MySQL学习笔记之MySQL8.0新特性
一、账户与安全
1)用户创建和授权
MySQL8.0创建用户和授权用户的命令需要分开执行:
创建用户:
create user '用户名'@'host' identified by '密码';
授权用户:
grant 权限列表 privileges on 数据库.数据表 to '用户名'@'host';
MySQL5.7版本中创建用户和授权用户一条命令即可完成:
grant 权限列表 privileges on 数据库.数据表 to '用户名'@'host' identified by '密码';
2)认证插件更新
MySQL8.0中默认的身份认证插件是caching_sh2_password,代替了之前的mysql_native_password。
可以使用
show variables like 'default_authentication%';
来查看MySQL的身份认证插件。
如果想在MySQL8.0中继续使用mysql_native_password插件认证,可以修改配置文件:
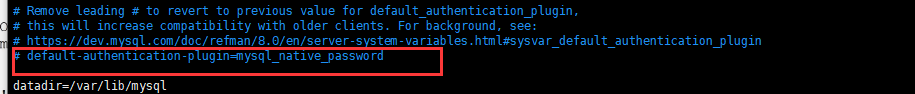
打开注释,重启MySQL服务器即可。
也可以使用alter命令修改用户的认证插件:
alter user '用户名'@'host' identified with mysql_native_password by '密码';
3)密码管理
MySQL8.0开始允许限制重复使用以前的密码。
password_history = n; # 表示不允许用户使用最近n次使用过的密码
password_reuse_interval=90; #表示不允许用户使用最近90天内使用过的密码
password_require_current=off; #默认OFF,修改密码时是否需要提供当前用户使用的密码,OFF不需要,ON需要
可以使用show variables like 'password%'来查看当前的密码修改策略,MySQL8.0之前没有改变量。
mysql> show variables like 'password%';
+--------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------------+-------+
| password_history | 0 |
| password_require_current | OFF |
| password_reuse_interval | 0 |
+--------------------------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
全局密码重置策略:
a)修改MySQL配置文件,在配置文件中添加:password_history=3;然后重启MySQL服务器。
b)使用set global password_history=3;使用这种方式只针对当前进程有效,MySQL服务器重启之后失效。
MySQL8.0新增了持久化更改变量的方法:
set persist password_history=3; #使用这种方式MySQL将变量设置持久化。
使用这种设置方式,MySQL8.0会在数据文件目录(/var/lib/mysql/)生成一个mysqld-auto.cnf文件,在MySQL启动时不仅会检查MySQL默认的配置文件,还会检查该文件。
针对某一用户设置密码重置策略:
alter user 'wyh'@'%' password history 5;
设置用户重置密码策略后,修改用户密码时会在mysql数据库的password_history中生成一条记录,记录当前设置的密码,再次修改密码时会根据设置的密码策略比对表中的记录。策略不通过将报‘ERROR 3638 (HY000): Cannot use these credentials for 'wyh@%' because they contradict the password history policy’错误。
password_reuse_interval和password_require_current重置密码策略的设置方法和password_history设置全局重置密码相同。
具有root权限的账户修改别的账户密码时,password_require_current策略无效。
4)角色管理
MySQL8.0提供的新功能。角色是一组权限的集合。
a)创建角色,创建角色之后会在mysql数据库的user表中创建一个以角色名命名的用户。
create role '角色名';
b)角色授权
grant 权限列表 on 数据库.表 to '角色名';
c)用户授予角色权限
grant '角色名' to '用户'@'host';
d)查看用户权限
show grants for '用户名'@'host';
e)查看用户通过某个角色获得的权限
show grants for '用户名'@'host' using '角色名';
f)查看当前用户激活的角色
select current_role();
用户首次登陆时(root除外)默认角色权限未激活,需要使用:
set role '权限名';
来激活角色。
g)为某个用户设置默认角色
set default role [none|角色名称] to '用户名'@'host';
或设置全部角色
set default role all to '用户名'@'host';
用户角色保存在mysql数据库中的default_roles表中,角色授权信息保存在mysql数据库中的role_edges表中。
h)撤销角色权限
revoke 权限列表 on 数据库.数据表 from '角色名';
二、优化器索引
MySQL8.0新增了三种索引方式:隐藏索引、降序索引、函数索引。
1)隐藏索引
MySQL8.0开始支持隐藏索引,即不可见索引。
隐藏索引不会被优化器使用,但仍然需要维护。
创建索引时可以添加索引是否隐藏选项:
create index 索引名 on 表名(字段列表) [invisible|visible]
查看查询优化器:
mysql> select @@optimizer_switch\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
@@optimizer_switch: index_merge=on,index_merge_union=on,index_merge_sort_union=on,index_merge_intersection=on,engine_condition_pushdown=on,index_condition_pushdown=on,mrr=on,mrr_cost_based=on,block_nested_loop=on,batched_key_access=off,materialization=on,semijoin=on,loosescan=on,firstmatch=on,duplicateweedout=on,subquery_materialization_cost_based=on,use_index_extensions=on,condition_fanout_filter=on,derived_merge=on,use_invisible_indexes=off,skip_scan=on,hash_join=on,subquery_to_derived=off,prefer_ordering_index=on,hypergraph_optimizer=off,derived_condition_pushdown=on
其中:use_invisible_indexes=off(默认不使用隐藏索引,即值为off时优化器不使用隐藏索引,值为on时优化器使用隐藏索引)
mysql> explain select * from students where name='李四'; #值为off时
+----+-------------+----------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+----------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | students | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 7 | 14.29 | Using where |
+----+-------------+----------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> set @@optimizer_switch='use_invisible_indexes=on';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from students where name='李四';
+----+-------------+----------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+----------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | students | NULL | ref | idx_name | idx_name | 51 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+----------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
设置索引是否可见:
alter table 表名 alter index 索引名 invisible|visible;
mysql> alter table students alter index idx_name visible;
注意:MySQL主键不可设置为隐藏索引。
2)降序索引
MySQL8.0开始真正支持降序索引,只有InnoDB存储引擎支持降序索引,只支持BTREE降序索引。
MySQL8.0不再对 group by 操作进行隐式排序。
MySQL5.7:
mysql> create table t2(c1 int,c2 int,index idx(c1 asc,c2 desc));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (1.43 sec)
mysql> show create table t2 \G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t2
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `t2` (
`c1` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`c2` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
KEY `idx` (`c1`,`c2`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from t2 order by c1,c2 desc;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | index | NULL | idx | 10 | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using index; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from t2 order by c1 desc,c2 desc;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | index | NULL | idx | 10 | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from t2 order by c1 desc,c2 asc;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | index | NULL | idx | 10 | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using index; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select count(*),c2 from t2 group by c2;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | index | idx | idx | 10 | NULL | 6 | 100.00 | Using index; Using temporary; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
MySQL8.0:
mysql> show create table t2 \G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t2
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `t2` (
`c1` int DEFAULT NULL,
`c2` int DEFAULT NULL,
KEY `idx` (`c1`,`c2` DESC)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from t2 order by c1,c2 desc;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | index | NULL | idx | 10 | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from t2 order by c1 desc,c2 asc;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | index | NULL | idx | 10 | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Backward index scan; Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from t2 order by c1 desc,c2 desc;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | index | NULL | idx | 10 | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using index; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.01 sec)
mysql> explain select count(*),c2 from t2 group by c2;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | index | idx | idx | 10 | NULL | 6 | 100.00 | Using index; Using temporary |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
通过以上MySQL5.7版本和MySQL8.0版本的对比可以看出有以下几点区别:
① MySQL5.7创建降序索引不起作用,仍然为默认的升序索引,MySQL8.0显示创建了降序索引。
② 使用explain分析查询语句,MySQL5.7在使用order by排序时,同向排序不使用 Using filesort,反向排序使用 Using filesort;MySQL8.0同向排序时使用 Using filesort,而反向排序不使用 Using filesort,在排序规则和创建索引的排序规则相反时,增加了一个Backward index scan(反向索引排序)。
③ 使用group by 分组查询时,MySQL5.7将使用 Using filesort,而MySQL8.0不使用Using filesort。
3)函数索引
MySQL8.0.13开始支持在索引中使用函数(表达式)的值并支持降序索引和JSON数据索引。
函数索引基于虚拟列功能实现。
mysql> create table t3(c1 varchar(10),c2 varchar(10)); #创建测试表
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> create index idx_c1 on t3(c1); #创建普通索引
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> create index idx_func_c2 on t3( (upper(c2)) ); #创建函数索引
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> show index from t3 \G; #查看索引
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t3
Non_unique: 1
Key_name: idx_c1
Seq_in_index: 1
Column_name: c1
Collation: A
Cardinality: 0
Sub_part: NULL
Packed: NULL
Null: YES
Index_type: BTREE
Comment:
Index_comment:
Visible: YES
Expression: NULL #表达式为空,基于列的索引
*************************** 2. row ***************************
Table: t3
Non_unique: 1
Key_name: idx_func_c2
Seq_in_index: 1
Column_name: NULL
Collation: A
Cardinality: 0
Sub_part: NULL
Packed: NULL
Null: YES
Index_type: BTREE
Comment:
Index_comment:
Visible: YES
Expression: upper(`c2`) #表达式为upper函数
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from t3 where upper(c1) = 'ABCD'; #没有使用索引
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t3 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from t3 where upper(c2) = 'ABCD'; #使用了函数索引
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t3 | NULL | ref | idx_func_c2 | idx_func_c2 | 43 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
MySQL5.7中可以使用虚拟列达到函数索引的效果:
在t3表的基础上新加一个计算列c3:
alter table t3 add column c3 varchar(10) generated always as (upper(c1));
创建索引:
create index idx_c3 on t3(c3);
mysql> explain select * from t3 where upper(c1)='ASDC'; #使用了c3的索引
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t3 | NULL | ref | idx_c3 | idx_c3 | 43 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
json数据索引
mysql> create table t4(data json, index( (cast(data->>'$.name' as char(30))) ));
由于json数据内容不固定,可以使用cast()函数对json数据中的某个节点进行数据转换,上例中就是将data中的name节点转换成30个字符的字符串进行创建索引。
mysql> show index from t4 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t4
Non_unique: 1
Key_name: functional_index
Seq_in_index: 1
Column_name: NULL
Collation: A
Cardinality: 0
Sub_part: NULL
Packed: NULL
Null: YES
Index_type: BTREE
Comment:
Index_comment:
Visible: YES
Expression: cast(json_unquote(json_extract(`data`,_utf8mb4\'$.name\')) as char(30) charset utf8mb4)
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> explain select * from t4 where cast(data->>'$.name' as char(30)) = 'abcd';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t4 | NULL | ref | functional_index | functional_index | 123 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.01 sec)
在使用json索引时,查询条件的字段也需要和创建索引时保持一致(cast(data->>'$.name' as char(30)) = 'abcd')。
三、通用表表达式(Common Table Express,CTE)
1)非递归CTE
基本语法:
WITH cte_name (column_list) AS ( query ) SELECT * FROM cte_name;
mysql> with cte1(id) as (select 1),cte2(id) as (select id+1 from cte1) select * from cte1 join cte2;
+----+----+
| id | id |
+----+----+
| 1 | 2 |
+----+----+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> with d as (select * from dept) , dp as (select * from dept) select * from d left join dp on d.id = dp.ceo limit 10;
2)递归CTE
在查询中引用自己的定义,使用recursive表示。
基本语法:
with recursive cte(n) as ( query ) select * from cte;
mysql> with recursive cte(id) as (
select 1 # 初始化值
union all
select id+1 from cte #递归查询
where id < 5 #终止递归的条件
) select * from cte;
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
使用递归CTE生成斐波那契数列:
mysql> with recursive test(n1,n2) as (select 0,0 union all select n1+n2,n1+1 from test where n1 < 500) select n2 from test;
+------+
| n2 |
+------+
| 0 |
| 1 |
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 5 |
| 8 |
| 13 |
| 21 |
| 34 |
| 55 |
| 89 |
| 144 |
| 233 |
| 377 |
+------+
15 rows in set (0.00 sec)
创建测试表:
CREATE TABLE `t_emp` (
`id` int DEFAULT NULL,
`name` varchar(20) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`manger_id` int DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
插入测试数据:
insert into t_emp(id,name,manger_id) values(m9,'Pedro',198),
(72,'Pierre',29),
(123,'Adil',692),
(198,'John',333),
(333,'Yasmina',null),
(692,'Tarek',333),
(4610,'Sarah',29);
使用递归CTE查询员工领导路径:
mysql> with recursive emp_paths(id,name,path) as ( select id,name,cast(id as char(200)) from t_emp where manger_id is null union all select e.id,e.name,concat(ep.id,',',e.id) from emp_paths ep join t_emp e on ep.id=e.manger_id ) select * from emp_paths order by path;
3)递归限制
递归表达式的查询中需要包含一个终止递归的条件。
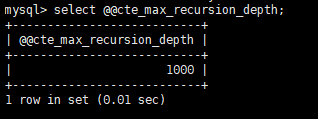
递归CTE有两个系统变量需要注意,可以避免递归进入死循环:
① cte_max_recursion_depth:最大递归次数,当递归查询次数超过该值时,将报“ERROR 3636 (HY000): Recursive query aborted after 1001 iterations. Try increasing @@cte_max_recursion_depth to a larger value.”错误,默认值为1000。
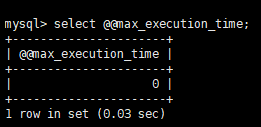
② max_execution_time:SQL语句最大执行时间
通用表表达式与派生表类似,就像语句级别的临时表或视图。
CTE可以在查询中多次引用,也可以引用其他CTE,可以实现递归。
CTE支持select/update/insert/delete等语句。
四、窗口函数
从MySQL8.0开始支持窗口函数(Window Function),也称为分析函数。主要用于数据分析。
窗口函数与分组聚合函数类似,但是每行数据都生成一个结果。
窗口函数使用基本语法:
select 查询列表,窗口聚合函数|窗口专用函数 over (参数) from 表名;
over参数:
partition by:按照什么进行分区,参数是可选的,默认把整张表作为一个分区。
order by:分组排序
frame_clause:
1)使用窗口聚合函数:sum、avg、max、min、count等
例如:查询每个学生的总分数和平均分数
mysql> select
s.name 姓名,su.name 科目,sc.score 分数,
sum(sc.score) over (partition by sc.student_id) 总分数,
avg(sc.score) over (partition by sc.student_id) 平均分
from students s
left join score sc on s.id=sc.student_id
left join subject su on su.id=sc.subject_id
where sc.score is not null
order by 姓名,总分数;
+-----------+--------+--------+-----------+-----------+
| 姓名 | 科目 | 分数 | 总分数 | 平均分 |
+-----------+--------+--------+-----------+-----------+
| 周芷若 | 语文 | 90 | 150 | 75.0000 |
| 周芷若 | NULL | 60 | 150 | 75.0000 |
| 李四 | 语文 | 86 | 325 | 81.2500 |
| 李四 | 数学 | 97 | 325 | 81.2500 |
| 李四 | 英语 | 85 | 325 | 81.2500 |
| 李四 | NULL | 57 | 325 | 81.2500 |
| 赵敏 | 语文 | 86 | 286 | 71.5000 |
| 赵敏 | 数学 | 87 | 286 | 71.5000 |
| 赵敏 | 英语 | 45 | 286 | 71.5000 |
| 赵敏 | NULL | 68 | 286 | 71.5000 |
+-----------+--------+--------+-----------+-----------+
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select s.name 姓名,su.name 科目,sc.score 分数,sum(sc.score) over (partition by sc.student_id order by sc.score rows unbounded preceding) 累计总分数,avg(sc.score) over (partition by sc.student_id rows between 1 preceding and 1 following) 移动平均分 from students s left join score sc on s.id=sc.student_id left join subject su on su.id=sc.subject_id where sc.score is not null order by 姓名,累计总分数;
+-----------+--------+--------+-----------------+-----------------+
| 姓名 | 科目 | 分数 | 累计总分数 | 移动平均分 |
+-----------+--------+--------+-----------------+-----------------+
| 周芷若 | NULL | 60 | 60 | 75.0000 |
| 周芷若 | 语文 | 90 | 150 | 75.0000 |
| 李四 | NULL | 57 | 57 | 71.0000 |
| 李四 | 英语 | 85 | 142 | 76.0000 |
| 李四 | 语文 | 86 | 228 | 89.3333 |
| 李四 | 数学 | 97 | 325 | 91.5000 |
| 赵敏 | 英语 | 45 | 45 | 56.5000 |
| 赵敏 | NULL | 68 | 113 | 66.3333 |
| 赵敏 | 语文 | 86 | 199 | 80.3333 |
| 赵敏 | 数学 | 87 | 286 | 86.5000 |
+-----------+--------+--------+-----------------+-----------------+
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)
over 参数相同时可以提取出来单独定义:
mysql> select s.name 姓名,su.name 科目,sc.score 分数,sum(sc.score) over w as '累计总分数',avg(sc.score) over w as '移动平均值' from students s left join score sc on s.id=sc.student_id left join subject su on su.id=sc.subject_id where sc.score is not null window w as (partition by sc.student_id rows unbounded preceding) order by 姓名,累计总分数;
2)专用的窗口函数:
创建测试数据表:
mysql> create table t1(c int);
插入测试数据:
mysql> insert into t1(c) values(1),(2),(3),(4),(5),(6),(7),(8),(9),(2),(4),(1),(8),(2),(7);
a)获取数据排名的排名函数:
row_number():
rank():
dense_rank():
percent_rank():
mysql> select c,row_number() over w 'row_number',rank() over w 'rank',dense_rank() over w 'dense_rank',percent_rank() over w 'percent_rank' from t1 window w as (order by c);
+------+------------+------+------------+---------------------+
| c | row_number | rank | dense_rank | percent_rank |
+------+------------+------+------------+---------------------+
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0.14285714285714285 |
| 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 0.14285714285714285 |
| 2 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0.14285714285714285 |
| 3 | 6 | 6 | 3 | 0.35714285714285715 |
| 4 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 0.42857142857142855 |
| 4 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 0.42857142857142855 |
| 5 | 9 | 9 | 5 | 0.5714285714285714 |
| 6 | 10 | 10 | 6 | 0.6428571428571429 |
| 7 | 11 | 11 | 7 | 0.7142857142857143 |
| 7 | 12 | 11 | 7 | 0.7142857142857143 |
| 8 | 13 | 13 | 8 | 0.8571428571428571 |
| 8 | 14 | 13 | 8 | 0.8571428571428571 |
| 9 | 15 | 15 | 9 | 1 |
+------+------------+------+------------+---------------------+
15 rows in set (0.00 sec)
b)获取窗口或分组中的第一名或最后一名的函数:
first_value():
last_value():
c)获取当前数据前面几名或后面几名的函数:
lead():
lag():
mysql> select c,first_value(c) over w 'first_value',last_value(c) over w 'last_value',lead(c) over w 'lead',lag(c) over w 'lag' from t1 window w as (order by c);
+------+-------------+------------+------+------+
| c | first_value | last_value | lead | lag |
+------+-------------+------------+------+------+
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | NULL |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 2 |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 6 | 4 |
| 6 | 1 | 6 | 7 | 5 |
| 7 | 1 | 7 | 7 | 6 |
| 7 | 1 | 7 | 8 | 7 |
| 8 | 1 | 8 | 8 | 7 |
| 8 | 1 | 8 | 9 | 8 |
| 9 | 1 | 9 | NULL | 8 |
+------+-------------+------------+------+------+
15 rows in set (0.00 sec)
d)数据分析中的累计分布函数:
cume_dist():
e)获取排名第几名函数:
nth_value():
f)百分位排名函数:
ntile():
mysql> select c,cume_dist() over w 'cume_dist',nth_value(c,2) over w 'nth_value',ntile(4) over w 'ntile' from t1 window w as (order by c);
+------+---------------------+-----------+-------+
| c | cume_dist | nth_value | ntile |
+------+---------------------+-----------+-------+
| 1 | 0.13333333333333333 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0.13333333333333333 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 0.3333333333333333 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 0.3333333333333333 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 0.3333333333333333 | 1 | 2 |
| 3 | 0.4 | 1 | 2 |
| 4 | 0.5333333333333333 | 1 | 2 |
| 4 | 0.5333333333333333 | 1 | 2 |
| 5 | 0.6 | 1 | 3 |
| 6 | 0.6666666666666666 | 1 | 3 |
| 7 | 0.8 | 1 | 3 |
| 7 | 0.8 | 1 | 3 |
| 8 | 0.9333333333333333 | 1 | 4 |
| 8 | 0.9333333333333333 | 1 | 4 |
| 9 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
+------+---------------------+-----------+-------+
15 rows in set (0.00 sec)
五、InnoDB增强
1)集成数据字典
MySQL8.0删除了之前版本的元数据文件,如:.frm, .par, .trn, .isl, .db,.opt等。
MySQL8.0将系统表(mysql)和数据字典表全部改为InnoDB存储引擎。
支持原子DDL语句。
简化了information_schema的实现,提高了访问性能。
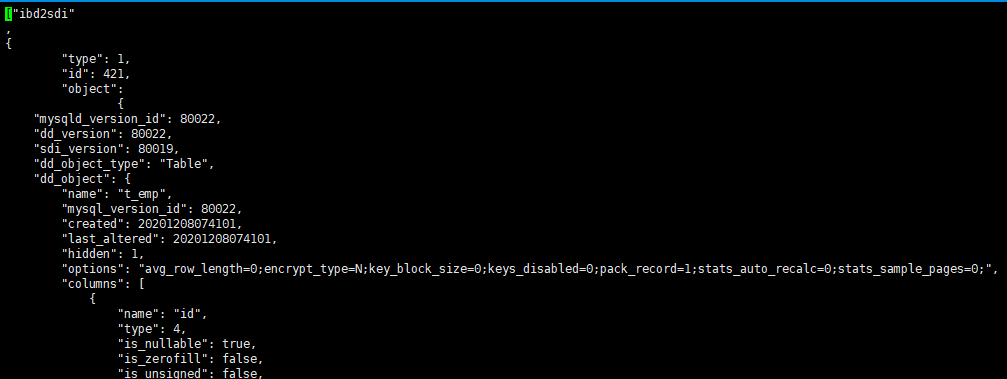
提供了序列化字典信息(SDI)的支持,以及idb2sdi工具。
ibd2sdi t_emp.ibd > t_emp.sdi #可以将数据表数据导出到sdi的文本文件。
数据字典使用上的差异,例如innodb_read_only影响所有的存储引擎;数据字典表不可见,不能直接查询和修改。
2)原子DDL操作
MySQL8.0开始支持原子DDL操作,其中与表相关的原子DDL只支持InnoDB存储引擎。
一个原子DDL操作内容通常包括:更新数据字典、存储引擎层的操作、在binlog中记录DDL操作。
支持与表相关DDL:数据库、表空间、表、索引的create|alter|drop、truncate table。
支持其他的DDL:存储程序、触发器、视图、UDF的create|drop以及alter语句。
支持账户管理相关的DDL:用户和角色的create|alter|drop以及适用的rename,以及grant和revoke语句。
在drop 多个 table时,若有不存在的表存在时,MySQL5.7报表不存在错误,但会删除存在的表,MySQL5.8报表不存在错误,但不会删除已存在的表,可以使用drop table if exists 表名来解决该问题。
3)自增列持久化
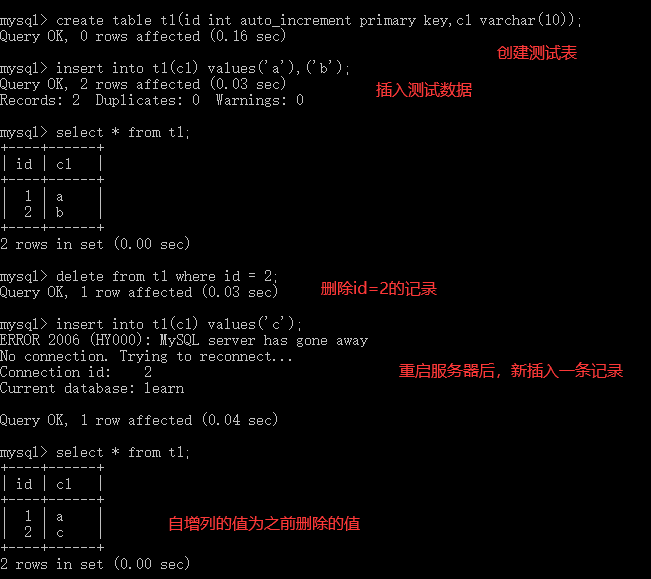
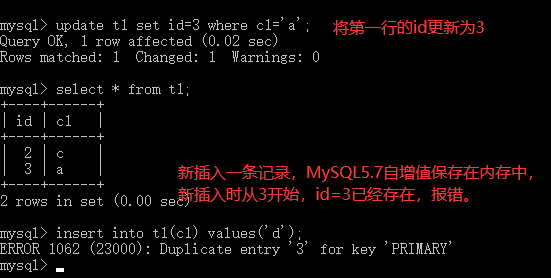
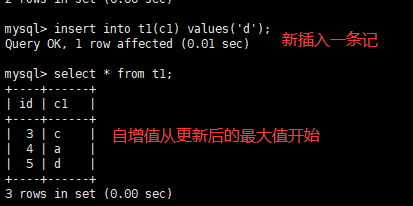
MySQL5.7及更早的版本中,InnoDB自增列计数器(auto_increment)的值只存储在内存中,当服务器出现故障或者其他需要重启MySQL服务的时候,会重新扫描表中的自增列的最大值,并以该最大值的下一个值作为新插入的自增列值,将会出现自增列重复的问题。而在MySQL8.0中每次自增列变化时都会将自增计数器的最大值写入redo log,同时在每次检查点将其写入引擎私有的系统表,已达到自增列持久化的目的。
对比MySQL5.7和MySQL8.0:
MySQL5.7
MySQL5.8
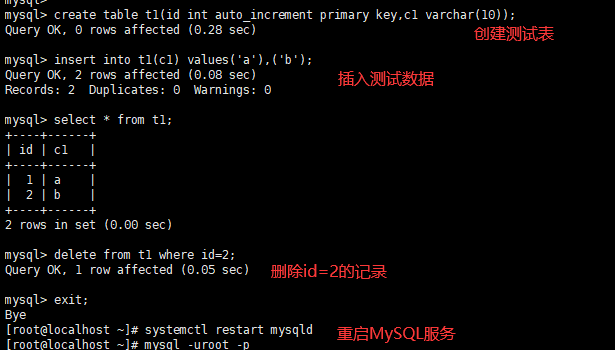
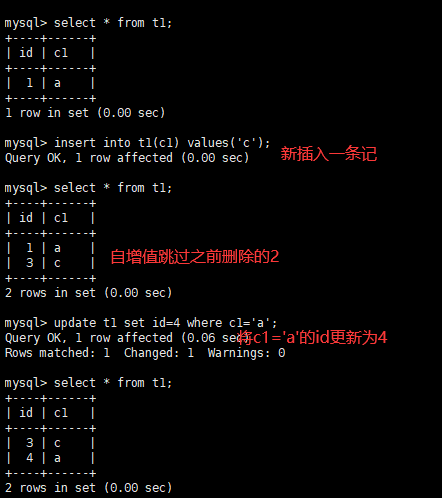
innodb_autoinc_lock_mode
4)死锁检查控制
innodb_deadlock_detect:
innodb_lock_wait_timeout:死锁等待时间
5)锁定语句选项
之前版本中的选项:
a)for share:共享锁
b)for update:排它锁
MySQL8.0新增选项:
a)nowait:如果请求的行被其他事务锁定时,语句立即返回。
b)skip locked:从返回的结果集中移除被锁定的行。
测试选项
窗口1:
mysql> select * from t1;
+----+------+
| id | c1 |
+----+------+
| 1 | a |
| 2 | b |
| 3 | c |
+----+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
开启事务
mysql> start transaction;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
更新数据,不提交不回滚
mysql> update t1 set c1='abcd' where id=3;
Query OK, 1 row affected (11.65 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
窗口2:
开启事务
mysql> start transaction;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
查询窗口1更新的数据并加排它锁,进入阻塞等待,当等待时间超过死锁等待时间将报“ERROR 1205 (HY000): Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction”错误。
mysql> select * from t1 where id=3 for update;
添加nowait选项后,立即返回错误提示。
mysql> select * from t1 where id=3 for update nowait;
ERROR 3572 (HY000): Statement aborted because lock(s) could not be acquired immediately and NOWAIT is set.
添加skip locked选项后,将跳过被锁定的行,返回其他未锁定的数据
mysql> select * from t1 where id=3 for update skip locked;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t1 for update skip locked;
+----+------+
| id | c1 |
+----+------+
| 1 | a |
| 2 | b |
+----+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
6)其他改进功能
支持部分快速DDL
InnoDB临时表使用共享的临时表空间ibtmp1。
新增静态变量innodb_dedicated_server,自动配置InnoDB内存参数:innodb_buffer_pool_size/innodb_log_file_size等。
新增表information_schema.innodb_cached_indexes,显示每个索引缓存在InnoDB缓冲池中的索引页数。
新增视图表information_schema.innodb_tablespaces_brief,为InnoDB表空间提供相关元数据信息。
默认创建2个undo表空间,不再使用系统表空间。
支持alter tablespace ... rename to 重命名通用表空间。
支持使用innodb_directories选项在服务器停止时将表空间文件移动到新的位置。
InnoDB表空间加密特性支持重做日志和撤销日志。
六、JSON增强
1)内联路径操作符
MySQL8.0增加了JSON操作符column->>path,等价于:JSON_UNQUOTE(column->path)、json_unquote(json_extract(column,path))
JSON 三种操作符示例:
mysql> with doc(data) as (select json_object('id','3','name','Jerry')) select json_unquote(data->'$.name') from doc;
+------------------------------+
| json_unquote(data->'$.name') |
+------------------------------+
| Jerry |
+------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.10 sec)
mysql> with doc(data) as (select json_object('id','3','name','Jerry')) select json_unquote(json_extract(data,'$.name')) from doc;
+-------------------------------------------+
| json_unquote(json_extract(data,'$.name')) |
+-------------------------------------------+
| Jerry |
+-------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> with doc(data) as (select json_object('id','3','name','Jerry')) select data->>'$.name' from doc;
+-----------------+
| data->>'$.name' |
+-----------------+
| Jerry |
+-----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL8.0也支持JSON范围查找:
mysql> select json_extract('["a","b","c","d","e"]','$[1]');
+----------------------------------------------+
| json_extract('["a","b","c","d","e"]','$[1]') |
+----------------------------------------------+
| "b" |
+----------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.03 sec)
mysql> select json_extract('["a","b","c","d","e"]','$[1 to 3]');
+---------------------------------------------------+
| json_extract('["a","b","c","d","e"]','$[1 to 3]') |
+---------------------------------------------------+
| ["b", "c", "d"] |
+---------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select json_extract('["a","b","c","d","e"]','$[ last - 2 to last]');
+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| json_extract('["a","b","c","d","e"]','$[ last - 2 to last]') |
+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| ["c", "d", "e"] |
+--------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
2)JSON聚合函数
MySQL8.0和MySQL5.7.22新增的两个JSON聚合函数
a)json_arrayagg():用于将多行数据组合成JSON数组
b)json_objectagg():用于生成JSON对象
JSON聚合函数具有相同属性的值时,后面的将覆盖前面的
mysql> select * from t1;
+----+------+-------+
| id | c1 | c2 |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | a | abc |
| 2 | b | bcd |
| 3 | c | cde |
| 4 | c | abcde |
+----+------+-------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select json_arrayagg(c1) as result from t1 group by c1;
+------------+
| result |
+------------+
| ["a"] |
| ["b"] |
| ["c", "c"] |
+------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select json_objectagg(c1,c2) as result from t1 group by c1;
+----------------+
| result |
+----------------+
| {"a": "abc"} |
| {"b": "bcd"} |
| {"c": "abcde"} |
+----------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3)JSON实用函数
MySQL8.0和MySQL5.7.22新增了一下几个JSON实用函数:
a)json_pretty():将JSON格式化
b)json_storage_size():返回JSON数据所占用的存储空间
c)json_storage_free():返回更新json列后相应的列可能释放出来的存储空间(MySQL8.0新增)
mysql> select json_object('id',3,'name','Jerry');
+------------------------------------+
| json_object('id',3,'name','Jerry') |
+------------------------------------+
| {"id": 3, "name": "Jerry"} |
+------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select json_pretty(json_object('id',3,'name','Jerry'));
+-------------------------------------------------+
| json_pretty(json_object('id',3,'name','Jerry')) |
+-------------------------------------------------+
| {
"id": 3,
"name": "Jerry"
} |
+-------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> create table t2(c1 json);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.13 sec)
mysql> insert into t2(c1) values(json_object('a',1000,'b','wxyz','c','[1,3,5,7]'));
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select c1,json_storage_size(c1),json_storage_free(c1) from t2;
+--------------------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------------------+
| c1 | json_storage_size(c1) | json_storage_free(c1) |
+--------------------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------------------+
| {"a": 1000, "b": "wxyz", "c": "[1,3,5,7]"} | 44 | 0 |
+--------------------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> update t2 set c1 = json_set(c1,'$.a',10,'$.b','wyh','$.c',12);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.03 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> select c1,json_storage_size(c1),json_storage_free(c1) from t2;
+--------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------------------+
| c1 | json_storage_size(c1) | json_storage_free(c1) |
+--------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------------------+
| {"a": 10, "b": "wyh", "c": 12} | 44 | 11 |
+--------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
4)JSON合并函数
a)json_merge_patch()
b)json_merge_preserve()
以上两个函数都是在MySQL8.0和MySQL5.7.22中新增的函数,都是将两个json对象合并成一个对象,区别在于:
json_merge_patch()函数将两个具有相同节点的JSON对象合并时,后面的节点的值将覆盖前面节点的值,而json_merge_preserve()函数将以json数组的格式保留所有的节点的值。
MySQL8.0废弃了json_merge()函数。
mysql> select json_object('a',1,'b',2),json_object('a',3,'c',4), json_merge_patch(json_object('a',1,'b',2),json_object('a',3,'c',4));
+--------------------------+--------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+
| json_object('a',1,'b',2) | json_object('a',3,'c',4) | json_merge_patch(json_object('a',1,'b',2),json_object('a',3,'c',4)) |
+--------------------------+--------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+
| {"a": 1, "b": 2} | {"a": 3, "c": 4} | {"a": 3, "b": 2, "c": 4} |
+--------------------------+--------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select json_object('a',1,'b',2),json_object('a',3,'c',4), json_merge_preserve(json_object('a',1,'b',2),json_object('a',3,'c',4));
+--------------------------+--------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| json_object('a',1,'b',2) | json_object('a',3,'c',4) | json_merge_preserve(json_object('a',1,'b',2),json_object('a',3,'c',4)) |
+--------------------------+--------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| {"a": 1, "b": 2} | {"a": 3, "c": 4} | {"a": [1, 3], "b": 2, "c": 4} |
+--------------------------+--------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
5)JSON表函数
json_table():将json数据转换为关系表。可以将该函数的返回结果当作一个普通的表,使用SQL进行查询。
mysql> SELECT * from json_table(
'[{"a":10},{"a":12},{"b":"wyh"},{"a":9},{"b":"sdw"},{"c":[1,2]}]',
"$[*]" columns(
id for ordinality,
c1 int exists path "$.a" ,
c2 varchar(10) path "$.b" default '0' on empty default '-1' on error,
c3 json path "$.c" default '{}' on empty)
) as tt;
+------+------+------+--------+
| id | c1 | c2 | c3 |
+------+------+------+--------+
| 1 | 1 | 0 | {} |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | {} |
| 3 | 0 | wyh | {} |
| 4 | 1 | 0 | {} |
| 5 | 0 | sdw | {} |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | [1, 2] |
+------+------+------+--------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)




