数据结构与算法
数据结构
1、链表
由不定数量的节点(Node)组成,每个节点仅知道下一个结点的位置,且向外仅仅暴露头(head),一切操作直接或者间接从头开始;
代码:单向链表的实现、链表反转、链表中间点查询、链表排序
1.1单向链表的实现
1 // 链表的实现 2 public class Test { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 NodeManager nodeManager = new NodeManager(); 5 nodeManager.addNode("大"); 6 nodeManager.addNode("家"); 7 nodeManager.addNode("好"); 8 nodeManager.addNode("才"); 9 nodeManager.addNode("是"); 10 nodeManager.addNode("真"); 11 nodeManager.addNode("的"); 12 nodeManager.delNode("好"); 13 nodeManager.print(); 14 } 15 } 16 //节点管理类--封装的增删改 17 class NodeManager { 18 19 private Node root;//根节点 20 21 //添加节点 22 public void addNode(String data) { 23 if (root == null) { 24 root = new Node(data); 25 } else { 26 root.addNode(data); 27 } 28 } 29 //删除节点 30 public void delNode (String data) { 31 if (root.data.equals(data)){ 32 root = root.next; 33 } else { 34 root.delNode(data); 35 } 36 } 37 //打印节点 38 public void print() { 39 if (root != null) { 40 System.out.print(root.data + " ->"); 41 root.print(); 42 } 43 } 44 45 46 47 // 节点类--节点结构和自带简易方法 48 class Node { 49 private String data;//数据源 50 private Node next;//指针域 51 52 public Node(String data) { 53 this.data = data; 54 } 55 //添加方法 56 public void addNode(String data) { 57 if (this.next == null) { 58 this.next = new Node(data); 59 } else { 60 this.next.addNode(data); 61 } 62 } 63 //删除方法 64 public void delNode(String name) { 65 if (this.next != null) { 66 if (this.next.data.equals(name)) { 67 this.next = this.next.next; 68 } else { 69 this.next.delNode(name); 70 } 71 } 72 } 73 //打印方法 74 public void print() { 75 if (this.next != null) { 76 System.out.print(this.next.data + "->"); 77 this.next.print(); 78 } 79 } 80 } 81 }
1.2链表反转
1 /** 2 * 链表反转 3 * 4 * @param head 5 * @return 6 */ 7 public Node ReverseIteratively(Node head) { 8 Node pReversedHead = head; 9 Node pNode = head; 10 Node pPrev = null; 11 while (pNode != null) { 12 Node pNext = pNode.next; 13 if (pNext == null) { 14 pReversedHead = pNode; 15 } 16 pNode.next = pPrev; 17 pPrev = pNode; 18 pNode = pNext; 19 } 20 this.head = pReversedHead; 21 return this.head; 22 }
1.3链表中间点查询
1 /** 2 * 查找单链表的中间节点 3 * 采用快慢指针的方式查找单链表的中间节点,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,当快指针走完时,慢指针刚好到达中间节点 4 * @param head 5 * @return 6 */ 7 public Node SearchMid(Node head) { 8 Node p = this.head, q = this.head; 9 while (p != null && p.next != null && p.next.next != null) { 10 p = p.next.next; 11 q = q.next; 12 } 13 System.out.println("Mid:" + q.data); 14 return q; 15 }
1.4链表排序
1 /** 2 * 排序 3 * 用当前的node和随后的所有的比较并进行位置互换,一波后挪一个节点 4 * @return 5 */ 6 public Node orderList() { 7 Node nextNode = null; 8 int tmp = 0; 9 Node curNode = head; 10 while (curNode.next != null) { 11 nextNode = curNode.next; 12 while (nextNode != null) { 13 if (curNode.data > nextNode.data) { 14 tmp = curNode.data; 15 curNode.data = nextNode.data; 16 nextNode.data = tmp; 17 } 18 nextNode = nextNode.next; 19 } 20 curNode = curNode.next; 21 } 22 return head; 23 }
2、队列与栈
栈:数据只能在栈的一端即栈顶位置进行插入和删除操作;先进后出,后进先出
队列:数据只能在队列的一端插入并在另一端进行删除操作;先进先出
代码:栈的实现、队列的实现
2.1栈的实现
1 //栈的实现push和pop 2 public void push(T data) { 3 if (data==null){ 4 throw new StackException("data can't be null"); 5 } 6 if(this.top==null){ 7 //调用pop()后top可能为null 8 this.top=new Node<T>(data); 9 }else if(this.top.data==null){ 10 this.top.data=data; 11 }else { 12 Node<T> p=new Node<T>(data,this.top); 13 top=p; 14 //更新栈顶 15 } 16 size++; 17 } 18 public T pop() { 19 if(isEmpty()){ 20 throw new EmptyStackException("Stack empty"); 21 } 22 23 T data=top.data; 24 top=top.next; 25 size--; 26 return data; 27 }
2.2队列实现
1 /** 2 * 队列入队算法 3 * @param data 4 * @author WWX 5 */ 6 public void enqueue(T data){ 7 //创建一个节点 8 Node s=new Node(data,null); 9 //将队尾指针指向新加入的节点,将s节点插入队尾 10 rear.next=s; 11 rear=s; 12 size++; 13 } 14 15 /** 16 * 队列出队算法 17 * @return 18 * @author WWX 19 */ 20 public T dequeue(){ 21 if(rear==front){ 22 try { 23 throw new Exception("堆栈为空"); 24 } catch (Exception e) { 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 return null; 28 }else{ 29 //暂存队头元素 30 Node p=front.next; 31 T x=p.data; 32 //将队头元素所在节点摘链 33 front.next=p.next; 34 //判断出队列长度是否为1 35 if(p.next==null) 36 rear=front; 37 //删除节点 38 p=null; 39 size--; 40 return x; 41 } 42 }
3、二叉树
二叉树:N个结点构成的有限集合;每个结点至多只有两棵子树(即二叉树中不存在度大于2的结点),并且,二叉树的子树有左右之分,其次序不能任意颠倒。
特性: (1)若根结点的层次为1,则二叉树第i层最多有2i−1(i≥1)个结点;在高度为h的二叉树中,最多有2h−1个结点(h≥0);
(2)满二叉树和完全二叉树
(3) 一棵具有n个结点的完全二叉树,对于序号为i(0≤i<n)的结点,则有如下规则
①若i=0,则i为根结点,无父母结点;若i>0,则i的父母结点序号为⌊i−12⌋(向下取整)。
②若2i+1<n,则i的左孩子结点序号为2i+1,否则i无左孩子。
③若2i+2>n,则i的右孩子结点序号为2i+2,否则i无右孩子。
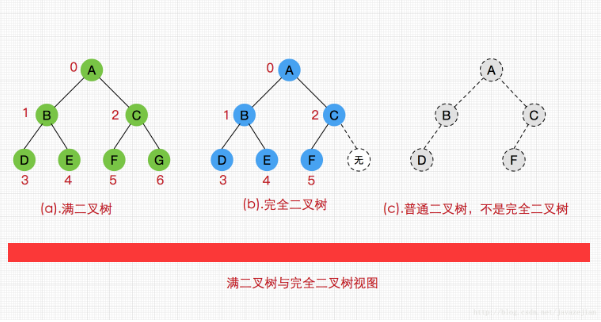
代码:二叉树实现、遍历
3.1二叉树实现
1 // 二叉树数据结构的实现 2 public class Test { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 BinaryTreeManger binaryTreeManger = new BinaryTreeManger(); 5 6 binaryTreeManger.add(1); 7 binaryTreeManger.add(3); 8 binaryTreeManger.add(4); 9 binaryTreeManger.add(8); 10 binaryTreeManger.add(6); 11 binaryTreeManger.print(); 12 } 13 } 14 15 class BinaryTreeManger{ 16 17 private Node root;//根节点 18 19 public void add(int data) { 20 if (root == null) { 21 root = new Node(data); 22 } else { 23 root.addNode(data); 24 } 25 } 26 public void print() { 27 root.print(); 28 } 29 class Node{ 30 private int data; 31 private Node left; //左子树 32 private Node right; //右子树 33 34 public Node(int data) { 35 this.data = data; 36 } 37 //添加节点 38 public void addNode(int data) { 39 //首先判断大小,来决定将data放在那个子树上 40 if (data > this.data){//当前数据较大,放在右子树 41 if (this.right == null) { 42 this.right = new Node(data); 43 } else { 44 this.right.addNode(data); 45 } 46 } else { //较小放在左子树上 47 if (this.left == null) { 48 this.left = new Node(data); 49 } else { 50 this.left.addNode(data); 51 } 52 53 } 54 55 } 56 //中序遍历 左 -> 根 -> 右 57 public void print() { 58 if (this.left != null) { 59 this.left.print(); 60 } 61 System.out.print(data); 62 if (this.right != null) { 63 this.right.print(); 64 } 65 } 66 } 67 }
3.2二叉树遍历
1 public void visted(TreeNode subTree){ 2 subTree.isVisted=true; 3 System.out.println("key:"+subTree.key+"--name:"+subTree.data);; 4 } 5 //前序遍历 6 public void preOrder(TreeNode subTree){ 7 if(subTree!=null){ 8 visted(subTree); 9 preOrder(subTree.leftChild); 10 preOrder(subTree.rightChild); 11 } 12 } 13 14 //中序遍历 15 public void inOrder(TreeNode subTree){ 16 if(subTree!=null){ 17 inOrder(subTree.leftChild); 18 visted(subTree); 19 inOrder(subTree.rightChild); 20 } 21 } 22 23 //后续遍历 24 public void postOrder(TreeNode subTree) { 25 if (subTree != null) { 26 postOrder(subTree.leftChild); 27 postOrder(subTree.rightChild); 28 visted(subTree); 29 } 30 } 31 32 //前序遍历的非递归实现 33 public void nonRecPreOrder(TreeNode p){ 34 Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>(); 35 TreeNode node=p; 36 while(node!=null||stack.size()>0){ 37 while(node!=null){ 38 visted(node); 39 stack.push(node); 40 node=node.leftChild; 41 } 42 while(stack.size()>0){ 43 node=stack.pop(); 44 node=node.rightChild; 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 49 //中序遍历的非递归实现 50 public void nonRecInOrder(TreeNode p){ 51 Stack<TreeNode> stack =new Stack<BinaryTree.TreeNode>(); 52 TreeNode node =p; 53 while(node!=null||stack.size()>0){ 54 //存在左子树 55 while(node!=null){ 56 stack.push(node); 57 node=node.leftChild; 58 } 59 //栈非空 60 if(stack.size()>0){ 61 node=stack.pop(); 62 visted(node); 63 node=node.rightChild; 64 } 65 } 66 } 67 68 //后序遍历的非递归实现 69 public void noRecPostOrder(TreeNode p){ 70 Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<BinaryTree.TreeNode>(); 71 TreeNode node =p; 72 while(p!=null){ 73 //左子树入栈 74 for(;p.leftChild!=null;p=p.leftChild){ 75 stack.push(p); 76 } 77 //当前结点无右子树或右子树已经输出 78 while(p!=null&&(p.rightChild==null||p.rightChild==node)){ 79 visted(p); 80 //纪录上一个已输出结点 81 node =p; 82 if(stack.empty()) 83 return; 84 p=stack.pop(); 85 } 86 //处理右子树 87 stack.push(p); 88 p=p.rightChild; 89 } 90 }
借鉴博客(版权已被声明):http://blog.csdn.net/javazejian/article/details/53727333
4、其他
串:若干个字符组成的有限序列;
数组:有限个类型相同的变量的集合;
广义表:若干个元素组成的有限序列;
排序算法
各种排序算法时间复杂度和空间复杂度

1、插入排序
插入排序:稳定,最好最坏均为O(n2);
原理:拿要后边要排序元素与前边已经排好的元素进行比较,从后向前扫描,找到位置并插入;
shell排序:不稳定,平均O(n1.5),最坏O(n2);
原理:数据等距离分组,组内插入排序;分组距离减半,组内继续插入排序....
1.1插入排序
1 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { 2 for (int j = i + 1; j < len && j > 0; j--) { 3 if (a[j] < a[j - 1]) { 4 int temp = a[j]; 5 a[j] = a[j - 1]; 6 a[j - 1] = temp; 7 } 8 } 9 }
1.2shell排序
1 int group, i, j, temp,len; 2 len = unsorted.length; 3 for (group = len / 2; group > 0; group /= 2) 4 { 5 for (i = group; i < len; i++) 6 { 7 for (j = i - group; j >= 0; j -= group) 8 { 9 if (unsorted[j] > unsorted[j + group]) 10 { 11 temp = unsorted[j]; 12 unsorted[j] = unsorted[j + group]; 13 unsorted[j + group] = temp; 14 } 15 } 16 } 17 }
2、选择排序
直接选择:不稳定,最好最坏均为O(n2);
原理:每次从当前位置到最末尾,获取最小数据互换到当前位置,并依次后移
堆排序:不稳定,最好最坏均为O(nlog2n);
原理:完全二叉树,大顶堆(父节点大于等于子节点),小顶堆(父节点小于等于子节点);
数据构建完全二叉树->大顶堆->根节点换到叶子节点左右侧(把最大数据放到最后)->大顶堆->根节点换到叶子节点左右侧(再次把第二大数据放到最后第二位置)....
2.1直接选择
1 //min 记录最小数据,index记录最小位置 2 int min = 0; 3 int index = 0; 4 int len = a.length; 5 for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) { 6 min = a[i]; 7 index = i; 8 for (int j = i + 1; j < len; j++) { 9 if (a[j] < min) { 10 min = a[j]; 11 index = j; 12 } 13 } 14 a[index] = a[i]; 15 a[i] = min; 16 }
2.2堆排序
1 //调整堆 2 void HeapAdjust(int *a,int i,int size) 3 { 4 int lchild=2*i; //i的左孩子节点序号 5 int rchild=2*i+1; //i的右孩子节点序号 6 int max=i; //临时变量 7 if(i<=size/2) //如果i是叶节点就不用进行调整 8 { 9 if(lchild<=size&&a[lchild]>a[max]) 10 { 11 max=lchild; 12 } 13 if(rchild<=size&&a[rchild]>a[max]) 14 { 15 max=rchild; 16 } 17 if(max!=i) 18 { 19 swap(a[i],a[max]); 20 HeapAdjust(a,max,size); //避免调整之后以max为父节点的子树不是堆 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 void BuildHeap(int *a,int size) //建立堆 25 { 26 int i; 27 for(i=size/2;i>=1;i--) //非叶节点最大序号值为size/2 28 { 29 HeapAdjust(a,i,size); 30 } 31 } 32 void HeapSort(int *a,int size) //堆排序 33 { 34 int i; 35 BuildHeap(a,size); 36 for(i=size;i>=1;i--) 37 { 38 swap(a[1],a[i]); //交换堆顶和最后一个元素,即每次将剩余元素中的最大者放到最后面 39 HeapAdjust(a,1,i-1); //重新调整堆顶节点成为大顶堆 40 } 41 }
3、交换排序
冒泡排序:稳定,平均最坏均为O(n2);
原理:重复走访数据,每加入一次数据,从该位置起,相邻数据两两比较,位置互换;
快速排序:不稳定,平均为O(nlog2n),最坏为O(n2);
原理:将数据分隔成两部分,左边<key<右边,依次递归,缩小范围
3.1冒泡排序
1 //j与j+1相邻比较 2 for(int i = 0; i < len-1; i++){ 3 for (int j = 0; j > len-i; j++){ 4 if (array[j] < array[j+1] ){ 5 swap(array,j,j+1); 6 } 7 } 8 }
3.2快速排序
1 public void sort(int[] a,int low,int high){ 2 int start = low; 3 int end = high; 4 int key = a[low]; 5 6 7 while(end>start){ 8 //从后往前比较 9 //如果没有比关键值小的,比较下一个,直到有比关键值小的交换位置,然后又从前往后比较 10 while(end>start&&a[end]>=key) 11 end--; 12 if(a[end]<=key){ 13 int temp = a[end]; 14 a[end] = a[start]; 15 a[start] = temp; 16 } 17 //从前往后比较 18 //如果没有比关键值大的,比较下一个,直到有比关键值大的交换位置 19 while(end>start&&a[start]<=key) 20 start++; 21 if(a[start]>=key){ 22 int temp = a[start]; 23 a[start] = a[end]; 24 a[end] = temp; 25 } 26 //此时第一次循环比较结束,关键值的位置已经确定了。 27 //左边的值都比关键值小,右边的值都比关键值大, 28 //但是两边的顺序还有可能是不一样的,进行下面的递归调用 29 } 30 //递归 31 if(start>low) sort(a,low,start-1);//左边序列。第一个索引位置到关键值索引-1 32 if(end<high) sort(a,end+1,high);//右边序列。从关键值索引+1到最后一个 33 }
4、归并排序
5、基数排序
平均O(n3/2),最坏O(n2)



