ELK 部署文档
1. 前言
在日常运维工作中,对于系统和业务日志的处理尤为重要。尤其是分布式架构,每个服务都会有很多节点,如果要手工一个一个的去取日志,运维怕是要累死。
简单介绍:
ELK 是 elasticsearch + logstash + kibana 三款开源软件的简称。
elasticsearch:是个开源的分布式搜索引擎,特点是:分布式、配置简单、自动发现、索引自动分片、索引副本机制、restful风格接口,多数据源,自动搜索负载等
logstash:可以对日志进行收集、滤过、并将其存储在 elasticsearch中
kibana:可以为 elasticsearch提供友好的用户交互界面,用户可以通过 kibana来分析、搜索甚至绘图来分析数据。
这里介绍下目前使用比较多的架构:
ELK + filebeat
Filebeat 是一个轻量级开源日志文件数据收集器,可以将它安装到需要收集的节点上,它会将日志输送到 logstash 或 elasticsearch
有了 ELK 就可以将分布到多台的日志统一规划起来。
网络上有很多关于 ELK 的部署方案,参考了很多发现要不就是老版本的,要不就是不太完善,因此自己做下记录。
注意:在安装 ELK 的时候,这三个软件的版本必须保持支持,否则出现各种bug
2. ELK搭建过程
实验拓扑图:
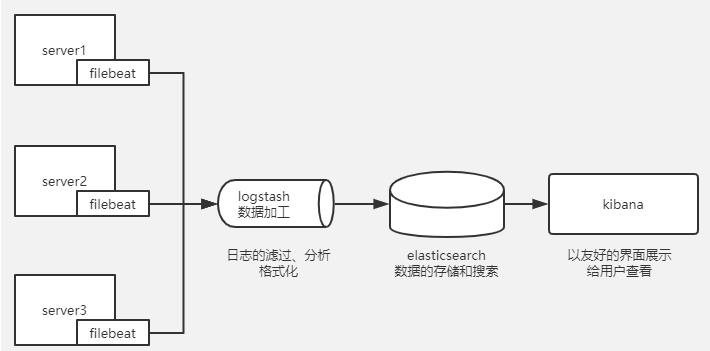
实验环境主机服务介绍:
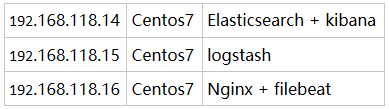
本次实验是收集 nginx 日志,并存储在 elasticsearch中。将 elasticsearch 和 kibana 安装在同一主机上可以避免不必要的网络IO操作,直接本机交互。
2.1 Elasticsearch 的安装过程
(1)初始化工作
- selinux、firewall 关闭
- 时间同步
- 主机名修改
- 修改打开文件最大数
时间同步:
[root@192.168.118.14 ~]#ntpdate tiger.sina.com.cn
修改主机名:
[root@192.168.118.14 ~]#hostnamectl set-hostname node1 修改完主机名别忘记在 /etc/hosts 中申明 192.168.118.14 node1
修改文件打开最大数:
[root@192.168.118.14 ~]#vim /etc/security/limits.conf * soft nproc 655350 * hard nproc 655350 * soft nofile 655350 * hard nofile 655350 [root@192.168.118.14 ~]#ulimit -SHn 655350
(2)配置 java 环境
[root@192.168.118.14 /usr/local/src]#tar xf jdk-8u77-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/ 在 /etc/profile 文件中追加 JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk1.8.0_77 JAVA_BIN=$JAVA_HOME/bin PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_BIN CLASSPATH=$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar export JAVA_HOME JAVA_BIN PATH CLASSPATH [root@192.168.118.14 /usr/local/src]#source /etc/profile [root@192.168.118.14 /usr/local/src]#ln -vs /usr/local/jdk1.8.0_77/bin/java /usr/bin/ [root@192.168.118.14 /usr/local/src]#java -version java version "1.8.0_77" Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_77-b03) Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.77-b03, mixed mode)
(3)安装 elasticsearch
下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/past-releases#elasticsearch
这里下载的是 6.8 的 rpm 包
直接安装:
[root@192.168.118.14 ~/ELK]#yum localinstall elasticsearch-6.8.2.rpm 修改配置文件如下: [root@192.168.118.14 ~/ELK]#egrep ^[a-z] /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml cluster.name: super-cluster node.name: node1 path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch bootstrap.memory_lock: true network.host: 0.0.0.0 http.port: 9200 discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.118.14"] http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*"

启动
[root@192.168.118.14 ~/ELK]#systemctl enable elasticsearch ; systemctl start elasticsearch
首次启动可能会启动失败,查看日志:
[root@192.168.118.14 ~/ELK]#tail /var/log/elasticsearch/super-cluster.log … [1]: memory locking requested for elasticsearch process but memory is not locked …
如上报错,需要修改启动脚本:
[root@192.168.118.14 ~/ELK]#vim /lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service 在 [Service] 配置段添加: … LimitMEMLOCK=infinity … [root@192.168.118.14 ~/ELK]#systemctl daemon-reload [root@192.168.118.14 ~/ELK]#systemctl start elasticsearch
查看端口,如果 9200 和 9300 监听,则说明 elasticsearch启动成功。
验证:
[root@192.168.118.14 ~/ELK]#curl http://localhost:9200/
{
"name" : "node1",
"cluster_name" : "super-cluster",
"cluster_uuid" : "1FD-KmYMTVCzWVPI9vn8zw",
"version" : {
"number" : "6.8.2",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "rpm",
"build_hash" : "b506955",
"build_date" : "2019-07-24T15:24:41.545295Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "7.7.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "5.6.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "5.0.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
到此,elasticsearch安装成功。
这里多安装一个elasticsearch-head 用来调试和查看数据是非常方便的。
程序下载地址:https://github.com/mobz/elasticsearch-head
首先安装依赖包
yum install git nodejs openssl-devel screen -y 克隆 elasticsearch-head项目 [root@192.168.118.14 ~]# git clone https://github.com/mobz/elasticsearch-head.git [root@192.168.118.14 ~]# cd elasticsearch-head/ 此时忽略phantomjs-prebuilt@2.1.16,执行命令如下 [root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# npm install phantomjs-prebuilt --ignore-scripts [root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# npm install …
这里是一个非常缓慢的过程。
启动 elasticsearch-head 服务
[root@192.168.118.14 ~]#cd elasticsearch-head/ [root@192.168.118.14 ~/elasticsearch-head]#screen [root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# npm run start Ctrl+a Ctrl+d 将进程放置到后台,这里不懂的查下 screen 命令,很好使。
查看端口 只要 9100 被监听,说明启动成功。
浏览器访问:
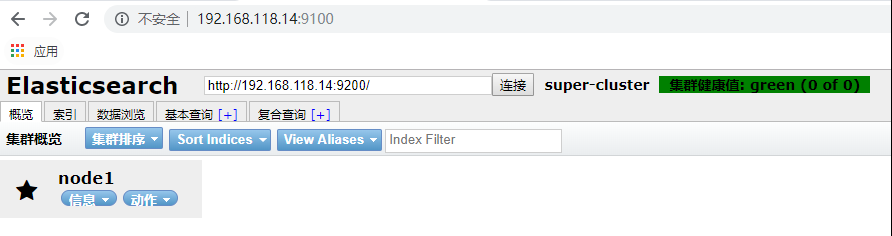
妥了,安装成功。通过 elasticsearch-head 可以查看 elasticsearch 中的所有数据。目前就一个 node1 索引。如果要深入学习 elasticsearch 推荐一本书《elasticsearch-the-definitive-guide-cn》 网上有 PDF 可以下载。
接下来,安装 kibana 。Kibana 和 elasticsearch安装到同一台主机的
Kibana 下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/past-releases#kibana
直接rpm包安装
[root@192.168.118.14 ~/ELK]#yum localinstall kibana-6.8.2-x86_64.rpm -y
修改配置文件:

这里注意,如果将 kibana 端口修改为 80 ,这里是需要修改kibana启动用户为 root 因为普通用户是不能启动 1024 以下端口的。
修改启动配置文件:
[root@192.168.118.14 ~]#vim /etc/systemd/system/kibana.service User=root Group=root 再次启动服务 [root@192.168.118.14 ~]#systemctl daemon-reload [root@192.168.118.14 ~]#systemctl restart kibana
查看 80 端口如果被监听就说明启动成功。
2.2 logstash 安装过程
根据规划,logstash 应该被安装到一台独立的主机上,logstash安装非常简单。
Logstash 下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/past-releases#logstash
和上面一样,初始化工作不要忘记,这里就不再描述了。
安装 jdk 也和上面一样的,jdk验证:
[root@192.168.118.15 /usr/local/src]#java -version java version "1.8.0_77" Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_77-b03) Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.77-b03, mixed mode)
安装 logstash
[root@192.168.118.15 ~]#yum localinstall logstash-6.8.2.rpm -y 将 logstash 命令添加到 PATH 环境变量中 [root@192.168.118.15 /etc/logstash]#vim /etc/profile.d/logstash.sh export PATH=/usr/share/logstash/bin:$PATH
Ok, 到这里已经安装完成,是不是很简单。
验证:
[root@192.168.118.15 ~]#logstash -e 'input { stdin {} } output { stdout{} }'
只要出现 Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9600} 就表示启动成功。
你好,中国
{
"@version" => "1",
"message" => "你好,中国",
"host" => "logstash-node1",
"@timestamp" => 2019-09-14T04:14:35.035Z
测试通过,logstash验证成功。
2.3 Filebeat 和 nginx 安装
Filebeat 下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/past-releases#filebeat
首先安装 nginx 直接yum安装
[root@192.168.118.16 ~]#yum install nginx -y 启动nginx [root@192.168.118.16 ~]#nginx
安装 filebeat
[root@192.168.118.16 ~]#yum localinstall filebeat-6.8.2-x86_64.rpm -y 开启nginx模块 [root@192.168.118.16 ~]#cd /etc/filebeat/ [root@192.168.118.16 /etc/filebeat]#filebeat modules enable nginx Enabled nginx
修改 filebeat主配置文件:
[root@192.168.118.16 ~]#vim /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml 注释掉输出到 elasticsearch #output.elasticsearch: # Array of hosts to connect to. #hosts: ["localhost:9200"] 开启输出到 logstash output.logstash: # The Logstash hosts hosts: ["192.168.118.16:5044"]
注意这里的 hosts 要写 logstash 主机的 IP
修改 nginx 模块配置文件:
[root@192.168.118.16 ~]#vim /etc/filebeat/modules.d/nginx.yml

启动 filebeat 服务
[root@192.168.118.16 ~]#systemctl start filebeat Filebeat 服务是没有监听端口的,只要状态是 running 就表示启动成功,可以查看 filebeat 日志 /var/log/filebeat/filebeat
到此,ELK + filebeat 已经部署完毕,接下来就可以安装需求来进行调整和收集数据,而这一块的工作都集中在 logstash,因此 ELK 编写 logstash 才是难点。Logstash 配置语法,强力建议查看官方文档,非常全面了。
2.4 编写 logstash 配置文件
这里采用循序渐进的方式展开,可以先写一个简单的测试。
编写一个将数据输出到屏幕的配置文件:
[root@192.168.118.15 /etc/logstash/conf.d]#vim test.conf

Logstash 可以根据配置文件来启动,启动方式如下:
[root@192.168.118.15 /etc/logstash/conf.d]#logstash -f test.conf 出现 Successfully started Logstash API endpoint 就表示启动成功。
启动成功后,我们尝试访问 nginx 生成日志数据。

日志文件已经传输过来了,接下来就是把这些数据写入到 elasticsearch 中。
继续修改配置文件:
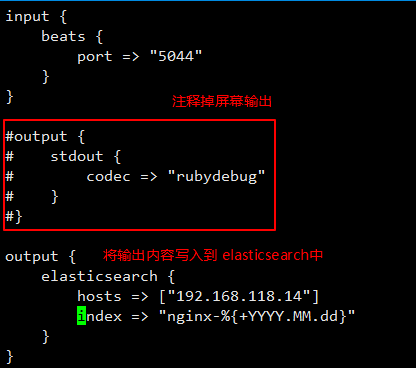
通过配置文件启动 logstash
[root@192.168.118.15 /etc/logstash/conf.d]#logstash -f test.conf
尝试访问 nginx 查看 elasticsearch-head中是否有新的索引被创建出来。

如上图,一个新的索引被创建出来,可以通过 elasticsearch-head 查看该索引中的数据。
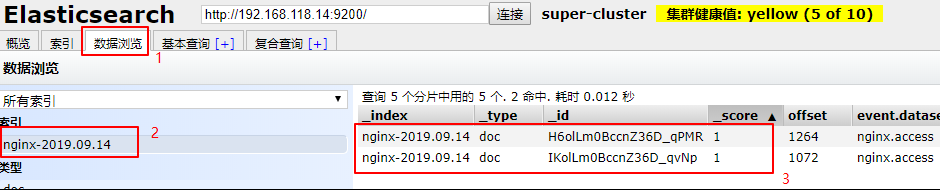
目前已经将日志数据写入到 elasticsearch中了, 然后通过 kibana 展示出来,浏览器访问上面装好的 kibana
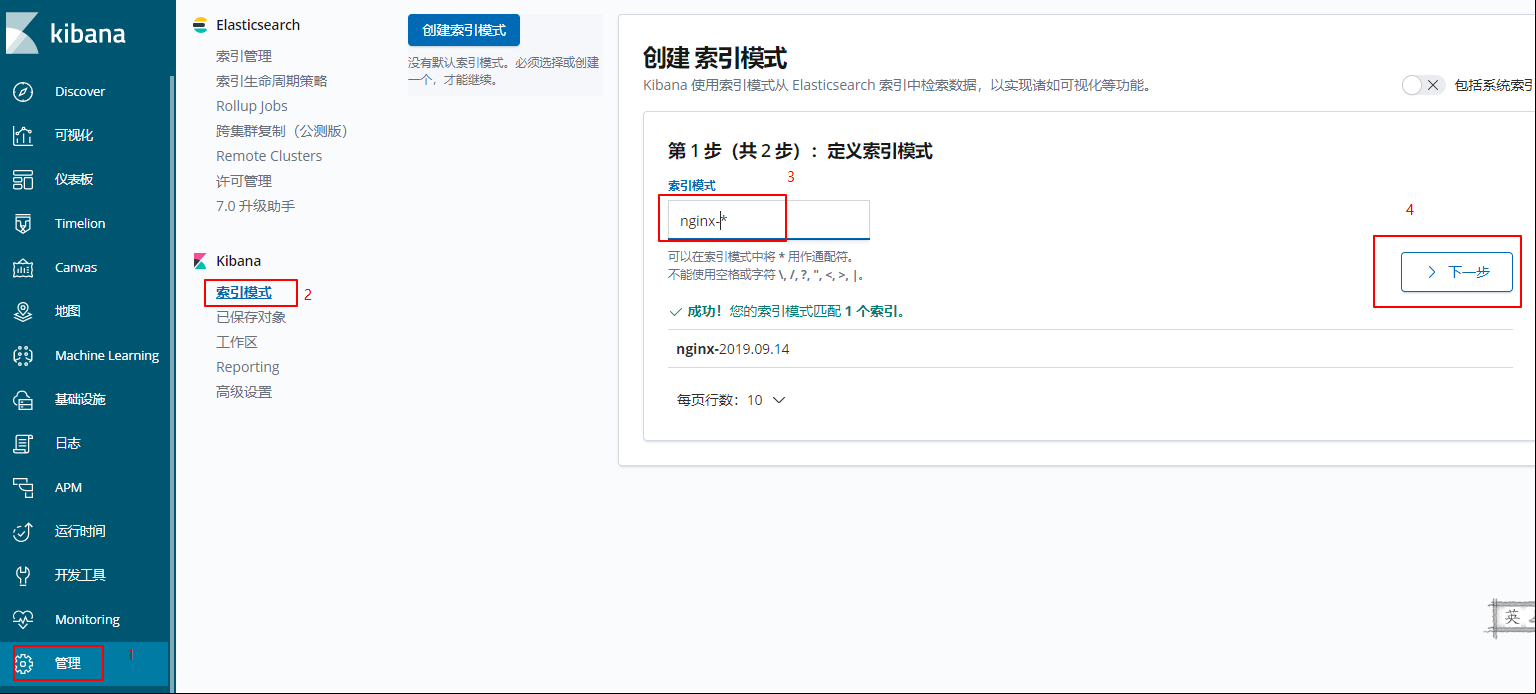

设置完成,直接点击 Discover
多访问几次nginx,查看日志是否展示出来。
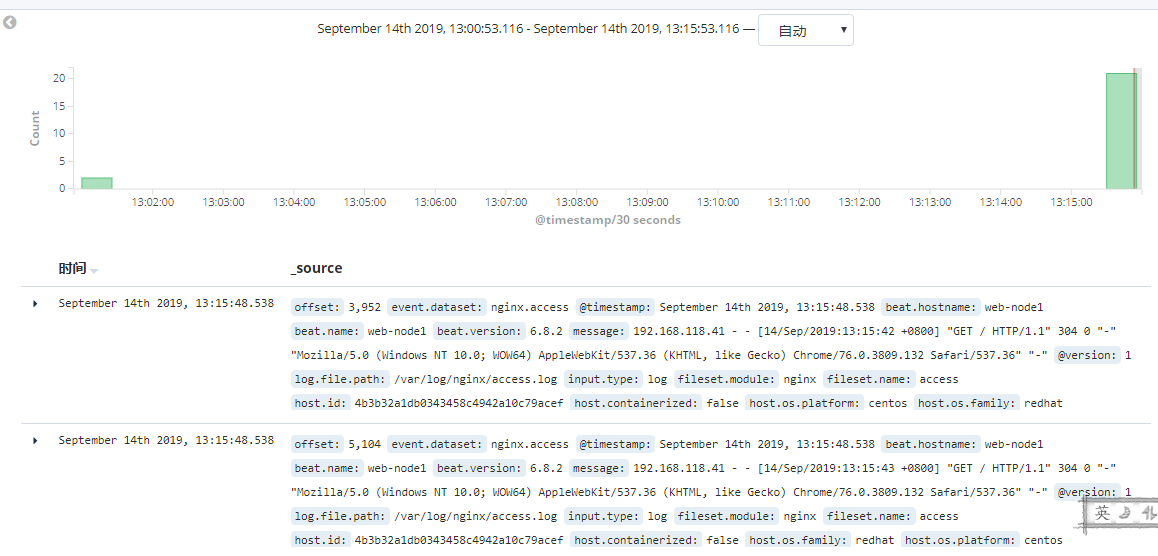
ok,到此, ELK + filebeat 获取 nginx 日志就完成了。虽然将日志展示出来了, 但是这样杂乱无章的日志数据看着还是很难受的,这就需要进一步的规整。
下一篇再写如果更详细的通过 logstash获取nginx日志数据,然后通过kibana展示更规整的数据及绘图。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号