2021/9/14 ~15(单链表 + 单链表反转)
2021/9/14 ~15(单链表)
dizzy day
单链表习题
对于单链表的再度学习,我明白了引用的概念,变量在栈区,new 出来的对象在堆区。
变量可以操作内存中的数据。a = head. 指变量a指向head变量所在的内存区。 即a和head都指向了一块内存区。a和head = 其他值并不会改变内存地址的值。
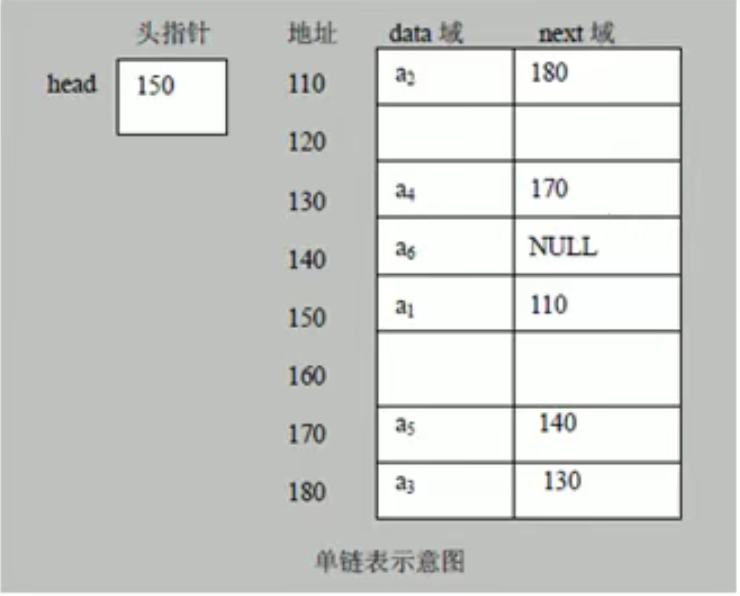
做题了。
单链表反转4种方式
http://c.biancheng.net/view/8105.html
我这里的头节点包含了信息,在某些操作时还是需要头节点指针的(纯粹)
package LinkedList;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* 我定义的单向链表,其中第一个元素index为1
*
* @param <T>
*/
public class MyLinkedList<T> {
private Node<T> head;
private Node<T> tail;
private int size; //仅仅记录链表长度,不做规定
public Node<T> getTail() {
return tail;
}
private class Node<T> {
private T data;
private Node<T> next;
public Node() {
data = null;
next = null;
}
public Node(T data) {
this.data = data;
next = null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"data=" + data +
", next=" +
'}';
}
}
public int getSize() {
return this.size;
}
public void setTail(Node<T> tail) {
this.tail = tail;
}
//构造函数
public MyLinkedList() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
}
public T getFirst() throws Exception {
rangeCheck();
return this.head.data;
}
public Node<T> getHead(){
return this.head;
}
private void rangeCheck() throws Exception {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("List is empty");
}
}
private void indexCheck(int index) throws Exception {
if (index > this.size || index <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Index");
}
}
public T getLast() throws Exception {
rangeCheck();
return this.tail.data;
}
public Boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size == 0;
}
public Boolean isNotEmpty() {
return !isEmpty();
}
/**
* 我定义第一个节点就为头节点,最后一个节点为size大小,index 从一开始
*/
public T getAt(int index) throws Exception {
return (T) getNodeAt(index).data;
}
/**
* 根据Node中的data查找在表中的位序
*
* @param data
*/
public int getIndexAt(T data) throws Exception {
int index = 1;
rangeCheck();
Node<T> tmp = this.head;
while (tmp != null && tmp.data != data) {
tmp = tmp.next;
index++;
}
if (tmp == null) return -1;
else return index;
}
public Node getNodeAt(int index) throws Exception {
rangeCheck();
indexCheck(index);
Node<T> temp = this.head;
for (int i = 1; i <= index - 1; i++) {
temp = temp.next; // 这段代码多多理解。temp = 一个内存地址
}
return temp;
}
/**
* 尾插法
*
* @param data
*/
public void addLast(T data) {
// create
Node<T> node = new Node();
node.data = data;
// attach
if (isNotEmpty()) {
this.tail.next = node;
}
if (isEmpty()) {
this.head = node;
}
this.tail = node;
this.size += 1;
}
/**
* 头插法
*
* @param data
*/
public void addFirst(T data) {
Node<T> node = new Node();
node.data = data;
if (isNotEmpty()) {
node.next = head;
}
if (isEmpty()) {
this.tail = node;
}
this.head = node;
this.size += 1;
}
public void addFirst(Node<T> node) {
if (isNotEmpty()) {
node.next = this.head;
}
if (isEmpty()) {
this.tail = node;
this.tail.next = null;
}
this.head = node;
this.size += 1;
}
/**
* 假如idx=1,那么头插,如果idx>siz,尾插
*
* @param data
* @param idx
*/
public void addAt(T data, int idx) throws Exception {
if (idx <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Index");
}
if (idx == 1) {
addFirst(data);
} else if (idx > size) {
addLast(data);
}
Node<T> node = new Node();
node.data = data;
Node preNode = getNodeAt(idx - 1);
node.next = preNode.next;
preNode.next = node;
}
public T removeFirst() throws Exception {
rangeCheck();
Node<T> tmp = this.head;
if (this.size == 1) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
} else {
head = head.next;
this.size--;
}
return tmp.data;
}
public T removeLast() throws Exception {
rangeCheck();
if (this.size == 1) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
}
Node<T> tmp = this.tail;
Node preNode = getNodeAt(this.size - 1);
preNode.next = null;
this.tail = preNode;
this.size--;
return tmp.data;
}
public T removeAt(int idx) throws Exception {
rangeCheck();
indexCheck(idx);
if (idx == 1) {
return removeFirst();
} else if (idx == this.size) {
return removeLast();
}
Node<T> prefix = getNodeAt(idx - 1);
Node<T> removeNode = prefix.next;
prefix.next = removeNode.next;
this.size--;
return removeNode.data;
}
public void removeAll() throws Exception {
while (this.size > 0) {
removeFirst();
}
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("========================");
Node<T> temp = this.head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.println(temp.data);
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println("Over");
}
/**
* 新的需求,根据id排序
* 今天状态好差我就不写了
* 思路:1。在头节点设置前缀:preHead
* 2。有bug tail怎么变化呢?
*/
public void addByOrder(Integer data) {
Node<Integer> node = new Node<Integer>(data);
Node<Integer> preHead = new Node<Integer>();
preHead.next = (Node<Integer>) this.head;
Node<Integer> tmp = preHead;
while (true) {
if (tmp.next == null) {
addLast((T) data); // 操作有设置tail
break;
}
if (tmp.next.data > node.data) {
node.next = tmp.next;
tmp.next = node;
break;
}
if (tmp.next.data == node.data) {
System.out.println("重复啦");
break;
}
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}
/**
* 习题练习一 : 获取链表节点个数
*/
public int getLength() {
Node<T> tmp = this.head;
int count = 0;
while (tmp != null) {
count++;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return count;
// return getSize();
}
/**
* 习题练习二:查找单链表中的倒数第index个节点、
* 解答:因为是单链表,只能从头开始,不能从尾巴开始,效率有点低
*
* @param index
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public Node<T> getIndexOfLast(int index) throws Exception {
return getNodeAt(size - index + 1);
}
/**
* 链表反转 解决方法一:头插法 2🌟🌟
*/
public MyLinkedList<T> linkedListReverse() throws Exception {
if (this.head==null || this.head.next==null){
System.out.println("链表为空or只有一个节点");
return null ;
}
MyLinkedList list = new MyLinkedList();
Node<T> tmp;
while(head!=null){
tmp = this.head;
head = head.next;
list.addFirst(tmp);
}
return list;
}
/**
* 链表反转 解决方法二:迭代反转 推荐指数🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟
* 注意点:下面这种while循环不会导致空指针!
*/
public void linkedListReverse2() {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
System.out.println("can't not reverse");
return;
}
Node<T> beg = null;
Node<T> mid = head;
Node<T> end = head.next;
while (true) {
mid.next = beg;
if (end == null) {
break;
}
beg = mid;
mid = end;
end = end.next;
}
Node<T> tmp = tail;
tail = head;
head = tmp;
}
/**
* 链表反转 解决方法三:迭代反转 思路NB
* 推荐指数🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟
* 迭代可以反着来
* 不知道为什么有bug ==>需要解决首位的位置
*/
public Node<T> linkedListReverse3(Node<T> head) throws Exception {
if (head==null || head.next==null){
// 需要交换首位的位置!!
Node<T> tmp = this.head;
this.head = head;
this.tail = tmp;
return head;
}
// newNode永远是尾
Node<T> newNode = linkedListReverse3(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newNode;
}
/**
* 逆序打印单链表 方式一:栈
*/
public void reverseListAndPrint(){
if (head==null){
return;
}
Stack<Node<T>> stack = new Stack<>();
Node<T> copyHead = head;
Node<T> tmp ;
while(head!=null){
tmp = head;
head = head.next;
stack.add(tmp);
}
this.head = copyHead;
while(stack.size()>0){
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}
/**
* 逆序打印单链表 方式二:递归
*
*/
public void reverseListAndPrint3(Node<T> head){
if(head !=null && head.next!=null){
reverseListAndPrint3(head.next);
}
System.out.println(head.data);
}
}
测试
package LinkedList;
import LinkedList.pojo.Person;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class MyLinkedListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MyLinkedList<Person> list = new MyLinkedList<Person>();
Person person = new Person(1,"22",1);
Person person2 = new Person(2,"22",1);
Person person3 = new Person(3,"22",1);
Person person4 = new Person(4,"22",1);
list.addLast(person);
list.addLast(person2);
list.addLast(person4);
list.addLast(person3);
list.display();
System.out.println("==");
list.reverseListAndPrint3(list.getHead());
System.out.println("size"+list.getSize());
System.out.println("firse"+list.getFirst());
System.out.println("last"+list.getLast());
System.out.println("000000000000000000000000000000");
// first element i.e.10 should be printed
// element at 3rd index i.e.40 should be printed
//System.out.println(list.getAt(3));
// a memory address of a node should be printed
System.out.println(list.getNodeAt(3));
// 10 should be removed and printed
System.out.println(list.removeFirst());
// 40 should be removed and printed
System.out.println(list.removeLast());
// list without 10 and 40 should be printed
list.display();
// 100 should be added at first
list.display();
// 30 should be removed
list.removeAt(2);
// 300 should be added at 2nd index
list.display();
System.out.println(list.getSize());
list.removeAll();
System.out.println(list.getSize());
}
}


