Spring MVC源码——Servlet WebApplicationContext
上一篇笔记(Spring MVC源码——Root WebApplicationContext)中记录了下 Root WebApplicationContext 的初始化代码.这一篇来看 Servlet WebApplicationContext 的初始化代码
DispatcherServlet 是另一个需要在 web.xml 中配置的类, Servlet WebApplicationContext 就由它来创建和初始化.
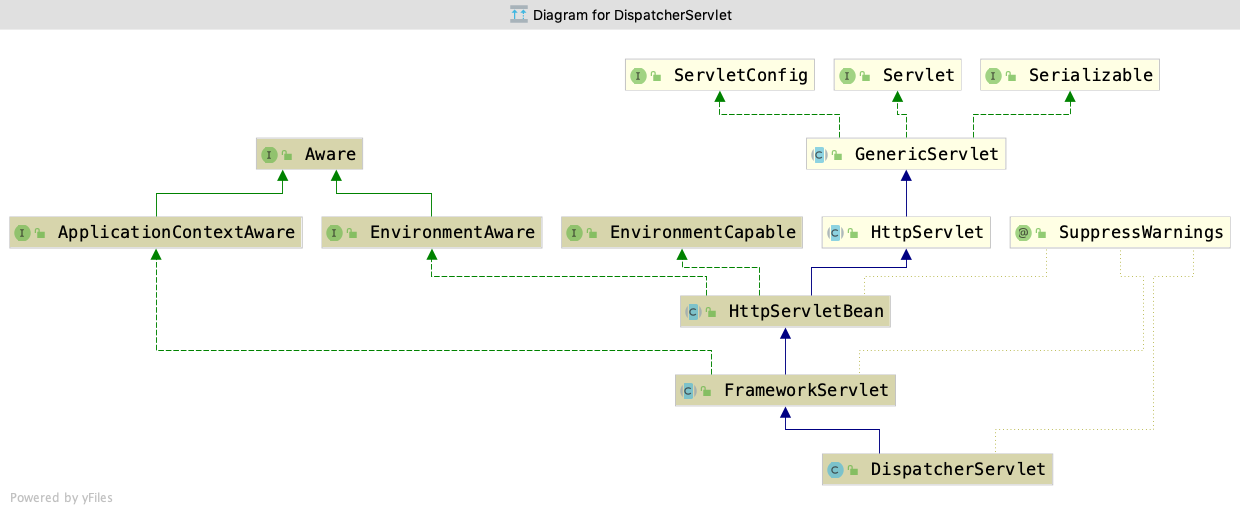
HttpServletBean
HttpServletBean 简单继承了 HttpServlet, 负责将 init-param 中的参数注入到当前 Servlet 实例的属性中, 并且为子类提供了增加 requiredProperties 的能力. HttpServletBean 并不依赖于 Spring 容器.
来看一下它的 init() 方法:
public final void init() throws ServletException { // Set bean properties from init parameters. // 从 ServletConfig 中取出初始化参数到 PropertyValues。ServletConfigPropertyValues 的构造器中将会检查是否缺失了必要属性 PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties); if (!pvs.isEmpty()) { try { // 将 servlet 对象包装成 BeanWrapper ,从而能够以 Spring 的方式(反射)来注入参数 BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this); ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext()); // 注册 PropertyEditor,遇到 Resource 类型的属性时,用 ResourceEditor 解析 bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment())); // 初始化 BeanWrapper,空方法 initBeanWrapper(bw); // 注入属性,忽略没有 setter 的属性 bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) { logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex); } throw ex; } } // Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like. // 由子类实现初始化逻辑 initServletBean(); }
private static class ServletConfigPropertyValues extends MutablePropertyValues { public ServletConfigPropertyValues(ServletConfig config, Set<String> requiredProperties) throws ServletException { // 将 requiredProperties 拷贝到新的 Set missingProps Set<String> missingProps = (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(requiredProperties) ? new HashSet<>(requiredProperties) : null); // 将 ServletConfig 中的初始化参数取出,添加到 MutablePropertyValues 中 Enumeration<String> paramNames = config.getInitParameterNames(); while (paramNames.hasMoreElements()) { String property = paramNames.nextElement(); Object value = config.getInitParameter(property); addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(property, value)); if (missingProps != null) { missingProps.remove(property); } } // Fail if we are still missing properties. if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(missingProps)) { // 存在必须出现的条件没出现 throw new ServletException( "Initialization from ServletConfig for servlet '" + config.getServletName() + "' failed; the following required properties were missing: " + StringUtils.collectionToDelimitedString(missingProps, ", ")); } } }
FrameworkServlet
FrameworkServlet 是一个更具体的 Servlet 基类. 它有以下两个功能:
- 每个 servket 管理一个
WebApplicationContext实例. - 无论请求是否成功, 根据请求处理发布事件.
FrameworkServlet 重写了 HttpServletBean 的 initServletBean() 方法, 这个方法会在 所有 servlet 的属性被注入之后执行, 来看一下代码:
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException { getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'"); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { // 初始化 webApplicationContext this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); // 在容器被加载后执行,由子类来实现一些必要的初始化 initFrameworkServlet(); } catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) { logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); throw ex; } // 略去打印日志的部分 ...
}
initWebApplicationContext() 方法会初始化并返回一个容器:
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { // 获取 Root WebApplicationContext WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null; if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { // A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it // 一个上下文已经被注入进来 wac = this.webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { // 如果是 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext, ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { // 没有激活,设置父容器,配置并且刷新容器 if (cwac.getParent() == null) { cwac.setParent(rootContext); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } if (wac == null) { // 尝试从 ServletContext 中获取一个容器 wac = findWebApplicationContext(); } if (wac == null) { // 创建一个新的容器并初始化 wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { // 没有触发过刷新时间 synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) { // 手动触发刷新事件 onRefresh(wac); } } if (this.publishContext) { // Publish the context as a servlet context attribute. // 将容器发布到 ServletContext 的属性上 String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); } return wac; }
onRefresh() 方法供子类来重写, DispatcherServlet 重写了这个方法来初始化 MVC 中的一些组件:
@Override protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { initStrategies(context); } protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { initMultipartResolver(context); initLocaleResolver(context); initThemeResolver(context); initHandlerMappings(context); initHandlerAdapters(context); initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); initViewResolvers(context); initFlashMapManager(context); }
initWebApplicationContext() 方法调用的其他方法其实和 ContextLoader 中的方法比较类似, 这里就不再放上来了, 有兴趣的可以访问我的源码注释.
总结
通过本篇博客以及上一篇博客,相信大家对springmvc的上下文有了明确的认识。总的来说,默认springmvc项目会有两个上下文(root webapplicationcontext 和 servlet webapplicationcontext)。接下来的博文会带大家认识一下springboot项目的上下文以及springmvc项目上下文和springboot项目上下文的异同点,敬请期待。
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/FJH1994/p/10813687.html
本文来自博客园,作者:hjzqyx,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/hujunzheng/p/10824788.html






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 展开说说关于C#中ORM框架的用法!