网络流24题(24/24)
01、飞行员配对方案问题
英国皇家空军从沦陷国征募了大量外籍飞行员。由皇家空军派出的每一架飞机都需要配备在航行技能和语言上能互相配合的2 名飞行员,其中1 名是英国飞行员,另1名是外籍飞行员。在众多的飞行员中,每一名外籍飞行员都可以与其他若干名英国飞行员很好地配合。如何选择配对飞行的飞行员才能使一次 派出最多的飞机。对于给定的外籍飞行员与英国飞行员的配合情况,试设计一个算法找出最佳飞行员配对方案,使皇家空军一次能派出最多的飞机。
对于给定的外籍飞行员与英国飞行员的配合情况,编程找出一个最佳飞行员配对方案,使皇家空军一次能派出最多的飞机。
二分图最大匹配

1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define min(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) 3 using namespace std; 4 const int MAXN = 100000; 5 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 6 inline void read(int &x) 7 { 8 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 9 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9')c = ch, ch = getchar(); 10 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0')x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 11 if(c == '-')x = -x; 12 } 13 14 struct Edge 15 { 16 int u,v,w,nxt; 17 Edge(int _u, int _v, int _w, int _nxt){u = _u;v = _v;w = _w;nxt = _nxt;} 18 Edge(){} 19 }edge[100010]; 20 int head[MAXN<<1],cnt = 1,q[MAXN<<1],h[MAXN<<1],ans=0,n,m,S,T,fa[MAXN <<1]; 21 inline void insert(int a,int b,int c) 22 { 23 edge[++cnt] = Edge(a,b,c,head[a]); 24 head[a] = cnt; 25 edge[++cnt] = Edge(b,a,0,head[b]); 26 head[b] = cnt; 27 } 28 bool bfs() 29 { 30 int he = 0, ta = 1; 31 memset(h, -1, sizeof(h)); 32 q[he] = S, h[S] = 0; 33 while(he < ta) 34 { 35 int now = q[he ++]; 36 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 37 { 38 int v = edge[pos].v; 39 if(h[v] == -1 && edge[pos].w) 40 { 41 h[v] = h[now] + 1; 42 q[ta ++] = v; 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 return h[T] != -1; 47 } 48 49 int dfs(int x, int f) 50 { 51 if(x == T) return f; 52 int w, used = 0; 53 for(int pos = head[x];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 54 { 55 int v = edge[pos].v; 56 if(h[v] == h[x] + 1) 57 { 58 w = dfs(v, min(f - used, edge[pos].w)); 59 if(w) fa[x] = v; 60 edge[pos].w -= w; 61 edge[pos ^ 1].w += w; 62 used += w; 63 if(used == f) return f; 64 } 65 } 66 if(!used) h[x] = -1; 67 return used; 68 } 69 70 void dinic() 71 { 72 while(bfs()) ans += dfs(S, INF); 73 } 74 75 int vis[MAXN << 1]; 76 77 int main() 78 { 79 read(m), read(n); 80 int tmp1, tmp2; 81 S = n + m + 2, T = n + m + 3; 82 while(scanf("%d %d", &tmp1, &tmp2) != EOF && tmp1 != -1) 83 insert(tmp1, tmp2, 1); 84 for(register int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 85 insert(S, i, 1); 86 for(register int i = m + 1;i <= m + n;++ i) 87 insert(i, T, 1); 88 dinic(); 89 printf("%d\n", ans); 90 if(ans == 0) printf("No Solution!\n"); 91 else 92 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 93 if(fa[i]) 94 printf("%d %d\n", i, fa[i]); 95 return 0; 96 }
02、太空飞行计划问题
W 教授正在为国家航天中心计划一系列的太空飞行。每次太空飞行可进行一系列商业性实验而获取利润。现已确定了一个可供选择的实验集合E= {E1,E2,…,Em},和进行这些实验需要使用的全部仪器的集合I={I1,I2,…In}。实验Ej需要用到的仪器是I的子集RjÍI。配置仪器 Ik的费用为ck美元。实验Ej的赞助商已同意为该实验结果支付pj美元。W教授的任务是找出一个有效算法,确定在一次太空飞行中要进行哪些实验并因此而 配置哪些仪器才能使太空飞行的净收益最大。这里净收益是指进行实验所获得的全部收入与配置仪器的全部费用的差额。
对于给定的实验和仪器配置情况,编程找出净收益最大的试验计划。
最大(小)权闭合子图。S连实验,T连仪器,实验与对应仪器连INF,割与S连的边意味着不做这个实验,割与T连的边意味着用这个仪器
于是S集合代表选择的实验和仪器,求最小割,总收益-最小割即为答案

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <cstdlib> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <cmath> 9 #define min(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) 10 #define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) 11 #define abs(a) ((a) < 0 ? (-1 * (a)) : (a)) 12 template <class T> 13 inline void swap(T& a, T& b) 14 { 15 T tmp = a;a = b;b = tmp; 16 } 17 inline void read(int &x) 18 { 19 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 20 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 21 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 22 if(c == '-') x = -x; 23 } 24 25 const int INF = 100000; 26 const int MAXN = 3000 + 10; 27 const int MAXM = MAXN * MAXN; 28 29 struct Edge 30 { 31 int u,v,w,nxt; 32 Edge(int _u, int _v, int _w, int _nxt){u = _u;v = _v;w = _w;nxt = _nxt;} 33 Edge(){} 34 }edge[MAXM << 1]; 35 int head[MAXN], cnt = 1; 36 inline void insert(int u, int v, int w) 37 { 38 edge[++cnt] = Edge(u,v,w,head[u]); 39 head[u] = cnt; 40 edge[++cnt] = Edge(v,u,0,head[v]); 41 head[v] = cnt; 42 } 43 44 int q[MAXN << 1], h[MAXN << 1], ans, S, T, he, ta; 45 46 bool bfs() 47 { 48 int he = 0, ta = 1; 49 memset(h, -1, sizeof(h)); 50 q[he] = S, h[S] = 0; 51 while(he < ta) 52 { 53 int now = q[he ++]; 54 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 55 { 56 int v = edge[pos].v; 57 if(h[v] == -1 && edge[pos].w) 58 { 59 h[v] = h[now] + 1; 60 q[ta ++] = v; 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 return h[T] != -1; 65 } 66 67 int dfs(int x, int f) 68 { 69 if(x == T) return f; 70 int w, used = 0; 71 for(int pos = head[x];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 72 { 73 int v = edge[pos].v; 74 if(h[v] == h[x] + 1) 75 { 76 w = dfs(v, min(f - used, edge[pos].w)); 77 edge[pos].w -= w; 78 edge[pos ^ 1].w += w; 79 used += w; 80 if(used == f) return f; 81 } 82 } 83 if(!used) h[x] = -1; 84 return used; 85 } 86 87 void dinic() 88 { 89 while(bfs()) ans += dfs(S, INF); 90 } 91 92 int n,m,sum,vis[MAXN]; 93 94 int main() 95 { 96 read(m), read(n);S = n + m + 100;T = n + m + 200; 97 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 98 { 99 char c = 0;int w, tmp = 0; 100 read(w);sum += w; 101 insert(S, i, w); 102 while(c != '\n' && c != '\r') 103 { 104 c = getchar(); 105 while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') 106 tmp = tmp * 10 + c - '0', c = getchar(); 107 if(tmp) insert(i, tmp + m, INF), tmp = 0; 108 } 109 } 110 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 111 { 112 int tmp;read(tmp); 113 insert(i + m, T, tmp); 114 } 115 dinic(); 116 for(int pos = head[S];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 117 if(edge[pos].w) 118 vis[edge[pos].v] = 1; 119 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) if(h[i] != -1) printf("%d ", i); 120 putchar('\n'); 121 for(int i = m + 1;i <= n + m;++ i) if(h[i] != -1) printf("%d ", i - m);putchar('\n'); 122 printf("%d", sum - ans); 123 return 0; 124 }
03、最小路径覆盖问题
«问题描述:
给定有向图G=(V,E)。设P 是G 的一个简单路(顶点不相交)的集合。如果V 中每个顶点恰好在P 的一条路上,则称P是G 的一个路径覆盖。P 中路径可以从V 的任何一个顶点开始,长度也是任意的,特别地,可以为0。G 的最小路径覆盖是G 的所含路径条数最少的路径覆盖。设计一个有效算法求一个有向无环图G 的最小路径覆盖。提示:设V={1,2,.... ,n},构造网络G1=(V1,E1)如下:

每条边的容量均为1。求网络G1的( 0 x , 0 y )最大流。
«编程任务:
对于给定的给定有向无环图G,编程找出G的一个最小路径覆盖。
每个点拆成x,x',S->x, x'->T,对于x->y一条边,连x->y'。X集合为点x,Y集合为点x'
正确性:每条路径上的点度数最大为2。x点代表点x的出度,x'点代表点x的入度。一条边会占用一个点的出度和另一个点的入度。对于每条路径,发现起点只有出度,没有入度,那么Y集合中没有被连的点就是某条路径的起点。于是n - 最大匹配 = 最小路径数

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <cstdlib> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <cmath> 9 #define min(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) 10 #define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) 11 #define abs(a) ((a) < 0 ? (-1 * (a)) : (a)) 12 template <class T> 13 inline void swap(T& a, T& b) 14 { 15 T tmp = a;a = b;b = tmp; 16 } 17 inline void read(int &x) 18 { 19 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 20 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 21 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 22 if(c == '-') x = -x; 23 } 24 25 const int INF = 100000; 26 const int MAXN = 300 + 10; 27 const int MAXM = MAXN * MAXN; 28 29 struct Edge 30 { 31 int u,v,w,nxt; 32 Edge(int _u, int _v, int _w, int _nxt){u = _u;v = _v;w = _w;nxt = _nxt;} 33 Edge(){} 34 }edge[MAXM << 1]; 35 int head[MAXN], cnt = 1; 36 inline void insert(int u, int v, int w) 37 { 38 edge[++cnt] = Edge(u,v,w,head[u]); 39 head[u] = cnt; 40 edge[++cnt] = Edge(v,u,0,head[v]); 41 head[v] = cnt; 42 } 43 44 int q[MAXN << 1], h[MAXN << 1], ans, S, T, he, ta, fa[MAXN << 1],vis[MAXN]; 45 std::vector<int> node[MAXN << 1]; 46 47 bool bfs() 48 { 49 int he = 0, ta = 1; 50 memset(h, -1, sizeof(h)); 51 q[he] = S, h[S] = 0; 52 while(he < ta) 53 { 54 int now = q[he ++]; 55 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 56 { 57 int v = edge[pos].v; 58 if(h[v] == -1 && edge[pos].w) 59 { 60 h[v] = h[now] + 1; 61 q[ta ++] = v; 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 return h[T] != -1; 66 } 67 68 int dfs(int x, int f) 69 { 70 if(x == T) return f; 71 int w, used = 0; 72 for(int pos = head[x];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 73 { 74 int v = edge[pos].v; 75 if(h[v] == h[x] + 1) 76 { 77 w = dfs(v, min(f - used, edge[pos].w)); 78 if(w) fa[x] = v, node[v].push_back(x); 79 edge[pos].w -= w; 80 edge[pos ^ 1].w += w; 81 used += w; 82 if(used == f) return f; 83 } 84 } 85 if(!used) h[x] = -1; 86 return used; 87 } 88 89 void dinic() 90 { 91 while(bfs()) ans += dfs(S, INF); 92 } 93 94 int n,m; 95 96 void dfs(int x) 97 { 98 vis[x] = 1; 99 printf("%d ", x); 100 if(fa[x]) dfs(fa[x] - n); 101 } 102 103 int main() 104 { 105 read(n), read(m); 106 S = n * 2 + 1, T = n * 2 + 2; 107 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) insert(S, i, 1); 108 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 109 { 110 int tmp1,tmp2; 111 read(tmp1), read(tmp2); 112 insert(tmp1, tmp2 + n, 1); 113 } 114 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) insert(i + n, T, 1); 115 dinic(); 116 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 117 if(fa[i]) 118 vis[fa[i] - n] = 1; 119 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 120 if(!vis[i]) 121 dfs(i), putchar('\n'); 122 printf("%d", n - ans); 123 return 0; 124 }
04、魔术球问题
«问题描述:
假设有n根柱子,现要按下述规则在这n根柱子中依次放入编号为1,2,3,...的球。
(1)每次只能在某根柱子的最上面放球。
(2)在同一根柱子中,任何2个相邻球的编号之和为完全平方数。
试设计一个算法,计算出在n根柱子上最多能放多少个球。例如,在4 根柱子上最多可放11 个球。
«编程任务:
对于给定的n,计算在n根柱子上最多能放多少个球。
最小路径覆盖变种。二分放多少个球,如果x能放到y上面,就有x->y,答案即为图上的最小路径覆盖数。
发现二分放多少个求,还不如直接从1开始枚举放的求数,每多一个球加一个的边,跑一次增广。

1 // luogu-judger-enable-o2 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <cstdlib> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <queue> 8 #include <vector> 9 #include <cmath> 10 #define min(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) 11 #define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) 12 #define abs(a) ((a) < 0 ? (-1 * (a)) : (a)) 13 template <class T> 14 inline void swap(T& a, T& b) 15 { 16 T tmp = a;a = b;b = tmp; 17 } 18 inline void read(int &x) 19 { 20 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 21 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 22 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 23 if(c == '-') x = -x; 24 } 25 26 const int INF = 100000; 27 const int MAXN = 100000; 28 const int MAXM = 100000; 29 30 struct Edge 31 { 32 int u,v,w,nxt; 33 Edge(int _u, int _v, int _w, int _nxt){u = _u;v = _v;w = _w;nxt = _nxt;} 34 Edge(){} 35 }edge[MAXM << 1]; 36 int head[MAXN << 1], cnt = 1, S, T, ans, fa[MAXN << 1], h[MAXN << 1], q[MAXN << 1], he, ta; 37 inline void insert(int a, int b, int c) 38 { 39 edge[++cnt] = Edge(a,b,c,head[a]); 40 head[a] = cnt; 41 edge[++cnt] = Edge(b,a,0,head[b]); 42 head[b] = cnt; 43 } 44 bool bfs() 45 { 46 memset(h, -1, sizeof(h)); 47 he = 0, ta = 1, q[0] = S, h[S] = 0; 48 while(he < ta) 49 { 50 int now = q[he ++]; 51 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 52 { 53 int v = edge[pos].v; 54 if(h[v] == -1 && edge[pos].w) q[ta ++] = v, h[v] = h[now] + 1; 55 } 56 } 57 return h[T] != -1; 58 } 59 int dfs(int x, int f) 60 { 61 if(x == T) return f; 62 int used = 0, w; 63 for(int pos = head[x];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 64 { 65 int v = edge[pos].v; 66 if(h[v] == h[x] + 1) 67 { 68 w = dfs(v, min(f - used, edge[pos].w)); 69 if(w) fa[x] = v; 70 edge[pos].w -= w; 71 edge[pos ^ 1].w += w; 72 used += w; 73 if(used == f) return f; 74 } 75 } 76 if(!used) h[x] = -1; 77 return used; 78 } 79 void Dinic() 80 { 81 while(bfs()) ans += dfs(S, INF); 82 } 83 84 int n, ma, vis[MAXN]; 85 86 void dfs(int x) 87 { 88 vis[x] = 1; 89 printf("%d ", x); 90 if(fa[x]) dfs(fa[x] - 2000); 91 } 92 93 int main() 94 { 95 read(n);S = 10000, T = S + 1; 96 for(ma = 1;;++ ma) 97 { 98 insert(S, ma, 1); insert(ma + 2000, T, 1); 99 for(int j = sqrt(ma) + 1;j * j - ma < ma;++ j) 100 insert(j * j - ma, ma + 2000, 1); 101 Dinic(); 102 if(ma - ans == n + 1) break; 103 } 104 -- ma; 105 printf("%d\n", ma); 106 memset(head, 0, sizeof(head)), cnt = 0, memset(fa, 0, sizeof(fa)), ans = 0; 107 for(int i = 1;i <= ma;++ i) 108 { 109 insert(S, i, 1); insert(i + 2000, T, 1); 110 int t = sqrt(i); 111 for(int j = sqrt(i) + 1;j * j - i < i;++ j) 112 insert(j * j - i, i + 2000, 1); 113 Dinic(); 114 } 115 for(int i = 1;i <= ma;++ i) 116 if(fa[i]) vis[fa[i] - 2000] = 1; 117 for(int i = 1;i <= ma;++ i) if(!vis[i]) dfs(i), putchar('\n'); 118 return 0; 119 }
05、圆桌问题
假设有来自m 个不同单位的代表参加一次国际会议。每个单位的代表数分别为ri (i =1,2,……,m)。
会议餐厅共有n 张餐桌,每张餐桌可容纳ci (i =1,2,……,n)个代表就餐。
为了使代表们充分交流,希望从同一个单位来的代表不在同一个餐桌就餐。试设计一个算法,给出满足要求的代表就餐方案。
对于给定的代表数和餐桌数以及餐桌容量,编程计算满足要求的代表就餐方案。
有点裸

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <cstdlib> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <cmath> 9 #define min(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) 10 #define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) 11 #define abs(a) ((a) < 0 ? (-1 * (a)) : (a)) 12 template <class T> 13 inline void swap(T& a, T& b) 14 { 15 T tmp = a;a = b;b = tmp; 16 } 17 inline void read(int &x) 18 { 19 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 20 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 21 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 22 if(c == '-') x = -x; 23 } 24 25 const int INF = 100000; 26 const int MAXN = 10000; 27 const int MAXM = 100000; 28 29 struct Edge 30 { 31 int u,v,w,nxt; 32 Edge(int _u, int _v, int _w, int _nxt){u = _u;v = _v;w = _w;nxt = _nxt;} 33 Edge(){} 34 }edge[MAXM << 1]; 35 int head[MAXN << 1], cnt = 1, S, T, ans, h[MAXN << 1], q[MAXN << 1], he, ta; 36 inline void insert(int a, int b, int c) 37 { 38 edge[++cnt] = Edge(a,b,c,head[a]); 39 head[a] = cnt; 40 edge[++cnt] = Edge(b,a,0,head[b]); 41 head[b] = cnt; 42 } 43 bool bfs() 44 { 45 memset(h, -1, sizeof(h)); 46 he = 0, ta = 1, q[0] = S, h[S] = 0; 47 while(he < ta) 48 { 49 int now = q[he ++]; 50 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 51 { 52 int v = edge[pos].v; 53 if(h[v] == -1 && edge[pos].w) 54 { 55 q[ta ++] = v, h[v] = h[now] + 1; 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 return h[T] != -1; 60 } 61 int dfs(int x, int f) 62 { 63 if(x == T) return f; 64 int used = 0, w; 65 for(int pos = head[x];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 66 { 67 int v = edge[pos].v; 68 if(h[v] == h[x] + 1) 69 { 70 w = dfs(v, min(f - used, edge[pos].w)); 71 edge[pos].w -= w; 72 edge[pos ^ 1].w += w; 73 used += w; 74 if(used == f) return f; 75 } 76 } 77 if(!used) h[x] = -1; 78 return used; 79 } 80 void Dinic() 81 { 82 while(bfs()) ans += dfs(S, INF); 83 } 84 int n,m,tmp,sum,vis[MAXN]; 85 86 int main() 87 { 88 read(m), read(n); S = n + m + 1, T = S + 1; 89 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) read(tmp), sum += tmp, insert(S, i, tmp); 90 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) read(tmp), insert(i + m, T, tmp); 91 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 92 for(int j = 1;j <= n;++ j) 93 insert(i, j + m, 1); 94 Dinic(); 95 if(ans != sum){printf("0\n");return 0;} 96 printf("1"); 97 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 98 { 99 int flag = 1; 100 for(int pos = head[i];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 101 if(edge[pos].v == S) continue; 102 else if(!edge[pos].w) 103 if(flag) printf("\n%d ", edge[pos].v - m), flag = 0; 104 else printf("%d ", edge[pos].v - m); 105 } 106 return 0; 107 }
06、最长不下降子序列问题
«问题描述:
给定正整数序列x1,...,xn 。
(1)计算其最长不下降子序列的长度s。
(2)计算从给定的序列中最多可取出多少个长度为s的不下降子序列。
(3)如果允许在取出的序列中多次使用x1和xn,则从给定序列中最多可取出多少个长度为s的不下降子序列。
«编程任务:
设计有效算法完成(1)(2)(3)提出的计算任务。
第一、二个问题都有nlogn解法,详见http://www.cnblogs.com/huibixiaoxing/p/7398826.html第三题
这里讨论网络流解法
第一问直接暴力dp即可,设答案为k
第二问,相当于每个点限流1,用最大流模拟转移,考虑拆点。对于点x,拆成x和x',x - > x',容量1, 对于i和j,i < j,若有s[j] >= s[i],就从i’ - > j,容量为1。对于f[i] = k的点i,连i' - > T,容量为1,可以证明每一个序列都可以通过一个流表示出来。跑最大流即可
第三问,相当于x1和xn可以取无数次,那就把x1->x1',xn->xn',S->x1',S->xn',xn'->T(如果存在),x1'->T(如果存在)改成正无穷即可

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <cstdlib> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <cmath> 9 #define min(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) 10 #define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) 11 #define abs(a) ((a) < 0 ? (-1 * (a)) : (a)) 12 template <class T> 13 inline void swap(T& a, T& b) 14 { 15 T tmp = a;a = b;b = tmp; 16 } 17 inline void read(int &x) 18 { 19 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 20 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 21 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 22 if(c == '-') x = -x; 23 } 24 25 const int INF = 100000; 26 const int MAXN = 10000; 27 const int MAXM = 100000; 28 29 struct Edge 30 { 31 int u,v,w,nxt; 32 Edge(int _u, int _v, int _w, int _nxt){u = _u;v = _v;w = _w;nxt = _nxt;} 33 Edge(){} 34 }edge[MAXM << 1]; 35 int head[MAXN << 1], cnt = 1, S, T, ans, h[MAXN << 1], q[MAXN << 1], he, ta; 36 inline void insert(int a, int b, int c) 37 { 38 edge[++cnt] = Edge(a,b,c,head[a]); 39 head[a] = cnt; 40 edge[++cnt] = Edge(b,a,0,head[b]); 41 head[b] = cnt; 42 } 43 bool bfs() 44 { 45 memset(h, -1, sizeof(h)); 46 he = 0, ta = 1, q[0] = S, h[S] = 0; 47 while(he < ta) 48 { 49 int now = q[he ++]; 50 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 51 { 52 int v = edge[pos].v; 53 if(h[v] == -1 && edge[pos].w) 54 { 55 q[ta ++] = v, h[v] = h[now] + 1; 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 return h[T] != -1; 60 } 61 int dfs(int x, int f) 62 { 63 if(x == T) return f; 64 int used = 0, w; 65 for(int pos = head[x];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 66 { 67 int v = edge[pos].v; 68 if(h[v] == h[x] + 1) 69 { 70 w = dfs(v, min(f - used, edge[pos].w)); 71 edge[pos].w -= w; 72 edge[pos ^ 1].w += w; 73 used += w; 74 if(used == f) return f; 75 } 76 } 77 if(!used) h[x] = -1; 78 return used; 79 } 80 void Dinic() 81 { 82 while(bfs()) ans += dfs(S, INF); 83 } 84 85 int n, f[MAXN], num[MAXN], ma; 86 87 int main() 88 { 89 read(n); 90 for(register int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 91 { 92 insert(i, i + n, 1); 93 read(num[i]); 94 f[i] = 1; 95 for(register int j = 1;j < i;++ j) 96 if(num[j] <= num[i]) f[i] = max(f[i], f[j] + 1); 97 ma = max(ma, f[i]); 98 } 99 printf("%d\n", ma); 100 if(ma == 1) 101 { 102 printf("%d\n%d", n, n); 103 return 0; 104 } 105 S = n + n + 1, T = S + 1; 106 for(register int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 107 if(f[i] == 1) insert(S, i, 1); 108 else if(f[i] == ma) insert(i + n, T, 1); 109 for(register int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 110 for(register int j = 1;j < i;++ j) 111 if(num[j] <= num[i] && f[i] == f[j] + 1) 112 insert(j + n, i, 1); 113 Dinic(); 114 printf("%d\n", ans); 115 insert(1, n + 1, INF), insert(n, n + n, INF); 116 if(f[1] == 1) insert(S, 1, INF); 117 if(f[1] == ma) insert(1 + n, T, INF); 118 if(f[n] == 1) insert(S, n, INF); 119 if(f[n] == ma) insert(n + n, T, INF); 120 Dinic(); 121 printf("%d", ans); 122 return 0; 123 }
07、试题库问题
«问题描述:
假设一个试题库中有n道试题。每道试题都标明了所属类别。同一道题可能有多个类别属性。现要从题库中抽取m 道题组成试卷。并要求试卷包含指定类型的试题。试设计一个满足要求的组卷算法。
«编程任务:
对于给定的组卷要求,计算满足要求的组卷方案。
有点裸

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <cstdlib> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <cmath> 9 #define min(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) 10 #define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) 11 #define abs(a) ((a) < 0 ? (-1 * (a)) : (a)) 12 template <class T> 13 inline void swap(T& a, T& b) 14 { 15 T tmp = a;a = b;b = tmp; 16 } 17 inline void read(int &x) 18 { 19 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 20 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 21 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 22 if(c == '-') x = -x; 23 } 24 25 const int INF = 100000; 26 const int MAXN = 100000 + 10; 27 const int MAXM = 1000000 + 10; 28 29 struct Edge 30 { 31 int u,v,w,nxt; 32 Edge(int _u, int _v, int _w, int _nxt){u = _u;v = _v;w = _w;nxt = _nxt;} 33 Edge(){} 34 }edge[MAXM << 1]; 35 int head[MAXN << 1], cnt = 1, S, T, ans, h[MAXN << 1], fa[MAXN << 1], q[MAXN << 1], he, ta; 36 inline void insert(int a, int b, int c) 37 { 38 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(a,b,c,head[a]); 39 head[a] = cnt; 40 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(b,a,0,head[b]); 41 head[b] = cnt; 42 } 43 bool bfs() 44 { 45 he = 0, ta = 1, q[he] = S, memset(h, -1, sizeof(h)), h[S] = 0; 46 while(he < ta) 47 { 48 int now = q[he ++]; 49 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 50 { 51 int v = edge[pos].v; 52 if(h[v] == -1 && edge[pos].w) 53 h[v] = h[now] + 1, q[ta ++] = v; 54 } 55 } 56 return h[T] != -1; 57 } 58 int dfs(int x, int f) 59 { 60 if(x == T) return f; 61 int w,used = 0; 62 for(int pos = head[x];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 63 { 64 int v = edge[pos].v; 65 if(h[v] == h[x] + 1) 66 { 67 w = dfs(v, min(f - used, edge[pos].w)); 68 edge[pos].w -= w; 69 edge[pos ^ 1].w += w; 70 if(w) fa[x] = v; 71 used += w; 72 if(used == f) return f; 73 } 74 } 75 if(!used) h[x] = -1; 76 return used; 77 } 78 void Dinic() 79 { 80 while(bfs()) ans += dfs(S, INF); 81 } 82 int k,n,tmp,tmp2,sum; 83 int main() 84 { 85 read(k), read(n); 86 S = n + k + 1, T = S + 1; 87 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) insert(S, i, 1); 88 for(int i = 1;i <= k;++ i) read(tmp), sum += tmp, insert(n + i, T, tmp); 89 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 90 { 91 read(tmp); 92 for(int j = 1;j <= tmp;++ j) read(tmp2), insert(i, tmp2 + n, 1); 93 } 94 Dinic(); 95 if(ans != sum){printf("No Solution!\n");return 0;} 96 for(int i = 1;i <= k;++ i) 97 { 98 printf("%d: ", i); 99 for(int j = 1;j <= n;++ j) if(fa[j] == i + n) printf("%d ", j); 100 putchar('\n'); 101 } 102 return 0; 103 }
08、机器人路径规划问题
机器人 Rob 可在一个树状路径上自由移动。给定树状路径 T 上的起点 s 和终点 t,机器人 Rob 要从 s 运动到 t。树状路径 T 上有若干可移动的障碍物。由于路径狭窄,任何时刻在路径的任何位置不能同时容纳 2 个物体。每一步可以将障碍物或机器人移到相邻的空顶点上。设计一个有效算法用最少移动次数使机器人从 s 运动到 t。对于给定的树 T,以及障碍物在树 T 中的分布情况。计算机器人从起点 s 到终点 t 的最少移动次数。
据说此题网络流不可做。其他做法也不太好,复杂度很高网络流24题:我们之中出了个叛徒!
09、方格取数问题
在一个有 m*n 个方格的棋盘中,每个方格中有一个正整数。现要从方格中取数,使任意 2 个数所在方格没有公共边,且取出的数的总和最大。试设计一个满足要求的取数算法。对于给定的方格棋盘,按照取数要求编程找出总和最大的数。
看见方格就黑白染色。发现不能放在相邻的异色格子上。想到最小割。
对于白色格点(i,j),向黑色格点(i + 1, j)和(i,j + 1)连边,容量INF,S向白色格点连权值,黑色格点向T连权值,每一条S->T的路径都对应一个不满足条件的放法,因此要使得取出的数S->T不存在,割掉一条边意味着不取出这个方格中的数,求最小割即为留下的最少,取出的用总和减

1 // luogu-judger-enable-o2 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <cstdlib> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <queue> 8 #include <vector> 9 #include <cmath> 10 #define min(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) 11 #define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) 12 #define abs(a) ((a) < 0 ? (-1 * (a)) : (a)) 13 #define hao(a, b) ((a) * m + (b)) 14 template <class T> 15 inline void swap(T& a, T& b) 16 { 17 T tmp = a;a = b;b = tmp; 18 } 19 inline void read(int &x) 20 { 21 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 22 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 23 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 24 if(c == '-') x = -x; 25 } 26 27 const int INF = 100000; 28 const int MAXN = 100000 + 10; 29 const int MAXM = 1000000 + 10; 30 31 struct Edge 32 { 33 int u,v,w,nxt; 34 Edge(int _u, int _v, int _w, int _nxt){u = _u, v = _v, w = _w, nxt = _nxt;} 35 Edge(){} 36 }edge[MAXM << 1]; 37 int head[MAXN << 1], cnt = 1, q[MAXN << 1], h[MAXN << 1], S, T, ans, he, ta; 38 inline void insert(int a, int b, int c) 39 { 40 edge[++cnt] = Edge(a,b,c,head[a]); 41 head[a] = cnt; 42 edge[++cnt] = Edge(b,a,0,head[b]); 43 head[b] = cnt; 44 } 45 bool bfs() 46 { 47 memset(h, -1, sizeof(h)), he = 0, ta = 1, q[0] = S, h[S] = 0; 48 while(he < ta) 49 { 50 int now = q[he ++]; 51 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 52 { 53 int v = edge[pos].v; 54 if(h[v] == -1 && edge[pos].w) 55 h[v] = h[now] + 1, q[ta ++] = v; 56 } 57 } 58 return h[T] != -1; 59 } 60 int dfs(int x, int f) 61 { 62 if(x == T) return f; 63 int used = 0, w; 64 for(int pos = head[x];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 65 { 66 int v = edge[pos].v; 67 if(h[v] == h[x] + 1) 68 { 69 w = dfs(v, min(f - used, edge[pos].w)); 70 edge[pos].w -= w; 71 edge[pos ^ 1].w += w; 72 used += w; 73 if(used == f) return f; 74 } 75 } 76 if(!used) h[x] = -1; 77 return used; 78 } 79 void Dinic() 80 { 81 while(bfs()) ans += dfs(S, INF); 82 } 83 84 int n,m,g[150][150],sum; 85 86 int main() 87 { 88 read(n), read(m); 89 S = hao(n, m) + 1, T = S + 1; 90 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 91 for(int j = 1;j <= m;++ j) 92 { 93 int tmp; read(tmp);sum += tmp; 94 if((i + j) & 1) 95 { 96 insert(S, hao(i, j), tmp); 97 if(i + 1 <= n) insert(hao(i, j), hao(i + 1, j), INF); 98 if(j + 1 <= m) insert(hao(i, j), hao(i, j + 1), INF); 99 } 100 else 101 { 102 insert(hao(i, j), T, tmp); 103 if(i + 1 <= n) insert(hao(i + 1, j), hao(i, j), INF); 104 if(j + 1 <= m) insert(hao(i, j + 1), hao(i, j), INF); 105 } 106 } 107 Dinic(); 108 printf("%d", sum - ans); 109 return 0; 110 }
10、餐巾计划问题
一个餐厅在相继的 NNN 天里,每天需用的餐巾数不尽相同。假设第 iii 天需要 rir_iri块餐巾( i=1,2,...,N)。餐厅可以购买新的餐巾,每块餐巾的费用为 ppp 分;或者把旧餐巾送到快洗部,洗一块需 m 天,其费用为 f 分;或者送到慢洗部,洗一块需 nnn 天(n>mn>mn>m),其费用为 sss 分(s<fs<fs<f)。
每天结束时,餐厅必须决定将多少块脏的餐巾送到快洗部,多少块餐巾送到慢洗部,以及多少块保存起来延期送洗。但是每天洗好的餐巾和购买的新餐巾数之和,要满足当天的需求量。
试设计一个算法为餐厅合理地安排好 NNN 天中餐巾使用计划,使总的花费最小。编程找出一个最佳餐巾使用计划。
每天拆成两个点x(X集合),x(Y集合)',x表示第x天用完剩下的餐巾,x'表示第x天要用的餐巾,让x'连向T,容量为当天需要的餐巾数,把S连向x,容量为当天需要的餐巾数,考虑如何用X集合补满Y集合的流。
对于购买,从S连向Y集合,容量+∞,费用p
对于快洗,x->x + m,容量+∞,费用f
对于慢洗,x->x + nnn,容量+∞,费用sss
还有可能上一天的餐巾留到下一天,从x -> x + 1容量+∞,费用0(容易漏掉)

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <cstdlib> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <cmath> 9 #define min(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) 10 #define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) 11 #define abs(a) ((a) < 0 ? (-1 * (a)) : (a)) 12 template <class T> 13 inline void swap(T& a, T& b) 14 { 15 T tmp = a;a = b;b = tmp; 16 } 17 inline void read(long long &x) 18 { 19 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 20 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 21 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 22 if(c == '-') x = -x; 23 } 24 25 const long long INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; 26 const long long MAXN = 200000 + 10; 27 const long long MAXM = 1000000 + 10; 28 29 struct Edge 30 { 31 long long u,v,w,c,nxt; 32 Edge(long long _u, long long _v, long long _w, long long _c, long long _nxt){u = _u;v = _v;w = _w;c = _c;nxt = _nxt;} 33 Edge(){} 34 }edge[MAXN << 1]; 35 long long head[MAXN << 1], cnt = 1, q[MAXN << 1], he, ta, d[MAXN << 1], b[MAXN << 1], from[MAXN << 1], S, T, ans, nn; 36 inline void insert(long long a, long long b, long long c, long long d) 37 { 38 edge[++cnt] = Edge(a,b,c,d,head[a]); 39 head[a] = cnt; 40 edge[++cnt] = Edge(b,a,0,-d,head[b]); 41 head[b] = cnt; 42 } 43 bool bfs() 44 { 45 he = 0, ta = 1, memset(d, 0x3f3f3f3f, sizeof(d)), d[S] = 0, b[S] = 1, q[0] = S; 46 while(he < ta) 47 { 48 long long now = q[he ++]; 49 if(he > MAXN) he = 0; 50 for(long long pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 51 { 52 long long v = edge[pos].v; 53 if(edge[pos].w && d[v] > d[now] + edge[pos].c) 54 { 55 d[v] = d[now] + edge[pos].c, from[v] = pos; 56 if(!b[v]) 57 { 58 b[v] = 1, q[ta ++] = v; 59 if(ta > MAXN) ta = 0; 60 } 61 } 62 } 63 b[now] = 0; 64 } 65 return d[T] != INF; 66 } 67 void flow() 68 { 69 long long x = INF; 70 for(long long i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) x = min(x, edge[i].w); 71 for(long long i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) edge[i].w -= x, edge[i ^ 1].w += x, ans += edge[i].c * x; 72 } 73 void mcf() 74 { 75 while(bfs()) 76 flow(); 77 } 78 79 long long num[MAXN],p,m,f,n,s; 80 81 int main() 82 { 83 read(nn);S = nn + nn + 1, T = S + 1; 84 for(long long i = 1;i <= nn;++ i) read(num[i]); 85 read(p), read(m), read(f), read(n), read(s); 86 for(long long i = 1;i <= nn;++ i) 87 insert(S, i, num[i], 0); 88 for(long long i = 1;i < nn;++ i) 89 insert(i, i + 1, INF, 0); 90 for(long long i = 1;i <= nn - m;++ i) 91 insert(i, i + m + nn, INF, f); 92 for(long long i = 1;i <= nn - n;++ i) 93 insert(i, i + n + nn, INF, s); 94 for(long long i = 1;i <= nn;++ i) 95 insert(S, i + nn, INF, p); 96 for(long long i = 1;i <= nn;++ i) 97 insert(i + nn, T, num[i], 0); 98 mcf(); 99 printf("%lld", ans); 100 101 return 0; 102 }
11、航空路线问题
给定一张航空图,图中顶点代表城市,边代表 2 城市间的直通航线。现要求找出一条满足下述限制条件的且途经城市最多的旅行路线。
(1)从最西端城市出发,单向从西向东途经若干城市到达最东端城市,然后再单向从东向西飞回起点(可途经若干城市)。
(2)除起点城市外,任何城市只能访问 1 次。
对于给定的航空图,试设计一个算法找出一条满足要求的最佳航空旅行路线。
直接想成从起点到终点,找两条不相交最长路径即可
每个点限流一次,还是考虑拆点x,x',x - > x'容量为1,费用为0,特别的起点和终点可以流两次,S - S‘和T - > T',容量为2,费用为0
对于a -> b,连a' -> b,容量为1,费用为1(环上点数等于边数)
求最大费用最大流即可

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <cstdlib> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <map> 9 #include <string> 10 #include <cmath> 11 #define min(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) 12 #define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) 13 #define abs(a) ((a) < 0 ? (-1 * (a)) : (a)) 14 template <class T> 15 inline void swap(T& a, T& b) 16 { 17 T tmp = a;a = b;b = tmp; 18 } 19 inline void read(int &x) 20 { 21 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 22 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 23 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 24 if(c == '-') x = -x; 25 } 26 27 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 28 const int MAXN = 100000 + 10; 29 const int MAXM = 1000000 + 10; 30 31 struct Edge 32 { 33 int u,v,w,c,nxt; 34 Edge(int _u, int _v, int _w, int _c, int _nxt){u = _u;v = _v;w = _w;c = _c;nxt = _nxt;} 35 Edge(){} 36 }edge[MAXM << 1]; 37 int head[MAXN << 1], he, ta, cnt = 1, ans, anss, q[MAXN << 1], from[MAXN << 1], d[MAXN << 1], b[MAXN << 1], S, T; 38 void insert(int a, int b, int c, int d) 39 { 40 edge[++cnt] = Edge(a,b,c,d,head[a]); head[a] = cnt; 41 edge[++cnt] = Edge(b,a,0,-d,head[b]); head[b] = cnt; 42 } 43 bool spfa() 44 { 45 memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d)); 46 int he = 0, ta = 1; 47 d[S] = 0, b[S] = 1, q[he] = S; 48 while(he != ta) 49 { 50 int now = q[he ++]; 51 if(he > MAXN) he = 0; 52 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 53 if(edge[pos].w && d[edge[pos].v] > d[now] + edge[pos].c) 54 { 55 d[edge[pos].v] = d[now] + edge[pos].c; 56 from[edge[pos].v] = pos; 57 if(!b[edge[pos].v]) 58 { 59 b[edge[pos].v]=1; 60 q[ta ++] = edge[pos].v; 61 if(ta > MAXN)ta = 0; 62 } 63 } 64 b[now] = 0; 65 } 66 if(d[T] == INF)return 0; 67 return 1; 68 } 69 70 void flow() 71 { 72 int x = INF; 73 for(int i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) 74 x = min(x, edge[i].w); 75 for(int i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) 76 { 77 edge[i].w -= x; 78 edge[i^1].w += x; 79 ans += edge[i].c * x; 80 } 81 anss += x; 82 } 83 84 void mcf() 85 { 86 while(spfa()) flow(); 87 } 88 89 int n,m,vis[MAXN]; 90 std::string s[MAXN]; 91 std::map<std::string, int> mp; 92 93 void dfs(int x) 94 { 95 if(x == n) return; 96 vis[x] = 1; 97 std::cout << s[x] << std::endl; 98 x += n; 99 for(int pos = head[x];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 100 { 101 int v = edge[pos].v; 102 if(v > n || vis[v] || edge[pos].w) continue; 103 dfs(v);return; 104 } 105 } 106 void redfs(int x) 107 { 108 vis[x] = 1; 109 if(x == n) 110 { 111 std::cout << s[n] << std::endl; 112 return; 113 } 114 x += n; 115 for(int pos = head[x];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 116 { 117 int v = edge[pos].v; 118 if(v > n || vis[v] || edge[pos].w) continue; 119 redfs(v);break; 120 } 121 std::cout << s[x - n] << std::endl; 122 } 123 124 int main() 125 { 126 read(n), read(m);S = 1, T = n + n; 127 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 128 { 129 std::cin >> s[i]; 130 mp[s[i]] = i; 131 } 132 insert(1, 1 + n, 2, 0); 133 insert(n, n + n, 2, 0); 134 for(int i = 2;i < n;++ i) 135 insert(i, i + n, 1, 0); 136 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 137 { 138 std::string tmp1,tmp2; 139 std::cin >> tmp1 >> tmp2; 140 int ma1, ma2; 141 ma1 = mp[tmp1], ma2 = mp[tmp2]; 142 if(ma1 > ma2) swap(ma1, ma2); 143 if(ma1 == 1 && ma2 == n) insert(ma1 + n, ma2, 2, -1); 144 else insert(ma1 + n, ma2, 1, -1); 145 } 146 mcf(); 147 if(anss != 2) printf("No Solution!\n"); 148 else 149 { 150 printf("%d\n", -ans); 151 dfs(1); 152 redfs(1); 153 } 154 return 0; 155 }
12、软件补丁问题
T 公司发现其研制的一个软件中有 n 个错误,随即为该软件发放了一批共 m 个补丁程序。每一个补丁程序都有其特定的适用环境,某个补丁只有在软件中包含某些错误而同时又不包含另一些错误时才可以使用。一个补丁在排除某些错误的同时,往往会加入另一些错误。
换句话说,对于每一个补丁 i,都有 2 个与之相应的错误集合 B1[i]和 B2[i],使得仅当软件包含 B1[i]中的所有错误,而不包含 B2[i]中的任何错误时,才可以使用补丁 i。补丁 i 将修复软件中的某些错误 F1[i],而同时加入另一些错误 F2[i]。另外,每个补丁都耗费一定的时间。
试设计一个算法,利用 T 公司提供的 m 个补丁程序将原软件修复成一个没有错误的软件,并使修复后的软件耗时最少。对于给定的 n 个错误和 m 个补丁程序,找到总耗时最少的软件修复方案。
把每个状态看做节点,状态与状态之间的转移看做边,形成一张“决策图”(根据决策树yy的名词),spfa/dij即可

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <cstdlib> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <map> 9 #include <string> 10 #include <cmath> 11 inline int abs(int x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;} 12 inline int max(int a, int b){return a > b ? a : b;} 13 inline int min(int a, int b){return a < b ? a : b;} 14 inline int swap(int& a, int& b){int tmp = a;a = b;b = tmp;} 15 inline void read(int &x) 16 { 17 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 18 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 19 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 20 if(c == '-') x = -x; 21 } 22 23 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 24 const int MAXN = 21; 25 const int MAXM = 100 + 5; 26 27 int n,m,t[MAXM]; 28 int B1[MAXM], B2[MAXM], F1[MAXM], F2[MAXM]; 29 char s[MAXM]; 30 31 struct Node 32 { 33 int v,w; 34 Node(int _v, int _w){v = _v, w = _w;} 35 Node(){v = w = 0;} 36 }; 37 struct cmp 38 { 39 bool operator()(Node a, Node b) 40 { 41 return a.w > b.w; 42 } 43 }; 44 std::priority_queue<Node, std::vector<Node>, cmp> q; 45 int d[1 << MAXN], vis[1 << MAXN]; 46 47 void dij() 48 { 49 memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d)); 50 int S = (1 << n) - 1; 51 d[S] = 0; 52 q.push(Node(S, 0)); 53 Node now; 54 while(q.size()) 55 { 56 now = q.top();q.pop(); 57 if(vis[now.v]) continue; 58 vis[now.v] = 1; 59 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 60 if((now.v | B1[i]) == now.v && !(now.v & B2[i])) 61 { 62 int tmp = ((now.v | F1[i]) ^ F1[i]) | F2[i]; 63 if(d[tmp] > d[now.v] + t[i]) 64 { 65 d[tmp] = d[now.v] + t[i]; 66 q.push(Node(tmp, d[tmp])); 67 } 68 } 69 } 70 } 71 72 int main() 73 { 74 read(n), read(m); 75 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 76 { 77 read(t[i]);scanf("%s", s + 1); 78 for(int j = 1;j <= m;++ j) 79 if(s[j] == '+') 80 B1[i] |= 1 << (j - 1); 81 else if(s[j] == '-') 82 B2[i] |= 1 << (j - 1); 83 scanf("%s", s + 1); 84 for(int j = 1;j <= m;++ j) 85 if(s[j] == '-') 86 F1[i] |= 1 << (j - 1); 87 else if(s[j] == '+') 88 F2[i] |= 1 << (j - 1); 89 } 90 dij(); 91 if(d[0] == INF) d[0] = 0; 92 printf("%d", d[0]); 93 return 0; 94 }
13、星际转移问题
由于人类对自然资源的消耗,人们意识到大约在 2300 年之后,地球就不能再居住了。于是在月球上建立了新的绿地,以便在需要时移民。令人意想不到的是,2177 年冬由于未知的原因,地球环境发生了连锁崩溃,人类必须在最短的时间内迁往月球。现有 n 个太空站位于地球与月球之间,且有 m 艘公共交通太空船在其间来回穿梭。每个太空站可容纳无限多的人,而每艘太空船 i 只可容纳 H[i]个人。每艘太空船将周期性地停靠一系列的太空站,例如:(1,3,4)表示该太空船将周期性地停靠太空站 134134134…。每一艘太空船从一个太空站驶往任一太空站耗时均为 1。人们只能在太空船停靠太空站(或月球、地球)时上、下船。初始时所有人全在地球上,太空船全在初始站。试设计一个算法,找出让所有人尽快地全部转移到月球上的运输方案。
对于给定的太空船的信息,找到让所有人尽快地全部转移到月球上的运输方案。
考虑把太空站按照天数拆点,连边即可。
二分天数需要重新建图跑dinic,复杂度堪忧。不如枚举天数,每次在原图的基础上增广即可。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <cstdlib> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <map> 9 #include <string> 10 #include <cmath> 11 inline int abs(int x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;} 12 inline int max(int a, int b){return a > b ? a : b;} 13 inline int min(int a, int b){return a < b ? a : b;} 14 inline int swap(int& a, int& b){int tmp = a;a = b;b = tmp;} 15 inline void read(int &x) 16 { 17 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 18 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 19 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 20 if(c == '-') x = -x; 21 } 22 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 23 const int MAXN = 13 + 5; 24 const int MAXM = 20 + 5; 25 const int MAXK = 50 + 5; 26 struct Edge 27 { 28 int v,w,nxt; 29 Edge(int _v, int _w, int _nxt){v = _v;w = _w;nxt = _nxt;} 30 Edge(){} 31 }edge[400010]; 32 int head[400010], cnt = 1; 33 inline void insert(int a, int b, int c) 34 { 35 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(b, c, head[a]), head[a] = cnt; 36 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(a, 0, head[b]), head[b] = cnt; 37 } 38 int S, T, h[400010], q[400010], he, ta, ans; 39 bool bfs() 40 { 41 memset(h, -1, sizeof(h)); 42 he = ta = 0, q[ta ++] = S, h[S] = 0; 43 while(he < ta) 44 { 45 int now = q[he ++]; 46 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 47 { 48 int v = edge[pos].v; 49 if(h[v] == -1 && edge[pos].w) 50 h[v] = h[now] + 1, q[ta ++] = v; 51 } 52 } 53 return h[T] != -1; 54 } 55 int dfs(int x, int f) 56 { 57 if(x == T) return f; 58 int used = 0, w; 59 for(int pos = head[x];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 60 { 61 int v = edge[pos].v; 62 if(h[v] == h[x] + 1) 63 { 64 w = dfs(v, min(f - used, edge[pos].w)); 65 edge[pos].w -= w, edge[pos ^ 1].w += w; 66 used += w; 67 if(used == f) return f; 68 } 69 } 70 if(!used) h[x] = -1; 71 return used; 72 } 73 void dinic() 74 { 75 while(bfs()) ans += dfs(S, INF); 76 } 77 int n,m,k,hh[MAXM],r[MAXM], sta[MAXM][MAXN + 2], tot[MAXN + 2], pre[MAXN + 2]; 78 int fa[MAXN]; 79 int find(int x) 80 { 81 return x == fa[x] ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]); 82 } 83 int main() 84 { 85 read(n), read(m), read(k); 86 for(int i = 1;i <= n + 2;++ i) fa[i] = i; 87 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 88 { 89 read(hh[i]), read(r[i]); 90 int f1,f2; 91 for(int j = 1;j <= r[i];++ j) 92 { 93 read(sta[i][j]); 94 if(sta[i][j] == 0) 95 sta[i][j] = n + 1; 96 else if(sta[i][j] == -1) 97 sta[i][j] = n + 2; 98 } 99 for(int j = 2;j <= r[i];++ j) 100 { 101 f1 = find(sta[i][j - 1]), f2 = find(sta[i][j]); 102 if(f1 != f2) fa[f1] = f2; 103 } 104 } 105 if(find(n + 1) != find(n + 2)) printf("0"); 106 else 107 { 108 S = 399999, T = 400000; 109 int now = n + 2, pnow = 0, day; 110 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 111 { 112 if(r[i] == 1) continue; 113 tot[i] = 2, pre[i] = 1; 114 } 115 insert(S, pnow + n + 1, INF); 116 insert(pnow + n + 2, T, INF); 117 for(day = 1;;++ day) 118 { 119 insert(S, now + n + 1, INF); 120 insert(now + n + 2, T, INF); 121 for(int i = 1;i <= n + 2;++ i) 122 insert(pnow + i, now + i, INF); 123 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 124 { 125 if(r[i] == 1) continue; 126 insert(sta[i][pre[i]] + pnow, sta[i][tot[i]] + now, hh[i]); 127 pre[i] = tot[i]; 128 tot[i] = tot[i] % r[i] + 1; 129 } 130 dinic(); 131 if(ans >= k) break; 132 pnow += n + 2, now += n + 2; 133 } 134 printf("%d", day); 135 } 136 return 0; 137 }
14、汽车加油行驶问题
给定一个 N×NN \times NN×N 的方形网格,设其左上角为起点◎,坐标(1,1)(1,1)(1,1) ,XXX 轴向右为正, YYY 轴向下为正,每个方格边长为 111 ,如图所示。
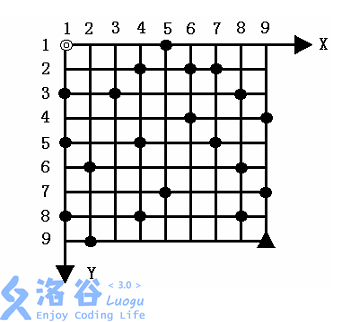
一辆汽车从起点◎出发驶向右下角终点▲,其坐标为 (N,N)(N,N)(N,N) 。
在若干个网格交叉点处,设置了油库,可供汽车在行驶途中加油。汽车在行驶过程中应遵守如下规则:
-
汽车只能沿网格边行驶,装满油后能行驶 KKK 条网格边。出发时汽车已装满油,在起点与终点处不设油库。
-
汽车经过一条网格边时,若其 XXX 坐标或 YYY 坐标减小,则应付费用 BBB ,否则免付费用。
-
汽车在行驶过程中遇油库则应加满油并付加油费用 AAA 。
-
在需要时可在网格点处增设油库,并付增设油库费用 CCC (不含加油费用AAA )。
- N,K,A,B,CN,K,A,B,CN,K,A,B,C 均为正整数, 且满足约束: 2≤N≤100,2≤K≤102\leq N\leq 100,2 \leq K \leq 102≤N≤100,2≤K≤10 。
设计一个算法,求出汽车从起点出发到达终点所付的最小费用。
有一个坑点,满油到加油站就不用加油了。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <stack> 9 #include <cmath> 10 inline int max(int a, int b){return a > b ? a : b;} 11 inline int min(int a, int b){return a < b ? a : b;} 12 inline int abs(int x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;} 13 inline void swap(int &x, int &y){int tmp = x;x = y;y = tmp;} 14 inline void read(int &x) 15 { 16 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 17 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 18 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 19 if(c == '-') x = -x; 20 } 21 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 22 const int MAXN = 200 + 10; 23 const int MAXK = 100 + 2; 24 const int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}; 25 const int dy[4] = {0, -1, 0, 1}; 26 int n,k,a,b[4],c,g[MAXN][MAXN],num[MAXN][MAXN][MAXK]; 27 struct Edge 28 { 29 int v,w,nxt; 30 Edge(int _v, int _w, int _nxt){v = _v, w = _w, nxt = _nxt;} 31 Edge(){} 32 }edge[1000010]; 33 int head[1000010], cnt; 34 inline void insert(int a, int b, int c) 35 { 36 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(b, c, head[a]), head[a] = cnt; 37 } 38 struct Node 39 { 40 int v, w; 41 Node(int _v, int _w){v = _v;w = _w;} 42 Node(){v = w = 0;} 43 }; 44 struct cmp 45 { 46 bool operator()(Node a, Node b) 47 { 48 return a.w > b.w; 49 } 50 }; 51 std::priority_queue<Node, std::vector<Node>, cmp> q; 52 int d[1000010], vis[1000010]; 53 void dij() 54 { 55 memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d)), d[num[1][1][k]] = 0; 56 q.push(Node(num[1][1][k], 0));Node now; 57 while(q.size()) 58 { 59 now = q.top(), q.pop(); 60 if(vis[now.v]) continue; 61 vis[now.v] = 1; 62 for(int pos = head[now.v];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 63 { 64 int v = edge[pos].v; 65 if(d[v] > d[now.v] + edge[pos].w) 66 { 67 d[v] = d[now.v] + edge[pos].w; 68 q.push(Node(v, d[v])); 69 } 70 } 71 } 72 } 73 int main() 74 { 75 read(n), read(k), read(a), read(b[0]), b[1] = b[0], read(c); 76 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 77 for(int j = 1;j <= n;++ j) 78 { 79 read(g[i][j]); 80 for(int l = 0;l <= k;++ l) 81 num[i][j][l] = (i - 1) * (n *(k + 1)) + (j - 1) * (k + 1) + l + 1; 82 } 83 /* 84 如果 在加油站 连向满油,费用为a 85 如果 不在加油站 86 如果 油空 连向油满, 费用为a + c 87 如果 油不空 向四周连边 ,费用为0/b 88 */ 89 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 90 for(int j = 1;j <= n;++ j) 91 for(int l = 0;l <= k;++ l) 92 if(g[i][j] && l < k) 93 insert(num[i][j][l], num[i][j][k], a); 94 else if(!g[i][j] && !l) 95 insert(num[i][j][l], num[i][j][k], a + c); 96 else 97 for(int p = 0;p < 4;++ p) 98 { 99 int xx = i + dx[p], yy = j + dy[p]; 100 if(xx <= 0 || yy <= 0 || xx > n || yy > n) continue; 101 insert(num[i][j][l], num[xx][yy][l - 1], b[p]); 102 } 103 dij();int ans = INF; 104 for(int l = 0;l <= k;++ l) ans = min(ans, d[num[n][n][l]]); 105 printf("%d", ans); 106 return 0; 107 }
15、孤岛营救问题
1944 年,特种兵麦克接到国防部的命令,要求立即赶赴太平洋上的一个孤岛,营救被敌军俘虏的大兵瑞恩。瑞恩被关押在一个迷宫里,迷宫地形复杂,但幸好麦克得到了迷宫的地形图。迷宫的外形是一个长方形,其南北方向被划分为 NNN 行,东西方向被划分为 MMM 列,于是整个迷宫被划分为 N×MN\times MN×M 个单元。每一个单元的位置可用一个有序数对(单元的行号,单元的列号)来表示。南北或东西方向相邻的 222 个单元之间可能互通,也可能有一扇锁着的门,或者是一堵不可逾越的墙。迷宫中有一些单元存放着钥匙,并且所有的门被分成PPP 类,打开同一类的门的钥匙相同,不同类门的钥匙不同。
大兵瑞恩被关押在迷宫的东南角,即 (N,M)(N,M)(N,M) 单元里,并已经昏迷。迷宫只有一个入口,在西北角。也就是说,麦克可以直接进入 (1,1)(1,1)(1,1) 单元。另外,麦克从一个单元移动到另一个相邻单元的时间为 111 ,拿取所在单元的钥匙的时间以及用钥匙开门的时间可忽略不计。
试设计一个算法,帮助麦克以最快的方式到达瑞恩所在单元,营救大兵瑞恩。
决策图最短路。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <stack> 9 #include <cmath> 10 inline int max(int a, int b){return a > b ? a : b;} 11 inline int min(int a, int b){return a < b ? a : b;} 12 inline int abs(int x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;} 13 inline void swap(int &x, int &y){int tmp = x;x = y;y = tmp;} 14 inline void read(int &x) 15 { 16 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 17 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 18 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 19 if(c == '-') x = -x; 20 } 21 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 22 const int MAXN = 10 + 1; 23 const int MAXK = 150 + 1; 24 const int MAXS = 14; 25 const int dx[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0}; 26 const int dy[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1}; 27 int n,m,p,k,s,g[MAXN][MAXN][MAXN][MAXN],key[MAXN][MAXN][MAXN + 2],ans = INF; 28 29 struct Node 30 { 31 int x, y, S, w; 32 Node(int _x, int _y, int _S, int _w){x = _x, y = _y, S = _S, w = _w;} 33 Node(){} 34 }q[MAXN * MAXN * (1 << MAXN)]; 35 int he, ta, vis[MAXN][MAXN][1 << MAXN]; 36 37 void bfs() 38 { 39 for(int i = 1;i <= p;++ i) 40 if(key[1][1][i]) 41 q[0].S |= 1 << (i - 1); 42 q[0].x = q[0].y = 1;q[0].w = 0; 43 he = 0, ta = 1, vis[1][1][0] = 1; 44 Node tmp; 45 while(he < ta) 46 { 47 tmp = q[he ++]; 48 int x = tmp.x, y = tmp.y, S = tmp.S, w = tmp.w; 49 50 // printf("%d %d %d %d\n", x, y, S, w); 51 52 if(x == n && y == m) 53 { 54 ans = min(ans, w); 55 continue; 56 } 57 for(int i = 0;i < 4;++ i) 58 { 59 int xx = x + dx[i], yy = y + dy[i], t = g[x][y][xx][yy]; 60 S = tmp.S; 61 if(xx <= 0 || yy <= 0 || xx > n || yy > m || t == 0) continue; 62 if(t == -1) 63 { 64 for(int i = 1;i <= p;++ i) 65 if(key[xx][yy][i]) 66 S |= 1 << (i - 1); 67 if(!vis[xx][yy][S]) 68 q[ta ++] = Node(xx, yy, S, w + 1), vis[xx][yy][S] = 1; 69 } 70 else if((S & (1 << (t - 1)))) 71 { 72 for(int i = 1;i <= p;++ i) 73 if(key[xx][yy][i]) 74 S |= 1 << (i - 1); 75 if(!vis[xx][yy][S]) 76 q[ta ++] = Node(xx, yy, S, w + 1), vis[xx][yy][S] = 1; 77 } 78 } 79 } 80 } 81 82 int main() 83 { 84 read(n), read(m), read(p), read(k); 85 memset(g, -1, sizeof(g)); 86 for(int i = 1;i <= k;++i) 87 { 88 int tmp1,tmp2,tmp3,tmp4; 89 read(tmp1), read(tmp2), read(tmp3), read(tmp4); 90 read(g[tmp1][tmp2][tmp3][tmp4]); 91 g[tmp3][tmp4][tmp1][tmp2] = g[tmp1][tmp2][tmp3][tmp4]; 92 } 93 read(s); 94 for(int i = 1;i <= s;++ i) 95 { 96 int tmp1,tmp2,tmp3;read(tmp1), read(tmp2), read(tmp3); 97 ++ key[tmp1][tmp2][tmp3]; 98 } 99 bfs(); 100 if(ans == INF) ans = -1; 101 printf("%d", ans); 102 return 0; 103 }
16、数字梯形问题
给定一个由 nnn 行数字组成的数字梯形如下图所示。
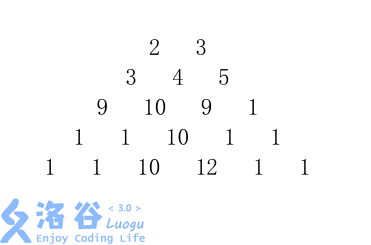
梯形的第一行有 mmm 个数字。从梯形的顶部的 mmm 个数字开始,在每个数字处可以沿左下或右下方向移动,形成一条从梯形的顶至底的路径。
分别遵守以下规则:
-
从梯形的顶至底的 mmm 条路径互不相交;
-
从梯形的顶至底的 mmm 条路径仅在数字结点处相交;
- 从梯形的顶至底的 mmm 条路径允许在数字结点相交或边相交。
第一个,拆点限流即可。
第二个,正常连边,边上限流即可。
第三个,dp(划掉)边上不限流即可

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <stack> 9 #include <cmath> 10 inline int max(int a, int b){return a > b ? a : b;} 11 inline int min(int a, int b){return a < b ? a : b;} 12 inline int abs(int x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;} 13 inline void swap(int &x, int &y){int tmp = x;x = y;y = tmp;} 14 inline void read(int &x) 15 { 16 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 17 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 18 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 19 if(c == '-') x = -x; 20 } 21 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 22 const int MAXN = 20 + 5; 23 int n,m,num[MAXN][MAXN], hao[MAXN][MAXN], tot; 24 25 struct Edge 26 { 27 int u,v,w,c,nxt; 28 Edge(int _u, int _v, int _w, int _c, int _nxt){u = _u;v = _v;w = _w;c = _c;nxt = _nxt;} 29 Edge(){} 30 }edge[10000010]; 31 int head[1000010], cnt = 1, d[1000010], vis[1000010], from[1000010], q[1000010], he, ta, S, T, ans; 32 inline void insert(int a, int b, int c, int d) 33 { 34 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(a, b, c, d, head[a]), head[a] = cnt; 35 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(b, a, 0, -d, head[b]), head[b] = cnt; 36 } 37 bool spfa() 38 { 39 memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d)), d[S] = 0, he = 0, ta = 1, q[0] = S, vis[S] = 1; 40 while(he != ta) 41 { 42 int now = q[he ++];if(he > 1000000) he = 0; 43 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 44 { 45 int v = edge[pos].v; 46 if(edge[pos].w && d[v] > d[now] + edge[pos].c) 47 { 48 d[v] = d[now] + edge[pos].c, from[v] = pos; 49 if(!vis[v]) 50 { 51 q[ta ++] = v, vis[v] = 1; 52 if(ta > 1000000) ta = 0; 53 } 54 } 55 } 56 vis[now] = 0; 57 } 58 return d[T] != INF; 59 } 60 void flow() 61 { 62 int mi = INF; 63 for(int i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) mi = min(mi, edge[i].w); 64 for(int i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) edge[i].w -= mi, edge[i ^ 1].w += mi, ans += mi * edge[i].c; 65 } 66 void mcf() 67 { 68 while(spfa()) flow(); 69 } 70 void build1() 71 { 72 int SS = (tot << 1) + 1;S = SS + 1, T = S + 1; 73 insert(S, SS, m, 0); 74 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) insert(SS, hao[1][i], 1, -num[1][i]); 75 for(int i = 1;i <= m + n - 1;++ i) insert(hao[n][i] + tot, T, 1, 0); 76 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 77 for(int j = 1;j <= m + i - 1;++ j) 78 insert(hao[i][j], tot + hao[i][j], 1, 0); 79 for(int i = 1;i < n;++ i) 80 for(int j = 1;j <= m + i - 1;++ j) 81 { 82 insert(tot + hao[i][j], hao[i + 1][j], 1, -num[i + 1][j]); 83 insert(tot + hao[i][j], hao[i + 1][j + 1], 1, -num[i + 1][j + 1]); 84 } 85 mcf(); 86 } 87 void build2() 88 { 89 memset(head, 0, sizeof(head)), cnt = 1, ans = 0, memset(from, 0, sizeof(from)); 90 int SS = tot + 1;S = SS + 1, T = S + 1; 91 insert(S, SS, m, 0); 92 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) insert(SS, hao[1][i], 1, -num[1][i]); 93 for(int i = 1;i <= m + n - 1;++ i) insert(hao[n][i], T, m, 0); 94 for(int i = 1;i < n;++ i) 95 for(int j = 1;j <= m + i - 1;++ j) 96 { 97 insert(hao[i][j], hao[i + 1][j], 1, -num[i + 1][j]); 98 insert(hao[i][j], hao[i + 1][j + 1], 1, -num[i + 1][j + 1]); 99 } 100 mcf(); 101 } 102 void build3() 103 { 104 memset(head, 0, sizeof(head)), cnt = 1, ans = 0, memset(from, 0, sizeof(from)); 105 int SS = tot + 1;S = SS + 1, T = S + 1; 106 insert(S, SS, m, 0); 107 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) insert(SS, hao[1][i], 1, -num[1][i]); 108 for(int i = 1;i <= m + n - 1;++ i) insert(hao[n][i], T, m, 0); 109 for(int i = 1;i < n;++ i) 110 for(int j = 1;j <= m + i - 1;++ j) 111 { 112 insert(hao[i][j], hao[i + 1][j], m, -num[i + 1][j]); 113 insert(hao[i][j], hao[i + 1][j + 1], m, -num[i + 1][j + 1]); 114 } 115 mcf(); 116 } 117 int main() 118 { 119 read(m), read(n); 120 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 121 for(int j = 1;j <= m + i - 1;++ j) 122 read(num[i][j]), hao[i][j] = ++ tot; 123 build1();printf("%d\n", -ans); 124 build2();printf("%d\n", -ans); 125 build3();printf("%d\n", -ans); 126 return 0; 127 }
17、运输问题
公司有 mm 个仓库和 nn 个零售商店。第 iii 个仓库有 aia_i 个单位的货物;第 jj 个零售商店需要 bjb_jb 个单位的货物。
货物供需平衡,即∑i=1mai=∑j=1nbj\sum\limits_{i=1}^{m}a_i=\sum\limits_{j=1}^{n}b_j。
从第 iii 个仓库运送每单位货物到第 jj个零售商店的费用为 cijc_{ij}。
试设计一个将仓库中所有货物运送到零售商店的运输方案,使总运输费用最少。
板子题。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <stack> 9 #include <cmath> 10 inline int max(int a, int b){return a > b ? a : b;} 11 inline int min(int a, int b){return a < b ? a : b;} 12 inline int abs(int x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;} 13 inline void swap(int &x, int &y){int tmp = x;x = y;y = tmp;} 14 inline void read(int &x) 15 { 16 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 17 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 18 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 19 if(c == '-') x = -x; 20 } 21 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 22 const int MAXN = 100 + 10; 23 struct Edge 24 { 25 int u, v, w, c, nxt; 26 Edge(int _u, int _v , int _w, int _c, int _nxt){u = _u, v = _v, w = _w, c = _c, nxt = _nxt;} 27 Edge(){} 28 }edge[MAXN * MAXN << 1]; 29 int head[MAXN << 2], cnt = 1, S, T, q[MAXN << 2], he, ta, from[MAXN << 2], d[MAXN << 2], vis[MAXN << 2], ans; 30 inline void insert(int a, int b, int c, int d) 31 { 32 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(a, b, c, d, head[a]), head[a] = cnt; 33 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(b, a, 0, -d, head[b]), head[b] = cnt; 34 } 35 bool spfa() 36 { 37 memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d)), d[S] = 0, vis[S] = 1, he = 0, ta = 1, q[0] = S; 38 while(he < ta) 39 { 40 int now = q[he ++];if(he > (MAXN << 2) - 2) he = 0; 41 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 42 { 43 int v = edge[pos].v; 44 if(edge[pos].w && d[v] > d[now] + edge[pos].c) 45 { 46 d[v] = d[now] + edge[pos].c, from[v] = pos; 47 if(!vis[v]) 48 { 49 q[ta ++] = v, vis[v] = 1; 50 if(ta > (MAXN << 2) - 2) ta = 0; 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 vis[now] = 0; 55 } 56 return d[T] != INF; 57 } 58 void flow() 59 { 60 int mi = INF; 61 for(int i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) mi = min(mi, edge[i].w); 62 for(int i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) edge[i].w -= mi, edge[i ^ 1].w += mi, ans += mi * edge[i].c; 63 } 64 void mcf() 65 { 66 while(spfa()) flow(); 67 } 68 int n,m,a[MAXN], b[MAXN], g[MAXN][MAXN]; 69 int main() 70 { 71 read(m), read(n); 72 S = m + n + 1, T = S + 1; 73 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 74 read(a[i]), insert(S, i, a[i], 0); 75 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 76 read(b[i]), insert(m + i, T, b[i], 0); 77 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 78 for(int j = 1;j <= n;++ j) 79 read(g[i][j]), insert(i, m + j, INF, g[i][j]); 80 mcf(); 81 printf("%d\n", ans); 82 83 memset(head, 0, sizeof(head)), memset(from, 0, sizeof(from)), ans = 0; 84 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 85 insert(S, i, a[i], 0); 86 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 87 insert(m + i, T, b[i], 0); 88 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 89 for(int j = 1;j <= n;++ j) 90 insert(i, m + j, INF, -g[i][j]); 91 mcf(); 92 printf("%d\n", -ans); 93 return 0; 94 }
18、分配问题
有 nn 件工作要分配给 nn个人做。第 iii 个人做第 jj 件工作产生的效益为 cijc_{ij} 。试设计一个将 nn件工作分配给 nn个人做的分配方案,使产生的总效益最大。
KM算法板子题。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <stack> 9 #include <cmath> 10 inline int max(int a, int b){return a > b ? a : b;} 11 inline int min(int a, int b){return a < b ? a : b;} 12 inline int abs(int x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;} 13 inline void swap(int &x, int &y){int tmp = x;x = y;y = tmp;} 14 inline void read(int &x) 15 { 16 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 17 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 18 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 19 if(c == '-') x = -x; 20 } 21 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 22 const int MAXN = 100 + 5; 23 int g[MAXN][MAXN], n1, n2, lab1[MAXN], lab2[MAXN], lk1[MAXN], lk2[MAXN], pre[MAXN], sla[MAXN], vis[MAXN]; 24 void fac(int x) 25 { 26 memset(pre, 0, sizeof(pre)), memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)), memset(sla, 0x3f, sizeof(sla)), vis[0] = 1; 27 int y; 28 do 29 { 30 y = 0; 31 for(int i = 1;i <= n2;++ i) 32 { 33 if(vis[i]) continue; 34 if(lab1[x] + lab2[i] - g[x][i] < sla[i]) sla[i] = lab1[x] + lab2[i] - g[x][i], pre[i] = x; 35 if(sla[i] < sla[y]) y = i; 36 } 37 int d = sla[y]; 38 for(int i = 1;i <= n1;++ i) if(vis[lk1[i]]) lab1[i] -= d; 39 for(int i = 1;i <= n2;++ i) if(vis[i]) lab2[i] += d; else sla[i] -= d; 40 vis[y] = 1; 41 }while(x = lk2[y]); 42 for(;y;swap(y, lk1[lk2[y] = pre[y]])); 43 } 44 int KM() 45 { 46 for(int i = 1;i <= n1;++ i) fac(i); 47 int ans = 0; 48 for(int i = 1;i <= n1;++ i) ans += g[i][lk1[i]]; 49 return ans; 50 } 51 int main() 52 { 53 read(n1), n2 = n1; 54 for(int i = 1;i <= n1;++ i) 55 for(int j = 1;j <= n2;++ j) 56 read(g[i][j]), g[i][j] = -g[i][j]; 57 printf("%d\n", -KM()); 58 59 memset(lab1, 0, sizeof(lab1)), memset(lab2, 0, sizeof(lab2)); 60 memset(lk1, 0, sizeof(lk1)), memset(lk2, 0, sizeof(lk2)); 61 for(int i = 1;i <= n1;++ i) 62 for(int j = 1;j <= n2;++ j) 63 g[i][j] = -g[i][j], lab1[i] = max(lab1[i], g[i][j]); 64 printf("%d", KM()); 65 return 0; 66 }
19、负载平衡问题
G 公司有 nn 个沿铁路运输线环形排列的仓库,每个仓库存储的货物数量不等。如何用最少搬运量可以使 nn个仓库的库存数量相同。搬运货物时,只能在相邻的仓库之间搬运。
可数学做法(环形纸牌加强版)
也可最小费用最大流

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <stack> 9 #include <cmath> 10 inline int max(int a, int b){return a > b ? a : b;} 11 inline int min(int a, int b){return a < b ? a : b;} 12 inline int abs(int x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;} 13 inline void swap(int &x, int &y){int tmp = x;x = y;y = tmp;} 14 inline void read(int &x) 15 { 16 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 17 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 18 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 19 if(c == '-') x = -x; 20 } 21 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 22 const int MAXN = 100 + 10; 23 struct Edge 24 { 25 int u, v, w, c, nxt; 26 Edge(int _u, int _v , int _w, int _c, int _nxt){u = _u, v = _v, w = _w, c = _c, nxt = _nxt;} 27 Edge(){} 28 }edge[MAXN * MAXN << 1]; 29 int head[MAXN << 2], cnt = 1, S, T, q[MAXN << 2], he, ta, from[MAXN << 2], d[MAXN << 2], vis[MAXN << 2], ans; 30 inline void insert(int a, int b, int c, int d) 31 { 32 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(a, b, c, d, head[a]), head[a] = cnt; 33 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(b, a, 0, -d, head[b]), head[b] = cnt; 34 } 35 bool spfa() 36 { 37 memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d)), d[S] = 0, vis[S] = 1, he = 0, ta = 1, q[0] = S; 38 while(he < ta) 39 { 40 int now = q[he ++];if(he > (MAXN << 2) - 2) he = 0; 41 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 42 { 43 int v = edge[pos].v; 44 if(edge[pos].w && d[v] > d[now] + edge[pos].c) 45 { 46 d[v] = d[now] + edge[pos].c, from[v] = pos; 47 if(!vis[v]) 48 { 49 q[ta ++] = v, vis[v] = 1; 50 if(ta > (MAXN << 2) - 2) ta = 0; 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 vis[now] = 0; 55 } 56 return d[T] != INF; 57 } 58 void flow() 59 { 60 int mi = INF; 61 for(int i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) mi = min(mi, edge[i].w); 62 for(int i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) edge[i].w -= mi, edge[i ^ 1].w += mi, ans += mi * edge[i].c; 63 } 64 void mcf() 65 { 66 while(spfa()) flow(); 67 } 68 int n, num[MAXN],sum,ave; 69 int main() 70 { 71 read(n);for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) read(num[i]), sum += num[i]; 72 S = n + 1, T = S + 1, ave = sum / n; 73 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 74 if(num[i] > ave) insert(S, i, num[i] - ave, 0); 75 else if(num[i] < ave) insert(i, T, ave - num[i], 0); 76 insert(n, 1, INF, 1), insert(1, n, INF, 1); 77 for(int i = 1;i < n;++ i) insert(i, i + 1, INF, 1), insert(i + 1, i, INF, 1); 78 mcf(); 79 printf("%d", ans); 80 return 0; 81 }
20、深海机器人问题
深海资源考察探险队的潜艇将到达深海的海底进行科学考察。
潜艇内有多个深海机器人。潜艇到达深海海底后,深海机器人将离开潜艇向预定目标移动。
深海机器人在移动中还必须沿途采集海底生物标本。沿途生物标本由最先遇到它的深海机器人完成采集。
每条预定路径上的生物标本的价值是已知的,而且生物标本只能被采集一次。
本题限定深海机器人只能从其出发位置沿着向北或向东的方向移动,而且多个深海机器人可以在同一时间占据同一位置。
用一个 P×QP\times QP×Q 网格表示深海机器人的可移动位置。西南角的坐标为 (0,0)(0,0)(0,0) ,东北角的坐标为 (Q,P)(Q,P)(Q,P) 。
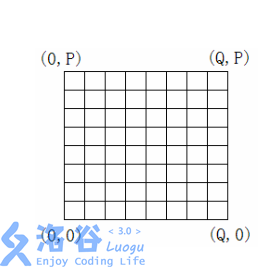
给定每个深海机器人的出发位置和目标位置,以及每条网格边上生物标本的价值。
计算深海机器人的最优移动方案, 使深海机器人到达目的地后,采集到的生物标本的总价值最高。
裸。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <stack> 9 #include <cmath> 10 inline int max(int a, int b){return a > b ? a : b;} 11 inline int min(int a, int b){return a < b ? a : b;} 12 inline int abs(int x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;} 13 inline void swap(int &x, int &y){int tmp = x;x = y;y = tmp;} 14 inline void read(int &x) 15 { 16 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 17 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 18 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 19 if(c == '-') x = -x; 20 } 21 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 22 struct Edge 23 { 24 int u, v, w, c, nxt; 25 Edge(int _u, int _v , int _w, int _c, int _nxt){u = _u, v = _v, w = _w, c = _c, nxt = _nxt;} 26 Edge(){} 27 }edge[10000010]; 28 int head[1000010], cnt = 1, S, T, q[1000010], he, ta, from[1000010], d[1000010], vis[1000010], ans; 29 inline void insert(int a, int b, int c, int d) 30 { 31 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(a, b, c, d, head[a]), head[a] = cnt; 32 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(b, a, 0, -d, head[b]), head[b] = cnt; 33 } 34 bool spfa() 35 { 36 memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d)), d[S] = 0, vis[S] = 1, he = 0, ta = 1, q[0] = S; 37 while(he < ta) 38 { 39 int now = q[he ++];if(he > 1000010) he = 0; 40 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 41 { 42 int v = edge[pos].v; 43 if(edge[pos].w && d[v] > d[now] + edge[pos].c) 44 { 45 d[v] = d[now] + edge[pos].c, from[v] = pos; 46 if(!vis[v]) 47 { 48 q[ta ++] = v, vis[v] = 1; 49 if(ta > 1000010) ta = 0; 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 vis[now] = 0; 54 } 55 return d[T] != INF; 56 } 57 void flow() 58 { 59 int mi = INF; 60 for(int i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) mi = min(mi, edge[i].w); 61 for(int i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) edge[i].w -= mi, edge[i ^ 1].w += mi, ans += mi * edge[i].c; 62 } 63 void mcf() 64 { 65 while(spfa()) flow(); 66 } 67 int a, b, p, qq, tmp, tmp1, tmp2, ma; 68 inline int num(int x, int y) 69 { 70 ma = max(ma, (x - 1) * p + y); 71 return (x - 1) * p + y; 72 } 73 int main() 74 { 75 read(a), read(b), read(p), read(qq); 76 ++ p, ++ qq; 77 S = p * qq + 1, T = S + 1; 78 for(int i = 1;i <= p;++ i) 79 for(int j = 1;j < qq;++ j) 80 read(tmp), insert(num(j, i), num(j + 1, i), 1, -tmp), insert(num(j, i), num(j + 1, i), INF, 0); 81 for(int i = 1;i <= qq;++ i) 82 for(int j = 1;j < p;++ j) 83 read(tmp), insert(num(i, j), num(i, j + 1), 1, -tmp), insert(num(i, j), num(i, j + 1), INF, 0); 84 for(int i = 1;i <= a;++ i) 85 read(tmp), read(tmp1), read(tmp2), insert(S, num(tmp2 + 1, tmp1 + 1), tmp, 0); 86 for(int i = 1;i <= b;++ i) 87 read(tmp), read(tmp1), read(tmp2), insert(num(tmp2 + 1, tmp1 + 1), T, tmp, 0); 88 mcf(); 89 printf("%d", -ans); 90 return 0; 91 }
21、最长k可重线段集问题
给定平面 x−O−yx-O-yx−O−y 上 nnn 个开线段组成的集合 III ,和一个正整数 kkk 。试设计一个算法,从开线段集合 III 中选取出开线段集合 S⊆IS\subseteq IS⊆I ,使得在 xxx 轴上的任何一点 ppp ,SSS 中与直线 x=px=px=p 相交的开线段个数不超过 kkk ,且∑z∈S∣z∣\sum\limits_{z\in S}|z|z∈S∑∣z∣ 达到最大。这样的集合 SSS 称为开线段集合 III 的最长 kkk 可重线段集。∑z∈S∣z∣\sum\limits_{z\in S}|z|z∈S∑∣z∣ 称为最长 kkk 可重线段集的长度。
对于任何开线段 zzz ,设其断点坐标为 (x0,y0)(x_0,y_0)(x0,y0) 和 (x1,y1)(x_1,y_1)(x1,y1) ,则开线段 zzz 的长度 ∣z∣|z|∣z∣ 定义为:∣z∣=⌊(x1−x0)2+(y1−y0)2⌋ |z|=\lfloor\sqrt{(x_1-x_0)^2+(y_1-y_0)^2}\rfloor∣z∣=⌊(x1−x0)2+(y1−y0)2
对于给定的开线段集合 III 和正整数 kkk ,计算开线段集合 III 的最长 kkk 可重线段集的长度。
考虑线段不垂直于x轴的情况。
把横坐标离散化,然后S连向1,流量为k,费用0,之后所有的i连向i + 1,流量INF,费用0,最后一个点连向T,流量k,费用0
对于一条线段,将两段的x连起来,小的连向大的,费用为线段长。
跑最大流即可。
为什么是对的呢?
跑一个流相当于找到了几段不相交的区间。
这样,从S流出的流动过程中有费用流量为i时,一定有i个区间重叠。
如果没有。。那我强行加区间不就好了吗。。答案不就更优了吗。。。
还需要说明得到的流是最优的。
如果得到的不是最优的,说明还能选一些线段进来,这时S->1的流一定流满了(没流慢不就把没选的选进来了吗。。)
考虑增加流,一个一个加,先加一个流,如果多流区间,那么设这个区间与p个区间相交,p = k时条件不满足,p < k时,说明存在已经流了的k - p条流可以流没选的区间但却没有流
感性理解一下。。
还有一个问题,这里没考虑线段垂直于x轴的情况。
拆点就好了。因为离散化写炸调了很久。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <map> 7 #include <cmath> 8 inline long long max(long long a, long long b){return a > b ? a : b;} 9 inline long long min(long long a, long long b){return a < b ? a : b;} 10 inline long long abs(long long x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;} 11 inline void swap(long long &x, long long &y){long long tmp = x;x = y;y = tmp;} 12 inline void read(long long &x) 13 { 14 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 15 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 16 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 17 if(c == '-') x = -x; 18 } 19 const long long INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; 20 struct Edge 21 { 22 long long u, v, w, c, nxt; 23 Edge(long long _u, long long _v , long long _w, long long _c, long long _nxt){u = _u, v = _v, w = _w, c = _c, nxt = _nxt;} 24 Edge(){} 25 }edge[2000010]; 26 long long head[2000010], cnt = 1, S, T, q[2000010], he, ta, from[2000010], d[2000010], vis[2000010], ans; 27 inline void insert(long long a, long long b, long long c, long long d) 28 { 29 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(a, b, c, d, head[a]), head[a] = cnt; 30 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(b, a, 0, -d, head[b]), head[b] = cnt; 31 } 32 bool spfa() 33 { 34 memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d)), d[S] = 0, vis[S] = 1, he = 0, ta = 1, q[0] = S; 35 while(he < ta) 36 { 37 long long now = q[he ++];if(he > 2000000) he = 0; 38 for(long long pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 39 { 40 long long v = edge[pos].v; 41 if(edge[pos].w && d[v] > d[now] + edge[pos].c) 42 { 43 d[v] = d[now] + edge[pos].c, from[v] = pos; 44 if(!vis[v]) 45 { 46 q[ta ++] = v, vis[v] = 1; 47 if(ta > 2000000) ta = 0; 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 vis[now] = 0; 52 } 53 return d[T] != INF; 54 } 55 void flow() 56 { 57 long long mi = INF; 58 for(long long i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) mi = min(mi, edge[i].w); 59 for(long long i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) edge[i].w -= mi, edge[i ^ 1].w += mi, ans += mi * edge[i].c; 60 } 61 void mcf() 62 { 63 while(spfa()) flow(); 64 } 65 long long n, k; 66 struct Node 67 { 68 long long x1, y1, x2, y2; 69 }node[20010]; 70 std::map<long long, long long> mp; 71 std::map<long long, long long> mpp; 72 long long num[20010], tot; 73 long long dis(long long x1, long long y1, long long x2, long long y2) 74 { 75 return sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2)); 76 } 77 int main() 78 { 79 read(n), read(k); 80 for(long long i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 81 { 82 read(node[i].x1), num[++ tot] = node[i].x1, 83 read(node[i].y1), num[++ tot] = node[i].y1, 84 read(node[i].x2), num[++ tot] = node[i].x2, 85 read(node[i].y2), num[++ tot] = node[i].y2; 86 if(node[i].x1 > node[i].x2) 87 swap(node[i].x1, node[i].x2), swap(node[i].y1, node[i].y2); 88 } 89 std::sort(num + 1, num + 1 + tot); 90 tot = std::unique(num + 1, num + 1 + tot) - num - 1; 91 for(long long i = 1;i < tot;++ i) 92 mp[num[i]] = i; 93 int tmp = tot; 94 mp[num[tot]] = tot; 95 for(long long i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 96 if(node[i].x1 == node[i].x2 && !mpp.count(mp[node[i].x1])) 97 mpp[mp[node[i].x1]] = ++ tot; 98 99 S = tot + 1, T = S + 1; 100 insert(S, 1, k, 0), insert(tmp, T, k, 0); 101 for(int i = 1;i < tmp;++ i) 102 { 103 if(mpp.count(i)) insert(i, mpp[i], INF, 0), insert(mpp[i], i + 1, INF, 0); 104 else insert(i, i + 1, INF, 0); 105 } 106 for(long long i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 107 if(node[i].x1 == node[i].x2) 108 insert(mp[node[i].x1], mpp[mp[node[i].x1]], 1, -abs(node[i].y1 - node[i].y2)); 109 else if(mpp.count(mp[node[i].x1])) 110 insert(mpp[mp[node[i].x1]], mp[node[i].x2], 1, -dis(node[i].x1, node[i].y1, node[i].x2, node[i].y2)); 111 else 112 insert(mp[node[i].x1], mp[node[i].x2], 1, -dis(node[i].x1, node[i].y1, node[i].x2, node[i].y2)); 113 mcf(); 114 printf("%lld", -ans); 115 return 0; 116 }
22、最长k可重区间集问题

对于给定的开区间集合 I 和正整数 k,计算开区间集合 I 的最长 k可重区间集的长度。
同上题。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <map> 7 #include <cmath> 8 inline long long max(long long a, long long b){return a > b ? a : b;} 9 inline long long min(long long a, long long b){return a < b ? a : b;} 10 inline long long abs(long long x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;} 11 inline void swap(long long &x, long long &y){long long tmp = x;x = y;y = tmp;} 12 inline void read(long long &x) 13 { 14 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 15 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 16 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 17 if(c == '-') x = -x; 18 } 19 const long long INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; 20 struct Edge 21 { 22 long long u, v, w, c, nxt; 23 Edge(long long _u, long long _v , long long _w, long long _c, long long _nxt){u = _u, v = _v, w = _w, c = _c, nxt = _nxt;} 24 Edge(){} 25 }edge[2000010]; 26 long long head[2000010], cnt = 1, S, T, q[2000010], he, ta, from[2000010], d[2000010], vis[2000010], ans; 27 inline void insert(long long a, long long b, long long c, long long d) 28 { 29 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(a, b, c, d, head[a]), head[a] = cnt; 30 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(b, a, 0, -d, head[b]), head[b] = cnt; 31 } 32 bool spfa() 33 { 34 memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d)), d[S] = 0, vis[S] = 1, he = 0, ta = 1, q[0] = S; 35 while(he < ta) 36 { 37 long long now = q[he ++];if(he > 2000000) he = 0; 38 for(long long pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 39 { 40 long long v = edge[pos].v; 41 if(edge[pos].w && d[v] > d[now] + edge[pos].c) 42 { 43 d[v] = d[now] + edge[pos].c, from[v] = pos; 44 if(!vis[v]) 45 { 46 q[ta ++] = v, vis[v] = 1; 47 if(ta > 2000000) ta = 0; 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 vis[now] = 0; 52 } 53 return d[T] != INF; 54 } 55 void flow() 56 { 57 long long mi = INF; 58 for(long long i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) mi = min(mi, edge[i].w); 59 for(long long i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) edge[i].w -= mi, edge[i ^ 1].w += mi, ans += mi * edge[i].c; 60 } 61 void mcf() 62 { 63 while(spfa()) flow(); 64 } 65 long long n, k; 66 struct Node 67 { 68 long long x1, x2; 69 }node[20010]; 70 std::map<long long, long long> mp; 71 long long num[20010], tot; 72 long long dis(long long x1, long long x2) 73 { 74 return abs(x1 - x2); 75 } 76 int main() 77 { 78 read(n), read(k); 79 for(long long i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 80 { 81 read(node[i].x1), num[++ tot] = node[i].x1, 82 read(node[i].x2), num[++ tot] = node[i].x2; 83 if(node[i].x1 > node[i].x2) 84 swap(node[i].x1, node[i].x2); 85 } 86 std::sort(num + 1, num + 1 + tot); 87 tot = std::unique(num + 1, num + 1 + tot) - num - 1; 88 for(long long i = 1;i < tot;++ i) 89 mp[num[i]] = i; 90 mp[num[tot]] = tot; 91 S = tot + 1, T = S + 1; 92 insert(S, 1, k, 0), insert(tot, T, k, 0); 93 for(int i = 1;i < tot;++ i) 94 insert(i, i + 1, INF, 0); 95 for(long long i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 96 insert(mp[node[i].x1], mp[node[i].x2], 1, -dis(node[i].x1, node[i].x2)); 97 mcf(); 98 printf("%lld", -ans); 99 return 0; 100 }
23、火星探险问题
火星探险队的登陆舱将在火星表面着陆,登陆舱内有多部障碍物探测车。登陆舱着陆后,探测车将离开登陆舱向先期到达的传送器方向移动。探测车在移动中还必须采集岩石标本。每一块岩石标本由最先遇到它的探测车完成采集。每块岩石标本只能被采集一次。岩石标本被采集后,其他探测车可以从原来岩石标本所在处通过。探测车不能通过有障碍的地面。本题限定探测车只能从登陆处沿着向南或向东的方向朝传送器移动,而且多个探测车可以在同一时间占据同一位置。如果某个探测车在到达传送器以前不能继续前进,则该车所采集的岩石标本将全部损失。
用一个 P·Q 网格表示登陆舱与传送器之间的位置。登陆舱的位置在(X1,Y1)处,传送器
的位置在(XP ,YQ)处。
X 1,Y 1 X 2 , Y 1 X 3 , Y 1 ... X P-1, Y 1 X P , Y 1
X 1,Y 2 X 2 , Y 2 X 3 , Y 2 ... X P-1, Y 2 X P , Y 2
X 1, Y 3 X 2 , Y 3 X 3 ,Y 3 ... X P-1, Y 3 X P , Y 3
... ...
X 1 ,Y Q-1 X 2 , Y Q-1 X 3 , Y Q-1 ... X P-1, Y Q-1 X P , Y Q-1
X 1,Y Q X 2 , Y Q X 3 , Y Q ... X P-1, Y Q X P ,Y Q
给定每个位置的状态,计算探测车的最优移动方案,使到达传送器的探测车的数量最多,
而且探测车采集到的岩石标本的数量最多
拆点即可。
输出路径注意细节。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <map> 7 #include <cmath> 8 inline int max(int a, int b){return a > b ? a : b;} 9 inline int min(int a, int b){return a < b ? a : b;} 10 inline int abs(int x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;} 11 inline void swap(int &x, int &y){int tmp = x;x = y;y = tmp;} 12 inline void read(int &x) 13 { 14 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 15 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 16 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 17 if(c == '-') x = -x; 18 } 19 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 20 struct Edge 21 { 22 int u, v, w, c, nxt; 23 Edge(int _u, int _v, int _w, int _c, int _nxt){u = _u;v = _v;w = _w;c = _c;nxt = _nxt;} 24 Edge(){} 25 }edge[1000010]; 26 int head[100010], cnt = 1, q[100010], he, ta, vis[100010], d[100010], from[100010], ans1, ans2, S, T; 27 28 inline void insert(int a, int b, int c, int d) 29 { 30 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(a, b, c, d, head[a]), head[a] = cnt; 31 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(b, a, 0, -d, head[b]), head[b] = cnt; 32 } 33 bool spfa() 34 { 35 memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d)), d[S] = 0, vis[S] = 1, he = 0, ta = 1, q[0] = S; 36 while(he != ta) 37 { 38 int now = q[he ++];if(he > 100000) he = 0; 39 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 40 { 41 int v = edge[pos].v; 42 if(edge[pos].w && d[v] > d[now] + edge[pos].c) 43 { 44 d[v] = d[now] + edge[pos].c, from[v] = pos; 45 if(!vis[v]) 46 { 47 vis[v] = 1, q[ta ++] = v; 48 if(ta > 100000) ta = 0; 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 vis[now] = 0; 53 } 54 return d[T] != INF; 55 } 56 void flow() 57 { 58 int mi = INF; 59 for(int i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) mi = min(mi, edge[i].w); 60 for(int i = from[T];i;i = from[edge[i].u]) edge[i].w -= mi, edge[i ^ 1].w += mi, ans2 += mi * edge[i].c; 61 ans1 += mi; 62 } 63 void mcf() 64 { 65 while(spfa()) flow(); 66 } 67 int n, p, qq, tot, num[1010][1010][2], g[1010][1010], x[100010], y[100010]; 68 int cntt; 69 void dfs(int from, int u, int tag) 70 { 71 for(int pos = head[u];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 72 { 73 if(!(pos & 1) && edge[pos ^ 1].w) 74 { 75 -- edge[pos ^ 1].w; 76 int v = edge[pos].v; 77 if(!tag) 78 { 79 dfs(from, v, tag ^ 1); 80 return; 81 } 82 printf("%d ", cntt); 83 if(x[v] - x[from] == 1) printf("0\n"); 84 else printf("1\n"); 85 dfs(v, v, tag ^ 1); 86 return; 87 } 88 } 89 } 90 //笔 本子 投影仪上的高考题// 91 int main() 92 { 93 read(n), read(p), read(qq); 94 swap(p, qq); 95 for(int i = 1;i <= p;++ i) 96 for(int j = 1;j <= qq;++ j) 97 { 98 read(g[i][j]), 99 num[i][j][0] = ++ tot, x[tot] = i, y[tot] = j; 100 num[i][j][1] = ++ tot, x[tot] = i, y[tot] = j; 101 if(g[i][j] == 2) insert(num[i][j][0], num[i][j][1], 1, -1); 102 if(g[i][j] != 1) insert(num[i][j][0], num[i][j][1], INF, 0); 103 } 104 S = tot + 1, T = S + 1; 105 insert(S, num[1][1][0], n, 0), insert(num[p][qq][1], T, n, 0); 106 for(int i = 1;i <= p;++ i) 107 for(int j = 1;j <= qq;++ j) 108 { 109 if(j + 1 <= qq) insert(num[i][j][1], num[i][j + 1][0], INF, 0); 110 if(i + 1 <= p) insert(num[i][j][1], num[i + 1][j][0], INF, 0); 111 } 112 mcf(); 113 for(int i = 1;i <= ans1;++ i) 114 ++ cntt, dfs(num[1][1][1], num[1][1][1], 0); 115 return 0; 116 }
24、骑士共存问题
在一个 n*n个方格的国际象棋棋盘上,马(骑士)可以攻击的棋盘方格如图所示。棋盘上某些方格设置了障碍,骑士不得进入
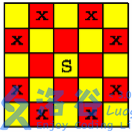
对于给定的 n*n 个方格的国际象棋棋盘和障碍标志,计算棋盘上最多可以放置多少个骑士,使得它们彼此互不攻击
黑白染色,最大独立集
之前写过一个二分图最大独立集的题解,这次写一个最小割的。
首先把方格黑白染色,对于每个黑格,他能跳到的地方都是白格,反之亦然。
于是每个黑格向能跳到的白格连边。每条边所连的两个点只能选一个,另一个必须割掉。
最小割。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <map> 7 #include <cmath> 8 inline int max(int a, int b){return a > b ? a : b;} 9 inline int min(int a, int b){return a < b ? a : b;} 10 inline int abs(int x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;} 11 inline void swap(int &x, int &y){int tmp = x;x = y;y = tmp;} 12 inline void read(int &x) 13 { 14 x = 0;char ch = getchar(), c = ch; 15 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') c = ch, ch = getchar(); 16 while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); 17 if(c == '-') x = -x; 18 } 19 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 20 const int dx[8] = {1, 1, 2, 2, -1, -1, -2, -2}; 21 const int dy[8] = {2, -2, 1, -1, 2, -2, 1, -1}; 22 struct Edge 23 { 24 int u,v,w,nxt; 25 Edge(int _u, int _v, int _w, int _nxt){u = _u;v = _v;w = _w;nxt = _nxt;} 26 Edge(){} 27 }edge[1000010]; 28 int head[100010], cnt = 1, S, T, q[100010], he, ta, h[100010], ans; 29 inline void insert(int a, int b, int c) 30 { 31 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(a, b, c, head[a]), head[a] = cnt; 32 edge[++ cnt] = Edge(b, a, 0, head[b]), head[b] = cnt; 33 } 34 bool bfs() 35 { 36 memset(h, -1, sizeof(h)), h[S] = 0, he = ta = 0, q[ta ++] = S; 37 while(he < ta) 38 { 39 int now = q[he ++]; 40 for(int pos = head[now];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 41 { 42 int v = edge[pos].v; 43 if(edge[pos].w && h[v] == -1) 44 h[v] = h[now] + 1, q[ta ++] = v; 45 } 46 } 47 return h[T] != -1; 48 } 49 int dfs(int x, int f) 50 { 51 if(x == T) return f; 52 int used = 0, w; 53 for(int pos = head[x];pos;pos = edge[pos].nxt) 54 { 55 int v = edge[pos].v; 56 if(h[v] == h[x] + 1) 57 { 58 w = dfs(v, min(edge[pos].w, f - used)); 59 edge[pos].w -= w; 60 edge[pos ^ 1].w += w; 61 used += w; 62 if(used == f) return f; 63 } 64 } 65 if(!used) h[x] = -1; 66 return used; 67 } 68 void dinic() 69 { 70 while(bfs()) ans += dfs(S, INF); 71 } 72 int n, m, n1, n2, g[505][505], num[505][505], tot; 73 int main() 74 { 75 read(n), read(m); 76 for(int i = 1;i <= m;++ i) 77 { 78 int tmp1, tmp2; 79 read(tmp1), read(tmp2); 80 g[tmp1][tmp2] = 1; 81 } 82 S = n * n + 1, T = S + 1; 83 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 84 for(int j = 1;j <= n;++ j) 85 num[i][j] = ++ tot; 86 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) 87 for(int j = 1;j <= n;++ j) 88 { 89 if(g[i][j]) continue; 90 if((i + j) & 1) insert(num[i][j], T, 1); 91 else 92 { 93 insert(S, num[i][j], 1); 94 for(int k = 0;k < 8;++ k) 95 { 96 int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k]; 97 if(x < 1 || y < 1 || x > n || y > n || g[x][y]) continue; 98 insert(num[i][j], num[x][y], INF); 99 } 100 } 101 } 102 dinic(); 103 printf("%d", n * n - m - ans); 104 return 0; 105 }
The end.


