实验6
实验任务四:
Vector.hpp
#ifndef VECTOR_HPP #define VECTOR_HPP #include <iostream> #include <memory> #include <stdexcept> template <typename T> class Vector { private: T *data; // 存储动态数组的指针 size_t size; // 数组的大小 public: // 构造函数,支持动态指定大小 explicit Vector(int size = 0, T value = T()) : size(size), data(nullptr) { if (size < 0) { // 使用 int 类型,可以检查负数 throw std::length_error("Size cannot be negative."); // 如果大小为负数,抛出异常 } if (size > 0) { data = new T[size]; // 动态分配数组 for (size_t i = 0; i < size; ++i) { data[i] = value; // 初始化数组元素为指定值 } } } // 拷贝构造函数,实现深拷贝 Vector(const Vector &other) : size(other.size), data(nullptr) { if (size > 0) { data = new T[size]; for (size_t i = 0; i < size; ++i) { data[i] = other.data[i]; // 深拷贝 } } } // 析构函数,释放内存 ~Vector() { delete[] data; } // 获取数组大小 size_t get_size() const { return size; } // at()方法,通过索引访问,检查越界,返回引用 T &at(size_t index) { if (index >= size) { throw std::out_of_range("Index out of range."); } return data[index]; } const T &at(size_t index) const { if (index >= size) { throw std::out_of_range("Index out of range."); } return data[index]; } // 重载运算符[],提供直接访问 T &operator[](size_t index) { return data[index]; } const T &operator[](size_t index) const { return data[index]; } // 友元函数,用于输出Vector中的数据 friend void output(const Vector<T> &v) { for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size; ++i) { std::cout << v.data[i] << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; } }; #endif
task4.cpp
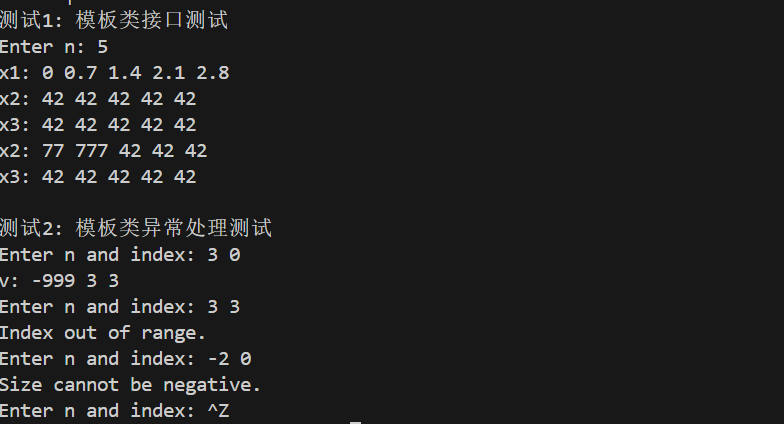
#include "Vector.hpp" #include <iostream> using namespace std; void test1() { using namespace std; int n; cout << "Enter n: "; cin >> n; Vector<double> x1(n); for (auto i = 0; i < n; ++i) x1.at(i) = i * 0.7; cout << "x1: "; output(x1); Vector<int> x2(n, 42); const Vector<int> x3(x2); cout << "x2: "; output(x2); cout << "x3: "; output(x3); x2.at(0) = 77; x2.at(1) = 777; cout << "x2: "; output(x2); cout << "x3: "; output(x3); } void test2() { using namespace std; int n, index; while (cout << "Enter n and index: ", cin >> n >> index) { try { Vector<int> v(n, n); v.at(index) = -999; cout << "v: "; output(v); } catch (const exception &e) { cout << e.what() << endl; } } } int main() { cout << "测试1: 模板类接口测试\n"; test1(); cout << "\n测试2: 模板类异常处理测试\n"; test2(); }
实验任务五:
task5.cpp
#include <algorithm> #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <sstream> #include <string> #include <vector> using namespace std; // 定义一个结构体来存储学生信息 struct Student { string student_id; string name; string major; int score; }; // 读取数据函数 vector<Student> read_data(const string &file_name) { ifstream file(file_name); vector<Student> students; string line; // 跳过标题行 getline(file, line); // 读取每一行数据 while (getline(file, line)) { stringstream ss(line); Student student; ss >> student.student_id >> student.name >> student.major >> student.score; students.push_back(student); } return students; } // 排序函数,按照专业字典序和分数降序排序 bool compare_students(const Student &a, const Student &b) { if (a.major == b.major) { return a.score > b.score; // 专业相同时按分数降序排序 } return a.major < b.major; // 按专业字典序排序 } // 打印结果并保存到文件 void output_results(const vector<Student> &sorted_data, const string &output_file) { // 打印到屏幕 for (const auto &student : sorted_data) { cout << student.student_id << " " << student.name << " " << student.major << " " << student.score << endl; } // 保存到文件 ofstream file(output_file); file << "学号 姓名 专业 分数\n"; // 输出标题行 for (const auto &student : sorted_data) { file << student.student_id << " " << student.name << " " << student.major << " " << student.score << endl; } } // 主程序 int main() { string input_file = "data5.txt"; string output_file = "ans5.txt"; // 读取数据 vector<Student> students = read_data(input_file); // 排序数据 sort(students.begin(), students.end(), compare_students); // 打印并保存结果 output_results(students, output_file); return 0; }





