标志
int s_need_sync_fs; //文件系统同步标志
atomic_t s_active;
void *s_security;
struct xattr_handler **s_xattr;
struct list_head s_inodes; /* all inodes,所有索引节点*/
struct list_head s_dirty; /* dirty inodes, 已修改的索引节点形成的链表 */
struct list_head s_io; /* parked for writeback,等待写回磁盘的索引节点 */
struct hlist_head s_anon; /* anonymous dentries for (nfs) exporting */
struct list_head s_files; //文件对象的链表
struct block_device *s_bdev; //指向块设备驱动程序描述符指针
struct list_head s_instances;
struct quota_info s_dquot; /* Diskquota specific options */
int s_frozen;
wait_queue_head_t s_wait_unfrozen;
char s_id[32]; /* Informational name */
void *s_fs_info; /* Filesystem private info,指向特定文件系统超级块 */
/*
* The next field is for VFS *only*. No filesystems have any business
* even looking at it. You had been warned.
*/
struct semaphore s_vfs_rename_sem; /* Kludge */
/* Granuality of c/m/atime in ns.
Cannot be worse than a second */
u32 s_time_gran;
};
//超级块链表(fs/super.c)
LIST_HEAD(super_blocks);
//超级块操作函数
struct super_operations {
struct inode *(*alloc_inode)(struct super_block *sb);
void (*destroy_inode)(struct inode *);
void (*read_inode) (struct inode *);
void (*dirty_inode) (struct inode *);
int (*write_inode) (struct inode *, int);
void (*put_inode) (struct inode *);
void (*drop_inode) (struct inode *);
void (*delete_inode) (struct inode *);
void (*put_super) (struct super_block *);
void (*write_super) (struct super_block *);
int (*sync_fs)(struct super_block *sb, int wait);
void (*write_super_lockfs) (struct super_block *);
void (*unlockfs) (struct super_block *);
int (*statfs) (struct super_block *, struct kstatfs *);
int (*remount_fs) (struct super_block *, int *, char *);
void (*clear_inode) (struct inode *);
void (*umount_begin) (struct super_block *);
int (*show_options)(struct seq_file *, struct vfsmount *);
ssize_t (*quota_read)(struct super_block *, int, char *, size_t, loff_t);
ssize_t (*quota_write)(struct super_block *, int, const char *, size_t, loff_t);
};
//include/linux/fs.h
//文件系统类型
struct file_system_type {
const char *name; //文件系统名称
int fs_flags; //文件系统类型的标志
struct super_block *(*get_sb) (struct file_system_type *, int,
const char *, void *); //读超级块的方法
void (*kill_sb) (struct super_block *); //删除超级块的方法
struct module *owner;//实现文件系统的模块
struct file_system_type * next; //文件系统类型链表的下一个元素
struct list_head fs_supers; //具有相同文件系统类型的超级块对象链表头
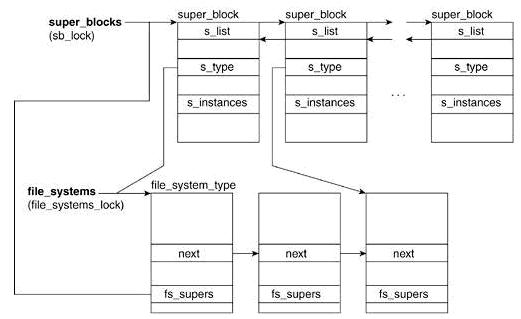
};超级块和文件系统类型的关系如下:
5.1.2、inode对象

 Code
Code
//索引节点对象(fs/fs.h)
struct inode {
struct hlist_node i_hash; //散列链表
struct list_head i_list; //索引结点链表
struct list_head i_sb_list;
struct list_head i_dentry; //引用索引节点的目录项对象链表
unsigned long i_ino; //索引节点号
atomic_t i_count; //引用计数
umode_t i_mode;
unsigned int i_nlink; //硬链接数量
uid_t i_uid;
gid_t i_gid;
dev_t i_rdev; //实设备标识
loff_t i_size; //文件的字节数
struct timespec i_atime;
struct timespec i_mtime;
struct timespec i_ctime;
unsigned int i_blkbits; //块的位数
unsigned long i_blksize; //块的字节数
unsigned long i_version;
unsigned long i_blocks; //文件的块数
unsigned short i_bytes; //文件中最后一块的字节数
unsigned char i_sock;
spinlock_t i_lock; /* i_blocks, i_bytes, maybe i_size */
struct semaphore i_sem;
struct rw_semaphore i_alloc_sem;
struct inode_operations *i_op; //索引节点的操作函数
struct file_operations *i_fop; /* former ->i_op->default_file_ops,默认文件操作函数 */
struct super_block *i_sb; //指向超级块
struct file_lock *i_flock; //文件锁
struct address_space *i_mapping;
struct address_space i_data;
#ifdef CONFIG_QUOTA
struct dquot *i_dquot[MAXQUOTAS];
#endif
/* These three should probably be a union */
struct list_head i_devices;
struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe;
struct block_device *i_bdev; //块设备
struct cdev *i_cdev; //字符设备
int i_cindex;
__u32 i_generation;
#ifdef CONFIG_DNOTIFY
unsigned long i_dnotify_mask; /* Directory notify events */
struct dnotify_struct *i_dnotify; /* for directory notifications */
#endif
unsigned long i_state;
unsigned long dirtied_when; /* jiffies of first dirtying */
unsigned int i_flags;
atomic_t i_writecount;
void *i_security;
union {
void *generic_ip;
} u;
#ifdef __NEED_I_SIZE_ORDERED
seqcount_t i_size_seqcount;
#endif
};
//fs/inode.c
LIST_HEAD(inode_in_use); //正在使用的索引节点链表
LIST_HEAD(inode_unused); //有效未使用的索引节点链表
//索引节点对象存放的散列表
static struct hlist_head *inode_hashtable;
//索引节点缓存
static kmem_cache_t * inode_cachep;
//索引节点操作函数
struct inode_operations {
int (*create) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,int, struct nameidata *);
struct dentry * (*lookup) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, struct nameidata *);
int (*link) (struct dentry *,struct inode *,struct dentry *);
int (*unlink) (struct inode *,struct dentry *);
int (*symlink) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,const char *);
int (*mkdir) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,int);
int (*rmdir) (struct inode *,struct dentry *);
int (*mknod) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,int,dev_t);
int (*rename) (struct inode *, struct dentry *,
struct inode *, struct dentry *);
int (*readlink) (struct dentry *, char __user *,int);
int (*follow_link) (struct dentry *, struct nameidata *);
void (*put_link) (struct dentry *, struct nameidata *);
void (*truncate) (struct inode *);
int (*permission) (struct inode *, int, struct nameidata *);
int (*setattr) (struct dentry *, struct iattr *);
int (*getattr) (struct vfsmount *mnt, struct dentry *, struct kstat *);
int (*setxattr) (struct dentry *, const char *,const void *,size_t,int);
ssize_t (*getxattr) (struct dentry *, const char *, void *, size_t);
ssize_t (*listxattr) (struct dentry *, char *, size_t);
int (*removexattr) (struct dentry *, const char *);
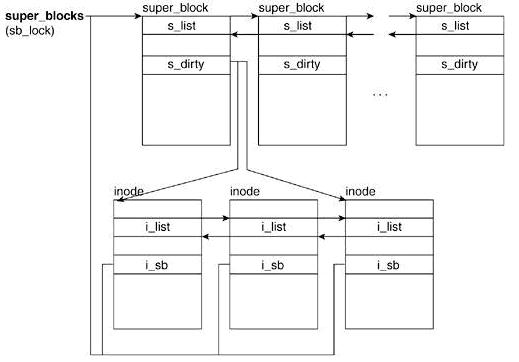
};索引节点与超级块的关系:
5.1.3、目录项对象

 Code
Code
//include/linux/dcache.h
struct dentry {
atomic_t d_count; //引用计数
unsigned int d_flags; /* protected by d_lock */
spinlock_t d_lock; /* per dentry lock */
struct inode *d_inode; /* Where the name belongs to - NULL is
* negative,相关的索引节点*/
/*
* The next three fields are touched by __d_lookup. Place them here
* so they all fit in a 16-byte range, with 16-byte alignment.
*/
struct dentry *d_parent; /* parent directory,父目录的目录对象*/
struct qstr d_name; //文件名
struct list_head d_lru; /* LRU list,用于未使用目录项链表*/
struct list_head d_child; /* child of parent list,同一父目录的目录项链表*/
struct list_head d_subdirs; /* our children,子目录链表*/
struct list_head d_alias; /* inode alias list,连接同一索引节点的目录项链表*/
unsigned long d_time; /* used by d_revalidate */
struct dentry_operations *d_op; //目录操作函数
struct super_block *d_sb; /* The root of the dentry tree,指向文件的超级对象*/
void *d_fsdata; /* fs-specific data */
struct rcu_head d_rcu;
struct dcookie_struct *d_cookie; /* cookie, if any */
struct hlist_node d_hash; /* lookup hash list,目录项对象散列表*/
int d_mounted;
unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN_MIN]; /* small names */
};
//dcache.c
//目录项对象缓存
static kmem_cache_t *dentry_cache;
//目录项对象散列表
static struct hlist_head *dentry_hashtable;
/*
**所有"未使用"目录项对象都存放在一个LRU双向链表中.该变量存放LRU链表的首元素和尾元素的地址.
*/
static LIST_HEAD(dentry_unused);
struct dentry_operations {
int (*d_revalidate)(struct dentry *, struct nameidata *);
int (*d_hash) (struct dentry *, struct qstr *);
int (*d_compare) (struct dentry *, struct qstr *, struct qstr *);
int (*d_delete)(struct dentry *);
void (*d_release)(struct dentry *);
void (*d_iput)(struct dentry *, struct inode *);
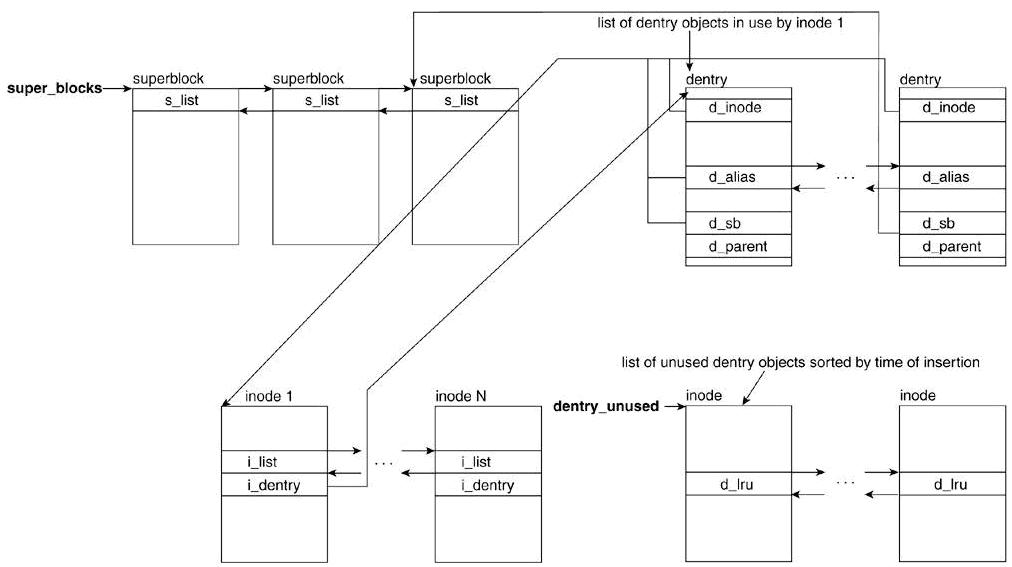
};超级块、索引节点与目录项的关系:
5.1.4、文件对象

 Code
Code
//文件对象(fs/fs.h)
struct file {
struct list_head f_list;
struct dentry *f_dentry; //与文件相关的目录项对象
struct vfsmount *f_vfsmnt; //含有该文件的文件系统的安装点
struct file_operations *f_op;
atomic_t f_count; //引用计数
unsigned int f_flags;
mode_t f_mode;
int f_error;
loff_t f_pos; //文件偏移
struct fown_struct f_owner;
unsigned int f_uid, f_gid;
struct file_ra_state f_ra;
size_t f_maxcount;
unsigned long f_version;
void *f_security;
/* needed for tty driver, and maybe others */
void *private_data;
#ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL
/* Used by fs/eventpoll.c to link all the hooks to this file */
struct list_head f_ep_links;
spinlock_t f_ep_lock;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL */
struct address_space *f_mapping;
};
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*aio_read) (struct kiocb *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t);
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*aio_write) (struct kiocb *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t);
int (*readdir) (struct file *, void *, filldir_t);
unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
int (*ioctl) (struct inode *, struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *);
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*flush) (struct file *);
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*fsync) (struct file *, struct dentry *, int datasync);
int (*aio_fsync) (struct kiocb *, int datasync);
int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int);
int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
ssize_t (*readv) (struct file *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*writev) (struct file *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*sendfile) (struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, read_actor_t, void *);
ssize_t (*sendpage) (struct file *, struct page *, int, size_t, loff_t *, int);
unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area)(struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long);
int (*check_flags)(int);
int (*dir_notify)(struct file *filp, unsigned long arg);
int (*flock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
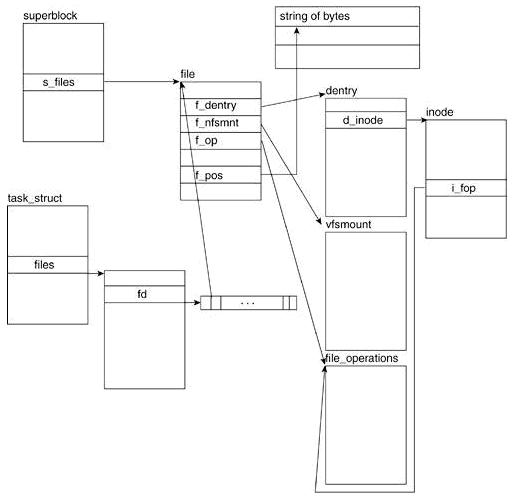
};超级块、索引节点、目录项和文件对象的关系:
5.2、与进程相关的数据结构
//include/linux/namespace.h
//命名空间
struct namespace {
atomic_t count; //引用计数(共享命名空间的进程数)
struct vfsmount * root; //命名空间的根目录的安装文件系统描述符
struct list_head list; //所有安装文件系统描述符的链表头
struct rw_semaphore sem; //读写信号量
};
//include/linux/fs_struct.h
//进程的根目录和当前目录
struct fs_struct {
atomic_t count; //引用计数(共享该结构的进程的个数)
rwlock_t lock;
int umask;
struct dentry * root, * pwd, * altroot; //根目录对应的目录项,当前工作目录对应的目录项
struct vfsmount * rootmnt, * pwdmnt, * altrootmnt; //根目录的安装点,当前工作目录的安装占
};
//include/linux/file.h
//进程打开的文件表
struct files_struct {
atomic_t count; //共享该表的进程个数
spinlock_t file_lock; /* Protects all the below members. Nests inside tsk->alloc_lock */
int max_fds; /*当前文件对象的最大数*/
int max_fdset; /*当前文件描述符的最大数*/
int next_fd; /*已分配的文件描述符加1*/
struct file ** fd; /* 指向文件对象指针数组的指针 */
fd_set *close_on_exec; /*指向执行exec( )时需要关闭的文件描述符*/
fd_set *open_fds; /*指向打开文件描述符的指针*/
fd_set close_on_exec_init; /* 执行exec( )时需要关闭的文件描述符的初值集合*/
fd_set open_fds_init; /*文件描述符的初值集合*/
struct file * fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT]; /*文件对象指针的初始化数组*/
};
//include/linux/sched.h
struct task_struct {
//
struct fs_struct *fs; //文件系统信息
/* open file information */
struct files_struct *files;//打开的文件
/* namespace */
struct namespace *namespace;//文件系统命名空间
//
}


 Code超级块和文件系统类型的关系如下:
Code超级块和文件系统类型的关系如下:
 Code索引节点与超级块的关系:
Code索引节点与超级块的关系:
 Code超级块、索引节点与目录项的关系:
Code超级块、索引节点与目录项的关系:
 Code超级块、索引节点、目录项和文件对象的关系:
Code超级块、索引节点、目录项和文件对象的关系:














