Java线程总结(一)
首先,先贴上一个简单的线程实例:
public class MyThread extends Thread{ @Override public void run(){ try { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ int time = 1000; Thread.sleep(time); System.out.println("run = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread myThread = new MyThread(); myThread.setName("MyThread"); myThread.start(); try{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ int time = 1000; Thread.sleep(time); System.out.println("main = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
运行结果如下:
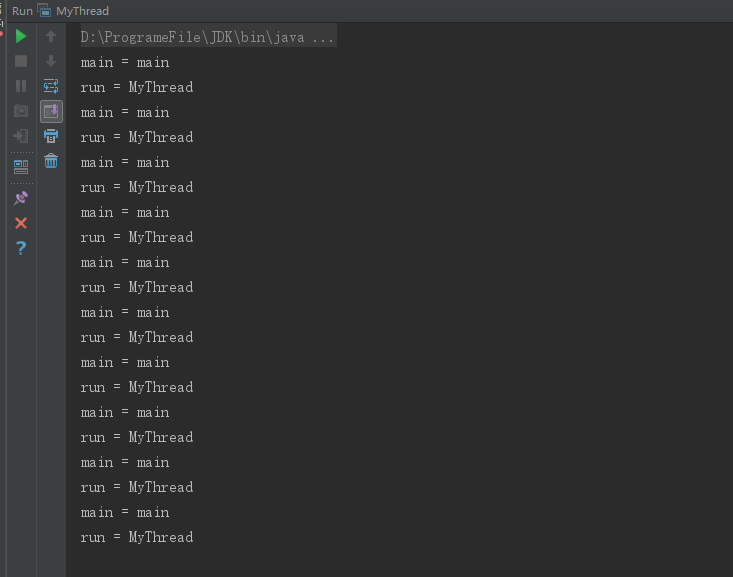
由运行结果可以看出,程序中有两个线程,一个是主线程,另一个是我手动创建的线程,主线程都是jvm创建的。
线程执行start()方法不代表线程的启动顺序,如下例:
public class MyThread extends Thread{ private int i; public MyThread(int i){ super(); this.i = i; } @Override public void run(){ System.out.println(i); } public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread thread1 = new MyThread(1); MyThread thread2 = new MyThread(2); MyThread thread3 = new MyThread(3); MyThread thread4 = new MyThread(4); MyThread thread5 = new MyThread(5); MyThread thread6 = new MyThread(6); MyThread thread7 = new MyThread(7); MyThread thread8 = new MyThread(8); MyThread thread9 = new MyThread(9); MyThread thread10 = new MyThread(10); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread3.start(); thread4.start(); thread5.start(); thread6.start(); thread7.start(); thread8.start(); thread9.start(); thread10.start(); } }
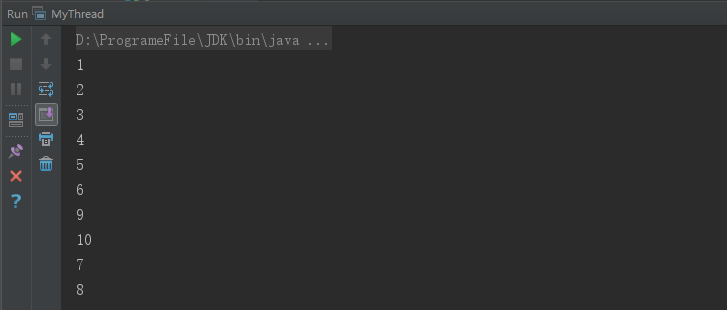
运行结果如下,执行顺序与调用start()方法的顺序不一致:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号