教你如何使用Zig实现Cmpp协议
本文分享自华为云社区《华为云短信服务教你用Zig实现Cmpp协议》,作者: 张俭。
引言&协议概述
中国网络通信集团短信网关协议(CNGP)是中国网通为实现短信业务而制定的一种通信协议,全称叫做China Netcom Short Message Gateway Protocol,用于在PHS短消息网关(SMGW)和服务提供商(SP)之间、短消息网关(SMGW)和短消息网关(SMGW)之间通信。
Zig 是一种性能优异、安全性高的系统编程语言,适合用于实现底层网络协议。它提供了强大的类型系统、编译时计算和错误处理机制。
CNGP 协议基于客户端/服务端模型工作。由客户端(短信应用,如手机,应用程序等)先和短信网关(SMGW Short Message Gateway)建立起 TCP 长连接,并使用 CNGP 命令与SMGW进行交互,实现短信的发送和接收。在CNGP协议中,无需同步等待响应就可以发送下一个指令,实现者可以根据自己的需要,实现同步、异步两种消息传输模式,满足不同场景下的性能要求。
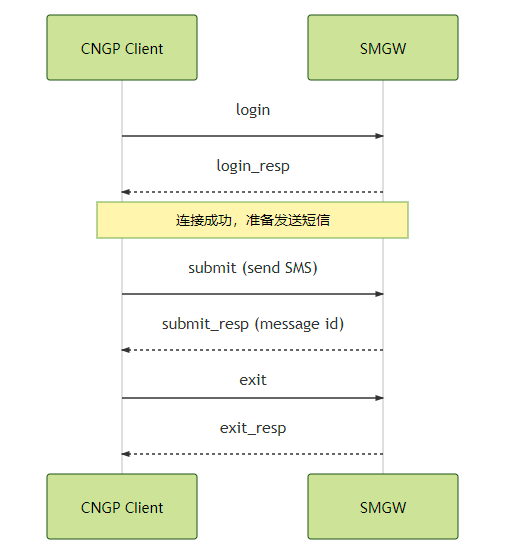
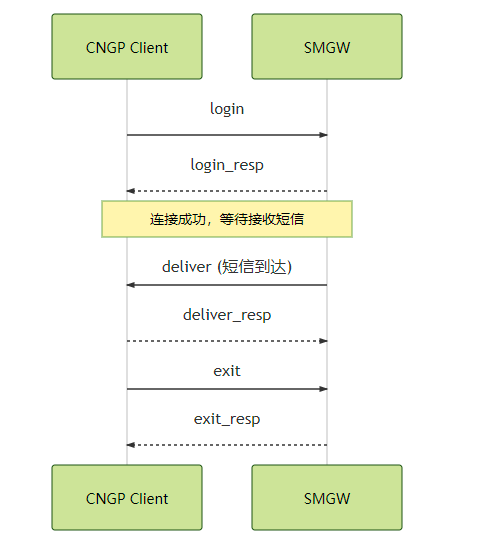
时序图
连接成功,发送短信

连接成功,从SMGW接收到短信

协议帧介绍
在CNGP协议中,每个PDU都包含两个部分:CNGP Header和CNGP Body

CNGP Header
Header包含以下字段,大小长度都是4字节
- Total Length:整个PDU的长度,包括Header和Body。
- Command ID:用于标识PDU的类型(例如,Login、Submit等)。
- Common Status:命令状态
- Sequence Id:序列号,用来匹配请求和响应。
使用Zig实现CNGP协议栈里的建立连接
.
├── src
│ └── bound_atomic.zig
│ ├── cngp_client.zig
│ ├── cngp_client_login_example.zig
│ ├── constant.zig
│ ├── protocol.zig
- bound_atomic.zig:原子递增工具类,用来做SequenceId
- cngp_client.zig:这个文件包含Cngp的定义,该类负责与CNGP服务进行通信,例如建立连接、发送短信等
- cngp_client_login_example.zig:示例代码
- constant.zig:存放常量
- protocol.zig:这个文件包含 CNGP 协议相关的定义和实现,例如协议的命令 ID、PDU 格式等。
constant.zig存放相关commandId
pub const CommandId = enum(u32) { Login = 0x00000001, LoginResp = 0x80000001, Submit = 0x00000002, SubmitResp = 0x80000002, Deliver = 0x00000003, DeliverResp = 0x80000003, ActiveTest = 0x00000004, ActiveTestResp = 0x80000004, Exit = 0x00000006, ExitResp = 0x80000006, };
protocol.zig协议编解码
const std = @import("std"); const io = std.io; const CommandId = @import("constant.zig").CommandId; pub const CngpLogin = struct { clientId: []const u8, authenticatorClient: []const u8, loginMode: u8, timeStamp: i32, version: u8, pub fn length(self: *const CngpLogin) usize { return self.clientId.len + self.authenticatorClient.len + 1 + 4 + 1; } pub fn encode(self: *const CngpLogin, writer: anytype) !void { try writer.writeAll(self.clientId); try writer.writeAll(self.authenticatorClient); try writer.writeByte(self.loginMode); try writer.writeIntBig(i32, self.timeStamp); try writer.writeByte(self.version); } }; pub const CngpLoginResp = struct { authenticatorServer: []const u8, version: u8, pub fn decode(buffer: []u8) !CngpLoginResp { var stream = std.io.fixedBufferStream(buffer); var reader = stream.reader(); var authenticatorServerBuffer: [16]u8 = undefined; var fixedSize = try reader.read(&authenticatorServerBuffer); if (fixedSize != 16) { return error.InvalidLength; } const version = try reader.readByte(); return CngpLoginResp{ .authenticatorServer = authenticatorServerBuffer[0..], .version = version, }; } }; pub const CngpHeader = struct { total_length: i32, command_id: CommandId, command_status: i32, sequence_id: i32, }; pub const CngpBody = union(enum) { Login: CngpLogin, LoginResp: CngpLoginResp, }; pub const CngpPdu = struct { header: CngpHeader, body: CngpBody, pub fn length(self: *const CngpPdu) usize { return 16 + switch (self.body) { .Login => |login| login.length(), else => 0, }; } pub fn encode(self: *const CngpPdu) ![]u8 { const len = self.length(); var buffer = try std.heap.page_allocator.alloc(u8, len); var stream = std.io.fixedBufferStream(buffer); var writer = stream.writer(); try writer.writeInt(i32, @as(i32, @intCast(len)), .Big); try writer.writeInt(u32, @intFromEnum(self.header.command_id), .Big); try writer.writeInt(i32, self.header.command_status, .Big); try writer.writeInt(i32, self.header.sequence_id, .Big); switch (self.body) { .Login => |login| try login.encode(writer), else => unreachable, } return buffer; } pub fn decode_login_resp(buffer: []u8) !CngpPdu { var header: CngpHeader = undefined; header.total_length = 0; header.command_id = CommandId.LoginResp; header.command_status = std.mem.readIntLittle(i32, buffer[8..12]); header.sequence_id = std.mem.readIntLittle(i32, buffer[12..16]); const body = try CngpLoginResp.decode(buffer[12..]); return CngpPdu{ .header = header, .body = CngpBody{ .LoginResp = body }, }; } };
利用原子类型实现sequenceId递增
const std = @import("std"); pub const BoundAtomic = struct { min: i32, max: i32, integer: std.atomic.Atomic(i32), pub fn new(min: i32, max: i32) BoundAtomic { return BoundAtomic{ .min = min, .max = max, .integer = std.atomic.Atomic(i32).init(min), }; } pub fn nextVal(self: *BoundAtomic) i32 { while (true) { const current = self.integer.load(.SeqCst); const next = if (current == self.max) self.min else current + 1; if (self.integer.compareAndSwap(current, next, .SeqCst, .SeqCst) == null) { return next; } } } };
实现client以及login方法
const std = @import("std"); const net = std.net; const CngpBody = @import("protocol.zig").CngpBody; const CngpLogin = @import("protocol.zig").CngpLogin; const CngpPdu = @import("protocol.zig").CngpPdu; const CommandId = @import("constant.zig").CommandId; const BoundAtomic = @import("bound_atomic.zig").BoundAtomic; pub const CngpClient = struct { host: []const u8, port: u16, sequenceId: BoundAtomic, stream: ?std.net.Stream, pub fn init(host: []const u8, port: u16) CngpClient { return CngpClient{ .host = host, .port = port, .sequenceId = BoundAtomic.new(1, 0x7FFFFFFF), .stream = null, }; } pub fn connect(self: *CngpClient) !void { const peer = try net.Address.parseIp4(self.host, self.port); self.stream = try net.tcpConnectToAddress(peer); } pub fn login(self: *CngpClient, body: CngpLogin) !CngpPdu { const sequenceId = self.sequenceId.nextVal(); const pdu = CngpPdu{ .header = .{ .total_length = 0, // Will be calculated in encode method .command_id = CommandId.Login, .command_status = 0, .sequence_id = sequenceId, }, .body = CngpBody{ .Login = body }, }; const data = try pdu.encode(); if (self.stream) |s| { const size = try s.write(data); if (size != data.len) { return error.WriteFailed; } var buffer: [4]u8 = undefined; const readLengthSize = try s.read(buffer[0..]); if (readLengthSize != 4) { return error.ReadFailed; } const remainLength = std.mem.readInt(u32, buffer[0..], .Big) - 4; var responseBuffer = try std.heap.page_allocator.alloc(u8, remainLength); defer std.heap.page_allocator.free(responseBuffer); var reader = s.reader(); const readSize = try reader.read(responseBuffer[0..remainLength]); if (readSize != remainLength) { return error.ReadFailed; } const response = try CngpPdu.decode_login_resp(responseBuffer); return response; } else { return error.UnexpectedNull; } } pub fn close(self: *CngpClient) void { if (self.stream) |s| { s.close(); self.stream = null; } } };
运行Example,验证连接成功
const std = @import("std"); const CngpClient = @import("cngp_client.zig").CngpClient; const CngpLogin = @import("protocol.zig").CngpLogin; pub fn main() !void { const host = "127.0.0.1"; const port: u16 = 9890; var client = CngpClient.init(host, port); defer client.close(); const clientId = "1234567890"; const authenticatorClient = "1234567890123456"; const loginMode: u8 = 1; const timeStamp: i32 = 123456789; const version: u8 = 1; const loginBody = CngpLogin{ .clientId = clientId, .authenticatorClient = authenticatorClient, .loginMode = loginMode, .timeStamp = timeStamp, .version = version, }; try client.connect(); const response = try client.login(loginBody); try std.io.getStdOut().writer().print("Login response: {}\n", .{response}); }

相关开源项目
- netty-codec-sms 存放各种SMS协议(如cmpp、sgip、smpp)的netty编解码器
- sms-client-java 存放各种SMS协议的Java客户端
- sms-server-java 存放各种SMS协议的Java服务端
- cmpp-python cmpp协议的python实现
- cngp-zig cmpp协议的python实现
- smpp-rust smpp协议的rust实现
总结
本文简单对CNGP协议进行了介绍,并尝试用zig实现协议栈,但实际商用发送短信往往更加复杂,面临诸如流控、运营商对接、传输层安全等问题,可以选择华为云消息&短信(Message & SMS)服务,华为云短信服务是华为云携手全球多家优质运营商和渠道,为企业用户提供的通信服务。企业调用API或使用群发助手,即可使用验证码、通知短信服务。

