大连acm hdu 5876 补图
题目:http://hdu.hustoj.com/showproblem.php?pid=5876
In graph theory, the complement of a graph G is a graph H on the same vertices such that two distinct vertices of H are adjacent if and only if they are not adjacent in G.
Now you are given an undirected graph G of N nodes and M bidirectional edges of unit length. Consider the complement of G, i.e., H. For a given vertex S on H, you are required to compute the shortest distances from S to all N−1 other vertices.
Input
There are multiple test cases. The first line of input is an integer T(1≤T<35) denoting the number of test cases. For each test case, the first line contains two integers N(2≤N≤200000) and M(0≤M≤20000). The following M lines each contains two distinct integers u,v(1≤u,v≤N) denoting an edge. And S (1≤S≤N) is given on the last line.
Output
For each of T test cases, print a single line consisting of N−1 space separated integers, denoting shortest distances of the remaining N−1 vertices from S (if a vertex cannot be reached from S, output ``-1" (without quotes) instead) in ascending order of vertex number.
Sample Input
1
2 0
1
Sample Output
1
Source
题意: 给你1样例
给你n个点和m条边
输入m条边后
输入起点s
求原图的补图中,,起点s到各个点的最短距离并输出
补图 ; 一个n个点的图有n*(n-1)*0.5条边,,,除去原图上的边剩下的所有边组成补图
概念如图 ;
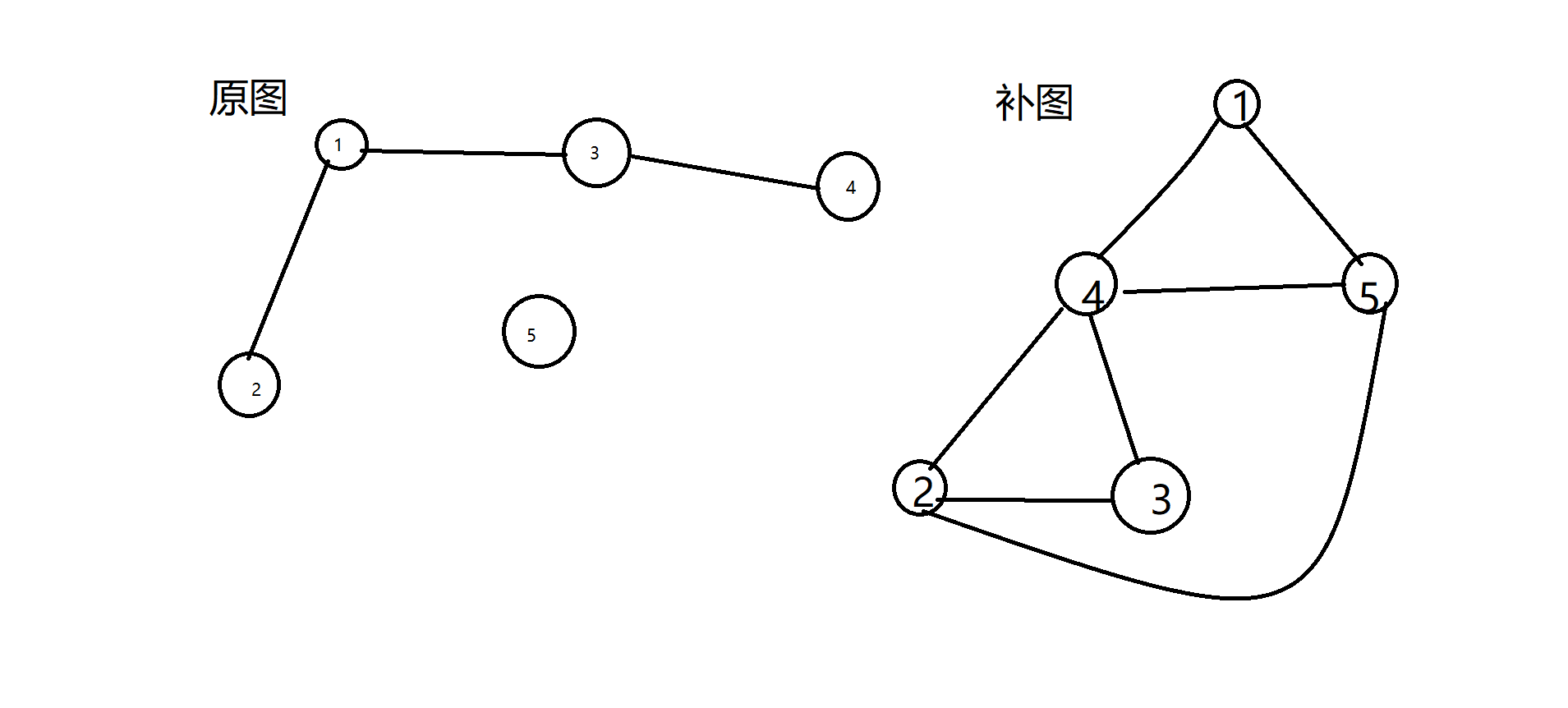
好了题意清楚了,,其实刚开始想法很简单,,不就是补图嘛,,通过原来的图把补图还原出来,直接迪杰就ok
但是复杂度过高,优化是不可能的,,所以又找到了一种做法 因为只会出现3种答案吧(-1,,1,,2)
从起点找起,,把和起点没有联系的点用队列存起来,如图就是存4和5 更新dis[4]和dis[5]=1 从队列中取出4和5 分别为起点 找没有联系的点3和2 更新队列和dis[3],,dis[2]=dis[4]+1;
好了方法已经找到了,,写出来了也,,但是还是超时 ,,想半天原来红色区域的查找复杂度也有n*(n-x)*(n-x)....显然超时
怎么办呢,,想到了set维护,,set能跟快速的管理和查找删除 所需要的元素 所以代码就出来了 因为对于set的维护还不熟悉只能看别人的代码,,实力太弱
对着网上写的代码:后面会补上自己的代码
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<cmath> #include<queue> #include<set> #include<algorithm> #include<map> #define maxn 200005 using namespace std; int n,m,s; int x,y; set<int>book;//存所有没扩展到的点 set<int>mp[maxn]; //存原图 int ans[maxn]; // 最短距离 void bfs(int s) { ans[s]=0; queue<int>que; que.push(s); //把起点存入队列 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(i!=s)book.insert(i); //所有点先存入 } set<int>del; //存要删除的已访问的点 while(!que.empty()) { int now=que.front(); que.pop(); set<int>::iterator it; del.clear(); //清空所有元素 for(it=book.begin();it!=book.end();it++) //查找与now没有连接的点 可以说是这题的难点所在 { if(!mp[now].count(*it)) //返回mp[now]的元素个数 { if(ans[*it]==-1) { ans[*it]=ans[now]+1; del.insert(*it); que.push(*it); } } } for(it=del.begin();it!=del.end();it++) { book.erase(*it); //删除book里的已经访问元素 } } } int main() { int t; cin>>t; while(t--) { cin>>n>>m; memset(ans,-1,sizeof(ans)); //初始化ans数组 for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) { mp[i].clear(); //清空mp } book.clear(); //清空book for(int i=0;i<m;i++) { cin>>x>>y; mp[x].insert(y); mp[y].insert(x); //双向存点 } cin>>s; bfs(s); // 以下是输出格式 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(s==i)continue; cout<<ans[i]; if(s==n) { if(i!=n-1)printf(" "); else cout<<endl; } else { if(i!=n)cout<<" "; else cout<<endl; } } } return 0; }
思路并不复杂,,就是想要维护操作的时候想不到




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步