Java面向对象之泛型
主要介绍:
- 认识泛型
- 构造方法中使用泛型
- 设置多个泛型
- 通配符
- 泛型接口
- 泛型方法
- 泛型数组
一、认识泛型

具体实例如下:
1 package com.huolongluo.newfeatures; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by 火龙裸 on 2019/7/5. 5 * desc : 认识泛型 6 * version: 1.0 7 */ 8 public class GenericDemo01 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Point<Integer> p = new Point<>(); 11 p.setX(0); 12 p.setY(12); 13 int px = p.getX(); 14 int py = p.getY(); 15 16 System.out.println("px = " + px +" py = " + py); 17 } 18 19 static class Point<T> { 20 private T x; 21 private T y; 22 23 public T getX() { 24 return x; 25 } 26 27 public void setX(T x) { 28 this.x = x; 29 } 30 31 public T getY() { 32 return y; 33 } 34 35 public void setY(T y) { 36 this.y = y; 37 } 38 } 39 }
运行结果:
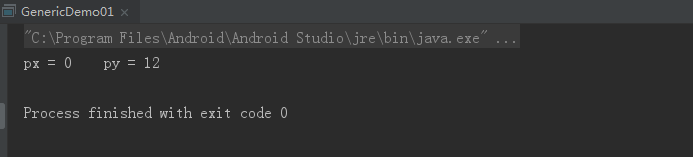
二、构造方法中使用泛型

具体实例如下:
1 package com.huolongluo.newfeatures; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by 火龙裸 on 2019/7/5. 5 * desc : 构造方法中使用泛型 6 * version: 1.0 7 */ 8 public class GenericDemo02 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Con<String> con = new Con<>("构造方法中使用泛型 huolongluo"); 11 System.out.println(con.getValue()); 12 } 13 14 static class Con<T> { 15 private T value; 16 17 public Con(T value) { 18 this.value = value; 19 } 20 21 public T getValue() { 22 return value; 23 } 24 25 public void setValue(T value) { 26 this.value = value; 27 } 28 } 29 }
运行结果:

三、指定多个泛型

具体实例如下:
1 package com.huolongluo.newfeatures; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by 火龙裸 on 2019/7/5. 5 * desc : 指定多个泛型 6 * version: 1.0 7 */ 8 public class GenericDemo03 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Gen<String, Integer> gen = new Gen<>(); 11 gen.setKey("火龙裸"); 12 gen.setTake(200); 13 System.out.println(gen.getKey() + " " + gen.getTake()); 14 } 15 16 static class Gen<K, T> { 17 private K key; 18 private T take; 19 20 public K getKey() { 21 return key; 22 } 23 24 public void setKey(K key) { 25 this.key = key; 26 } 27 28 public T getTake() { 29 return take; 30 } 31 32 public void setTake(T take) { 33 this.take = take; 34 } 35 } 36 }
运行结果:

四、通配符
通配符比较简单,直接通过实例进行展示:
1 package com.huolongluo.newfeatures; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by 火龙裸 on 2019/7/5. 5 * desc : 通配符 : ? 6 * version: 1.0 7 */ 8 public class GenericDemo04 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Info<String> info = new Info<>(); 11 info.setKey("我是火龙裸"); 12 tell(info); 13 } 14 15 /** 16 * 通配符 : ? 17 * */ 18 public static void tell(Info<?> i) { 19 System.out.println("打印:" + i); 20 } 21 22 static class Info<T> { 23 private T key; 24 25 public T getKey() { 26 return key; 27 } 28 29 public void setKey(T key) { 30 this.key = key; 31 } 32 33 @Override 34 public String toString() { 35 return "Info{" + 36 "key=" + key + 37 '}'; 38 } 39 } 40 }
运行结果:

五、泛型在接口当中使用

具体实例如下:
1 package com.huolongluo.newfeatures; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by 火龙裸 on 2019/7/5. 5 * desc : 泛型在接口当中的使用 6 * version: 1.0 7 */ 8 public class GenericDemo05 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Gin gin = new Gin("我是火龙裸"); 11 System.out.println(gin.getInfo()); 12 } 13 14 interface GenInter<T> { 15 void say(); 16 } 17 18 static class Gin<T> implements GenInter<T> { 19 private T info; 20 21 public Gin(T info) { 22 this.info = info; 23 } 24 25 public T getInfo() { 26 return info; 27 } 28 29 public void setInfo(T info) { 30 this.info = info; 31 } 32 33 @Override 34 public void say() { 35 36 } 37 } 38 }
运行结果:

六、泛型方法

具体实例如下:
1 package com.huolongluo.newfeatures; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by 火龙裸 on 2019/7/5. 5 * desc : 泛型方法 6 * version: 1.0 7 */ 8 public class GenericDemo06 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Gener gener = new Gener(); 11 12 String str = gener.tell("我是huolongluo"); 13 System.out.println(str); 14 15 int i = gener.tell(1200); 16 System.out.println(i); 17 } 18 19 static class Gener { 20 public <T> T tell(T t) { 21 return t; 22 } 23 } 24 }
运行结果:
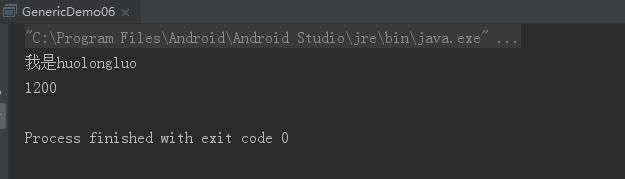
七、泛型数组
泛型数组的使用,其实跟泛型犯法,是要相搭配来使用的。

具体实例如下:
1 package com.huolongluo.newfeatures; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by 火龙裸 on 2019/7/5. 5 * desc : 泛型数组 6 * version: 1.0 7 */ 8 public class GenericDemo07 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 String arr0[] = {"www", "huolongluo", "com"}; 11 tell(arr0); 12 13 Integer arr1[] = {1, 2, 3, 4}; 14 tell(arr1); 15 } 16 17 static <T>void tell(T arr[]) { 18 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 19 System.out.println(arr[i]); 20 } 21 } 22 }
运行结果:

OK,一气呵成。程序员,抛砖引玉很重要。



