[ python ] 文件读写操作
python3 文件读写操作
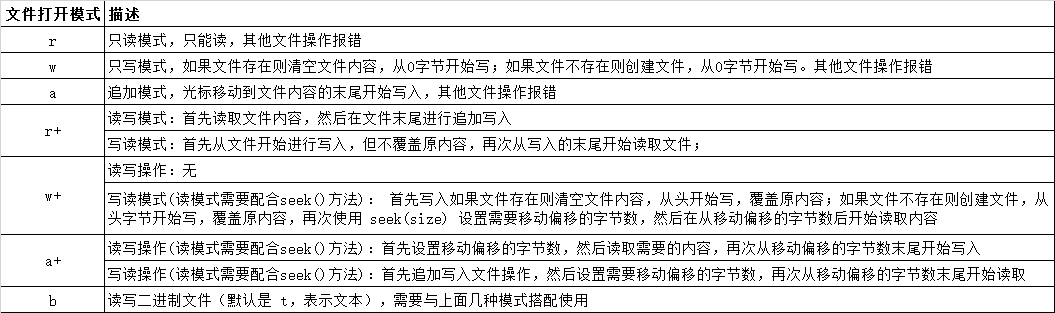
1. 文件打开模式
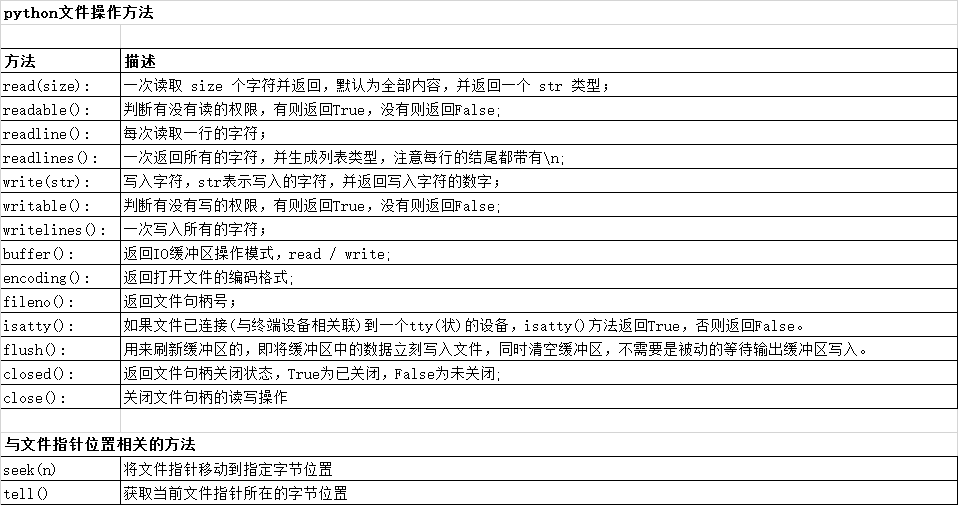
2. 文件操作方法
文件读写与字符编码

python文件操作步骤示例
以读取为例,这样一个文件:text.txt, 该文件的字符编码为 utf-8
总有一天总有一年会发现 有人默默的陪在你的身边 也许 我不该在你的世界 当你收到情书 也代表我已经走远
1. 基本实现
f = open('text.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8')
print(f.read())
f.close()
2. 中级实现
在基本实现的的基础上,可能要考虑到一些可能出现的意外因素。因为文件读写时都有可能产生IO错误(IOError),一旦出错,后面包括 f.close() 在内的所有代码都不会执行了,因此我们要保证文件无论如何都应该关闭。
f = '' # 全局要申明下 f 变量,不然 f.close() 会报黄
try:
f = open('text.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8')
print(f.read())
finally:
if f:
f.close()
在上面的代码中,就是 try 中的代码出现了报错,依然会执行 finally 中的代码,即文件关闭操作被执行。
3. 最佳实践
为了避免忘记或者为了避免每次都要手动关闭文件,且过多的代码量,我们可以使用 with 语句,with 语句会在其代码块执行完毕之后自动关闭文件。
with open('text.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
print(f.read())
print(f.closed) # 通过 closed 获取文件是否关闭,True关闭,False未关闭
# 执行结果:
# 总有一天总有一年会发现
# 有人默默的陪在你的身边
# 也许 我不该在你的世界
# 当你收到情书
# 也代表我已经走远
# True
用户注册登录实例
要求:
1. 用户可注册不同的账户,并将用户信息保存到本地文件中;
2. 下次登录,注册过的用户都可实现登录
代码:

#!/usr/bin/python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Author: hkey import os def file_oper(file, mode, *args): if mode == 'r': list_user = [] with open(file, mode) as f: for line in f: list_user.append(line.strip()) return list_user elif mode == 'a+': data = args[0] with open(file, mode) as f: f.write(data) class User(object): def __init__(self, name, passwd): self.name = name self.passwd = passwd self.file = 'user.db' def regist(self): data = '%s|%s\n' % (self.name, self.passwd) file_oper(self.file, 'a+', data) if os.path.isfile('user.db'): print('\033[32;1m注册成功.\033[0m') def login(self): list_user = file_oper(self.file, 'r') print('list_user:', list_user) user_info = '%s|%s' % (self.name, self.passwd) if user_info in list_user: print('\033[32;1m登录成功.\033[0m') else: print('\033[31;1m登录失败.\033[0m') def start(): while True: print('1. 注册\n' '2. 登录\n' '3. 退出') choice = input('\033[34;1m>>>\033[0m').strip() if choice == '1': username = input('\033[34;1musername:\033[0m').strip() password = input('\033[34;1mpassword:\033[0m').strip() user = User(username, password) user.regist() elif choice == '2': username = input('\033[34;1musername:\033[0m').strip() password = input('\033[34;1mpassword:\033[0m').strip() user = User(username, password) user.login() elif choice == '3': break else: print('\033[31;1m错误:输入序号错误。\033[0m') if __name__ == '__main__': start()
2019-12-23 再次编写:

from os.path import isfile class User: def __init__(self, username, passwd, file_info): self.user = username self.pwd = passwd self.file_db = file_info @staticmethod def file_oper(file, mode, *args): if mode == 'a+': data = args[0] with open(file, mode) as f: f.write(data) elif mode == 'r': with open(file, mode) as f: data = f.read() return data def regist(self): list_user = [] if isfile(self.file_db): with open(self.file_db, 'r') as f: for line in f: username = line.strip().split(':')[0] list_user.append(username) if self.user not in list_user: try: with open(self.file_db, 'a+') as f: user_info = '%s:%s\n' %(self.user, self.pwd) f.write(user_info) print('\033[32;1m注册成功。\033[0m') except Exception as e: print('Error: ', e) else: print('\033[31;1m该用户已存在.\033[0m') def login(self): list_user = [] u_list = '%s:%s' %(self.user, self.pwd) with open(self.file_db, 'r') as f: for line in f: list_user.append(line.strip()) if u_list in list_user: print('\033[32;1m登录成功.\033[0m') else: print('\033[31;1m用户名或密码错误.\033[0m') def start(): while True: print('1. 注册\n' '2. 登录\n' '3. 退出') choice = input('>>>').strip() if choice.isdigit() and 0 < int(choice) < 4: if choice == '1': username = input('用户名:').strip() passwd = input('密码:').strip() user = User(username, passwd, 'user.db') user.regist() elif choice == '2': username = input('用户名:').strip() passwd = input('密码:').strip() user = User(username, passwd, 'user.db') user.login() elif choice == '3': break else: print('输入错误.') if __name__ == '__main__': start()
更多参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yyds/p/6186621.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号