【数据结构】常见的几种数据结构
常见的数据结构:数组、链表、队列、栈、、堆、二叉树、B树、哈希表、图
数组
因为数组内的元素是连续存储的,所以数组中元素的地址,可以通过其索引计算出来。根据索引查找元素,时间复杂度是
动态数组
动态数组具体代码实现
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class DynamicArray implements Iterable<Integer> {
private int capacity;
private int size;
private int[] array;
public DynamicArray(int capacity){
this.capacity = capacity;
}
/**
* 向最后位置 [size] 添加元素
*
* @param element 待添加元素
*/
public void addLast(int element){
add(size, element);
}
/**
* 向 [0 .. size] 位置添加元素
*
* @param index 索引位置
* @param element 待添加元素
*/
public void add(int index, int element){
checkAndGrow();
checkIndex(index);
if(index <size ){
System.arraycopy(array, index, array, index+1, size - index);
}
array[index] = element;
size++;
}
/**
* 从 [0 .. size) 范围删除元素
*
* @param index 索引位置
* @return 被删除元素
*/
public int remove(int index){
checkIndex(index);
int removed = array[index];
if(index < size -1){
System.arraycopy(array, index+1, array, index, size - index -1);
}
size--;
return removed;
}
/**
* 查询元素
*
* @param index 索引位置, 在 [0..size) 区间内
* @return 该索引位置的元素
*/
public int get(int index){
checkIndex(index);
return array[index];
}
/**
* 遍历方法1
*
* @param consumer 遍历要执行的操作, 入参: 每个元素
*/
public void foreach(Consumer<Integer> consumer){
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
consumer.accept(array[i]);
}
}
/**
* 遍历方法2 - 迭代器遍历
*/
@Override
public Iterator<Integer> iterator() {
return new Iterator<Integer>(){
int index = 0;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() { // 有没有下一个元素
return index < size;
}
@Override
public Integer next() { // 返回当前元素,并移动到下一个元素
return array[index++];
}
};
}
/**
* 遍历方法3 - stream 遍历
*
* @return stream 流
*/
public IntStream stream(){
return IntStream.of(Arrays.copyOfRange(array, 0, size));
}
/**
* 检查是否需要扩容
* */
private void checkAndGrow(){
if(size == 0){
array = new int[capacity];
}
if(size == capacity){
capacity += capacity >> 1;
int[] newArray = new int[capacity];
System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, size);
array = newArray;
}
}
/**
* 检查索引是否合法
*/
private void checkIndex(int index){
if(index<0 || index>size){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
}
}
链表
单向链表、双向链表、环形链表、跳表
队列
双端队列、优先队列、阻塞队列、单调队列
链表实现队列
单向环形带哨兵链表方式来实现队列
链表实现队列
import java.util.Iterator;
public class LinkedListQueue<E> implements Queue<E>, Iterable<E>{
private static class Node<E>{
E value;
Node<E> next;
public Node(E value, Node<E> next){
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
private final Node<E> head = new Node<>(null, null); //哨兵
private Node<E> tail = head; //尾指针,指向最后一个节点
private int size = 0;
private int capacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
{
tail.next = head; // 环形队列,最后一个节点指向哨兵节点。
}
public LinkedListQueue(){
}
public LinkedListQueue(int capacity){
this.capacity = capacity;
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
Node<E> added = new Node<>(value, head);
tail.next = added;
tail = added;
size++;
return true;
}
@Override
public E poll() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
Node<E> removed = head.next;
head.next = removed.next;
if(removed == tail){
//如果删除的是尾节点,即队列只有一个节点时,尾指针指向head,此时队列为空
tail = head;
}
size--;
return removed.value;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
return head.next.value;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return size == capacity;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Iterator<E>() {
Node<E> curr = head.next;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return curr != head;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E value = curr.value;
curr = curr.next;
return value ;
}
};
}
}
数组实现队列
环形数组实现队列
环形数组实现
import java.util.Iterator;
public class ArrayQueue<E> implements Queue<E>, Iterable<E>{
private int head = 0; //头指针,指向第一个元素
private int tail = 0; //尾指针,指向下一个新添元素的位置,即最后一个元素的后一位
private int length; //环形数组长度,比指定容量大1,空一个位置
private E[] array;
public ArrayQueue(int capacity){
length = capacity + 1; // 最后一个位置不存储元素,以便区别队列满时和队列空时
array = (E[]) new Object[capacity];
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
array[tail] = value;
tail = (tail + 1) % length;
return true;
}
@Override
public E poll() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
E value = array[head];
head = (head + 1) % length;
return value;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return array[head];
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == tail;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return (tail + 1) % length == head;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Iterator<E>(){
int p = head;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return p != tail;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E value = array[p];
p = (p + 1) % length;
return value;
}
};
}
}
可维护一个变量size来判断队列空或满。或者head和tail指针不断增加,需要用到索引再对容量取模,为了取模运算快,可使容量为2次幂,tips:对二次幂取模m等价于&(m-1)。
双端队列
环形双向链表实现双端队列
链表实现双端队列
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* 基于环形双向链表的双端队列
* @param <E> 元素类型
*/
public class LinkedListDeque<E> implements Deque<E>, Iterable<E> {
private static class Node<E>{
Node<E> prev;
E value;
Node<E> next;
public Node(Node<E> prev, E value, Node<E> next){
this.prev = prev;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
private Node<E> sentinel = new Node<>(null, null,null); //头尾哨兵
private int size = 0;
private int capacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public LinkedListDeque(){
sentinel.next = sentinel;
sentinel.prev = sentinel;
}
public LinkedListDeque(int capacity){
this();
this.capacity = capacity;
}
@Override
public boolean offerFirst(E value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
Node<E> added = new Node<E>(sentinel, value, sentinel.next);
sentinel.next.prev = added;
sentinel.next = added;
size++;
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean offerLast(E value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
Node<E> added = new Node<E>(sentinel.prev, value, sentinel);
sentinel.prev.next = added;
sentinel.prev = added;
size++;
return true;
}
@Override
public E pollFirst() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
Node<E> removed = sentinel.next;
sentinel.next = removed.next;
removed.next.prev = sentinel;
size--;
removed.next = null;
removed.prev = null; //有利于垃圾回收
return removed.value;
}
@Override
public E pollLast() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
Node<E> removed = sentinel.prev;
removed.prev.next = sentinel;
sentinel.prev = removed.prev;
size--;
removed.next = null;
removed.prev = null; //有利于垃圾回收
return removed.value;
}
@Override
public E peekFirst() {
return isEmpty()?null:sentinel.next.value;
}
@Override
public E peekLast() {
return isEmpty()?null:sentinel.prev.value;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return size == capacity;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Iterator<>() {
Node<E> curr = sentinel.next;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return curr != sentinel;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E value = curr.value;
curr = curr.next;
return value;
}
};
}
}
循环数组实现双端队列
数组实现双端队列
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* 基于循环数组实现, 特点
* <ul>
* <li>tail 停下来的位置不存储, 会浪费一个位置</li>
* </ul>
* @param <E>
*/
public class ArrayDeque<E> implements Deque<E>, Iterable<E> {
private int head = 0;
private int size = 0;
private final E[] array;
private final int capacity;
public ArrayDeque(int capacity){
this.capacity = capacity;
array = (E[]) new Object[capacity];
}
@Override
public boolean offerFirst(E value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
head = (head-1+capacity)%capacity;
array[head] = value;
size++;
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean offerLast(E value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
array[(head+size)%capacity] = value;
size++;
return true;
}
@Override
public E pollFirst() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
E value = array[head];
array[head] = null; //垃圾回收
head = (head+1)%capacity;
size--;
return value;
}
@Override
public E pollLast() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
int last = (head + size - 1) % capacity;
E value = array[last];
array[last] = null;
size--;
return value;
}
@Override
public E peekFirst() {
return isEmpty()?null:array[head];
}
@Override
public E peekLast() {
return isEmpty()?null:array[(head+size-1)%capacity];
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return size == array.length;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Iterator<>(){
int index = head;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return index != (index+size)%capacity;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E value = array[index];
index = (index+1)%capacity;
return value;
}
};
}
}
优先级队列
定义优先级接口
public interface Priority {
/**
* 返回元素优先级,越大优先级越高
* */
int priority();
}
无序数组实现优先级队列
/**
* 无序数组实现
* 1. 入队保持顺序
* 2. 出队前找到优先级最高的出队,相当于一次选择排序,并将元素往前移*/
public class PriorityQueue1<E extends Priority> implements Queue<E>{
private final Priority[] array;
private int size = 0;
public PriorityQueue1(int capacity){
array = new Priority[capacity];
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
array[size++] = value;
return true;
}
private int selectMax(){
int max = 0;
for(int i=1; i<size; i++){
if(array[i].priority() > array[max].priority()){
max = i;
}
}
return max;
}
private void remove(int index){
if(index < size-1){
System.arraycopy(array, index+1, array, index, size - index - 1);
}
array[--size] = null;
}
@Override
public E poll() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
int max = selectMax();
E value = (E) array[max];
remove(max);
return value;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return (E) array[selectMax()];
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return size == array.length;
}
}
有序数组实现优先级队列
/**
* 有序数组实现优先级队列
* 有序地插入元素,最后一个元素出队*/
public class PriorityQueue2<E extends Priority> implements Queue<E>{
private Priority[] array;
private int size = 0;
public PriorityQueue2(int capacity){
array = new Priority[capacity];
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
int index = size-1;
while(index >=0 && value.priority() < array[index].priority()){
array[index + 1] = array[index];
index--;
}
array[++index] = value;
size++;
return true;
}
@Override
public E poll() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
E value = (E) array[--size];
array[--size] = null;
return value;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return (E) array[size - 1];
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return size == array.length;
}
}
堆实现优先级队列
堆通常用完全二叉树实现,完全二叉树又可以用数组表示,从索引0开始,节点
的父节点为 。节点 的左子节点为 ,右子节点为 。
堆实现优先队列
/**
* 利用大顶堆实现优先级队列*/
public class PriorityQueue3<E extends Priority> implements Queue<E>{
private Priority[] array;
private int size;
public PriorityQueue3(int capacity){
array = new Priority[capacity];
}
/**
* 下潜,从索引index下潜到合适位置*/
private void down(int index, int size){
int max = index;
if(2*index + 1 < size &&
array[2*index + 1].priority() > array[index].priority()){
max = 2*index + 1;
}
if(2*index + 2 < size &&
array[2*index + 2].priority() > array[index].priority()){
max = 2*index + 2;
}
if(max != index){
swap(max, index);
down(max, size);
}
}
/**
* 上浮,从索引index上浮到合适位置*/
private void up(int index){
int parent = (index - 1)/2;
if(parent >= 0 && array[index].priority() > array[parent].priority()){
swap(parent, index);
up(parent);
}
}
private void swap(int i, int j){
Priority temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
array[size++] = value;
up(size-1);
return true;
}
@Override
public E poll() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
E value = (E) array[0];
swap(0, --size);
down(0,size);
array[size] = null;
return value;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return (E) array[0];
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return size == array.length;
}
}
阻塞队列
单锁实现
ReentrantLock 配合条件变量来实现
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition tailWaits = lock.newCondition(); // 条件变量
int size = 0;
public void offer(String e) {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (isFull()) {//使用while避免虚假唤醒
tailWaits.await(); // 当队列满时, 当前线程进入 tailWaits 等待
}
array[tail] = e;
tail++;
size++;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private boolean isFull() {
return size == array.length;
}
- 条件变量底层也是个队列,用来存储这些需要等待的线程,当队列满了,就会将 offer 线程加入条件队列,并暂时释放锁
- 将来我们的队列如果不满了(由 poll 线程那边得知)可以调用 tailWaits.signal() 来唤醒 tailWaits 中首个等待的线程,被唤醒的线程会再次争抢锁,从上次 await 处继续向下运行
/**
* 单锁实现
* @param <E> 元素类型
*/
public class BlockingQueue1<E> implements BlockingQueue<E> {
private final E[] array;
private int head = 0;
private int tail = 0;
private int size = 0; // 元素个数
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public BlockingQueue1(int capacity) {
array = (E[]) new Object[capacity];
}
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition tailWaits = lock.newCondition();
Condition headWaits = lock.newCondition();
@Override
public void offer(E e) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (isFull()) {
tailWaits.await();
}
array[tail] = e;
if (++tail == array.length) {
tail = 0;
}
size++;
headWaits.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public void offer(E e, long timeout) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
long t = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(timeout);
while (isFull()) {
if (t <= 0) {
return;
}
t = tailWaits.awaitNanos(t);//方法返回剩余时间
}
array[tail] = e;
if (++tail == array.length) {
tail = 0;
}
size++;
headWaits.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public E poll() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (isEmpty()) {
headWaits.await();
}
E e = array[head];
array[head] = null; // help GC
if (++head == array.length) {
head = 0;
}
size--;
tailWaits.signal();
return e;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
private boolean isFull() {
return size == array.length;
}
}
双锁实现
单锁的缺点在于:
- 生产和消费几乎是不冲突的,唯一冲突的是生产者和消费者它们有可能同时修改 size
- 冲突的主要是生产者之间:多个 offer 线程修改 tail
- 冲突的还有消费者之间:多个 poll 线程修改 head
如果希望进一步提高性能,可以用两把锁
- 一把锁保护 tail
- 另一把锁保护 head
ReentrantLock headLock = new ReentrantLock(); // 保护 head 的锁
Condition headWaits = headLock.newCondition(); // 队列空时,需要等待的线程集合
ReentrantLock tailLock = new ReentrantLock(); // 保护 tail 的锁
Condition tailWaits = tailLock.newCondition(); // 队列满时,需要等待的线程集合
size 并不受 tailLock 保护,tailLock 与 headLock 是两把不同的锁,并不能实现互斥的效果。因此,size 需要用下面的代码保证原子性
AtomicInteger size = new AtomicInteger(0); // 保护 size 的原子变量
size.getAndIncrement(); // 自增
size.getAndDecrement(); // 自减
难点:如何通知 headWaits 和 tailWaits 中等待的线程
条件变量的 await(), signal() 等方法需要先获得与之关联的锁,不能使用headLock锁来唤醒tailwaits中的线程。
解决办法:先获取相关锁,在唤醒对应的线程。为了避免嵌套而产生死锁,两段加锁改为平级。
性能还可以进一步提升
-
代码调整后 offer 并没有同时获取 tailLock 和 headLock 两把锁,因此两次加锁之间会有空隙,这个空隙内可能有其它的 offer 线程添加了更多的元素,那么这些线程都要执行 signal(),通知 poll 线程队列非空吗?
- 每次调用 signal() 都需要这些 offer 线程先获得 headLock 锁,成本较高,要想法减少 offer 线程获得 headLock 锁的次数
- 可以加一个条件:当 offer 增加前队列为空,即从 0 变化到不空,才由此 offer 线程来通知 headWaits,其它情况不归它管
-
队列从 0 变化到不空,会唤醒一个等待的 poll 线程,这个线程被唤醒后,肯定能拿到 headLock 锁,因此它具备了唤醒 headWaits 上其它 poll 线程的先决条件。如果检查出此时有其它 offer 线程新增了元素(不空,但不是从0变化而来),那么不妨由此 poll 线程来唤醒其它 poll 线程
这个技巧被称之为级联通知(cascading notifies),类似的原因
- 在 poll 时队列从满变化到不满,才由此 poll 线程来唤醒一个等待的 offer 线程,目的也是为了减少 poll 线程对 tailLock 上锁次数,剩下等待的 offer 线程由这个 offer 线程间接唤醒
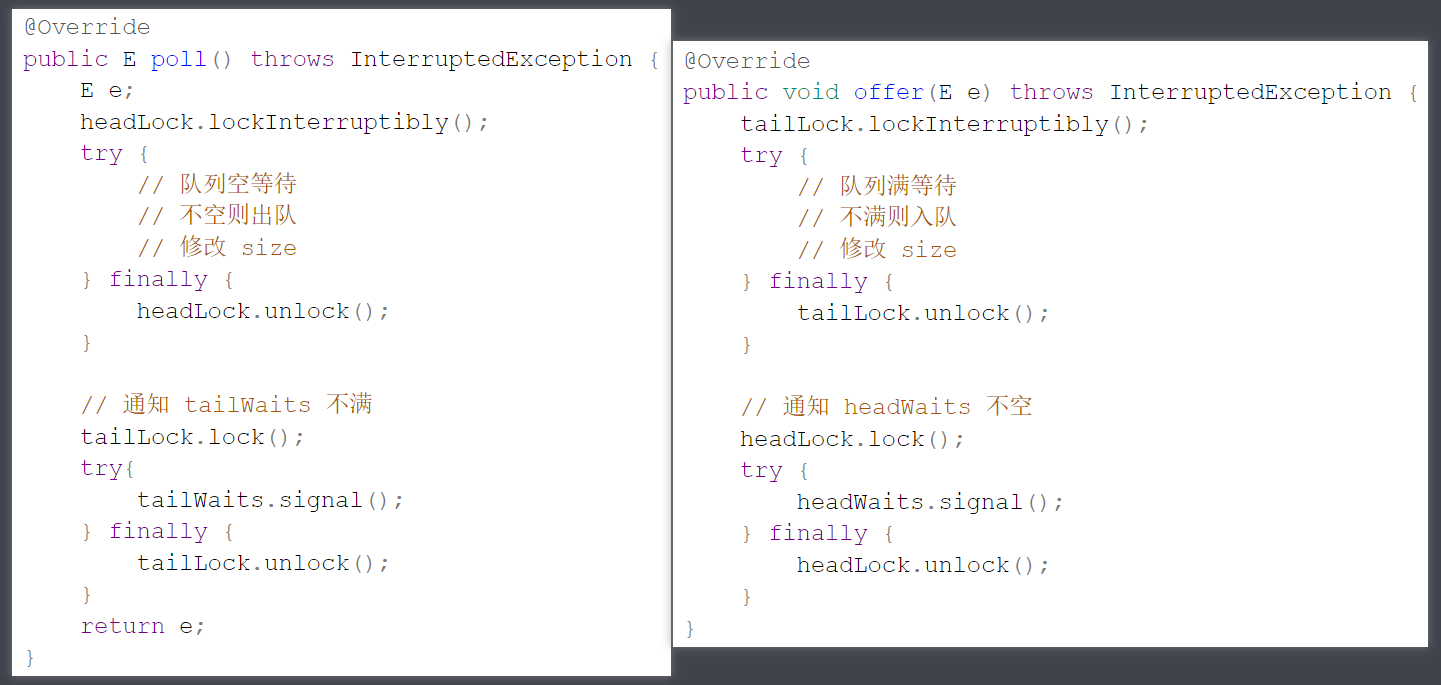
最终双锁实现代码
public class BlockingQueue2<E> implements BlockingQueue<E> {
private final E[] array;
private int head = 0;
private int tail = 0;
private final AtomicInteger size = new AtomicInteger(0);
ReentrantLock headLock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition headWaits = headLock.newCondition();
ReentrantLock tailLock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition tailWaits = tailLock.newCondition();
public BlockingQueue2(int capacity) {
this.array = (E[]) new Object[capacity];
}
@Override
public void offer(E e) throws InterruptedException {
int c;
tailLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (isFull()) {
tailWaits.await();
}
array[tail] = e;
if (++tail == array.length) {
tail = 0;
}
c = size.getAndIncrement();
// a. 队列不满, 但不是从满->不满, 由此offer线程唤醒其它offer线程
if (c + 1 < array.length) {
tailWaits.signal();
}
} finally {
tailLock.unlock();
}
// b. 从0->不空, 由此offer线程唤醒等待的poll线程
if (c == 0) {
headLock.lock();
try {
headWaits.signal();
} finally {
headLock.unlock();
}
}
}
@Override
public E poll() throws InterruptedException {
E e;
int c;
headLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (isEmpty()) {
headWaits.await();
}
e = array[head];
if (++head == array.length) {
head = 0;
}
c = size.getAndDecrement();
// b. 队列不空, 但不是从0变化到不空,由此poll线程通知其它poll线程
if (c > 1) {
headWaits.signal();
}
} finally {
headLock.unlock();
}
// a. 从满->不满, 由此poll线程唤醒等待的offer线程
if (c == array.length) {
tailLock.lock();
try {
tailWaits.signal();
} finally {
tailLock.unlock();
}
}
return e;
}
private boolean isEmpty() {
return size.get() == 0;
}
private boolean isFull() {
return size.get() == array.length;
}
}
栈
单调栈、最小栈
链表实现栈
单向带头哨兵链表实现栈
链表实现
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* 链表实现栈*/
public class LinkedListStack<E> implements Stack<E>, Iterable<E>{
private static class Node<E>{
E value;
Node<E> next;
public Node(E value, Node<E> next){
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
private final Node<E> sentinel = new Node<>(null, null); //哨兵节点
private int size = 0;
private final int capacity;
public LinkedListStack(int capacity){
this.capacity = capacity;
}
@Override
public boolean push(E value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
size++;
sentinel.next = new Node<>(value, sentinel.next);
return true;
}
@Override
public E pop() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
Node<E> head = sentinel.next;
sentinel.next = head.next;
size--;
return head.value;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return sentinel.next.value;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return size == capacity;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Iterator<>(){
Node<E> curr = sentinel.next;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return curr != null;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E value = curr.value;
curr = curr.next;
return value;
}
};
}
}
数组实现栈
数组实现栈
import java.util.Iterator;
public class ArrayStack<E> implements Stack<E>, Iterable<E>{
private int top = 0;
private E[] array;
public ArrayStack(int capacity){
array = (E[]) new Object[capacity];
}
@Override
public boolean push(E value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
array[top++] = value;
return true;
}
@Override
public E pop() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return array[--top];
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return array[top - 1];
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return top == array.length;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Iterator<E>() {
int index = top - 1;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return index != -1;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E value = array[index];
index--;
return value;
}
};
}
}
堆
堆的主要方法:下潜、上浮、建堆、交换。
下潜(down): 将 parent 索引处的元素下潜: 与两个孩子较大者交换, 直至没孩子或孩子没它大
private void down(int parent) {
int left = parent * 2 + 1;
int right = left + 1;
int max = parent;
if (left < size && array[left] > array[max]) {
max = left;
}
if (right < size && array[right] > array[max]) {
max = right;
}
if (max != parent) { // 找到了更大的孩子
swap(max, parent);
down(max);
}
}
上浮(up):将 offered 元素上浮: 直至 offered 小于父元素或到堆顶,index为offered的索引
private void up(int offered, int index) {
int child = index;
while (child > 0) {
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
if (offered > array[parent]) {
array[child] = array[parent];
} else {
break;
}
child = parent;
}
array[child] = offered;
}
建堆(heapify):1. 找到最后一个非叶子节点。2. 从后向前,对每个节点执行下潜
private void heapify() {
// 如何找到最后这个非叶子节点 size / 2 - 1
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
down(i);
}
}
交换(swap):交换两个索引处的元素
private void swap(int i, int j) {
int t = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = t;
}
最大堆代码实现
public class MaxHeap {
private int[] array;
private int size;
public MaxHeap(int capacity){
array = new int[capacity];
}
/**
* 接收array数组,建堆*/
public MaxHeap(int[] array) {
this.array = array;
this.size = array.length;
heapify();
}
private void heapify(){
for(int i = size/2 -1; i>=0; --i){
down(i);
}
}
/**
* 获取堆顶元素
*
* @return 堆顶元素
*/
public int peek(){
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return array[0];
}
/**
* 删除堆顶元素
*
* @return 堆顶元素
*/
public int poll(){
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
int value = array[--size];
swap(0, size);
down(0);
return value;
}
/**
* 删除指定索引处元素
* 先上浮到堆顶,再删除
* @param index 索引
* @return 被删除元素
*/
public int poll(int index){
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
if(index<-1 || index>=size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("超出索引范围");
}
int value = array[index];
up(Integer.MAX_VALUE, index);
poll();
return value;
}
/**
* 替换堆顶元素
*
* @param replaced 新元素
*/
public void replace(int replaced){
array[0] = replaced;
down(0);
}
/**
* 堆的尾部添加元素
*
* @param offered 新元素
* @return 是否添加成功
*/
public boolean offer(int offered){
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
up(offered, size);
size++;
return true;
}
// 将 index 索引处的元素下潜: 与两个孩子较大者交换, 直至没孩子或孩子没它大
private void down(int index){
int left = 2 * index + 1;
int right = left + 1;
int max = index;
if(left < size && array[left] > array[max]){
max = left;
}
if(right < size && array[right] > array[max]){
max = right;
}
if(max != index){
swap(max, index);
down(max);
}
}
// 将 index 索引处元素上浮: 直至 元素 小于父元素或到堆顶
private void up(int offered, int index){
int child = index;
while(child > 0){
int parent = (child - 1) >>> 1;
if(offered > array[parent]){
array[child] = array[parent];
}else{
break;
}
child = parent;
}
array[child] = offered;
}
private void swap(int i, int j){
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
public boolean isFull(){
return size == array.length;
}
}
二叉树
二叉搜索树、AVL数、红黑树
广度优先遍历:
- 初始化,将根节点加入队列
- 循环处理队列中每个节点,直至队列为空
- 每次循环内处理节点后,将它的孩子节点(即下一层的节点,从左孩子到右孩子)加入队列
前序遍历迭代实现
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
while(!stack.empty() || curr != null){
while(curr != null){
list.add(curr.val); //处理当前中间节点,前序遍历为中左右
stack.push(curr);//将当前中间节点压栈,
curr = curr.left;//将左子节点压栈
}
TreeNode node = stack.pop();//弹出中间节点
curr = node.right; //将右子节点压栈
}
return list;
}
}
class TreeNode{
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right){
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
中序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
while(!stack.empty() || curr != null){
while(curr != null){
stack.push(curr);//将当前中间节点压栈,
curr = curr.left;//将左子节点压栈
}
TreeNode node = stack.pop();//弹出中间节点
list.add(node.val); //左边节点处理完,处理当前中间节点,中序遍历为左中右
curr = node.right; //将右子节点压栈
}
return list;
}
}
后序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
TreeNode prev = null;
while(!stack.empty() || curr != null){
while(curr != null){
stack.push(curr);//将当前中间节点压栈,
curr = curr.left;//将左子节点压栈
}
TreeNode node = stack.peek();//通过中间节点访问右边
if(node.right == null || node.right == prev){//没有右孩子,或者右边已经处理过
//弹出并处理中间节点,后序遍历为左右中
list.add(stack.pop().val);
prev = node; //最新处理完的节点
}else{
curr = node.right; //将右子节点压栈
}
}
return list;
}
}
统一写法
LinkedList<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode curr = root; // 代表当前节点
TreeNode pop = null; // 最近一次弹栈的元素
while (curr != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (curr != null) {
colorPrintln("前: " + curr.val, 31);
stack.push(curr); // 压入栈,为了记住回来的路
curr = curr.left;
} else {
TreeNode peek = stack.peek();
// 右子树可以不处理, 对中序来说, 要在右子树处理之前打印
if (peek.right == null) {
colorPrintln("中: " + peek.val, 36);
pop = stack.pop();
colorPrintln("后: " + pop.val, 34);
}
// 右子树处理完成, 对中序来说, 无需打印
else if (peek.right == pop) {
pop = stack.pop();
colorPrintln("后: " + pop.val, 34);
}
// 右子树待处理, 对中序来说, 要在右子树处理之前打印
else {
colorPrintln("中: " + peek.val, 36);
curr = peek.right;
}
}
}
public static void colorPrintln(String origin, int color) {
System.out.printf("\033[%dm%s\033[0m%n", color, origin);
}
二叉搜索树
迭代遍历找到插入位置的父节点
新增操作
public void put(int key, Object value) {
BSTNode node = root;
BSTNode parent = null;
while (node != null) {
parent = node;
if (key < node.key) {
node = node.left;
} else if (node.key < key) {
node = node.right;
} else {
// 1. key 存在则更新
node.value = value;
return;
}
}
// 2. key 不存在则新增
if (parent == null) {
root = new BSTNode(key, value);
} else if (key < parent.key) {
parent.left = new BSTNode(key, value);
} else {
parent.right = new BSTNode(key, value);
}
}
前驱和后继节点
节点有左子树,此时前驱节点就是左子树的最大值。节点没有左子树,若离它最近的祖先自从左而来,此祖先即为前驱。
public Object predecessor(int key) {
BSTNode ancestorFromLeft = null;
BSTNode p = root;
while (p != null) {
if (key < p.key) {
p = p.left;
} else if (p.key < key) {
ancestorFromLeft = p;//最近左边的祖先
p = p.right;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (p == null) {
return null;
}
// 情况1 - 有左孩子
if (p.left != null) {
return max(p.left);
}
// 情况2 - 有祖先自左而来
return ancestorFromLeft != null ? ancestorFromLeft.value : null;
}
public Object successor(int key) {
BSTNode ancestorFromRight = null;
BSTNode p = root;
while (p != null) {
if (key < p.key) {
ancestorFromRight = p;
p = p.left;
} else if (p.key < key) {
p = p.right;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (p == null) {
return null;
}
// 情况1 - 有右孩子
if (p.right != null) {
return min(p.right);
}
// 情况2 - 有祖先自右而来
return ancestorFromRight != null ? ancestorFromRight.value : null;
}
删除操作
被删节点只有一个孩子时将另一个孩子直接传递给其父节点(托孤),包括没有孩子的情况。有两个孩子时,找到后继节点,用后继节点取代被删除节点,注意孩子之间的处理。
/**
* <h3>根据关键字删除</h3>
*
* @param key 关键字
* @return 被删除关键字对应值
*/
public Object delete(int key) {
BSTNode p = root;
BSTNode parent = null;
while (p != null) {
if (key < p.key) {
parent = p;
p = p.left;
} else if (p.key < key) {
parent = p;
p = p.right;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (p == null) {
return null;
}
// 删除操作
if (p.left == null) {
shift(parent, p, p.right); // 情况1
} else if (p.right == null) {
shift(parent, p, p.left); // 情况2
} else {
// 情况4
// 4.1 被删除节点找后继
BSTNode s = p.right;
BSTNode sParent = p; // 后继父亲
while (s.left != null) {
sParent = s;
s = s.left;
}
// 4.2 删除和后继不相邻, 处理后继的后事
if (sParent != p) {
shift(sParent, s, s.right); // 不可能有左孩子
s.right = p.right;
}
// 4.3 后继取代被删除节点
shift(parent, p, s);
s.left = p.left;
}
return p.value;
}
/**
* 托孤方法
*
* @param parent 被删除节点的父亲
* @param deleted 被删除节点
* @param child 被顶上去的节点
*/
// parent指向child
private void shift(BSTNode parent, BSTNode deleted, BSTNode child) {
if (parent == null) {
root = child;
} else if (deleted == parent.left) {
parent.left = child;
} else {
parent.right = child;
}
}
AVL树
失衡的四种情况
- LL:失衡节点左子树比右子树高,且其左孩子也是左子树比右子树高
- LR:失衡节点左子树比右子树高,但其左孩子是右子树比左子树高
- RR:失衡节点右子树比左子树高,且其右孩子也是右子树比左子树高
- RL:失衡节点右子树比左子树高,但其右孩子是左子树比右子树高
四种旋转处理失衡
右旋
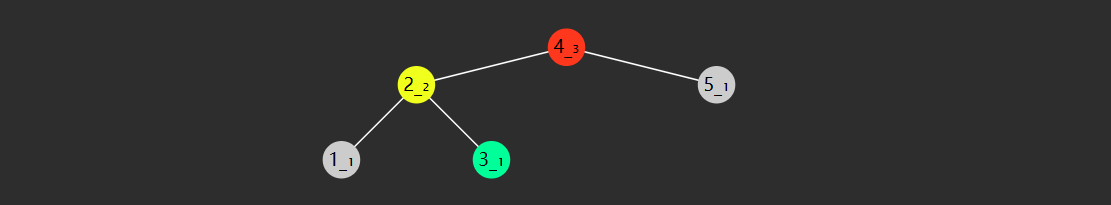
private AVLNode rightRotate(AVLNode red) {
AVLNode yellow = red.left;
AVLNode green = yellow.right;
yellow.right = red;
red.left = green;
return yellow;
}
左旋
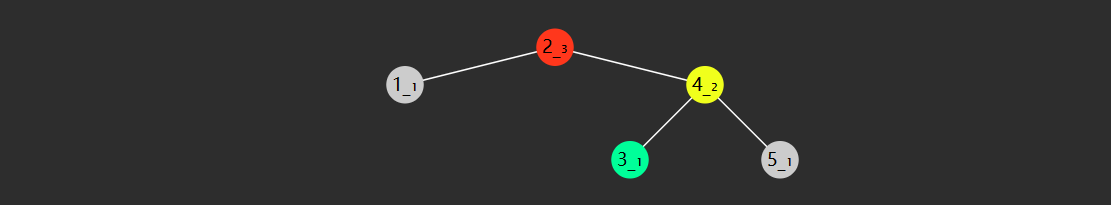
private AVLNode leftRotate(AVLNode red) {
AVLNode yellow = red.right;
AVLNode green = yellow.left;
yellow.left = red;
red.right = green;
return yellow;
}
左右旋--指先左旋左子树,再右旋根节点(失衡),这时一次旋转并不能解决失衡
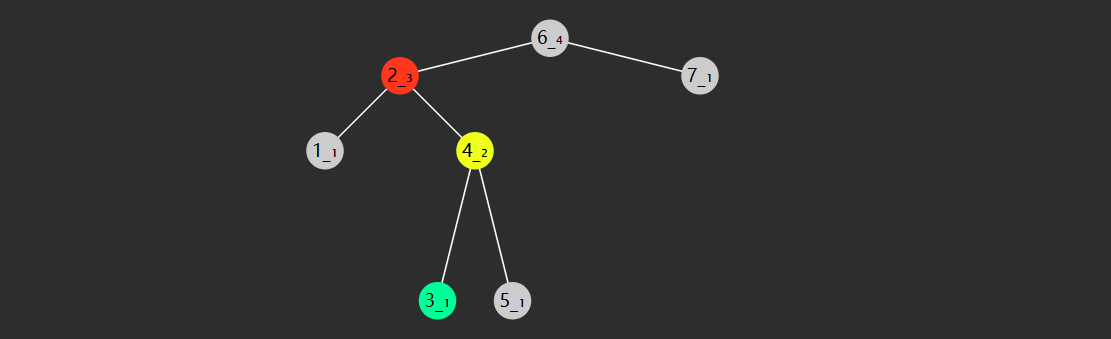
private AVLNode leftRightRotate(AVLNode root) {
root.left = leftRotate(root.left);
return rightRotate(root);
}
右左旋--指先右旋右子树,再左旋根节点(失衡)
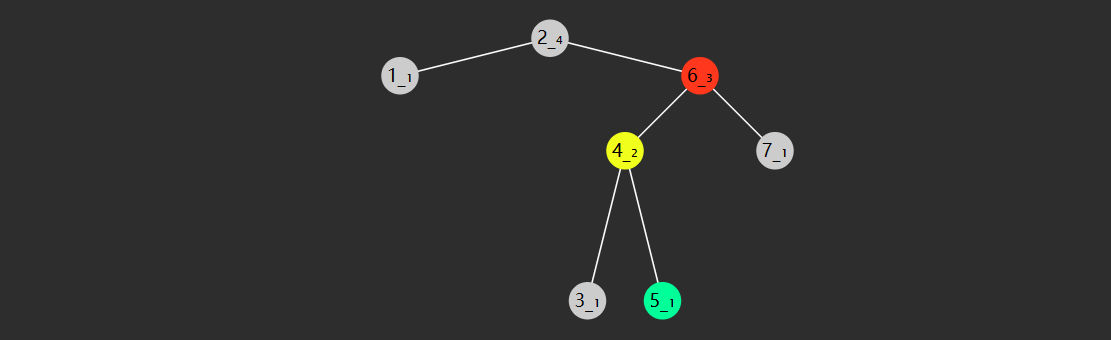
private AVLNode rightLeftRotate(AVLNode root) {
root.right = rightRotate(root.right);
return leftRotate(root);
}
判断及调整平衡代码
bf为左子树高度-右子树高度,节点有一个高度属性
private AVLNode balance(AVLNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
int bf = bf(node);
if (bf > 1 && bf(node.left) >= 0) {//LL
return rightRotate(node);
} else if (bf > 1 && bf(node.left) < 0) {//LR
return leftRightRotate(node);
} else if (bf < -1 && bf(node.right) > 0) {//RL
return rightLeftRotate(node);
} else if (bf < -1 && bf(node.right) <= 0) {//RR
return leftRotate(node);
}
return node;
}
新增
public void put(int key, Object value) {
root = doPut(root, key, value);
}
private AVLNode doPut(AVLNode node, int key, Object value) {
if (node == null) {
return new AVLNode(key, value);
}
if (key == node.key) {
node.value = value;
return node;
}
if (key < node.key) {
node.left = doPut(node.left, key, value);
} else {
node.right = doPut(node.right, key, value);
}
updateHeight(node);
return balance(node);
}
删除
public void remove(int key) {
root = doRemove(root, key);
}
private AVLNode doRemove(AVLNode node, int key) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
if (key < node.key) {
node.left = doRemove(node.left, key);
} else if (node.key < key) {
node.right = doRemove(node.right, key);
} else {
if (node.left == null) {
node = node.right;
} else if (node.right == null) {
node = node.left;
} else {
AVLNode s = node.right;
while (s.left != null) {
s = s.left;
}
s.right = doRemove(node.right, s.key);
s.left = node.left;
node = s;
}
}
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
updateHeight(node);
return balance(node);
}
小结
AVL是一个自平衡的二叉搜索树,新增和删除操作和二叉搜索树类似,就是多一个更新高度和平衡的操作。
红黑树
红黑树特性
- 所有节点都有两种颜色:红🔴、黑⚫
- 所有 null (叶子节点null)视为黑色⚫
- 红色🔴节点不能相邻
- 根节点是黑色⚫
- 从根到任意一个叶子节点(null节点),路径中的黑色⚫节点数一样
新增操作
插入节点均视为红色🔴
case 1:插入节点为根节点,将根节点变黑⚫
case 2:插入节点的父亲若为黑色⚫,树的红黑性质不变,无需调整。
插入节点的父亲为红色🔴,触发红红相邻
case 3:叔叔为红色🔴
- 父亲变为黑色⚫,为了保证黑色平衡,连带的叔叔也变为黑色⚫
- 祖父如果是黑色不变,会造成这颗子树黑色过多,因此祖父节点变为红色🔴
- 祖父如果变成红色,可能会接着触发红红相邻,因此对将祖父进行递归调整
case 4:叔叔为黑色⚫
- 父亲为左孩子,插入节点也是左孩子,此时即 LL 不平衡
- 让父亲变黑⚫,为了保证这颗子树黑色不变,将祖父变成红🔴,但叔叔子树少了一个黑色
- 祖父右旋,补齐一个黑色给叔叔,父亲旋转上去取代祖父,由于它是黑色,不会再次触发红红相邻
- 父亲为左孩子,插入节点是右孩子,此时即 LR 不平衡
- 父亲左旋,变成 LL 情况,按 1. 来后续处理
- 父亲为右孩子,插入节点也是右孩子,此时即 RR 不平衡
- 让父亲变黑⚫,为了保证这颗子树黑色不变,将祖父变成红🔴,但叔叔子树少了一个黑色
- 祖父左旋,补齐一个黑色给叔叔,父亲旋转上去取代祖父,由于它是黑色,不会再次触发红红相邻
- 父亲为右孩子,插入节点是左孩子,此时即 RL 不平衡
- 父亲右旋,变成 RR 情况,按 3. 来后续处理
删除操作
case0:如果删除节点有两个孩子
- 交换删除节点和后继节点的 key,value,递归删除后继节点,直到该节点没有孩子或只剩一个孩子
如果删除节点没有孩子或只剩一个孩子
case 1:删的是根节点
- 删完了,直接将 root = null
- 用剩余节点替换了根节点的 key,value,根节点孩子 = null,颜色保持黑色⚫不变
删黑色会失衡,删红色不会失衡,但删黑色有一种简单情况
case 2:删的是黑⚫,剩下的是红🔴,剩下这个红节点变黑⚫
删除节点和剩下节点都是黑⚫,触发双黑,双黑意思是,少了一个黑
case 3:被调整节点的兄弟为红🔴,此时两个侄子定为黑 ⚫
- 删除节点是左孩子,父亲左旋
- 删除节点是右孩子,父亲右旋
- 父亲和兄弟要变色,保证旋转后颜色平衡
- 旋转的目的是让黑侄子变为删除节点的黑兄弟,对删除节点再次递归,进入 case 4 或 case 5
case 4:被调整节点的兄弟为黑⚫,两个侄子都为黑 ⚫
- 将兄弟变红🔴,目的是将删除节点和兄弟那边的黑色高度同时减少 1
- 如果父亲是红🔴,则需将父亲变为黑,避免红红,此时路径黑节点数目不变
- 如果父亲是黑⚫,说明这条路径还是少黑,再次让父节点触发双黑
case 5:被调整节点的兄弟为黑⚫,至少一个红🔴侄子
- 如果兄弟是左孩子,左侄子是红🔴,LL 不平衡
- 将来删除节点这边少个黑,所以最后旋转过来的父亲需要变成黑⚫,平衡起见,左侄子也是黑⚫
- 原来兄弟要成为父亲,需要保留父亲颜色
- 如果兄弟是左孩子,右侄子是红🔴,LR 不平衡
- 将来删除节点这边少个黑,所以最后旋转过来的父亲需要变成黑⚫
- 右侄子会取代原来父亲,因此它保留父亲颜色
- 兄弟已经是黑了⚫,无需改变
- 如果兄弟是右孩子,右侄子是红🔴,RR 不平衡
- 将来删除节点这边少个黑,所以最后旋转过来的父亲需要变成黑⚫,平衡起见,右侄子也是黑⚫
- 原来兄弟要成为父亲,需要保留父亲颜色
- 如果兄弟是右孩子,左侄子是红🔴,RL 不平衡
- 将来删除节点这边少个黑,所以最后旋转过来的父亲需要变成黑⚫
- 左侄子会取代原来父亲,因此它保留父亲颜色
- 兄弟已经是黑了⚫,无需改变
完整代码
/**
* <h3>红黑树</h3>
*/
public class RedBlackTree {
enum Color {
RED, BLACK;
}
Node root;
static class Node {
int key;
Object value;
Node left;
Node right;
Node parent; // 父节点
Color color = RED; // 颜色
public Node(int key, Object value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public Node(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
public Node(int key, Color color) {
this.key = key;
this.color = color;
}
public Node(int key, Color color, Node left, Node right) {
this.key = key;
this.color = color;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
if (left != null) {
left.parent = this;
}
if (right != null) {
right.parent = this;
}
}
// 是否是左孩子
boolean isLeftChild() {
return parent != null && parent.left == this;
}
// 叔叔
Node uncle() {
if (parent == null || parent.parent == null) {
return null;
}
if (parent.isLeftChild()) {
return parent.parent.right;
} else {
return parent.parent.left;
}
}
// 兄弟
Node sibling() {
if (parent == null) {
return null;
}
if (this.isLeftChild()) {
return parent.right;
} else {
return parent.left;
}
}
}
// 判断红
boolean isRed(Node node) {
return node != null && node.color == RED;
}
// 判断黑
boolean isBlack(Node node) {
// return !isRed(node);
return node == null || node.color == BLACK;
}
// 右旋 1. parent 的处理 2. 旋转后新根的父子关系
private void rightRotate(Node pink) {
Node parent = pink.parent;
Node yellow = pink.left;
Node green = yellow.right;
if (green != null) {
green.parent = pink;
}
yellow.right = pink;
yellow.parent = parent;
pink.left = green;
pink.parent = yellow;
if (parent == null) {
root = yellow;
} else if (parent.left == pink) {
parent.left = yellow;
} else {
parent.right = yellow;
}
}
// 左旋
private void leftRotate(Node pink) {
Node parent = pink.parent;
Node yellow = pink.right;
Node green = yellow.left;
if (green != null) {
green.parent = pink;
}
yellow.left = pink;
yellow.parent = parent;
pink.right = green;
pink.parent = yellow;
if (parent == null) {
root = yellow;
} else if (parent.left == pink) {
parent.left = yellow;
} else {
parent.right = yellow;
}
}
/**
* 新增或更新
* <br>
* 正常增、遇到红红不平衡进行调整
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
*/
public void put(int key, Object value) {
Node p = root;
Node parent = null;
while (p != null) {
parent = p;
if (key < p.key) {
p = p.left;
} else if (p.key < key) {
p = p.right;
} else {
p.value = value; // 更新
return;
}
}
Node inserted = new Node(key, value);
if (parent == null) {
root = inserted;
} else if (key < parent.key) {
parent.left = inserted;
inserted.parent = parent;
} else {
parent.right = inserted;
inserted.parent = parent;
}
fixRedRed(inserted);
}
void fixRedRed(Node x) {
// case 1 插入节点是根节点,变黑即可
if (x == root) {
x.color = BLACK;
return;
}
// case 2 插入节点父亲是黑色,无需调整
if (isBlack(x.parent)) {
return;
}
/* case 3 当红红相邻,叔叔为红时
需要将父亲、叔叔变黑、祖父变红,然后对祖父做递归处理
*/
Node parent = x.parent;
Node uncle = x.uncle();
Node grandparent = parent.parent;
if (isRed(uncle)) {
parent.color = BLACK;
uncle.color = BLACK;
grandparent.color = RED;
fixRedRed(grandparent);
return;
}
// case 4 当红红相邻,叔叔为黑时
if (parent.isLeftChild() && x.isLeftChild()) { // LL
parent.color = BLACK;
grandparent.color = RED;
rightRotate(grandparent);
} else if (parent.isLeftChild()) { // LR
leftRotate(parent);
x.color = BLACK;
grandparent.color = RED;
rightRotate(grandparent);
} else if (!x.isLeftChild()) { // RR
parent.color = BLACK;
grandparent.color = RED;
leftRotate(grandparent);
} else { // RL
rightRotate(parent);
x.color = BLACK;
grandparent.color = RED;
leftRotate(grandparent);
}
}
/**
* 删除
* <br>
* 正常删、会用到李代桃僵技巧、遇到黑黑不平衡进行调整
*
* @param key 键
*/
public void remove(int key) {
Node deleted = find(key);
if (deleted == null) {
return;
}
doRemove(deleted);
}
public boolean contains(int key) {
return find(key) != null;
}
// 查找删除节点
private Node find(int key) {
Node p = root;
while (p != null) {
if (key < p.key) {
p = p.left;
} else if (p.key < key) {
p = p.right;
} else {
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
// 查找剩余节点
private Node findReplaced(Node deleted) {
if (deleted.left == null && deleted.right == null) {
return null;
}
if (deleted.left == null) {
return deleted.right;
}
if (deleted.right == null) {
return deleted.left;
}
Node s = deleted.right;
while (s.left != null) {
s = s.left;
}
return s;
}
// 处理双黑 (case3、case4、case5)
private void fixDoubleBlack(Node x) {
if (x == root) {
return;
}
Node parent = x.parent;
Node sibling = x.sibling();
// case 3 兄弟节点是红色
if (isRed(sibling)) {
if (x.isLeftChild()) {
leftRotate(parent);
} else {
rightRotate(parent);
}
parent.color = RED;
sibling.color = BLACK;
fixDoubleBlack(x);
return;
}
if (sibling != null) {
// case 4 兄弟是黑色, 两个侄子也是黑色
if (isBlack(sibling.left) && isBlack(sibling.right)) {
sibling.color = RED;
if (isRed(parent)) {
parent.color = BLACK;
} else {
fixDoubleBlack(parent);
}
}
// case 5 兄弟是黑色, 侄子有红色
else {
// LL
if (sibling.isLeftChild() && isRed(sibling.left)) {
rightRotate(parent);
sibling.left.color = BLACK;
sibling.color = parent.color;
}
// LR
else if (sibling.isLeftChild() && isRed(sibling.right)) {
sibling.right.color = parent.color;
leftRotate(sibling);
rightRotate(parent);
}
// RL
else if (!sibling.isLeftChild() && isRed(sibling.left)) {
sibling.left.color = parent.color;
rightRotate(sibling);
leftRotate(parent);
}
// RR
else {
leftRotate(parent);
sibling.right.color = BLACK;
sibling.color = parent.color;
}
parent.color = BLACK;
}
} else {
// @TODO 实际也不会出现,触发双黑后,兄弟节点不会为 null
fixDoubleBlack(parent);
}
}
private void doRemove(Node deleted) {
Node replaced = findReplaced(deleted);
Node parent = deleted.parent;
// 没有孩子
if (replaced == null) {
// case 1 删除的是根节点
if (deleted == root) {
root = null;
} else {
if (isBlack(deleted)) {
// 双黑调整
fixDoubleBlack(deleted);
} else {
// 红色叶子, 无需任何处理
}
if (deleted.isLeftChild()) {
parent.left = null;
} else {
parent.right = null;
}
deleted.parent = null;
}
return;
}
// 有一个孩子
if (deleted.left == null || deleted.right == null) {
// case 1 删除的是根节点
if (deleted == root) {
root.key = replaced.key;
root.value = replaced.value;
root.left = root.right = null;
} else {
if (deleted.isLeftChild()) {
parent.left = replaced;
} else {
parent.right = replaced;
}
replaced.parent = parent;
deleted.left = deleted.right = deleted.parent = null;
if (isBlack(deleted) && isBlack(replaced)) {
// @TODO 实际不会有这种情况 因为只有一个孩子时 被删除节点是黑色 那么剩余节点只能是红色不会触发双黑
fixDoubleBlack(replaced);
} else {
// case 2 删除是黑,剩下是红
replaced.color = BLACK;
}
}
return;
}
// case 0 有两个孩子 => 有一个孩子 或 没有孩子
int t = deleted.key;
deleted.key = replaced.key;
replaced.key = t;
Object v = deleted.value;
deleted.value = replaced.value;
replaced.value = v;
doRemove(replaced);
}
}
B树
B+树
哈希表
布隆过滤器、一致性哈希
哈希冲突的解决办法
- 开放寻址法:我们在遇到哈希冲突时,去寻找一个新的空闲的哈希地址。
- 线性探测法:哈希值加一取模寻找空闲地址。
- 平方探测法:哈希值加减
取模向两边寻找。 - 再哈希法:使用多个哈希函数。
- 链地址法:将所有哈希地址相同的记录都链接在同一链表中。
- 公共溢出区:将哈希表分为基本表和溢出表,将发生冲突的都存放在溢出表中。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构