微信小程序:一起玩连线,一个算法来搞定
微信小程序:一起玩连线
游戏玩法
将相同颜色的结点连接在一起,连线之间不能交叉。

算法思想
转换为多个源点到达对应终点的路径问题,且路径之间不相交。按照dfs方式寻找两个结点路径,一条路径探索完之后,标记地图并记录路径,然后探索下一条路径,以此类推。路径探索失败之后,地图进行标记回退,路径也回退。
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serialize.LineSeparator; import java.util.*; import java.util.stream.IntStream; /** * @author hujunzheng * @create 2018-07-01 16:12 **/ public class LineTogether { private static final int[][] dir = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}}; private boolean[][] map; private List<TogetherNode> togetherNodes; public LineTogether() { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); int width = scanner.nextInt(); int height = scanner.nextInt(); int pairNodes = scanner.nextInt(); this.map = new boolean[width + 2][]; for (int i = 0; i < width + 2; ++i) { map[i] = new boolean[height + 2]; } for (int i = 1; i <= width; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j <= height; ++j) { map[i][j] = true; } } togetherNodes = new ArrayList<>(); IntStream.range(0, pairNodes).forEach(i -> { int bx = scanner.nextInt(); int by = scanner.nextInt(); map[bx][by] = false; Node begin = new Node(bx, by); int ex = scanner.nextInt(); int ey = scanner.nextInt(); map[ex][ey] = false; Node end = new Node(ex, ey); togetherNodes.add(new TogetherNode(begin, end)); }); this.printMap(); } public void resolve() { if (this.togetherNodes.size() == 0) { return; } Node begin = togetherNodes.get(0).begin; Node end = togetherNodes.get(0).end; boolean success = this.process(0, begin.x, begin.y, end.x, end.y); System.out.println(success ? "路径探测成功" : "路径探测失败"); } private void printMap() { StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < map.length; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < map[i].length; ++j) { result.append(map[i][j] ? 1 : 0).append(" "); } result.append(LineSeparator.Windows); } System.out.println(result.toString()); } private boolean process(int ix, int bx, int by, int ex, int ey) { //如果 map[bx][by] == false, 说明是端点 boolean endpoint = !map[bx][by]; map[bx][by] = false; List<Node> path = togetherNodes.get(ix).path; path.add(new Node(bx, by)); //到达终点 if (bx == ex && by == ey) { if (ix + 1 >= togetherNodes.size()) { return true; } Node begin = togetherNodes.get(ix + 1).begin; Node end = togetherNodes.get(ix + 1).end; //下一个路径探索 boolean success = this.process(ix + 1, begin.x, begin.y, end.x, end.y); if (success) return success; } else { for (int i = 0; i < dir.length; ++i) { int nextx = bx + dir[i][0]; int nexty = by + dir[i][1]; //如果节点标记为false,并且节点不是终节点的时候 if (!map[nextx][nexty] && !(nextx == ex && nexty == ey)) { continue; } boolean success = this.process(ix, nextx, nexty, ex, ey); if (success) return true; } } if (!endpoint) { map[bx][by] = true; } path.remove(path.size() - 1); return false; } public String fetchResult() { if (togetherNodes.size() == 0) { return ""; } StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(); togetherNodes.stream().map(TogetherNode::getPath).forEach( path -> { for (Iterator<Node> it = path.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) { Node node = it.next(); result.append("(") .append(node.x) .append(":") .append(node.y) .append(")"); if (it.hasNext()) { result.append("->"); } } result.append(LineSeparator.Windows); } ); return result.toString(); } private class Node { public int x; public int y; public Node(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } } private class TogetherNode { public Node begin; public Node end; private List<Node> path; public TogetherNode(Node begin, Node end) { this.begin = begin; this.end = end; path = new ArrayList<>(); } public List<Node> getPath() { return path; } } public static void main(String[] args) { LineTogether lt = new LineTogether(); lt.resolve(); System.out.println(lt.fetchResult()); } }
输入数据
5 5 5 3 1 1 4 4 1 4 5 4 2 2 3 4 4 5 5 1 5 2 4
输出数据
路径探测成功 (3:1)->(2:1)->(1:1)->(1:2)->(1:3)->(1:4) (4:1)->(5:1)->(5:2)->(5:3)->(4:3)->(3:3)->(3:4)->(3:5)->(4:5) (4:2)->(3:2)->(2:2)->(2:3) (4:4)->(5:4)->(5:5) (1:5)->(2:5)->(2:4)
操作效果
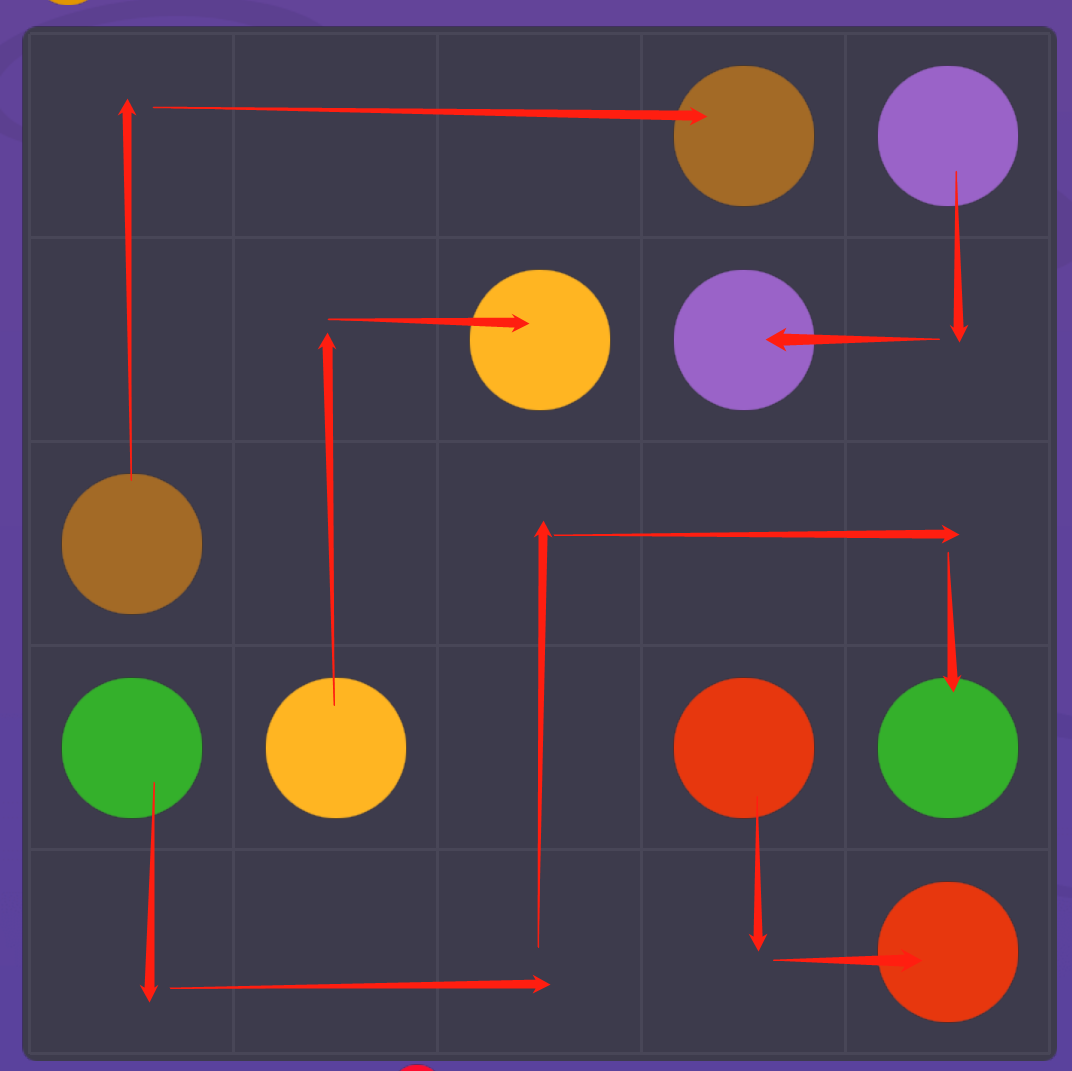
本文来自博客园,作者:hjzqyx,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/hujunzheng/p/9253505.html





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
2014-07-02 poj 2528 Mayor's posters(线段树+离散化)