Vue知识总结
基础知识
appDemo.js
var one = new Vue({ //实例一个vue对象
el:"#vue-app-one", //获取element,id为vue-app的element里此实例对象生效
data:{ //data,用于存储各种数据
age:30,
sex:"男",
website:"https://www.cnblogs.com/huihuihero/",
websiteTag:"<a href='https://www.cnblogs.com/huihuihero/'>链接</a>", //插入新元素
bindName:"jack", //双向绑定
colorChange:false, //动态改变class属性值
error:false, //v-if指令使用
success:true,
friends:[{name:"剑姬",age:22},{name:"亚索",age:24},{name:"剑圣",age:20}],
},
methods:{ //methods,用于存储各种方法
add:function(inc){
this.age+=inc; //通过this.age便可调用data里的age,不用this.data.age
},
subtract:function(dec){
this.age-=dc;
},
descSex:function(name){ //传参name
return name+"的性别是"+this.sex
},
inputThings:function(){ //键盘事件
console.log("您正在输入")
},
handleBindName:function(){ //双向绑定
this.bindName=this.$refs.bothBind.value; //通过 ref 双向绑定
console.log(this.bindName);
},
},
computed:{ //【计算属性computed】 methods里的一个方法执行时,其他不相干方法也会激活。而computed里的属性执行时则不会。
//因此若要在网页中使用搜索,大量计算等功能,使用methods来写方法则会很耗费性能。故使用computed
//此外计算属性是属性,调用时不能像方法那样调用,故不能带()。
addNumber:function(){
return this.age++
}
},
});
var two=new Vue({
el:"#vue-app-two",
data:{
},
methods:{
changeSex:function(){
one.sex="女" //通过这种方式在当前实例对象中改变其他实例对象的data
},
},
})
indexDemo.html
<div id="vue-app-one"> //根元素
<button v-on:click="add(1)">涨一岁</button> //【v-on用于绑定事件】,调用add方法,click单击事件
<button @click="add(1)">涨一岁</button> //v-on方法也可用@代替,效果是一样的
<button v-on:click="add(1)">减一岁</button>
<button v-on:dblclick="add(10)">涨十岁</button> //dblclick双击事件
<input type="text" v-bind:value="age" /> //v-bind绑定age值
<a v-bind:href="website">我的技术博客</a> //【v-bind用于绑定属性】,给属性绑定对应的值
<span>性别是:{{sex}}</span> // {{ }} 渲染data里的数据,直接调用sex即可,不用this.sex或者this.data.sex
<span>{{descSex("二狗")}}</span> // {{ }} 直接调用函数并传参,注意直接调用方法用{{}},且需要带()
<p v-html="websiteTag"></p> //【v-html识别元素】,用于插入新元素
<button v-on:click.once="add(1)">涨一岁</button> //【事件修饰符】,.once(执行一次),.stop(阻止事件冒泡),.prevent(阻止跳转,如a标签)
<input type="text" v-on:keyup="inputThings" /> //【键盘事件】,keyup,keydown
<input type="text" v-on:keyup.enter="inputThings" /> 【键值修饰符】,.enter(在点击键盘上enter键后输入),.alt.enter(可以链式,同时输入alt+enter)
<input type="text" v-model="bindName"/> 【双向绑定】第一种方法 v-model,v-model直接绑定data中定义的属性即可实现双向绑定,注意:v-model只能用在表单元素中(input select textarea checkbox等)
<input type="text" ref="bothBind" v-on:keyup="handleBindName" />双向第二种方法 这里ref定义的名称是bothBind,则在handleBindName中使用this.$refs.bothBind.value
<span>{{addNumber}}<span> //【计算属性】不是方法,调用时不用带()
<div v-bind:class="{red:true,blue:false}"></div> //【绑定class属性】,true则生效,false则不生效
<div v-on:click="colorChange=!colorChange" v-bind:class="{redColor:colorChange}"></div> //动态改变class,点击后data里定义的colorChange取反,class属性生效,再点击再取反,失效
<button v-on:click="error=!error">切换网络</button>
<div v-if="error">网络连接错误404</div> //【v-if v-else-if】,v-if指令为false时是直接抹除的,元素不占位。v-show指令为false时,元素还在,只是display:none了
<div v-else-if="success">网络连接成功200</div>
<div v-show="error">网络连接错误404</div> //【v-show】
<ul>
<li v-for="every in friends" :key="every.id">姓名:{{every.name}} - 年龄:{{every.age}}</li> //【v-for】循环遍历数组,严格来说每个遍历出来的标签都应该有:key="id"
</ul>
<ul>
<li v-for="(every,index) in friends">序号:{{index}} - 姓名:{{every.name}} - 年龄:{{every.age}}</li> //将index也遍历出来
</ul>
<template v-for="(every,index) in friends"> //v-for遍历【数组】,template是vue特定的元素,它只负责包裹元素,但不会被渲染出来,非常好用。此处若将template替换成div,则div会被渲染出来,会有些冗余
<div v-for="(val,key) in every"> //v-for遍历【对象】。其中key对应对象的“键”。val对应对象的“值”
<p>{{key}} - {{val}}</p>
</div>
</template>
</div>
组件
vue-app.js---------------------------------------
Vue.component("greeting",{ //自定义一个组件
template:`
<div> //要有一个根标签
<p>{{name}}:开黑吗?我亚索贼6</p>
<button v-on:click="changeName">改名字</button>
</div>
`,
data(){ //这里为什么这样写,这样每次都会return数值,保证了每一个组件都是独立运行互不干扰的
return {
name:"李二狗",
age:22,
}
},
methods:{
changeName:function(){
this.name="王铁蛋";
}
}
})
new Vue({
el:"#vue-app-one",
})
new Vue({
el:"#vue-app-two",
})
index.html----------------------------------------
<div id="vue-app-one">
<greeting></greeting> //这里会渲染greeting组件
</div>
<div id="vue-app-two">
<greeting></greeting> //这里也会渲染greeting组件,并且和上面vue-app-one里的greeting是各自独立互不干扰的
</div>
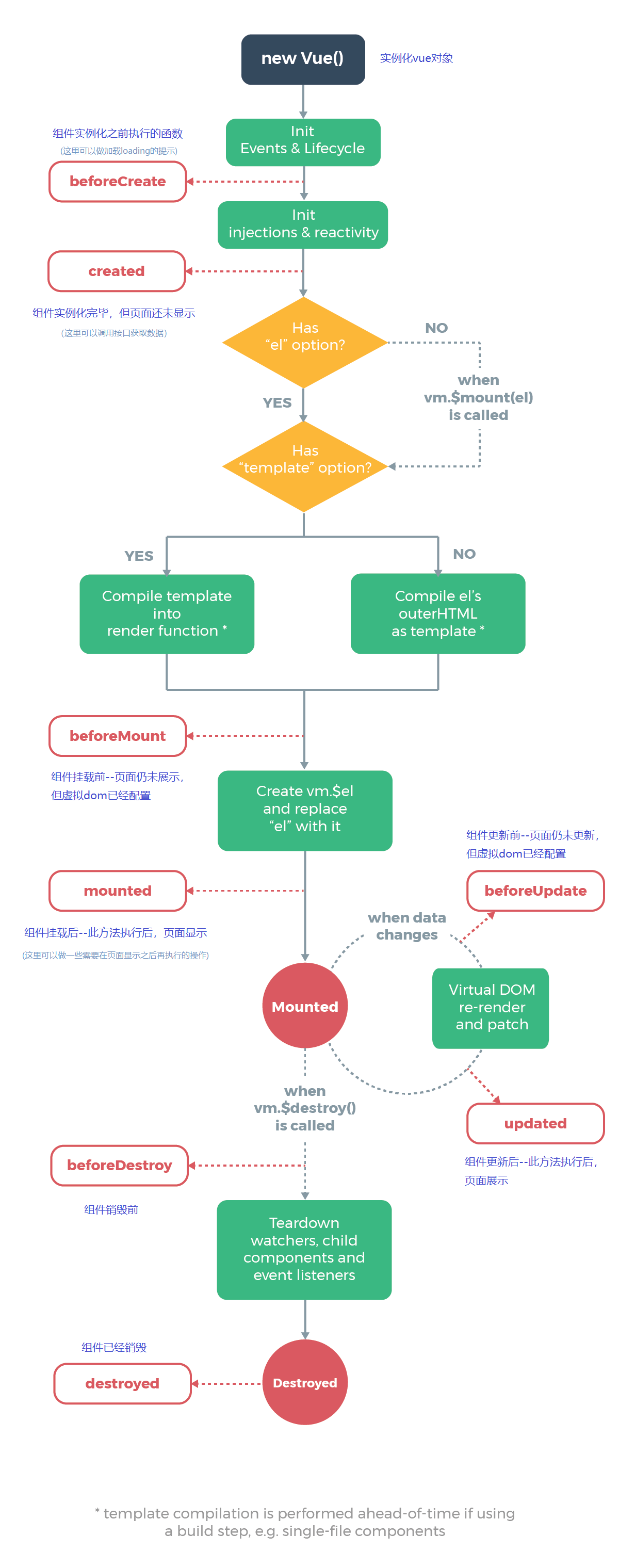
vue生命周期,直接上图
————————————————————
————————————————————


