链表
一 概念:
链表是一种数据结构,在内存中通过节点记录内存地址而相互链接形成一条链的储存方式。相比数组而言,链表在内存中不需要连续的区域,只需要每一个节点都能够记录下一个节点的内存地址,通过引用进行查找,这样的特点也就造就了链表增删操作时间消耗很小,而查找遍历时间消耗很大的特点。
我们日常在Java中使用的LinkedList即为双向链表。而在链表是由其基本组成单元节点(Node)来实现的。我们在日常中见到的链表大部分都是单链表和双链表,其中一个栈便是用单链表进行实现。这两种链表在实现思维上基本一致,只不过在插入、删除等操作实现上有所区别。
两种链表结构如图所示:
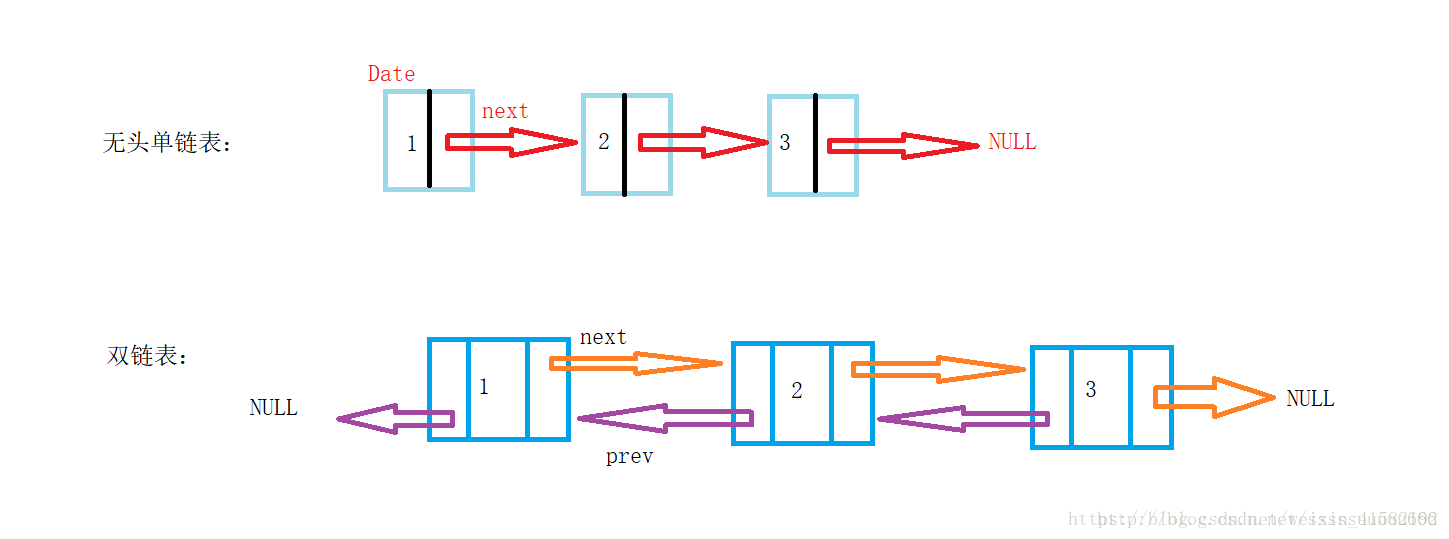
从图中可以看出,二者主要差别在于内部的Node类。单链表只需要一个指向下一个节点的引用Next,而双向链表则需要指向前一个Node的prev和下一个Node的Next。
下图为单链表的操作图
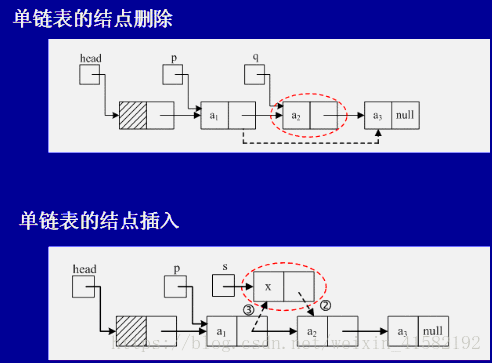
下图为双链表的操作图
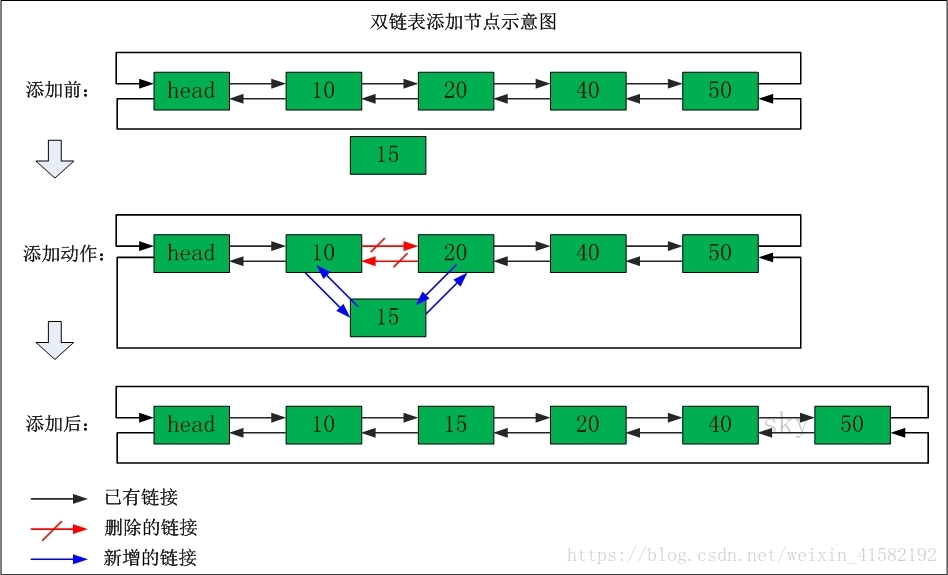
二 单链表的常用操作
如我们定义了单向链表的节点如下
/** * 单链表节点 * * @author hup * @data 2020-06-13 17:42 **/ public class Node { Node next = null; int data; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; } }
1 插入节点到指定位置
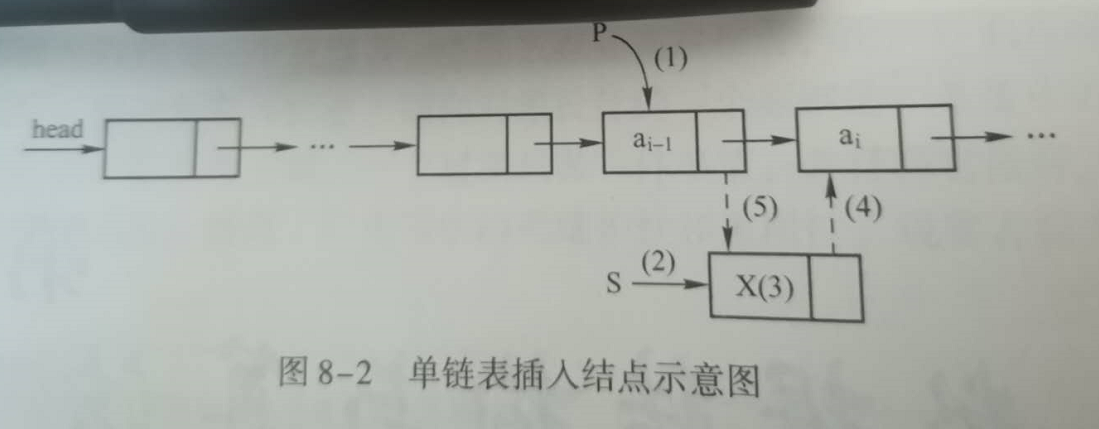
如上图,插入元素到ai-1 和 ai之间
代码实现插入节点
public class MyLinkedListTest { /** * 头节点 */ Node head = null; /** * 增加节点 链表末尾增加 * * @param data 节点值 */ public void add(int data) { Node newNode = new Node(data); if (head == null) { head = newNode; return; } Node curNode = head; while (curNode.next != null) { curNode = curNode.next; } curNode.next = newNode; }
2 删除指定位置节点
/** * 删除节点 * 假设索引是从1开始 */ public boolean delete(int index) { if (index < 1 || index > length(head)) { return false; } if(index == 1) { //删除头节点 Node nowNode = head; if(nowNode.next == null) { nowNode.data = 0; return true; } nowNode.data = nowNode.next.data; nowNode.next = nowNode.next.next; return true; } Node curNode = head; int i = 2; while (curNode.next != null) { i++; if (i == index) { curNode.next = curNode.next.next; return true; } curNode = curNode.next; } return true; }
3 求链表长度
/** * 链表长度 * * @return */ public int length(Node curNode) { int len = 1; while (curNode.next != null) { len++; curNode = curNode.next; } return len; }
4 链表排序,从小到大
/** * 链表排序 从小到大 并返回头节点 * * @return */ public Node sort() { //当前节点 Node curNode = head; //临时值 int temp = 0; while (curNode.next != null) { Node nextNode = curNode.next; while (nextNode != null) { if (curNode.data > nextNode.data) { //做数据交互 把数值小的换到前面 temp = curNode.data; curNode.data = nextNode.data; nextNode.data = temp; } nextNode = nextNode.next; } curNode = curNode.next; } return head; }
5 删除数据重复节点
/** * 删除重复节点 */ public void deleteSameNode() { Node curNode = head; while (curNode.next != null) { Node pNode = curNode; while (pNode.next != null) { //与外层循环节点比较 相同则删除内层循环的 if (curNode.data == pNode.next.data) { pNode.next = pNode.next.next; } else { pNode = pNode.next; } } curNode = curNode.next; } }
6 找到倒数第K个节点
/** * 找到倒数第K个节点 * 2个指针 相隔 k-1 */ public Node findEndKNode(int k) { Node smallNode = head; Node bigNode = head; //大节点比小节点提前右移k-1个单位 for (int i = 0; i < k - 1 && bigNode != null; i++) { bigNode = bigNode.next; } if (bigNode == null) { System.out.println("传入数字K不合法"); return null; } //2个指针一起右移,知道bigNode.next == null while (bigNode.next != null) { bigNode = bigNode.next; smallNode = smallNode.next; } return smallNode; }
7 从尾到头,输出单链表
/** * 从尾到头输出单链表 * 用递归实现 * * @param node 开始节点 */ public void printListReversely(Node node) { if (node.next != null) { printListReversely(node.next); System.out.println(node.data); } }
8 寻找中间节点
/** * 寻找中间节点 * 既然让寻找中间节点,肯定是奇数位 * 用2个右移速度差2倍的指针实现 * * node->node->node->node->node */ public Node findMiddleNode() { Node nodeSpeedOne = head; Node nodeSpeedTwo = head; while (nodeSpeedTwo.next != null && nodeSpeedTwo.next.next != null) { nodeSpeedOne = nodeSpeedOne.next; nodeSpeedTwo = nodeSpeedTwo.next.next; } return nodeSpeedOne; }
9 检查链表是否闭环
/** * 检查链表是否闭环 * 用2个右移速度差2倍的指针实现,当移动速度快的指针节点数据等于移动数据慢的时候,说明闭环 * * @return */ public boolean isLoop() { Node slow = head; Node fast = head; while (fast.next != null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (slow == fast) { //说明快的节点已经跑了至少一圈回来,追上了慢的节点,有闭环 return true; } } return false; }
10 查找环的入口节点
/** * 查找环的入口节点 * 使用了hashcode 值做对比 |hashcode| * * @return */ public Node findCircleDoorNode() { String stb = ""; StringBuilder split = new StringBuilder("|"); Node cureNode = head; while (cureNode.next != null) { if (stb.contains(split.append(cureNode.next.hashCode()).append(split).toString())) { return cureNode.next; } stb = split.append(cureNode.next.hashCode()).append(split).toString(); } return null; }
11 在不知道头节点的情况下,删除指定节点
/** * 在不知道头节点的情况下,删除节点 * * @param node * @return */ public boolean deleteWhenNotKnowHead(Node node) { if (node == null || node.next == null) { return false; //没有后继节点,无法删除 } // node0->node(*)->node2->node3 删除node(*) node.data = node.next.data; //把待删除节点后面节点的值,赋值给了待删除节点 node.next = node.next.next; //把node2节点从链表中摘除 return true; }
12 判断两个单向链表是否相交
/** * 判断2个单向链表是否相交 * 如果相交,有相同的尾节点 * * @return */ public boolean towListMeet(Node curNode1, Node curNode2) { if (curNode1 == null || curNode2 == null) { return false; } while (curNode1.next != null) { curNode1 = curNode1.next; } curNode2 = head; while (curNode2.next != null) { curNode2 = curNode2.next; } return curNode1 == curNode2; }
13 获取两个单向链表相交的交点
/** * 获取2个单向链表相交的交点 * * @return */ public Node getTowListMeetNode(Node curNode1, Node curNode2) {
//判断是否相交 if (!towListMeet(curNode1, curNode2)) { return null; } //分别求出2条链表长度 int length1 = length(curNode1); int length2 = length(curNode2); //对最长的,先右移 长度的差异位数 if (length1 > length2) { for (int i = 0; i < (length1 - length2); i++) { curNode1 = curNode1.next; } } else { for (int i = 0; i < (length2 - length1); i++) { curNode2 = curNode2.next; } } //然后再一起右移,直到相等 while (curNode2 != curNode1) { curNode1 = curNode1.next; curNode2 = curNode2.next; } return curNode2; }
测试一下这个链表是否生效
@Test public void test() { MyLinkedListTest myLinkedListTest = new MyLinkedListTest(); //加入3个节点 myLinkedListTest.add(10); myLinkedListTest.add(20); myLinkedListTest.add(30); //从尾到头输出 myLinkedListTest.printListReversely(myLinkedListTest.head); System.out.println("删除元素后"); //删除某个节点 myLinkedListTest.delete(1); //从尾到头输出 myLinkedListTest.printListReversely(myLinkedListTest.head); }
输出结果:
30
20
10
删除元素后
30
20
链表测试正常



