springboot 使用 swagger2
段时间,同事分享了一下 swagger-ui,于是自己尝试了一下。大致的使用过程这里记录一下:
1.添加依赖
<!--swagger-ui-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1</version>
</dependency>
第一个是API获取的包,第二是官方给出的一个ui界面
2.启用注解或者使用配置类的方式
- 注解方式:启动类上加 @EnableSwagger2 注解和 @ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.**"}) ,basePackages 取值 是你要扫描的具体的包名
- 配置类方式 。下面只是提供其中一种方式:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration @EnableSwagger2 public class SwaggerConfig {
// 这里是用来配置是否启用swagger 的。 @Value("${swagger.enable: true}") private boolean enableSwagger; public static final String SWAGGER_SCAN_BASE_PACKAGE = "com.test.web.controller"; public static final String VERSION = "1.0.0"; ApiInfo apiInfo() { return new ApiInfoBuilder() .title("Swagger API") .description("This is to show api description") .contact(new Contact("rh", "www.baidu.com", "ruhui@keking.cn")) .license("Apache 2.0") .licenseUrl("http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html") .termsOfServiceUrl("") .version(VERSION) .build(); } @Bean public Docket customImplementation(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .select() .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage(SWAGGER_SCAN_BASE_PACKAGE)) .build() .apiInfo(apiInfo()); } }
3.使用相关注解对项目里的方法或者类进行标识
@Api:用在类上,说明该类的作用
@ApiOperation:用在方法上,说明方法的作用
@ApiImplicitParams:用在方法上包含一组参数说明
@ApiImplicitParam:用在@ApiImplicitParams注解中,指定一个请求参数的各个方面
paramType:参数放在哪个地方
header-->请求参数的获取:@RequestHeader
query-->请求参数的获取:@RequestParam
path(用于restful接口)-->请求参数的获取:@PathVariable
body(不常用)
form(不常用)
name:参数名
dataType:参数类型
required:参数是否必须传
value:参数的意思
defaultValue:参数的默认值
@ApiResponses:用于表示一组响应
@ApiResponse:用在@ApiResponses中,一般用于表达一个错误的响应信息
code:数字,例如400
message:信息,例如"请求参数没填好"
response:抛出异常的类
@ApiModel:描述一个Model的信息(这种一般用在post创建的时候,使用@RequestBody这样的场景,请求参数无法使用@ApiImplicitParam注解进行描述的时候)
@ApiModelProperty:描述一个model的属性
注解有很多,下面列举一个在方法上使用的示例:
@ApiOperation(value = "根据Id获取用户信息", httpMethod = "GET")
@ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "query", name = "id", required = true, value = "用户id", defaultValue = "1")
@RequestMapping(value = "/get", method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public User userList(Integer id){
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i=1; i<= 5; i++){
User user = new User(i, "用户" + i);
userList.add(user);
}
return userList.get(id -1);
}
4.启动项目,打开地址 http://服务名:端口/swagger-ui.html#/. 如我的服务启动后打开地址:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html#/
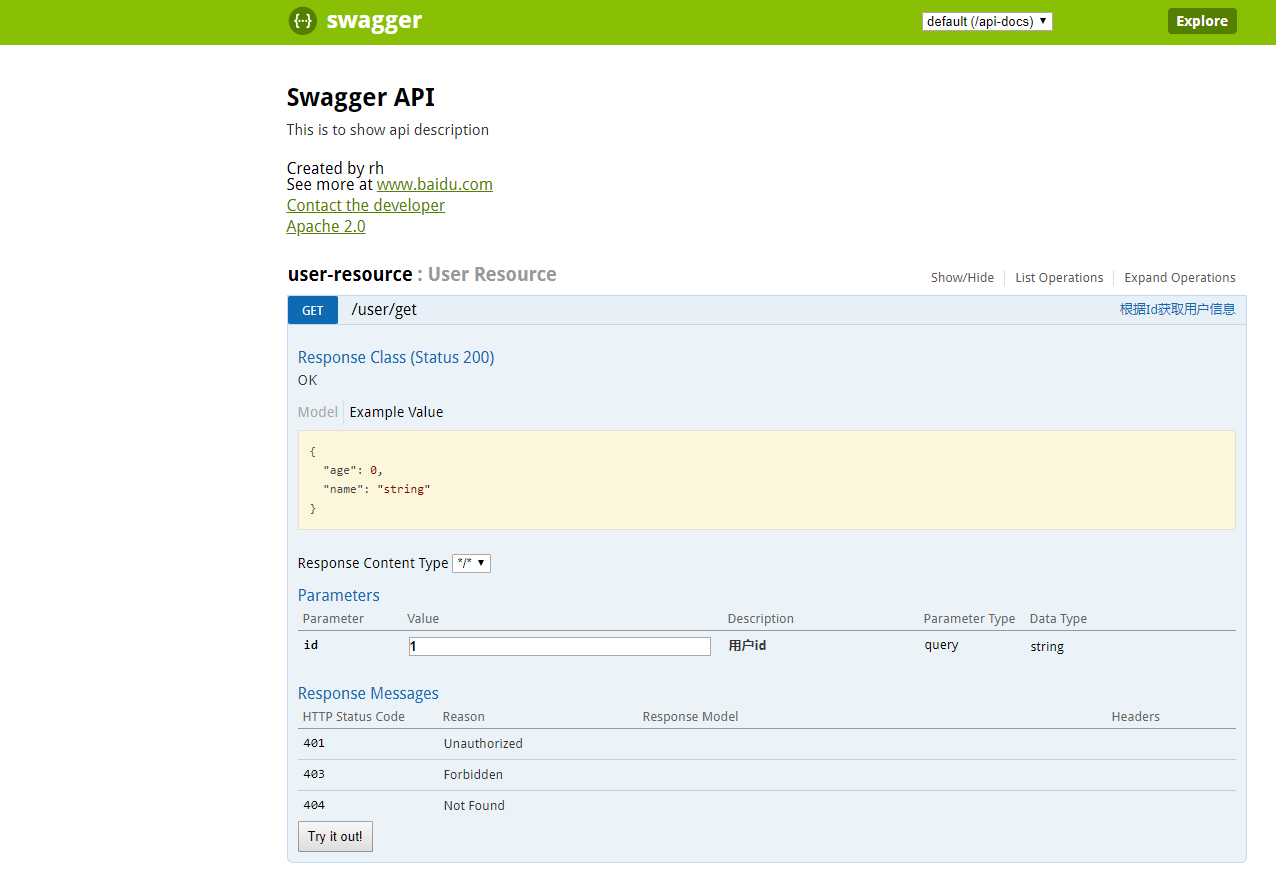
5.配置不同环境是否启用 swagger
- 请看第2步中:使用配置类方式。对 enable 属性进行赋值就行
@Bean public Docket customImplementation(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .select() .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage(SWAGGER_SCAN_BASE_PACKAGE)) .build() .apiInfo(apiInfo()); } - 通过 profile 方式。 在 SwaggerConfig 类上使用 Profile 注解,指定 profile 为 dev、uat,然后配置文件中指定 spring.profiles.active = dev 或者 uat。这个时候就启用了。
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
@Profile({"dev","uat"}) // 这里可以用来配置哪个环境启用swagger -- 对应属性spring.profiles.active
public class SwaggerConfig {
}
博客地址迁移,博客目前更新在 csdn: https://blog.csdn.net/H_Rhui

